JMeter is a performance analysis and measurement tool for several software products and services. This is solely a Java-free program for testing FTP or Web applications. It's used to run Web application performance tests, load testing, and functional tests. This blog looks at a crucial JMeter concept called JMeter Correlation.
- What is JMeter Correlation?
- What is Correlation?
- Why do we Need Correlation?
- Steps to Use Regular Expression Extractor
- JMeter Correlation: Demo
- Steps to Achieve Correlation in JMeter
- What is Correlation in Load Testing?
- Manual Correlation in JMeter
- Making Manual Correlation Easier
- Auto-Correlation in JMeter
- Auto-correlation in SmartJMX Key Points
- How do you do correlation and Parameterization in JMeter?
- How does JMeter handle dynamic values?
- How does JMeter correlate header values?
What is JMeter Correlation
Correlation is the process of obtaining information from one request that can be used in a future request or any other request that has to be completed. Processors are required for extracting values from a request. HTMLLinkParser and other pre-processors can remove all links from a page received in response.
In most cases, post-processors such as XPath and Regular Expression Extractor extract values from responses and store them in variables. The same variable can now be used in the following request and future submissions. In most circumstances, you'll find JMeter obtaining session, cooked, login credentials and then using them as a parameter in other proposals.
What is Correlation
Correlation is the process of transferring information from one step's response to another step's request. It catches and saves the server's dynamic answer before passing it on to other requests. When a reply returns different data for each iterating request, it is active. This might sometimes affect subsequent queries. Correlation is necessary for performance load test scripting because it will become ineffective if it is not handled correctly.

Why do we Need Correlation?
One of the most fundamental components of scripting is correlation. It retrieves dynamic data from previous requests and posts it to new submissions. Let's look at an example to see why we require correlation in the first place. Assume we've captured a scenario in which:
- A user inputs their login information and clicks the OK button.
- The user navigates to the home page and makes further actions.
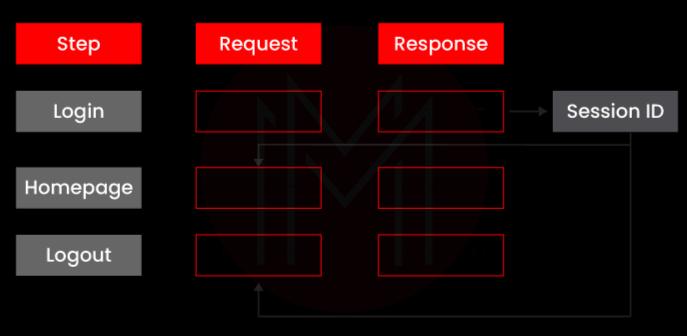
Session variables are produced dynamically when we log in to a website. These session variables are passed along to subsequent requests, assisting in validating and verifying the actions taken. Otherwise, the test will fail because the web requests do not match the dynamic variables. We'll need to employ the Regular Expression Extractor for correlation.
Steps to Use Regular Expression Extractor
When utilizing JMeter's Regular Expression Extractor, four stages follow. It contains the following items: When utilizing JMeter's Regular Expression Extractor, four steps follow. It includes the following items:
- Using JMeter to Create a Test Plan
- Regular Expression Extractor is being added to the Test Plan.
- In the next step, refer to the extracted value.
- Run the test and make sure it's valid.

JMeter Correlation: Demo
The JMeter program must first be downloaded and installed on your PC.
Steps to Achieve Correlation in JMeter
- To begin, open JMeter and pick the Test Plan.
- Next, right-click the Test Plan and select Add Thread Group from the menu.
- Then you must add an HTTP Request and enter any website's server name or IP address. This will be the Step 1 Request. Select Sampler and add HTTP Request by right-clicking on Thread Group.
- After you've added the Server Name to the HTTP Request, you'll need to add the Regular Expression Extractor to get some value out of Step 1's Response. Select Post Processors and add Regular Expression Extractor by right-clicking on HTTP Request.
- After you've added the Regular Expression Extractor, you'll need to fill out four critical fields to extract a response value.
- Name of created variable - Enter any word for the variable.
- Regular Expression - Any regular expression you wish to get from the server should be added here.
- Template - Add the number of Groups to your Regular Expression template.
- Match No - For your Regular Expression, enter any number of matches.
What is Correlation in Load Testing
The technique of recording and storing the server's dynamic response and passing it on to subsequent queries is known as correlation. When a reply might return different data for each iterating request, it is termed active, sometimes affecting the following questions. Correlation is a crucial step in performance load test scripting since if it isn't done correctly, our script will be rendered useless.
It is vital to determine which reaction is dynamic and static from testing (the data stays the same for iterating requests). Every HTTP web performance test typically includes data correlation. The correlation may be ignored when evaluating static content pages, such as some homepages and contacts. In other circumstances, correlation handling is unavoidable at some point throughout the test.
Manual Correlation in JMeter
The developer manually detects correlation points in the test flow and maps the values to be substituted in subsequent requests, known as manual correlation.
In Apache JMeterTM, correlation is handled in two steps:
- Extracting dynamic data from a key request and storing it in a variable (using "Add -> PostProcessor" components like the "Regular Expression Extractor").
- Reusing a variable in every instance where dynamic data is involved.
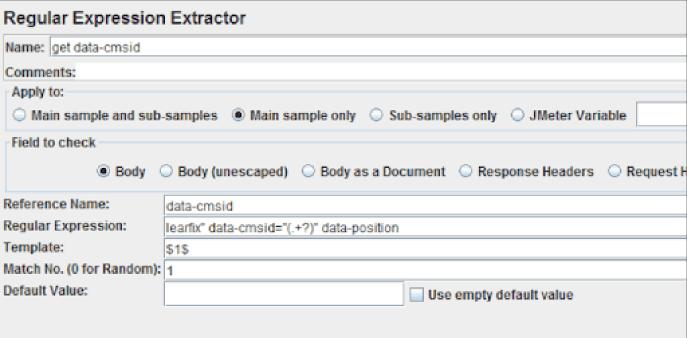
A "Regular Expression Extractor" may be seen in the image above, which extracts data from the preceding sample's body. The variable $data-cmsid, which will be dynamically mapped during execution, can be used in subsequent requests after this component. This blog post will teach you how to correlate manually.
Making Manual Correlation Easier
- You can manually correlate if your script is tiny and only has a few correlation points. On the other hand, manual correlation is time-consuming and error-prone when your writing is vast and has a lot of correlations.
- According to my experience, it's best to strengthen your test requirements analysis before working on a hypothetical "big script" with many correlation points.
- This can be accomplished by dividing the extensive test into smaller groupings of test requirements. In terms of development and execution, each subset should, if possible, be atomic.
- The breakdown process's final goal is to produce a tiny script aggregated/sequenced into the last run scenario, possibly right in JMeter's UI.
- On the other hand, this breakdown process involves expensive time and effort.
- Correlation might be automated, which would make things a lot more accessible.
Auto-Correlation in JMeter
For the desktop version, JMeter does not include a native autocorrelation function. However, for free, we can use the BlazeMeter SmartJMX, which is included in the BlazeMeter Proxy Recorder. According to the saved script, the recorder has generated a JMX script that is automatically correlated.
Auto-correlation in SmartJMX Key Points
- SmartJMX is part of Blazemeter's Proxy Recorder Technology and is accessible for free.
- Because the Proxy Recorder technology is integrated into the web workplace, it does not require installation.
- SmartJMX can record HTTP web pages, run native mobile apps, and use mobile browsers. Any HTTP-based application is compatible with it.
- AFTER RECORDING, the JMX file can now be processed on the local JMeter. The SmartJMX button displays once the script is recorded. A JMX file will be created with all of the correlation points automatically recognized when you click this. Given the importance of correlation in the script, it is recommended that the process be automated to avoid manual errors and save time.
How do you do correlation and Parameterization in JMeter?
When a script requires many different users, parameterization is utilized. CSV files can be used to retrieve other users and data. So, if a script runs with a thread count of 50, it will download a new user detail from the CSV file each time it runs. To Deal With Correlation The post-processor "Regular expression extractor" extracts the variable’s value from the first request for subsequent requests. Parameterization is concerned with the user's input values, whereas Correlation is examined with the data given by the server in response to the request made.
How does JMeter handle dynamic values?
To work with JMeter dynamic values, you must first receive and save the dynamic value from the response and then utilize that value in subsequent requests. The Regular expression extractor post-processor is used to do this.
How does JMeter correlate header values?
The "Regular expression extractor" post-processor is necessary to correlate header information in JMeter.
- In that case, Apply to The "Main sample" and pick "Response headers" in the field to verify.
- Fill in the blanks with the values for all of the fields.
- The value of the variable stored in JMeter will be named after the name specified in the name of the generated variable. If you enter an expression in the Reference expression area, the actual value of the response header parameter will be selected.
- Give the template a name of $1$.
- Now use $ and the variable name in braces to access the value, such as $ Variable name.
Conclusion
JMeter's correlation is a crucial feature. We learned about JMeter Correlation and the many sorts of correlations in this blog, like Manual JMeter Correlation and JMeter Auto-Correlation. We hope you found this information to be beneficial.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| JMeter Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| JMeter Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| JMeter Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| JMeter Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Viswanath is a passionate content writer of Mindmajix. He has expertise in Trending Domains like Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, etc. His articles help the learners to get insights about the Domain. You can reach him on Linkedin
















