New technology development has recently brought equally dynamic development of companies and corporations. Enterprises strive to protect themselves against various threats and attacks. Threats are usually identified as external threats, but there are also hard-to-detect internal threats. Meanwhile, employing many employees and using many systems, one should pay close attention to threats within the organization.
This type of risk is most often invisible, but its materialization can also significantly impact the company's financial condition. To enable full control over the conflict identification and resolution process and obtain compliance with various acts, the management decides to implement the appropriate GRC class tool. One such solution is a dedicated SAP GRC solution. Let us know what is SAP GRC exactly.
SAP GRC is a tool created to help organizations automate managing user access and monitor SoD risk violations. It allows for personalization and customized processes related to user access management, business roles management, analysis, and monitoring of the risk of segregation of duties (SoD), privileged / Firefighter access, and periodic reviews of access to specific, individual requirements of each enterprise. SAP GRC is software that allows you to manage this process in solutions from various developers.
| What is SAP GRC - Table of Contents |
What is SAP GRC?
SAP Governance, Risk, and Compliance (SAP GRC) is a powerful SAP security tool that can be used to ensure your company meets data security and authorization standards. SAP Governance, Risk, and Compliance solutions enable organizations to manage regulations and compliance and remove any risk in managing organizations' key operations. As per changing market situation, organizations are growing and rapidly changing and inappropriate documents; spreadsheets are unacceptable to external auditors and regulators.
SAP GRC helps an organization manage their regulations and compliance and perform the activities like easy integration of GRC activities into existing processes and automating key GRC activities, low complexity, and managing risk efficiently, improve risk management activities, managing fraud in business processes and audit management effectively, and help organizations perform better, and companies can protect their values. This was all about what is SAP GRC in brief. Let us move ahead with what it stands for.
Governance - Corporate governance involves the set of frameworks, rules, and policies used to achieve established business goals and objectives, including user roles and responsibilities, conflict resolution policies, ethical accountability, and more. While governance acts as a "rule book" for companies, it also offers the core functionality to connect organizational silos, align activities and goals, and keep all employees and processes in check. Good governance should help your organization reduce redundancies within your data, manage risk, limit unnecessary costs, ensure principled operations, and manage, handle, and validate data sources more accurately and efficiently.
Risk Management - From cybersecurity attacks to hacking, fraud, or a worldwide pandemic, risks are ever-present in any organization, regardless of size, location, or industry. But, properly outlined and defined risk management strategies can help identify, mitigate, and remediate any risks, including risks from both internal and external threats. With an outlined SAP risk management strategy and periodic risk assessment, companies can not only better understand the source of their security threats, but they can also predict potential issues within their SAP system and act proactively to resolve issues and minimize losses.
Compliance Management - Compliance deals with rules, laws, and regulations, and it involves outlining compliance processes to ensure companies remain compliant with local, State, and Federal regulations. Advanced compliance software provides functional tools for improved data management and analysis and offers enhanced compliance strategies and continuous monitoring capabilities to keep track of (and meet) key compliance requirements.
Now that we know what is SAP GRC, let us discuss it in detail.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in SAP GRC, then enroll in "SAP Security GRC Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
Why SAP GRC?
SAP GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) offers a range of significant benefits for organizations. Firstly, it enables the seamless integration of compliance activities into daily operations. Organizations can streamline their efforts to meet industry and government regulations by automating compliance processes and centralizing data. This integration eliminates manual tasks and reduces errors, ensuring efficient adherence to compliance requirements.
Secondly, SAP GRC provides real-time visibility into governance, risk, and compliance activities. Organizations gain access to up-to-date information and insights, empowering them to make informed decisions. With comprehensive data analytics and reporting capabilities, SAP GRC allows businesses to monitor compliance, identify potential risks, and proactively address issues. This real-time visibility ensures that organizations can stay ahead of compliance challenges and respond effectively to changing regulatory requirements.
Another notable reason why you must implement SAP GRC is enhanced risk management. By following a well-defined risk management strategy and conducting regular risk assessments, organizations can identify potential threats and take proactive measures to minimize losses. SAP GRC enables organizations to predict and address system issues, strengthening their overall risk management practices. This proactive approach to risk management helps organizations mitigate risks effectively and protect their assets.
Lastly, implementing SAP GRC demonstrates an organization's commitment to compliance and risk management, fostering consumer trust and building a positive reputation. Customers and stakeholders value organizations prioritizing data security, ethical practices, and regulatory compliance. SAP GRC provides the tools and controls necessary to enforce compliance, monitor risks, and maintain regulatory standards, resulting in increased consumer trust and a strong market reputation.
What are the Benefits of SAP GRC?
We now know what is SAP GRC very well. So, when it comes to benefits, GRC frameworks in SAP help integrate enterprise-wide processes, systems, and applications to more efficiently manage governance, risk, and compliance and ensure their established business strategies are aligned with its technology solutions. By integrating GRC tools with SAP systems and applications, users can do the following –
- Oversee enterprise risk management strategies and ensure regulatory compliance
- Leverage the internal controls and software support needed to achieve business goals and organizational objectives
- Enhance connectivity between business units through a unified business framework
- Provide secure, authorized access to company resources, tools, and data through defined user management strategies and granular authorization
- Detect access violations and cybersecurity threats with advanced SAP Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) software
- Simplify, manage, and optimize the audit management process for internal and external audits across the organization
SAP GRC Modules
1. SAP Risk Management
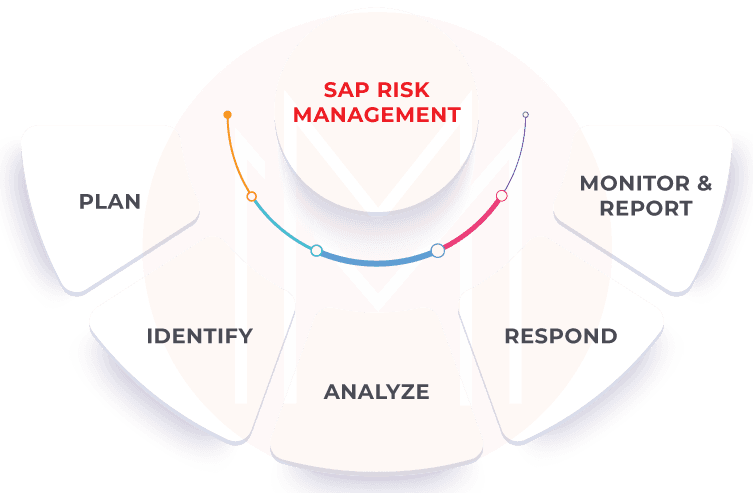
SAP Risk Management is an SAP GRC module that helps in the following -
- Plan risk management within the context of value to the organization
- Identify risks (including drivers and impacts), key risk indicators, and responses
- Analyze risk scenarios (qualitatively, quantitatively, or by scoring methods), model and simulate outcomes to understand exposure
- Respond to risk after balancing costs and benefits and launch workflow-driven responses with remediation tracking
- Monitor & report on risk thresholds, the effectiveness of risk responses, and corrective actions
Business risks fall into five basic categories, all, or any of which an organization's ERM and GRC strategies must be prepared to anticipate, mitigate, and, most importantly, prevent.
- The performance or operational risk has the broadest boundaries and the greatest potential variety. It comes from failures (accidental or intentional) across the structure, systems, people, products, or processes involved in any aspect of business operations.
- Compliance risk results from violations of laws, regulations, codes of conduct, or established standards of practice within an industry or organization.
- IT risk arises from the failure or misuse of IT, leading to loss or negative business outcomes. This can range from accidental IT failures to fraud, hacking, or cyberattacks.
- Financial risk as a business risk category means losing money on an investment or business venture. This may include credit or liquidity risk – or be combined with an operational risk such as fraud or mismanagement.
- Reputational risk can result from failures in any of the above four categories, leading to a weakened public perception of the business. Reputational risk offers less quantifiable loss but is one of the most potentially destructive to any company or brand.
2. SAP Process Control
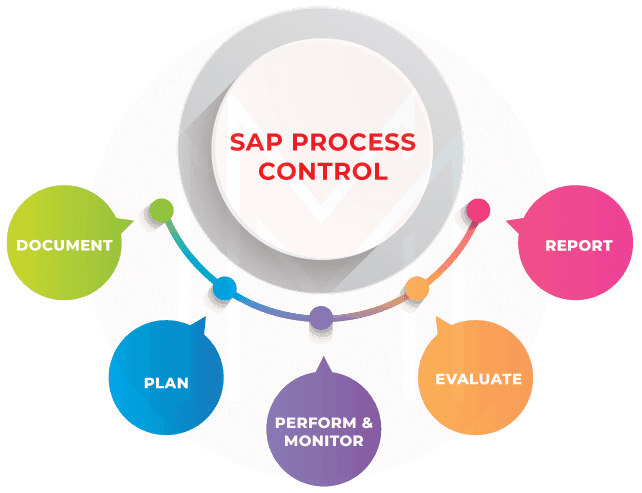
SAP Process Control help in the following -
- Document controls and policies centrally and map to key regulations
- Plan workflow-driven performance, assessments, and tests of effectiveness, but also distribute policies and related surveys
- Perform & monitor manual and automated controls, including continuous control monitoring of configurations, master data, transactions, and related changes
- Evaluate control design & effectiveness, but also raise and remediate issues
- Report compliance ratings and decisions and promote accountability with insightful analytics and sign-off
3. SAP Audit Management
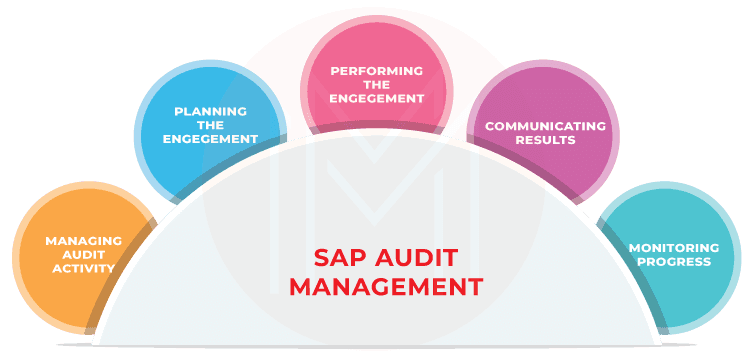
SAP Audit Management is an SAP GRC module that helps with the following -
- Enhance audit quality and provide trusted insights
- Managing audit activity by establishing a risk-based plan, prioritizing audit activities, and aligning with the needs of the enterprise
- Planning the engagement by developing and documenting a plan for each engagement
- Performing the engagement by identifying, analyzing, and documenting relevant information
- Communicating results on engagement objectives, scope, conclusions, findings, and recommendations
- Monitoring the progress of results reported to management
4. SAP Business Integrity Screening
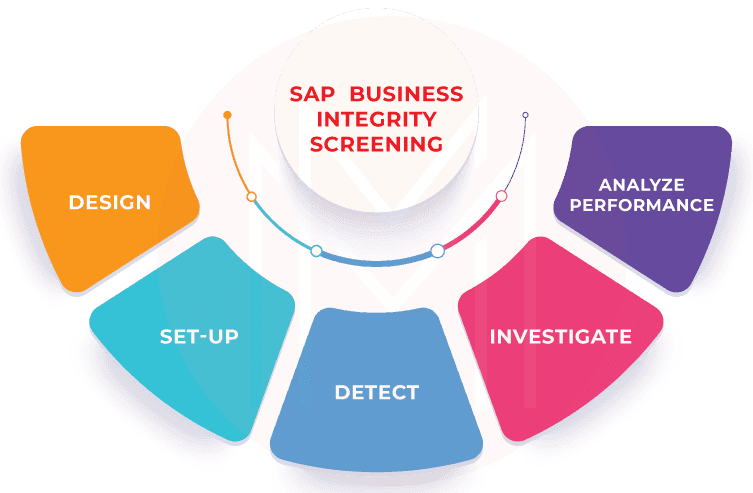
SAP Business Integrity Screening is an SAP GRC module that helps in the following –
- It is used for detecting, investigating, and analyzing irregularities in data, as well as for preventing fraud in ultra-high-volume environments.
- The solution can be used in any industry, including public sector, banking, healthcare, utilities, and high-tech.
- It creates detection strategies that sift through ultra-high volumes of data for clues of fraud and irregularities.
- Screen master data and business transactions against screening lists.
- It investigates the detected irregularities using efficient alert management.
- It continuously improves detection accuracy by minimizing false positives with real-time calibration and simulation capabilities
- It identifies common patterns with deterministic rules and predictive algorithms.
- It leverages machine learning to quickly react to permanently changing patterns.
5. SAP Global Trade Services
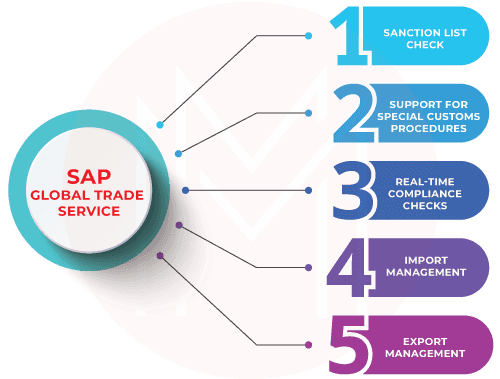
SAP Global Trade Services or GTS is a software that allows companies to support and define import and export trade processes in SAP. It helps in the following
- Export management for handling most trade regulations and localization for more than 25 countries.
- Import management to streamline processes through self-filing, importer security filing, duty calculation, and more.
- It is a preferential and free trade agreement to reduce duty and tax payments and manage vendor and customer declarations.
- It acts as a single data store for master, classification, and compliance data.
- It is a regional and industry compliance to automate compliance with processes such as the European Excise Movement and Control System (EMCS).
- SAP GTS can also be used to screen buyers and vendors to guard against doing business with restricted or denied entities, for example, those on terrorist watch lists.
6. SAP Enterprise Threat Detection
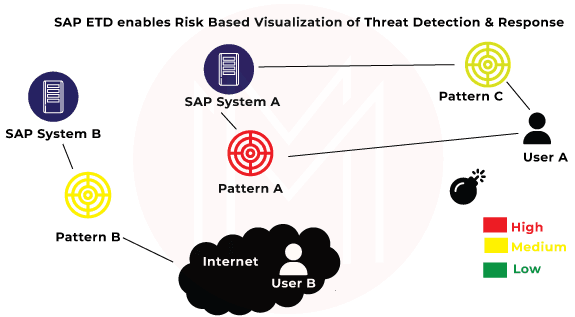
SAP Enterprise Threat Detection is an important SAP GRC module. It is a security tool that helps organizations identify and respond to potential threats to their SAP systems. It uses machine learning algorithms to analyze system behavior and detect anomalies that could indicate a security breach or other malicious activity.
- The tool alerts when potential threats are detected and offer recommendations for responding to and mitigating the risk.
- SAP Enterprise Threat Detection is designed to be integrated with other SAP security tools, such as SAP Identity Management and SAP Single Sign-On, to provide a comprehensive approach to securing SAP systems.
- It is designed to help organizations protect their SAP systems from external and internal threats. It does this by continuously monitoring system behaviour and looking for anomalies that could indicate a security breach or other malicious activity.
- The tool uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data from various sources, such as log files and user activity, to identify patterns that could indicate a potential threat.
- When a potential threat is detected, SAP Enterprise Threat Detection provides an alert and recommends actions that can be taken to mitigate the risk.
- SAP Enterprise Threat Detection also provides visibility into the security posture of an organization's SAP systems. It can generate reports that show the status of security controls, vulnerabilities, and compliance with security policies. This can help organizations identify areas where they need to improve their security posture and take proactive measures to reduce the risk of a security breach.
- It can be integrated with other SAP security tools, such as SAP Identity Management and SAP Single Sign-On, to provide a comprehensive approach to securing SAP systems.
7. SAP Privacy Governance
SAP Privacy Governance is an SAP GRC module that does the following –
- Simplify governance - It evaluates organizational maturity and establishes a security and privacy governance model by requirements and best practices.
- Operationalize privacy management - It embeds data-driven assessments within business processes to meet organizational privacy requirements.
- Manage the data subject rights request lifecycle - It facilitates self-service requests and automates the review and response process to enable better privacy management practices.
8. SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance

SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance or IAG is SAP's latest innovation for Access Governance. It helps in the following –
- SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance (IAG) is a multi-tenant solution built on the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) and SAP's proprietary HANA database.
- It is bundled with SAP Business Technology Platform or BTP Identity Provisioning Service (IPS) and Identity Authentication Service (IAS).
- It comes with product enhancements in the areas of Ariba Integration (via SCIM API), Mitigation Assignment Reporting, Management of User IDs mapped through multiple cloud applications, Added authorization checks for Access Control bridge integration, Conditional UI fields and more.
- It is also released with product enhancements in areas of integration with SAP Concur, SAP Sales Cloud, SAP Service Cloud, SAP Advanced Financial Closing, and SAP Intelligent Asset Management
- It is enhanced in areas such as customizing workflows for access management, additional properties to support OAuth 2.0 Authentication for SAP SuccessFactors, support for provisioning of unique universal ID(UUID) for SAP S/4HANA
- With SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance, customers can now integrate non-SAP solutions based on Open System for Cross-Domain Identity Management (SCIM)
9. SAP Access Control
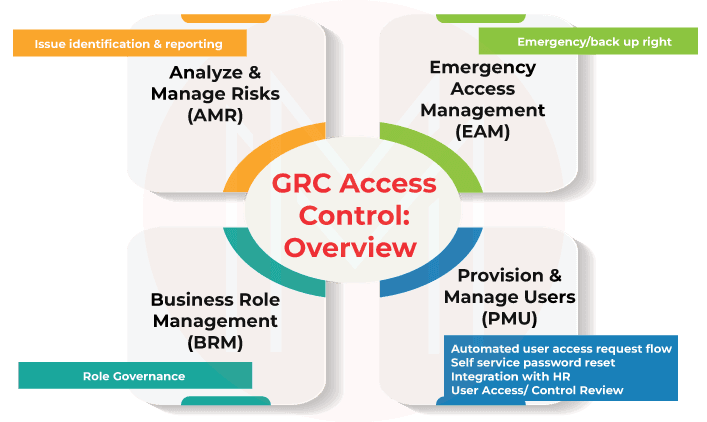
SAP Access Control is an enterprise software application that enables organizations to control access and prevent fraud across the enterprise while minimizing the time and cost of compliance. The SAP access control solution is an add-on to SAP NetWeaver and works with SAP applications and other applications, such as SAP Finance, SAP Sales and Distribution, Oracle, and JDE. The access control solution provides a framework for managing application authorization functions.
SAP access control analyzes risk
- Use a comprehensive, predefined rule set
- Perform cross-system analysis for enterprise applications in real-time or offline mode
- Take action to remediate and mitigate access risks
- Simulate changes to identify and prevent new risks
SAP access control manages access
- Self-service, automated access requests
- Workflow-driven approval process
- Embedded risk analysis simulations to "stay clean"
- Automated provisioning to enterprise applications
SAP access control maintains the role
- Rely on a configurable methodology for role definition and maintenance
- Define roles in business terms and align them with business processes
- Analyze and optimize business roles
SAP access control certifies authorizations
- Automate periodic user-access review
- Certify role content and assignment to users
- Automate review of mitigating control assignments
- Monitor Privileges
- Manage emergency access
- Review user and role transaction usage details
- Get proactive notification of conflicting or sensitive action usage
- Customize dashboards and reports
Segregation of Duties Management Process
Phase 1
- Risk Recognition - In this first step, you define a high-level list of applicable SOD conflicts that allow fraud or generate significant errors. The outcome of this step is that your business has determined what unacceptable risk they want to report on and manage via remediation or mitigation. This step is carried out outside the system and includes a fundamental understanding of business processes and their vulnerabilities.
- Rule building and validation - In the second step, you build the technical rule set based on the recognized risks from step 1. The outcome of this step is the technical rule set that allows you to analyze and identify risks on users, roles, or profiles. The technical rule set is built in the ARA module.
Phase 2
- Risk analysis - The first step in phase two is to analyze the result of the risk analysis. The ARA module allows you to perform a risk analysis against users, roles, profiles, and HR objects (positions, jobs, etc.). The result of the risk analysis will identify if a single user, a single role, a single profile, or a job/position can perform any conflicting functions defined in Step 1. As a security administrator, you can use the results to provide the business insight into alternatives for correcting or eliminating discovered risks.
- Remediation - This is one of the most important steps in the process. The goal is to remediate the occurrence of the conflict on a user level. Please note the occurrence of an SoD conflict happens the most when assigned to a user. Therefore, evaluate whether the conflicting tasks can be separated to another user.
In this step, role changes and reassignment of roles become necessary because only then is a hard remediation of access violations possible. The result of this step is to reduce the number of conflicts to a minimum so that only a few must be mitigated.
- Mitigation - If remediation isn't possible, the remaining risks must be mitigated. Mitigation requires a formal description and action to mitigate the risk appropriately. In most cases, mitigation is achieved by implementing additional monitoring procedures that ensure compensation for the risk after an action happens. Mitigating actions are, in most cases, performed after an event happens. Therefore, it's recommended to use mitigations as little as poss.
Phase 3
- Continuous compliance - In this final phase, it's important to establish a continuous process wherein every access request is reviewed against the SoD conflict matrix before provisioning. In addition, make sure that all role changes undergo risk analysis and are remediated before becoming available to end users. The result is that your system remains clean from violations.
Best Practices for Developing a Successful SAP GRC Strategy
- Establish Ongoing Controls - Use preventative controls and ongoing access analysis to maintain a continuous process. Implement periodic access reviews and controls around provisioning. Staying clean requires continuous compliance procedures. In addition, assess risks - which requires accurate visibility, and all possible scenarios that could occur in the event of a breach, then create well-defined rules based on industry best practices.
- Communicate and Align - It is important to have GRC knowledge at every level of the organization, especially given the survey’s finding that a distinct disparity exists between the security concerns of executives and those of frontline IT and security employees. Only 25 percent of executives reported being either very or extremely concerned about security, compared with 80 percent of the latte
- Train - Communicating and training across the company is critical. Organizations need to train managers and employees on GRC so that all are aware of their part in achieving compliance. Given the increased risks that arise when security concerns are not taken seriously at the executive level, organizations should seek outside counsel if help is needed to help increase understanding across the company.
- Leverage Frameworks - To help map controls that are relevant to the business, leverage security and compliance frameworks like NIST, COBIT, and ISO. Enforce compliance by conducting ongoing access reviews and automating these where possible. Automation reduces the GRC burden on both IT and audit teams.
SAP GRC Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the use of SAP GRC?
SAP GRC, or Governance, Risk, and Compliance, provides a set of tools designed to help companies integrate compliance activities into their day-to-day operations, offer real-time visibility for more informed business decisions, and enforce customized controls to monitor risks and maintain compliance.
2. Is SAP GRC and SAP security same?
GRC looks at what users can do and are doing in the system, then creates policies to remediate risks and meet regulatory compliance requirements. SAP security, on the other hand, implements those policies on a day-to-day basis. For example, by provisioning new users and investigating signs that the system is not operating in accordance with GRC requirements.
3. What are the Components of SAP GRC?
Following are the components of SAP GRC – Access control, process control, risk management, environment, health and safety, and global trade service. Further, Global Trade Service has three sub-modules. These are compliance management, customs management, and risk management.
4. Does SAP GRC require coding?
Yes, SAP GRC requires coding.
5. Is SAP GRC on demand?
Yes, SAP GRC is high on demand. It enables organizations to measure, monitor and report on their compliance and risk management activities. SAP GRC helps organizations identify, manage, and respond to evolving business risks, reduce the cost of compliance, and improve corporate governance. The suite is modular, allowing organizations to select the components that are most relevant to their business.
6. What are the Types of GRC?
SAP Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) is an integrated suite of software solutions designed to help organizations comply with various regulations, reduce risk, and optimize IT governance. It provides a comprehensive set of capabilities, such as policy management, compliance management, risk management and control management.
- Governance - Corporate governance involves the set of frameworks, rules, and policies used to achieve established business goals and objectives, including user roles and responsibilities, conflict resolution policies, ethical accountability, and more.
- Risk Management - SAP risk management strategy and periodic risk assessment, companies can not only better understand the source of their security threats, but they can also predict potential issues within their SAP system and act proactively to resolve issues and minimize losses.
- Compliance Management - Compliance deals with rules, laws, and regulations, and it involves outlining compliance processes to ensure companies remain compliant with local, State, and Federal regulations.
7. What are the types of risk in SAP GRC?
- The performance or operational risk has the broadest boundaries and the greatest potential variety. It comes from failures (accidental or intentional) across the structure, systems, people, products, or processes involved in any aspect of business operations.
- Compliance risk results from violations of laws, regulations, codes of conduct, or established standards of practice within an industry or organization.
- IT risk arises from the failure or misuse of IT, leading to loss or negative business outcomes. This can range from accidental IT failures to fraud, hacking, or cyberattacks.
- Financial risk as a business risk category means losing money on an investment or business venture. This may include credit or liquidity risk – or be combined with an operational risk such as fraud or mismanagement.
- Reputational risk can result from failures in any of the above four categories, leading to a weakened public perception of the business. Reputational risk offers less quantifiable loss but is one of the most potentially destructive to any company or brand.
8. What are the three categories of risk?
The three categories of risks are operational, financial, and compliance.
9. What are the general types of risk?
- The performance or operational risk has the broadest boundaries and the greatest potential variety. It comes from failures (accidental or intentional) across the structure, systems, people, products, or processes involved in any aspect of business operations.
- Compliance risk results from violations of laws, regulations, codes of conduct, or established standards of practice within an industry or organization.
- IT risk arises from the failure or misuse of IT, leading to loss or negative business outcomes. This can range from accidental IT failures to fraud, hacking, or cyberattacks.
- Financial risk as a business risk category means losing money on an investment or business venture. This may include credit or liquidity risk – or be combined with an operational risk such as fraud or mismanagement.
10. What are the categories of risk?
Risks can be operational, financial, technological, environmental, strategic, and more.
| Related Article - SAP GRC Interview Questions |
Conclusion
Technology plays a vital role in early risk detection – but enterprise risk management requires more than technology. The organization's values, processes, and commitment are vital to the way that it manages risk. A recent article in Forbes supports the growing need and desire for enterprise risk management (ERM) strategies that use "proactive, integrated solutions encompassing people, data, and infrastructure.” Thus, it is an unavoidable reality that SAP GRC modules must be completely integrated into organizational structures and roles from the top down to be successful. Although establishing the most effective strategy is a steep uphill battle, once you reach the summit, it is merely a matter of maintenance and continued education. Enroll in SAP Security GRC Training to enhance your Skills.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP GRC Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| SAP GRC Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| SAP GRC Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| SAP GRC Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















