SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) is a comprehensive solution designed to assist organizations in managing and optimizing their environmental, health, and safety processes. As businesses strive to meet more stringent regulations, lower risks, and promote sustainable practices, SAP EHS is proving to be a powerful tool for streamlining and improving these essential aspects of business operations.
Companies can evaluate, monitor, and manage operational risks because of the unified platform it provides that aggregates data from many sources. Through this blog, we’ll understand in detail about what SAP EHS is, its features, the benefits of using SAP EHS, and more. Let’s get right into it!
| SAP EHS: Table of Contents |
What is SAP EHS?
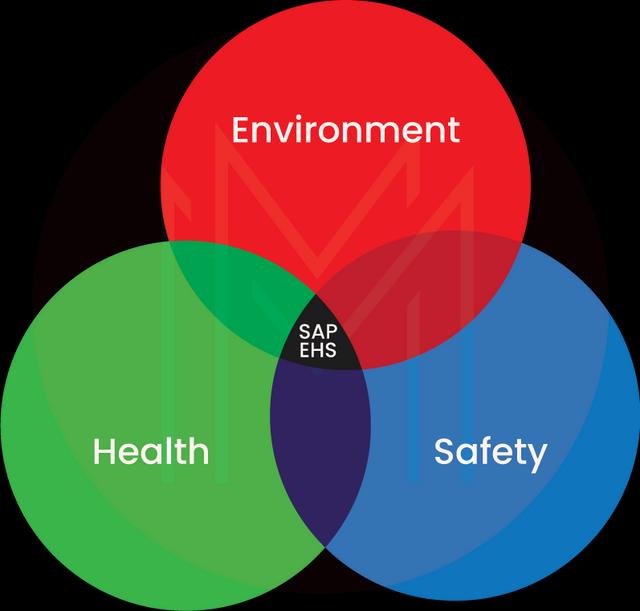
SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) allows organizations to monitor and enhance their environmental, health, and safety processes. It offers a range of modules and functionalities to support activities such as product safety and compliance, hazardous substance management, waste management, incident management, occupational health management, and more.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in SAP EHS, then enroll in "SAP EHS Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
Features of SAP EHS
The following are the key features of SAP EHS:
- Incident management: The Incident Management in SAP EHS is responsible for handling and documenting occurrences involving workplace health and safety, environmental issues, and product safety inside a business. By ensuring regulatory compliance and helping companies manage and resolve problems effectively, it promotes a safe workplace.
- Basic Data and Tools (EHS-BD): In SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety), the term "basic data and tools" refers to the basic elements and capabilities used to manage environmental, health, and safety-related data.
- Product Safety (EHS-SAF): In SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety), "product safety" refers to a group of activities and protocols designed to ensure the secure handling, archival, and disposal of products inside an organization. It comprises managing and lowering the hazards associated with dangerous products, materials, and substances throughout a product's lifecycle.
- Hazardous Substance Management (EHS-HSM): In SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety), the term "hazardous substance management" refers to the SAP system's features and protocols that let companies effectively manage and track dangerous substances during their entire lifecycle.
- Dangerous Goods Management (EHS-DGP): It deals with handling, storing, and moving potentially dangerous goods. It assists in identifying, labeling, and handling harmful objects in order to guarantee adherence to essential legislation.
- Waste Management (EHS-WA): In SAP EHS, the term "waste management" refers to system capabilities and operational practices that enable enterprises to manage and keep track of waste-related activities effectively. To help companies comply with regulatory requirements and implement efficient waste management practices, SAP EHS offers comprehensive waste management capabilities.
- Occupational Health (EHS-HEA): This module oversees employee health-related data, occupational health services, and medical monitoring initiatives. It helps track and report on employee health issues and ensures compliance with occupational health regulations.
- Industrial Hygiene and Safety (EHS-IHS): This part focuses on identifying and managing potential workplace hazards, doing risk analysis, and implementing safety procedures. It includes modules for risk analysis, incident management, and safety training.
- Emergency management: Emergency Management assists in planning, responding, and recovering from emergency circumstances. It is intended to assist organizations in effectively coping with and reducing the risks brought on by emergencies while ensuring the security of their people, property, and the environment.
Functionalities of the SAP EHS System
The following are the key functionalities of the SAP EHS System:
- Employee Health and Safety Functionality
Employee Health and Safety functionality in SAP EHS is designed to help enterprises manage and keep track of various aspects of employee health, safety, and wellness. It provides tools and features to ensure adherence to regulations controlling workplace health and safety, mitigating risks, and maintaining a safe working environment.
- Product Safety Functionality
The Product Safety functionality within SAP EHS is concerned with managing and assuring the compliance and safety of products throughout their lifecycle. It offers features and resources to assist businesses in adhering to the rules and regulations pertaining to product safety.
- Environmental Compliance Management Functionality
To help enterprises manage and guarantee compliance with environmental laws and standards, SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) has an element called environment compliance management. It provides tools and techniques for monitoring, assessing, and summarizing a variety of environmental compliance-related aspects.
- Product and REACH Compliance Functionality
Product Compliance and REACH Compliance are two crucial regulatory compliance features in SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety).
Product compliance refers to the management of legal requirements and restrictions pertaining to product development, distribution, and sale. While REACH compliance involves implementing and configuring various components and features within the SAP EHS module to ensure adherence to relevant regulations and standards.
Check Out: SAP EHS Interview Questions
SAP EHS Modules
The key SAP EHS modules are listed below:
#1.EHS-BD-TLS -> Tools
This is an SAP EHS submodule that stands for BASIC DATA and TOOLS. This submodule provides the ability to interchange and distribute data between systems as well as import data from legacy systems.
#2.EHS-BD-CCK-> Compliance check
In SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety), a compliance check is used to assess whether an organization's operations, products, and processes comply with relevant environmental, health, and safety regulations, standards, and requirements.
#3.Phrase Management (EHS-BD-PHR)
The process of managing and maintaining standard phrases or texts used in a range of EHS-related documents, such as safety data sheets, labels, reports, and notifications, is known as phrase management in SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety).
Phrase management aims to ensure that all EHS publications provide information in an accurate and consistent manner. Instead of manually creating and updating texts, organizations can save time, money, and effort by maintaining a central repository of phrases.
#4.Specific Information System (EHS -BD-SIS)
The Special Information System within SAP EHS offers a comprehensive framework for handling and processing regulatory data, including safety data sheets (SDS), substance properties, classification and labeling information, and legislative requirements. It helps businesses ensure their products adhere to all relevant laws and standards while enabling them to retain and distribute safety-related information effectively.
#5.Specification Management (EHS-BD-SPE)
Specification Management is an SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) module that manages and maintains specifications for various goods and substances used by a business. Its goals are to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements, sustain product quality, and make efficient data management possible.
#6.Basic Data (EHS-BD)
Using this EHS application module, we will be able to retrieve data from the legacy system.
#7.EHS-BD-RDF (Report definition)
Using this application module, you can get the output from certain databases, other SAP components, and graphic symbols on the report.
#8.EHS-HEA (Occupational Health)
The development and implementation of particular health surveillance protocols as well as general employee occupational health care are made possible in your organizations by this SAP EHS application module.
#9.EHS-HEA-BD (BASIC DATA)
This module can be used to create and maintain the core data you need to implement occupational health surveillance practices.
#10.Injury/illness Log (EHS-HEA-IIL)
This SAP EHS application module allows you to record and manage any type of medical assistance given to employees. You should maintain track of prior injury treatments, visits to the doctor, and other documents relating to injuries and illnesses in addition to the first aid treatment record.
#11.Reporting (EHS-HEA-REP)
This SAP EHS application module contains report programs that evaluate the entered occupational health data according to a number of standards. The data reports include information such as test results, restrictions, questions, and assignments.
#12.Schedule Planning (EHS-HEA-SCH)
Using this type of application module, you may identify which health surveillance protocols need to be updated, make the appropriate appointments, and send out invitations. Finding out which appointments are scheduled for which dates is straightforward when using daily list options and printing it out as necessary.
#13.Medical Services (EHS-HEA-SRV)
This module enables you to oversee all the steps required in maintaining the health surveillance protocols at the workplace health center. You set up a medical center for each person who needs to adhere to one or more health protocols. A medical service contains all the data relevant to the planned protocols, including work restrictions due to health difficulties, diagnoses, and examination results.
#14.EHS-IHS (Industrial Hygiene and Safety)
The primary functions of EHS-IHS are as follows:
Work areas that can be freely defined serve as the foundation for the organization of industrial hygiene and safety inside the organization.
-
- Defining and overseeing industrial measures and workplace cleanliness.
- Creation of risk assessments.
- Agent data creation and management
- Keep track of accidents or minor injuries.
#15.EHS-IHS-IA (Incident/ Accident Management)
Using this application module, users can record and handle work-related events. You can utilize it to uphold your legal commitments under local, state, federal, and international laws. The term "event" refers to anything you need to or want to record. covering a wide range of events, such as near misses, accidents, personal injuries, and property damage.
#16.Work Area Management (EHS-IHS-WA)
This module acts as the central repository for protocols like industrial hygiene and safety processes. Using the work area management (EHS-IHS-WA), you may choose how your work areas are divided and organized as well as submit information on industrial hygiene and safety.
#17.Risk Assessment (EHS-IHS-RSK)
Users can keep track of the agents (risks or hazards) present in your firm's various work areas with the help of this module. This can investigate and assess the exposure situation in accordance with accepted methodology, and if necessary, order and oversee industrial hygiene and safety activities with protective aims.
#18.Business Objects, Common Components Tables (EHS-MGM-FND-BOC)
This module can create and manage the essential data you require for organizing and carrying out occupational health surveillance protocols in organizations.
#19.EHS-MGM-RAS-AEV (Risk analysis and evaluations)
With the help of this module and its associated workflows, your business processes are carried out within the system. The workflow consists of a number of phases that are either manually or automatically started by the user or the system.
#20.AF (product safety)
Product safety is regarded as a very important module because of safety concerns. For instance, protecting people and the environment from the risks posed by any hazardous materials your company manufactures or distributes is crucial.
SAP EHS Advantages
The following are the key advantages of using SAP EHS:
- Acquire real-time situational awareness throughout the business to reduce noncompliance risk, foster a proactive safety culture, and improve decision-making and action.
- Monitor compliance by real-time analytics and the direct integration of data sources.
- Your workplace can be made safer by addressing risks, hazards, and exposures by promoting a proactive safety culture, documenting events, and demanding improvements.
SAP EHS FAQS
1. What are the roles and responsibilities of SAP EHS?
The roles and responsibilities of SAP EHS professionals may vary depending on the specific needs of the organization, but here are some common roles and responsibilities associated with SAP EHS:
- Implementing the SAP EHS solution within an organization.
- System Administration.
- Business Process Analysis.
- Customize the SAP EHS solution to meet specific business requirements.
- Managing data within the SAP EHS system.
2. What is SAP EHS certification?
The SAP EHS certification is designed to verify individual proficiency in deploying and employing the SAP EHS module. It proves that a person possesses the skills needed to configure, adapt, and use the EHS functions in SAP systems. Individuals can improve their job chances and show that they are competent in implementing and using SAP EHS by earning the SAP EHS certification.
3. What is product safety in SAP EHS?
In SAP EHS, Product safety refers to the functionality that helps organizations manage and ensure their products' safety and compliance throughout their life cycles. It is made to help businesses comply with industry standards and legal requirements for product safety, labeling, and hazardous material management.
4. What does risk mean in EHS?
In the context of SAP EHS (environmental, health, and safety), the risk is the possibility of harm or adverse effects as a result of hazardous interactions with people, property, or the environment. The possibility or probability of an incident happening and the seriousness of its repercussions are both factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SAP EHS is an effective solution to manage and improve the organizations' health, safety, and environmental performance. It gives businesses the power to enforce compliance, drive sustainability initiatives, and safeguard the welfare of their workforce by complying with global EHS standards.If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in SAP EHS, then enroll in "SAP EHS Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP EHS Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| SAP EHS Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| SAP EHS Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| SAP EHS Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .




