ArcSight is a security management solution designed to track, and compliance policy guidelines components analyze a company product's data insights. It's a portfolio that can operate with various products to address security issues and boost productivity. In this ArcSight tutorial, we covered every element of the ArcSight portal to assist you in obtaining a practical understanding of how to use the ArcSight portal to manage data and its components.
ArcSight Tutorial - Table of Content
- What is ArcSight
- Is ArcSight a SIEM tool
- ArcSight ESM Architecture
- Components of ArcSight
- ArcSight Latest Version
- Network model in ArcSight ESM
- ArcSight ESM Event Life Cycle
- What is Correlation and Aggregation in ArcSight
- Advantages and Disadvantages of ArcSight
What is ArcSight
ArcSight is an ESM (Enterprise Security Manager) platform. It is a tool built and applied to manage its security policy. It can detect, analyze, and resolve cyber security threats quickly. The ESM platform has products for event collection, real-time event management, log management, automatic response, and compliance management.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in ForgeRock, then enroll in "ArcSight Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
Is ArcSight a SIEM tool?
Yes, ArcSight Enterprise Security Manager (ESM), a robust, adaptive SIEM that brings real-time threat detection and native SOAR technology to your SOC, is a SIEM tool that can empower your security operations team.
Related Article: What is ArcSight SIEM
ArcSight ESM Architecture
ESM uses SmartConnectors to collect event data from your network. SmartConnectors convert device event data into a standardized schema that serves as the basis for correlation. In the CORR-Engine, the Manager processes and stores event data. Users can use the ArcSight Console or the ArcSight Command Center to monitor events, run reports, generate resources, conduct investigations, and manage the system. Additional ArcSight solutions that drive event flow, ease event analysis and provide security alerts and incident response are built on ESM's fundamental architecture.
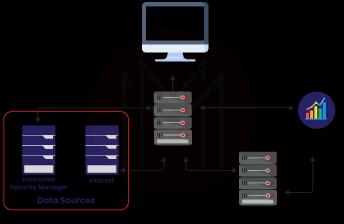
Components of ArcSight
ArcSight is a term used to define the components of a security model, which include features and functionalities for security monitoring. By gathering and preserving data for long-term use cases, ArcSight overcomes the issues of a variety of requirements.
-
Arcsight SIEM Platform
The security and visibility operations that use the monitoring platform architecture are part of the Arcsight SIEM Platform environment. The platform collects, normalizes, and categorizes all network and security device events and logs.
-
ArcSight ESM
The ArcSight ESM can collect a wide range of log data and combine it with a robust correlation engine to detect threats across various products and notify customers to take action on vulnerabilities.
-
ArcSight Logger
The ArcSight Logger enables automated compliance reporting and log management and storage. It has a storage capacity of up to 42TB of log data and can search for multiple events per second across organized and unstructured data. It enables SOX, PCI DSS, NERC, and other regulations' automated reporting.
-
ArcSight Express
ESM and logger's real-time correlation and log management capabilities are included in the ArcSight Express. The Express contains various built-in correlation rules, dashboards, and reports and is described as a "security expert in a box." It delivers infrastructure setup and monitoring solutions at a minimal cost.
-
ArcSight SmartConnectors
The ArcSight SmartConnectors take event data from network devices and standardize it into a schema. Data can be filtered via connections, saving network bandwidth and storage space. SmartConnectors increases efficiency by grouping events and reducing the number of affairs of the same type. The events may be organized into a legible manner, making it easier to use them to create filters, rules, and reports.
ArcSight Latest Version
ArcSight ESM version 7.0, ArcSight Express version 5.0, ArcSight Investigate version 2.20, and ArcSight Data Platform version 2.31 (containing ArcSight's Logger, ArcMC, and Event Broker technology) were all launched in January 2019.
Network model in ArcSight ESM
The correlation criteria are built using the ArcSight ESM Network model, a network and assert models blend.
- The network model represents the nodes and features of the network.
- The Assert model represents attributes.
The following resources make up the network model's elements.
- Asserts depict the network's nodes, such as servers, routers, and devices.
- Assert Ranges - This is a collection of network nodes with a single IP address block.
- Zones - A zone is a segment of the network divided into blocks of addresses.
- Networks - It distinguishes between the two private address spaces.
- Customers- Customers are the business units that are connected to the networks.
Asserts
- The Asserts resources identify any network endpoint within an IP address, MAC address, hostname, or external ID.
- An assert resource is a network identification specification that includes the following.
- Assert name.
- Network IP address.
- MAC address.
- Hostname.
- External ID.
Assert Ranges
- An Assert Ranges is a set of assertions tied to a network that employs a block of IP addresses.
- The SmartConnector identifies the endpoints of an event as a single asset or an asset that belongs to a specific assert range when it is processed. The event schema is pre-populated regarding an assert or asserts range identifier.
Zones
- A zone is a functional group within a network or a subnet, such as a LAN, VPN, or DMZ; an IP address block identifies that.
- A zone is assigned to every assertion or address range. ESM comes pre-configured with a global IP address, resolving problems without needing extra zones.
- Zones in the same network cannot have address ranges that overlap.
- When SmartConnector analyses an event, it looks for the zone associated with each IP address in an ordered list of networks. If a matching zone is identified, the search ends; if not, it moves to the following network in the order given during SmartConnector configuration.
Networks
- When IP ranges overlap, ArcSight resources called networks are employed to distinguish between the zones.
- For ESM, there are two standard networks: local and global.
- The SmartConnector will tag events with the relevant zone using network designations, allowing the manager to discover the correct model for assert events.
Customers
- Customer tagging is a tool created to help Managed Security Services Providers' (MSSP) settings.
- Instead of being considered a source or target of an event, a customer will be deemed its "owner."
- A fixed string or a velocity template variable can be used as client variables.
| Check out: ArcSight Interview Questions and Answers that help you grab high-paying jobs. |
ArcSight ESM Event Life Cycle
In ArcSight ESM, there are seven event life cycles.
-
Data collection and event processing
The information is obtained from a variety of sources and then processed.
-
Network model lookup and priority evaluation
We use the logical construction of a network with naming and structures to comprehend the environment and location, and then it's time to prioritize.
-
Correlation evaluation
The correlations will be analyzed in this step, followed by monitoring and investigation.
-
Monitoring and investigation
The scenarios must be thoroughly understood to know what they are to monitor them, and then an analyst must investigate them before moving on to the workflow.
-
Workflow
The workflow process model is implemented in this phase.
-
Incident analysis and Reporting
Here, we must report the data and analyze what has been gathered or received.
-
Event archival
Finally, the events will be archived in an off-site location. The information can be kept for a long time. All seven stages of an event must be completed before an event can be considered complete.
What is Correlation and Aggregation in ArcSight
-
Aggregation
At the SmartConnector level, aggregation limits the number of events consumed by the destination device (ESM / Logger). Suppose a SmartConnector is receiving events from a firewall device, for example. In that case, it will aggregate (i.e., summarize) similar circumstances over a defined period and deliver a single event to the destination. This can save you a lot of money in terms of bandwidth, storage, and processing.
-
Correlation
Correlation is a technique for determining the correlations between events. ESM's correlation engine, for example, employs the rules you create (or those provided by ESM) to correlate base and aggregated events coming in from SmartConnectors to identify if something of interest has occurred. For example, a failed login event on an endpoint may not be of interest in and of itself, but if the same failed login event occurs several times in a short period, it could indicate a brute force login attempt. This type of action can be monitored by a rule, which will generate a correlation event that can act.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ArcSight
Below are a few advantages of ArcSight
- Integration with intelligent logger and ESM for easy rule creation and management.
- Simple integration with all end-point security management tools (IPS/IDS, Firewall, Anti-Virus) and their consolidated output in a single location to effectively correct true and false positives.
- ArcSight is a powerful tool that can handle millions of EPS files.
- Clustering is possible using ArcSight.
- Integration with IT infrastructures such as ticketing systems, web applications, and threat feeds, among other things.
- Correlation in real-time is compelling.
- The use of dashboards and visualizations is excellent.
Below listed are the few disadvantages of ArcSight
- There is a storage issue that needs to be addressed to improve management.
- The search function needs to be improved.
- ArcSight is a complicated tool, and it's not easy to set up and maintain.
- If you have a vast environment, troubleshooting difficulties on ArcSight can be complex.
- The user terminal is quite large and takes a long time to load.
- The integration is solid, but it is not yet complete because Arcsight cannot directly link with several new popular apps.
- The user interface could've been enhanced.
Explore HP ArcSight ESM 6.5 Security Administrator Sample Resumes! Download & Edit, Get Noticed by Top Employers!
Conclusion
The ArcSight tutorial provides a clear picture of using and comprehending compliance policy guidelines components. We hope that the above information gives you a complete understanding of ArcSight.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| ArcSight Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| ArcSight Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| ArcSight Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| ArcSight Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Viswanath is a passionate content writer of Mindmajix. He has expertise in Trending Domains like Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, etc. His articles help the learners to get insights about the Domain. You can reach him on Linkedin
















