SaltStack holds a very important place in the IT industry. It helps IT organizations secure and maintain each infrastructural element that they use for executing digital business processes. SaltStack develops software that can help companies to automate and secure their digital infrastructure at a vast scale.
Earlier, tools like Chef and Puppet were used for configuration management, and these tools support very slow data processing. Fortunately, with the help of Saltstack, we are able to overcome all these limitations. In this SaltStack tutorial, we will study in detail the SaltStack, the features it supports, and its importance in the digital environment. The purpose of this tutorial is to represent how SaltStack can be helpful for business IT infrastructure management and security.
SaltStack Tutorial For Beginners
| Let’s take a look at the topics covered in this SaltStack Tutorial. |
What is SaltStack
Saltstack is an orchestration and configuration management tool which allows the system administrators to perform automation of server management. SaltStack provides high-speed data connectivity and faster communication between the different systems present in the IT organization. Its multithreaded design allows the users to run thousands of tasks simultaneously.
Why Saltstack?
SaltStack Architecture is developed for providing speed and scale. This is the reason why this architecture is used for managing the thousands of servers at Google, Linked In, and many more companies.
For example - If a user has thousands of servers and the user wants to perform functions on every server. A user would be required to log in to every server and perform functions one at a time. This process will be very complicated and time-consuming as functions like software installation and configuration based on particular criteria may consume a lot of time.
To overcome this problem, SaltStack Architecture has been introduced as one can perform different functions just by typing one command. Thus, SaltStack is a single solution to overcome all such issues
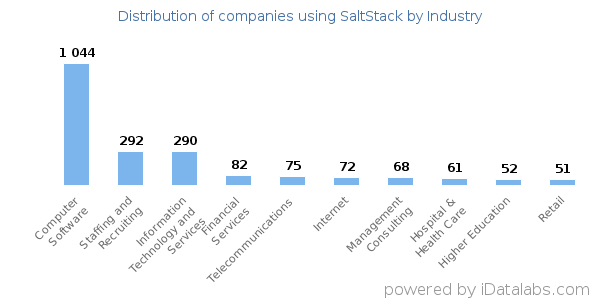
Most of the Saltstack customers are from the United States. The other users of SaltStack software reside in the UK, Canada, India, Brazil, Netherlands, Australia, Germany and, France.
As per the sources, 2821 companies are using the SaltSt ack, most of them are into IT.
Features of SaltStack
SaltStack supports many useful features that were not present in the previously used Configuration management tools. Some of the important SaltStack features are mentioned below:
Fault tolerance
Salt Minions are able to connect to multiple masters at a particular moment by the configuration of master configuration parameters as all the available master’s YAML lists. Every master is allowed to give commands to the Salt infrastructure.
| If you would like to Enrich your career and get a certified professional, then Enrol Our “SaltStack Online Training” Course. This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
Flexible
Saltstack supports a very flexible management approach. The approach can be deployed for following the popular system management models like Agent only, Server only, Agent and Server, or all of them within a similar environment.
Scalable Configuration Management
With the help of Saltstack, one can effectively manage thousands of minions per master.
Parallel Execution model
The parallel execution model of Saltstack enables the commands to parallelly execute the remote systems.
Python API
SaltStack supports a simple programming interface. It is easily extensible and modular thus, it is easy to mold to different applications.
Easy to Set Up
SaltStack is very easy to set up. The single remote execution architecture provided by Saltstack allows to effectively manage the different requirements of the different servers.
Language Agnostic
Saltstack templating engines, file types, or configuration files support the different types of languages.
| Related Article: SaltSalt Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers |
SaltStack Architecture
The SaltStack Architecture is designed to work efficiently with numerous servers - ranging from the Local Network systems to the deployment made over the various data centers. SaltStack Architecture is basically a Server/Client model having required functionalities that are built into a single set process.
Components of SaltStack
SaltMaster: The salt-master is a master daemon, this daemon is used for sending configurations and commands to the Salt Slaves. SaltMaster is basically a machine that manages the infrastructure and server's dictated policies. A single master is capable of handling multiple Masters.
Salt Minions: Salt Minions are slave daemons. Salt minions receive the configuration and commands from the master daemon. The slave daemons are installed on every managed machine and configured to interact with the master daemon. It is the responsibility of Salt Minion to execute the instructions sent by the salt master, report job success, and provide data related to the underlying host.
Execution: Ad-hoc commands and modules are executed against one or more salt-minion from the command line which delivers real-time monitoring.
Formula: Formulas are basically salt states which are already written. Formulas are just like the open-ended Salt States and can be used for performing task like installation of the package, the configuration of a service, setting up users or permissions, and many more.
Grains: Grain is an interface designed for providing information related to Minions, this information is static. When the Salt Minion begins, Grains also get loaded which simply indicates that information available in grains cannot be changed. Thus, the information in Grains could be related to the operating system for the running kernel. Grains are case-sensitive.
Pillar: A-pillar is an interface designed for generating or storing highly sensitive information specific to particular slave daemons, such as passwords and cryptographic keys. It stores the information in a key/value pair and the management of data is done just like the salt state tree.
Top file: It is used for matching the Salt States and Pillar Data to Slave Daemons.
Runners: It is a module present inside the Salt Master and responsible for performing tasks like reading data from the external APs, connection status, job status, query connected Salt Minions, and many more.
Returners: This component is responsible for returning the data from Salt Minion to the other system.
Reactor: A reactor is liable to trigger the reactions at the time when any of the events occur in the SaltStack environment.
Salt Cloud: Salt cloud provides a user with a powerful interface that helps to communicate with salt Minion.
SaltSSH: This component is used to Run the Salt commands on the Secure shell on the systems without any interference from Salt Minion.
So, these are the components included in the Salt Architecture which manages its working.
SaltStack Competitors
Salt, Chef, Puppet, and Ansible are the topmost Orchestration and Configuration management tools. Each of them follows a distinct path to server automation. They were developed for the easy configuration and management of thousands of servers.
Among all of them, Salt is considered to be the best. Let’s understand this concept in more detail that how Salt is a strong competitor for Chef, Ansible, and Puppet.
Platform and Support
The list of platforms that are supported by the SaltStack and its competitors is provided below:
- SaltStack - SaltStack is supported by the different versions of Linux, macOS, Windows, and, Unix.
- Puppet - It is supported by Scientific Linux, Red Hat Enterprise, CentOS, Oracle Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server and, Ubuntu.
- Ansible - Ansible is supported by Scientific Linux via Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL), Fedora distribution of Linux, and some other operating systems.
- Chef - Chef is supported by various platforms like Microsoft Windows, RHEL/CentOS, Solaris, FreeBSD, AIX, and Ubuntu. It is a Python-based configuration management tool that supports the ZeroMQ messaging system which enables users to collect and execute the data in a faster manner. Saltstack architecture is highly scalable and delivers very reliable performance. It uses the ‘Push Model’ to execute the commands through Secure Shell Protocol. The default configuration system used by SaltStack is Jinja templates and YAML.
- Origin Language
- SaltStack - Python.
- Puppet- Ruby.
- Ansible - Python.
- Chef- Ruby.
- Supported Language
- SaltStack Supports every language.
- Puppet supports Ruby.
- Ansible supports every language.
- Chef supports Ruby.
| Related Article: Linux Tutorial for Beginners |
Web User Interface
- SaltStack - The web user interface of SaltStack offers the view of jobs running, event logs, and minion status.
- Puppet- The web UI of Puppet manages the inventorying, reporting, and real-time node management.
- Ansible - The Web UI of Ansible allows to configure the users, groups, and inventories. It also applies the playbooks to inventories.
- Chef - Chef’s Web UI allows the users to find the inventory nodes, view node activities, and assign the roles.
Management Tools
- SaltStack - SaltStack Enterprise is the main tool used for the management of Cloud Orchestration and IT operations. It also managed DevOps.
- Puppet - Puppet supports two tools- Puppet Enterprise and the Open Source Puppet. Puppet Enterprise provides functionalities of the Open Source Puppet and along with that, it also provides API, GUI, and Command-line tools for managing the nodes.
- Ansible - The main tool used by Ansible for management is Ansible1.3.
- Chef - CFE Engine is the configuration management tool used by the Chef.
Performance
- SaltStack - SaltStack is designed for providing high scalability and improved performance. The communication system of Salt develops a continuous data pipeline between the Master daemon and Slave daemon by using ZeroMQ.
- Puppet - It is secure to use and delivers high performance. In puppet, you do not require agents.
- Ansible - It is secure to use, delivers high performance, and does not involve any agent.
- Chef - While using the Chef server, users often struggle to search as the search process is quite slow and not requested by the clients in a concurrent manner.
Price and Value
- SaltStack- It is an open-source, free version. The SaltStack Enterprise can cost up to $150 per machine every year.
- Puppet - Puppet is also a free, open-source version. The Puppet Enterprise may cost up to $1000 per machine every year.
- Ansible - Free and open-source version. Ansible is available free of cost for 10 machines and after that, you need to pay up to $250 per machine every year depending upon the support you require.
- Chef - It is an open-source version. The Enterprise Chef is free for the five machines, $120 for twenty machines, and $300 for fifty machines per month.
Usage
- SaltStack - SaltStack is being used by Rackspace and Cisco. Saltstack is capable of integration with any of the cloud-based platforms.
- Puppet - Puppet is used by Twitter, Paypal, Zynga, New York Stock Exchange, Google, and many more.
- Ansible - Ansible can be deployed to cloud environments, virtualization environments, DigitalOcean, Amazon Web services, Google Cloud Platform, Cloud Stack, and many more.
- Chef- Chef can be integrated with cloud-based platforms like Amazon EC2, OpenStack, and Internap. Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Rackspace.
SaltStack Installation
If you are setting up the SaltStack Environment for the first time, then, you must install the SaltMaster on a dedicated VM or Server. After that, you need to install the Salt Minion on every system which you want to manage by using SaltStack.
For the SaltStack installation, a user must complete the following requirements:
- A Linux Server ( having the latest Ubuntu Server)
- Root or Sudo access to the Linux Server.
To install the updates, use the following command.
Install SaltMaster
‘ sudo apt-get update’.
You can install the SaltMaster by using the given ‘apt-get’ command.
Command - ‘ sudo apt-get install salt-master’.
Install Salt Minion
For the installation of Salt Minion, you can use the following command.
Command - ‘sudo apt-get install salt-minion’.
Install Salt syndic
Install the Salt Syndic with the help of ‘apt-get’ command.
Master Configuration
The Salt-Master configuration can be done with the help of ‘Master Configuration File’. The Master Configuration file is present by default at /etc/salt/master directory. A notable exception can be ‘FreeBSD’ where the master configuration file is present at /usr/local/etc/salt directory.
Configuration
Interface
By default ‘0.0.0.0’ ( for all the interface). The local interface must have an IP address.
For example - interface <192.162.0.1>
Once you have updated the configuration file, you need to restart the Salt Master with the given below command.
‘sudo service salt-master restart’Minion Configuration
Salt Minion Configuration is an easy process. Basically, one value is required to be set as the Master Value so that Minion can easily find where the master is located.
By default, the Salt Minion Configuration is present in the ‘/etc/salt/minion’ directory. In case of exception, configuration is in ‘/usr/local/etc/salt/minion’
Configuration:
- #master: salt.
- master: <local ip address>.
After updating the configuration file, restart the Salt Minion by using the given command.
‘ sudo service salt-minion restart’. Key Management
For managing all the communication between the SaltMaster and Salt Minion, AES Encryption is used. Below the authenticated keys are mentioned which can be used for the communication between the Salt Master and Salt Minion.
‘Salt-key- L’.Outcomes produced by this key:
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
<local system name>
Rejected Keys:If you want to change the state of the minion, you can use ‘-d’ key, and later you can accept or reject the keys.
A user can accept all the keys by using the following command:
‘sudo salt-key - A’. The following keys will be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
<local system name>
Proceed? [n/Y] yKey for minion bala-Inspiron-N4010 accepted.
Issue command - ‘Salt Key Listing’:
It will produce the output as :
Accepted Keys:
<local system name>
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:Sending Commands
You can use ‘test.ping’ command for the communication between SaltMaster and Salt Minion.
Command - ‘sudo salt ‘*’ test.ping’. The output it will generate is
<local system name>
True. Here, ‘*’ sign is representing all the minions. As we have a single minion that is test.ping, it will execute the ping commands and analyze if the ping is successful or not.
SaltStack - Creating a Simple Environment
Now we will be creating a simple SaltStack Environment which is discussed along with simple steps:
Install VirtualBox Environment
Virtualbox is known as a Cross-Platform Virtualization application. This application allows users to run multiple operating systems simultaneously. Virtualbox runs on Linux, Solaris, Windows, and Macintosh. It supports and hosts a different Guest Operating System.
To download VirtualBox, visit: https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
Install Vagrant
Vagrant provides an easy to configure, portable, and reproducible work environment.
Download and install Vagrant from https://www.vagrantup.com
Once you have installed it, you need to configure it. For that, create a file with the name Vagrantfile in the folder and describe the machine type and properties.
Command to run Vagrant - vagrant up.
Command to stop Vagrant- vagrant halt.
Download the Demo Environment
SaltStack offers a demo environment as Vagrant Setup. This environment is hosted in GitHub.
Command to download the setup - cd /cd/to/path git clone https://github.com/UtahDave/salt-vagrant-demo
Start Environment
Command to start the demo environment - cd /cd/to/path/salt-vagrant-demo vagrant up
The response will display after executing the command as result.
Now, 3 servers are running. One server configured with the Salt Master and two with the Salt Minion.
Run Salt Master
Command to login to the SaltMaster - vagrant ssh master
Command to move to the root user - sudo su
Salt master is connected successfully. Below are some basic salt commands.
A command to verify the Salt Minion connection and check the status of connection - salt-key —list-all
The output will be -
Accepted Keys:
minion1
minion2
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:Verify Salt Minion
As all the keys are accepted, now you can send a command from Salt Master to check whether the Minions are listening or not.
Command to verify the Minions - salt '*' test.ping
The output will be -
minion1:
True
minion2:
TrueThe output is indicating that minions are listening.
SaltStack - Access Control System
SaltStack Access Control System allows the users to execute the task within the authorization. This system is used for configuring access to Non-Administrative Control Interfaces. A user can apply the process to different systems.
Access Control System helps the Non-Administrative users in the Salt commands’ execution.
There are three types of Salt Interfaces:
- Publisher ACL system
- External Auth system
- Peer system
Publisher ACL system
This system provides access to the users other than root for Salt command execution on Salt Minions from the SaltMaster. The configuration of the Publisher ACL system is done in the Master Configuration file through the ‘publisher_acl’ configuration option.
For example-
publisher_acl:
user1:
- .*
user2:
- web*:
- test.*
- pkg.Here, user 1 can execute anything whereas, user 2 can execute the only pkg and test ( only on the ‘web*’ minions’.
External Auth system
This system is used for providing access for executing the Salt commands on a particular minion via External Authorization Systems such as LDAP, PAM, and many more. This file is defined in the Master file as mentioned below:
external_auth:
pam:
user1:
- 'web*':
- test.*
- network.*
user2:
- .*User 1 can execute functions in the network or test modules on the Salt Minions which matches the ‘web*’ target.
User 2 can execute anything.
Option ‘-a’ is provided by the salt server for enabling external authentication.
For example - salt -a pam web* test.ping
Peer system
Salt Minions are allowed to pass their commands through the Peer Interface. The configuration of the Peer Interface can be done via the Master Configuration file. It allows SaltMinions to send the commands by using peer configuration from the master and also allows the minions to execute the runner using the peer-run configuration from the master.
Below are both configurations and explained briefly:
Peer Configuration
This configuration is defined in the SaltMaster File as mentioned below:
peer:
.*:
- .*The command is enabling the configuration for all the minions. It is advised to execute this command only in a secure environment.
Peer Run Configuration
This configuration lets the minion execute the runner from the master through the peer r-run option.
For example -
peer_run:
.*:
- .*This command will allow access to all minions to all runners.
How to execute the commands?
For executing ‘test.ping’ on all the minions, you can use ‘salt-call’ command including the ‘publish.publish’ module.
For example- salt-call publish.publish * test.ping
For executing the runner, you can use the below-mentioned command. salt-call publish.runner manage.up
Salt File Server
The SaltStack which comes along with a simple file server that is used for distributing the file to different Salt Minions is known as Salt File Server. It is basically a stateless ZeroMQ server that is developed into the Master.
The main purpose of the Salt File Server is to represent the files for their use in the Salt State System. The Salt File Server can be used for transferring the general file to Salt Minions from SaltMaster.
SaltStack - Git as a File Server
Git is basically an Open Source Distributed Version Control System that is used for keeping the track of modifications made in the file. Salt sends the files using Git File Server from the Git Repositories.
A user can configure the Git to ‘fileserver-backend’ list option and if the user wants to configure more than one repository, it can be done by using the gitfs_remotes option.
Benefits of SaltStack
There are a number of benefits of using the SaltStack, and they are mentioned below:
- Robust: Saltstack is a simple, powerful, robust configuration management framework that can work efficiently with thousands of systems simultaneously without hassle.
- Authentication: SaltStack supports secure authentication. It uses the Secure Shell protocol for authentication purposes.
- Secure: It maintains data security by using encrypted protocols.
- Fast: Saltstack is a very lightweight, fast communication bus that is a base for remote execution engines.
- Virtual Machine Automation: Saltstack uses Virtual Could Controller capabilities for virtual machine automation.
- Infrastructure as data, not code: Saltstack delivers model-driver configuration management, simple deployment, and commands execution framework.
Introduction to ZeroMQ
SaltStack works on the ZeroMQ library. ZeroMQ is an embeddable networking and fast messaging library. Its basic implementation is done in C or C++ and the native implementation for different languages include.Net and JAVA.
It is a peer-to-peer, broker-less messaging process that allows users to design a complex communication process in a simple manner.
There are five basic patterns followed by ZeroMQ
Synchronous Request/Response: It is used to send the request and receive the revert for every sent request.
Asynchronous Request/Response: A requestor will send the request message to start the conversation and wait for the revert. A provider will wait for the incoming messages and revert back as a response message.
Publish/Subscribe: It is used to distribute the data from a single process to different recipients. For example- From Publisher to Subscribers.
Push/Pull: It is responsible for sharing the data with all nodes connected.
Exclusive Pair: It is used to connect two peers in order to make a pair.
ZeroMQ is a flexible tool that allows exchanging messages among various clusters and multi-system environments. It is a default transport library presented in Salt.
Conclusion
The aforementioned information is providing all the details about the SaltStack Architecture. This architecture has resolved the user’s issue of executing multiple commands on different servers simultaneously, thanks to its remote execution capabilities. Salt Configuration Management develops a Master-Minion model to bring the components of infrastructure in line with a provided policy quickly, flexibly, and easily.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SaltStack Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| SaltStack Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| SaltStack Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| SaltStack Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |

Ravindra Savaram is a Technical Lead at Mindmajix.com. His passion lies in writing articles on the most popular IT platforms including Machine learning, DevOps, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, RPA, Deep Learning, and so on. You can stay up to date on all these technologies by following him on LinkedIn and Twitter.

