- Home
- Blog
- Oracle ADF
- Oracle ADF Tutorial

Oracle ADF, also known as Oracle Application Development Framework, is one of Oracle's key products. It offers declarative and visual approaches for building enterprise-level apps. With its extensive features and functionality, ADF has taken the IT industry by storm. As more businesses migrate to Oracle ADF, the opportunities for talented minds in this field are rising.
Through the medium of this Oracle ADF Tutorial, we'll go over all you need to know about Oracle ADF.
Here’s what you’ll learn in this Oracle ADF Tutorial:
Before going directly into advanced concepts of Oracle ADF, let’s first understand what Oracle ADF is.
What is Oracle ADF
Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) is an end-to-end application framework that leverages Java EE standards and open-source technologies to simplify and accelerate the development of enterprise applications. It's the ideal choice for developers who want to build applications that search, create, display, modify, and validate data utilizing the web, mobile, and desktop interfaces.
It is simple since users can use Oracle ADF to build an application entirely or utilize pieces of it in conjunction with other technologies. It is very adaptable, and it allows developers to create apps more quickly. It provides users with out-of-the-box infrastructure services and a visual and declarative application development environment.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in Oracle ADF, then visit Mindmajix - A Global Online Training Platform: " Oracle ADF Training " This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
Oracle ADF Models
The Oracle ADF Model is a declarative data binding technology that allows for a consistent way to bind user interfaces to business services without coding. Data controls and declarative ADF bindings are two technologies that enable the decoupling of user interface technology from business service implementation in the ADF Model.
You must first construct a data controller for your services before using the ADF Model layer to bind data. The data controller will then display in the Data Controls panel a tree structure, with each subnode representing an element such as a collection, operation, method, or attribute. To construct data-bound parts, you drag and drop the subnodes into the visual editor for a web page or another user interface component.
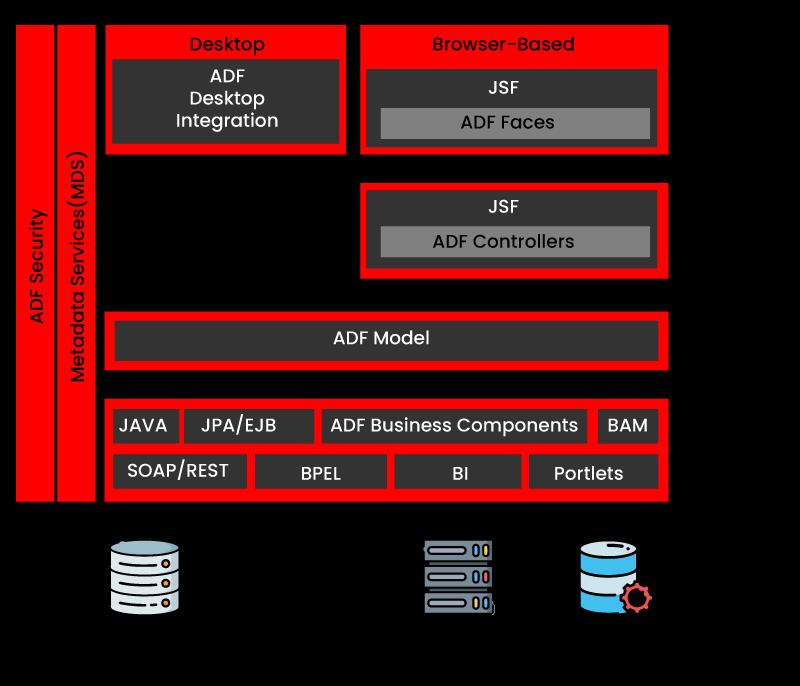
Oracle ADF Architecture
Oracle ADF follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern. In Oracle ADF's MVC implementation, there are four layers:
- Business Service layer: The Business Service layer handles data from diverse sources and business logic.
- Model layer: This layer provides an abstract layer on top of the business service layer, rather than directly handling business logic. This design pattern enables the view and controller to interact with a wide range of business service implementations.
- Controller layer: The web application flow gets controlled by the controller layer.
- View layer: The view layer provides the User interface.
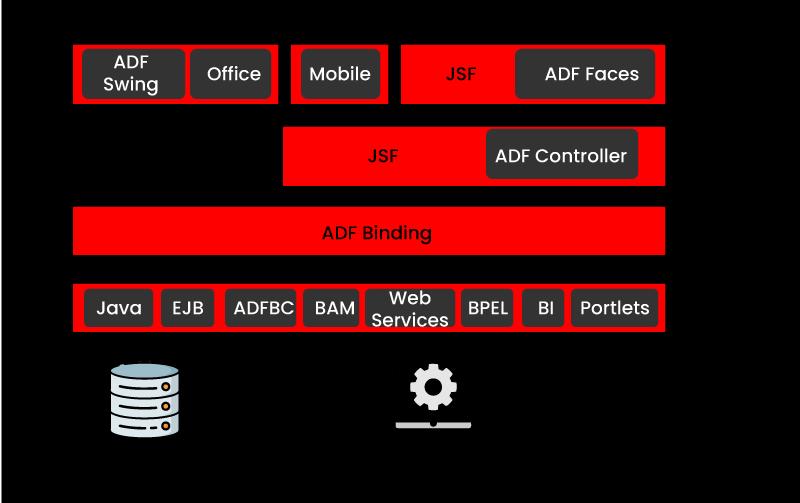
ADF Business Components
ADF Business Components is a technology that allows developers to design reusable data-aware business services quickly. Without writing any Java code, developers can create ADF Business Components services using wizards and visual editors. It's also feasible to add advanced functionality to the core ADF Business Components classes.
ADF Business Components services are made available to the application's display layer via ADF Model.
ADF Controller
ADF Controller is a JavaServer Faces-based advanced navigation and state management mechanism. It allows you to express page flows in a declarative manner. A task flow can contain page flows, allowing them to reuse. Task flows represent the control flow rules that specify the transitions between the activities. This workflow notion is not provided by JSF navigation alone.
The ADF Controller also allows you to call methods on managed beans or Java objects that aren't managed beans, in addition to navigation. Validation, state management, security, and declarative transaction control are among the features it supports.
Oracle ADF Faces
Oracle ADF Faces, a framework that includes over 150 Ajax-enabled JavaServer Faces (JSF) components, is based on the JSF 2.0 standard. ADF Faces was the first-generation set of JSF components handed to the Apache Software Foundation after it was developed. That set is now known as Apache MyFaces Trinidad (directly accessible from the Apache Software Foundation), and it is the basis for today's ADF Faces.
With ADF Faces and JSF 2.0, you can quickly create Ajax-based apps with little hand-coding. You may soon make a stock trader's dashboard app that allows a stock analyst to drag & drop new stock symbols into a table display, which is subsequently updated by the server model using powerful push technology.
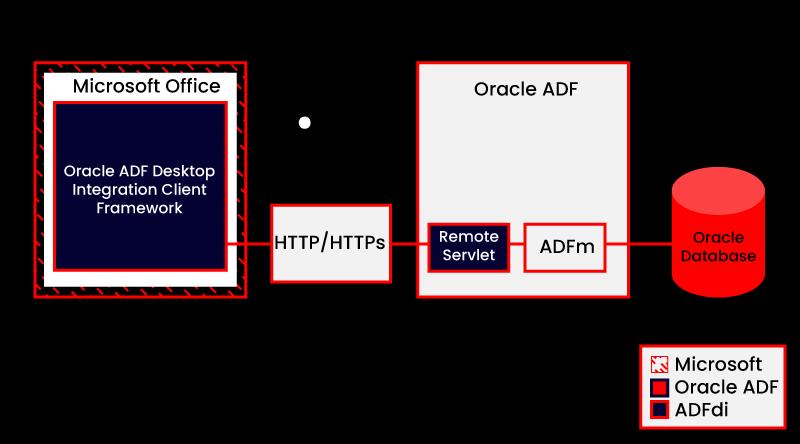
ADF Desktop Integration
Developers can use ADF Desktop Integration to extend the capability of Fusion web apps to desktop applications.
Many users of Fusion web applications utilize desktop apps to manage information used by their web application, such as Microsoft Excel. It enables business users to utilize Oracle ADF functionality even if not connected to their company network.
Business users may also prefer ADF Desktop Integration for using Excel's familiar user interface to accomplish information management tasks like performing complex computations or uploading large amounts of data quickly and easily.
The Oracle ADF architecture includes ADF Desktop Integration. The following diagram depicts the architecture of ADF Desktop Integration.
ADF Key Management Tools and Processes
Oracle ADF is used to create components for larger middleware applications. Oracle JDeveloper, an integrated development environment (IDE) with design-time support for ADF capabilities, is used to create ADF applications. JDeveloper provides complete testing and debugging settings and wizards to build functioning code for your business services. It also generates data binding code as you graphically design your user interfaces.
Oracle ADF Security
The Oracle Application Development Framework (Oracle ADF) includes the ADF Security framework to simplify robust application security. The Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) architecture, including the Java Authentication and Authorization Service (JAAS) and Java EE container-managed security, is the foundation for ADF Security.
Oracle ADF customization
Developers can customize Oracle Fusion Applications using JDeveloper using the customization options given by Oracle Metadata Services (MDS), making changes to meet the needs of a particular group, such as a specific country or site.
You can use JDeveloper to alter existing artifacts, which are then stored in a metadata repository and retrieved at runtime to reveal the customized application. You can also add custom artifacts to your application by packaging them in a JAR file and integrating them with current customizations.
Note that Oracle Fusion CRM Application Composer, which allows you to edit existing objects and expand an application with new things for the following CRM apps, can be used to do many types of customizations in the runtime environment:
- Sales
- Common
However, some adaptations (including all customizations to programs not specified above) necessitate a lower-level method, for which JDeveloper is a must.
Oracle ADF Deployment
Through the instructions below, you can deploy your application to a standalone server once developed. Running the application in Integrated WebLogic Server via JDeveloper is not included in these procedures.
- Create deployment profiles to specify how the contents of an application get packed into archive files for deployment to the target environment. A deployment profile comprises information such as dependency information, platform-specific instructions, and other information in addition to the format and contents of the archive file.
- Create or update the target server's deployment descriptors as needed. Deployment descriptors are XML server configuration files that define an application's deployment configuration and are deployed alongside the program when needed.
- Prepare the security policies and credentials for the application's migration to the standalone server. This includes removing any guidelines and certifications set up for testing from the application's configuration files and creating application roles that correspond to regular functions on the target server.
- Register any ADF MBeans you want to use in the web.xml file of the user interface project.
- ADF MBeans are associated with a variety of configuration files. You can alter configuration properties after the application deploys using the Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control MBean browser to access the ADF MBeans.
- Create an EAR file from the deployment profile in JDeveloper.
- To test deploying, create a standalone instance of the destination application server and install the ADF runtime.
- On the standalone server instance, migrate the application's policy store to the domain level.
- Any of the indicated procedures should be used to test and deploy the application and resolve any issues.
- Ensure that the ADF runtime libraries install on the target server, and then add the policy store for the application.
- Install the software on the target server.
Install Oracle JDeveloper 12c on Windows
To install the platform-agnostic installer on your Windows system, follow these steps:
- Log in to the host machine, and Oracle JDeveloper gets installed.
- Make sure the user account you're using to install Oracle JDeveloper has the necessary permissions. For further information, see "Selecting an Installation User" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Planning.
- Make sure the system you're about to install Oracle JDeveloper on has a certified JDK.
- Navigate to the place where you obtained the installation application using the command prompt.
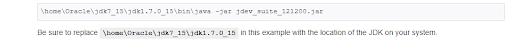
- Invoke java -jar from your system's JDK directory to start the installation software, as illustrated in the example below:
Create, Update and Delete Data using ADF
Create an application workspace and populate it with the business services you wish to use for data management.
To Create Data, follow these steps:
- Right-click the top-level node for the data model project in the application workspace and select New, then From Gallery.
- Expand Business Tier in the New Gallery, select Data Controls, choose the sort of data control you want to create and click OK.
- Complete the wizard's final steps.
- See the following chapters of this guide for information on creating adapter-based data controls and the various types of data controls.
To Update Data, follow these steps:
- In JDeveloper, open the project.
- Add a Commit action binding to the page definition file linked with the Excel worksheet that holds the ADF Table component if it isn't already there.
- See Using Page Definition Files in an Integrated Excel Workbook and ADF Table Component Page Definition Requirements for further information.
- Open the Excel workbook that gets merged.
- Select the ADF Table component field in the Excel worksheet and click the Edit Properties button on the Oracle ADF tab.
- Make that the RowAction properties of the ADF Table component get set.
To Delete Data, follow these steps:
- To make an "ADF Button," drag and drop the "Delete" object from "Data Controls" into the design window of emp. JSF:
- The current data row will be destroyed from the "RowSet" of View Object when the user selects the "Delete" button; it will not erase the record from the database.
- More information is available in the "Submit & Commit" section above and restart your website.
| Check out Oracle ADF Interview and Answers that help you grab high-paying jobs. |
Steps to create an ADF Fusion Web application using ADF Business Components
In this post, let’s use ADF Business Components to develop an ADF Fusion Web application.
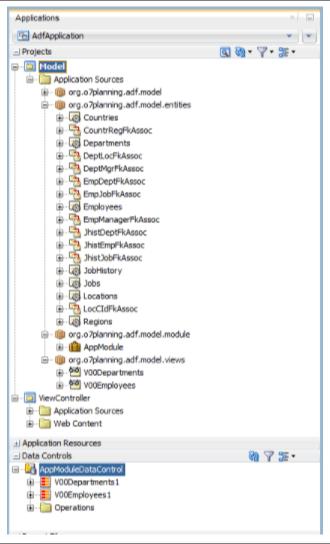
As shown in the diagram, an ADF application comprises two projects, which can alternatively be thought of as two modules (Model and ViewController).
- Create an ADF Fusion Web Application with the ADF Fusion Web Application type.
- Make a Model and a ViewController project.
- In the Oracle database, make a connection.
- On the Model Project, create the Application Module.
- On the Model Project, create an Entity Object.
- On the Model Project, create default View Objects and register them with the Application Module.
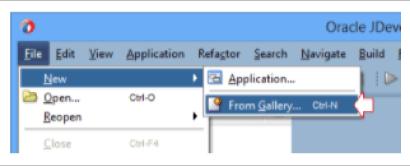
To Create ADF Web Application
1. (Select File/New/From Gallery) in JDeveloper.
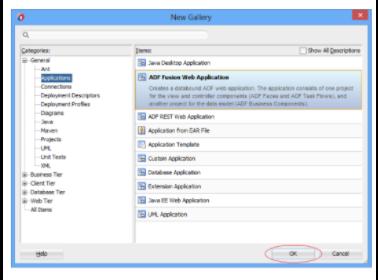
2. Select "ADF Fusion Web Application":
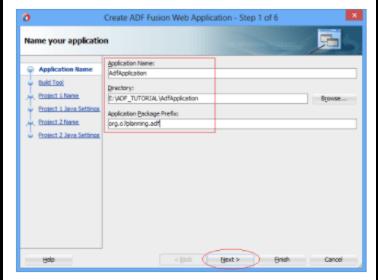
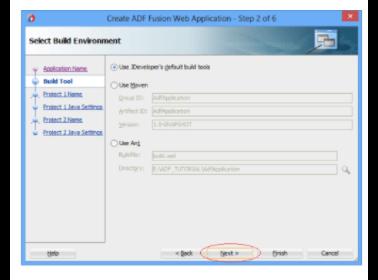
3. The JDeveloper will then build a Model Project with the default name of "Model." If you like, you can call it something else. The Project uses the following technologies:
- Java
- XML
- ADF Business Components
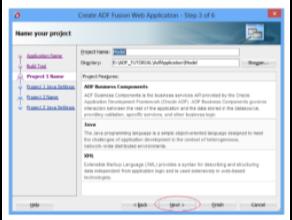
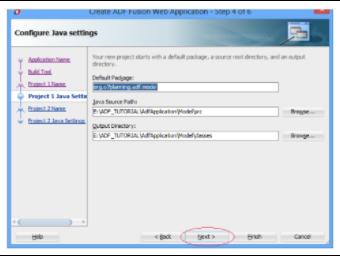
4. JDeveloper will then create the ViewController Project. "ViewController" is its default name. If you like, you can call it something else. The following technologies were utilized in this project:
- Faces of the ADF
- Page Flow in ADF
- Faces for JavaServer (JSF)
- Servlets and JSP
- Trinidad
- XML
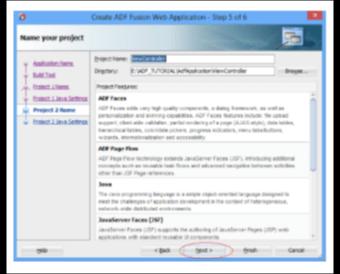
5. Your software has now been created.
Conclusion
Oracle ADF makes Java EE development easier by implementing design patterns and infrastructure code out of the box. ADF gives you the option of using a different development style, different technology, and a different deployment platform. We hope this Oracle ADF tutorial covered some valuable information to help you get started.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .















