Network troubleshooting is an important skill for any IT professional to have. It involves identifying, analyzing, and resolving network issues, ensuring that a network remains functioning properly.
Having a good grasp of the common network troubleshooting interview questions and possible answers can help you stand out among the competition and make a great impression. We have divided the interview questions into 3 sections below
Top 10 Network Troubleshooting Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the various network cables used in networking?
- What are the most frequent network issues?
- What is Netstat utility?
- What is the difference between a Workgroup and a Domain?
- Why is encryption so important on a network?
- How to troubleshoot IP-related problems?
- How are physical addresses and logical addresses different?
- What are the main elements of a protocol?
- What is the difference between Firewall and Antivirus?
- How can you tell what IP class a particular IP address belongs to?
Network Troubleshooting Interview Questions For Freshers
1) What is Network troubleshooting?
Network troubleshooting is a methodical process that aims to troubleshoot problems and get the network working normally again within the parameters and network. Troubleshooting of a network can be performed manually or automatically.
| If you want to enrich your carrer and become a proffessional in CCNA, then enroll in "CCNA Training and Certification" - This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2) What is a network?
A network is formed by connecting two or more devices so that they may exchange data. A network can be divided into subcategories based on its size, number of nodes, types of connections, functional links, topology, and purpose.
3) What is Troubleshooting?
Troubleshooting is the process of finding a problem, error, or fault in the software, a computer system, or any other device, making a plan to troubleshoot it, and putting the plan into action. It is possible to fix and restore a computer or software that is broken, won't work, or is acting strangely.
Troubleshooting fixes a faulty system or application. It's a strategy with one or more steps, depending on the situation. First, identify the problem, then create a solution, and finally implement it.
4) What are the various network cables used in networking?
When it comes to networks, there are a few distinct kinds of cables that are typically used:
- Coaxial Cable
- Wireless LANs
- Fibre Optic Cable
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
- Cable Installation Guides
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
5) How would you troubleshoot DHCP server problems?
Verify that a system set up on the network can communicate with the DHCP server using an IP address. Verify that both the DHCP server and the DHCP client have their respective services started. Using Nmap, verify if the DHCP server can be accessed.
6) Identify three steps used to diagnose FTP server-related problems?
The three steps to troubleshoot problems with an FTP server are:
- Check with Nmap if the ports are accessible (20 and 21).
- Determine if a firewall is blocking server traffic.
- Ping is used to test connectivity.
7) What are the most frequent network issues?
The following are the frequent problems with networks:-
- Cable Issue: A cable connecting two devices has the potential to malfunction, shorten, or be physically damaged.
- Software Issue: Due to problems with software compatibility and different versions, IP data packets can't get from the source to the destination.
- Connectivity Issue: A physical failure or malfunction of the device's specified port or interface could prevent data from being sent from the source host to the destination host.
- Network IP Issue: If the network's IP addresses, subnet masks, and next-hop router settings are incorrect, no data can go from the source to the destination IP address.
8) What are the steps for the network troubleshooting procedure?
Before you try to fix a problem, make sure you know what it is, how it happened, whom it affects, and how long it has been going on. Instead of wasting time on fixes that don't work, you'll have a much better chance of quickly troubleshooting the problem if you gather the necessary information and explain what's going on.
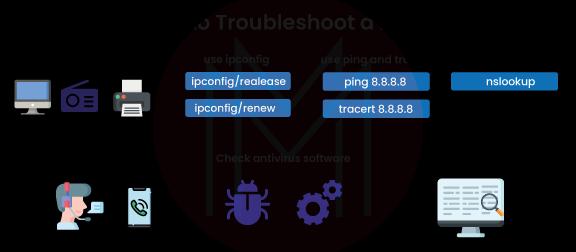
The steps to network troubleshooting are
- Check hardware
- Use ipconfig
- Use tracert and ping
- Perform a DNS check
- Contact the ISP
- Check antivirus software
- Review logs
9) What is a private IP address?
Exclusive usage of private IP addresses is permitted within private networks.
These IPs are reserved for private intranets and are not reachable from the wider Internet. This prevents any internal network conflicts from occurring. Concurrently, since intranets cannot "see" each other, the same pool of private IP addresses can be used for several different ones.

10) What is Netstat utility?
This command is often used for incoming and outgoing connections, listening ports, routing tables, and tracking how often a program is used.
Using the Netstat command, you can make graphs that show statistics about networks and protocols. In the form of a table, you can see the status of TCP and UDP endpoints and the routing table and interface information.
11) What are the benefits of sharing an address?
Instead of routing, sharing addresses makes things safer. This is because private IP addresses on the internal network are not visible to host PCs on the Internet; only the public IP address of the external interface on the computer does address translation.
12) How many different types of TCP/IP layers?
There are four primary layers in TCP/IP:
- Transport Layer
- Application Layer
- Network Layer
- Internet Layer
13) What is the Ipconfig command, and why is it used?
The IPCONFIG command shows the IP address information for a computer. From the output, we can find the IP address, DNS IP address, and gateway IP address given to the computer.
14) How can an antivirus recover data?
You can get a new computer and load it with the latest OS and antivirus programs. Then, add the contaminated HDD to the computer as an additional disc. The backup HDD should then be wiped and scanned. The data migration to the new platform can now begin.
| Related Article : Troubleshooting OpenStack |
Network Troubleshooting Interview Questions For Experienced
15) What is Network Topology?
Network topology is how the devices or nodes of a network (like printers, computers, hubs, servers, routers, switches, Etc.) are connected to each other over a communication medium.
It has two parts:
- The physical topology, which is how the cables (the media) are set up, and
- The logical topology, which shows how the hosts connect to the media.
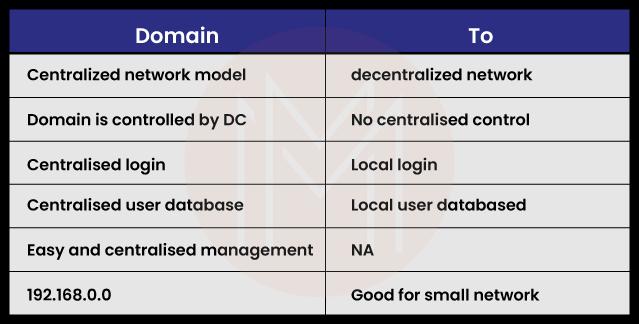
16) What is the difference between a Workgroup and a Domain?
The key difference between a workgroup and a domain is that network administrators in a domain utilize servers to administer all of the computers that are part of the domain.
However, in a workgroup, no one computer has authority over another computer in the group. In addition, devices that are part of a domain might be connected to a number of different local networks, but in a workgroup, all of the devices are members of the same local area network (LAN) or subnet.
17) Let's say a virtual machine is suddenly turned off. Which VM log files should be looked at to troubleshoot what's wrong?
If something like this happens, an administrator needs to analyze the issue by looking at the log files named vmware.log and hostd.log.
The hostd.log log files explain the agent that maintains and configures the ESXi host and virtual machines.
The Vmare.log log files keep track of the activity on the ESX host and the virtual machines it hosts.
18) What common problems with software can cause network problems?
Several of the following can contribute to network-related problems:
- Error in configuration
- Application conflicts
- Client-server problems
- Security issues
- Protocol mismatch
- User policy and rights issues
19) Why is encryption so important on a network?
Encryption is the procedure of transforming data into unintelligible code. The data is encrypted and then translated to its original format using a password or secret key.
During a mid-stream interception, encrypted data would still be inaccessible without the appropriate password or key.
20) What would you do to troubleshoot what was wrong with an FTP server?
If you're having issues with your FTP server, here are the three things you should try:
- Ping is a simple tool for checking network connectivity. The "echo request" is a part of ICMP that is used by the "ping" command (Internet Control Message Protocol). To check if a device is online or active, you can use the "ping" command, equivalent to sending an echo request.
- Check the available ports with Nmap (20 and 21). You may evaluate your firewall and other security measures with the help of the Nmap-hosted security tool. Ports in modern operating systems are numeric addresses used for networking. As a general rule, various services make use of separate ports. It is essential to know which ports are open and closed to prevent any security breaches resulting from the improper port configuration.
- Find out if a firewall is preventing traffic from reaching the server.
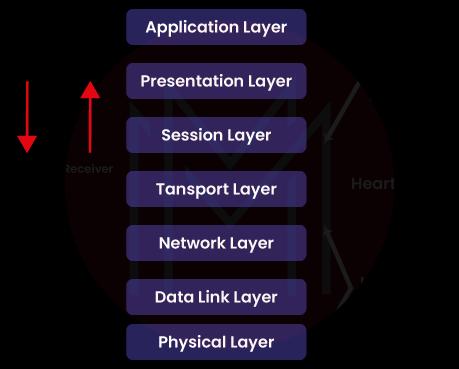
21) What are the OSI Reference Models' layers?
The seven levels that make up the OSI reference models are listed below:
- Physical Layer (Layer 1)
- Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
- Network Layer (Layer 3)
- Transport Layer (Layer 4)
- Session Layer (Layer 5)
- Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
- Application Layer (Layer 7)
22) How to troubleshoot IP-related problems?
If we are unable to communicate with the IP address of the destination and the TCP/IP protocol suite does not reveal a path to the next hop from any point in the network, we will make use of the PING and TRACEROUTE troubleshooting tools to determine the nature of the issue and its geographical origin.
23) What are the steps to troubleshoot IP-related network issues?
Here are some general steps for troubleshooting IP network problems that have to do with:
- The first step in troubleshooting a connectivity problem is pinpointing which devices are causing it between the source and destination hosts.
- Once you have discovered the devices using the tools, the failure could result from a physical connectivity issue. Therefore, you must check all the tethers and cables along the route.
- The LAN connectivity at your office may be malfunctioning. That's why you need to double-check your local area network. The source and the destination IP can't talk because the local port is faulty or unavailable.
- One possible source of the error is a problem with the router's connection to the network, as the data passes through several channels en route to the destination. Therefore, you should ensure the router is defined correctly for each intermediary hop.
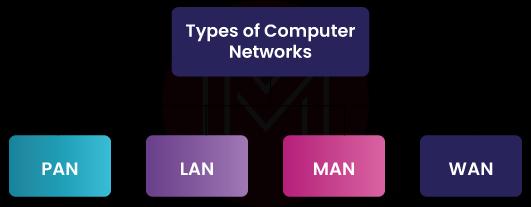
24) What are the different types of a network? Explain each briefly.
There are four main categories of networks. Let's analyze each one separately.
- Personal Area Network (PAN): It is the most basic and simplest type of network and is often used at home. It's a link between the computer and something else, like a phone, printer, modem, tablet, Etc.
- Local Area Network (LAN): LANs are commonly seen in settings such as Internet cafes and smaller businesses. They are typically employed in networked file transfers and online game activity.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): It has more power than LAN networks. MAN covers a small town, city, or other large areas. So much area has to be connected, so a big server is needed.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): It is more complicated than LAN and usually covers a large area and a long distance. WAN is not owned by just one organization; instead, it is owned by many different groups. The Internet is the biggest and most widespread WAN.
25) How are physical addresses and logical addresses different?
Logical Address: It's called an Ip Address (IPv4 -32 bit & IPv6 -128 bit)
Physical Address: It's called a MAC Address (48-bit)
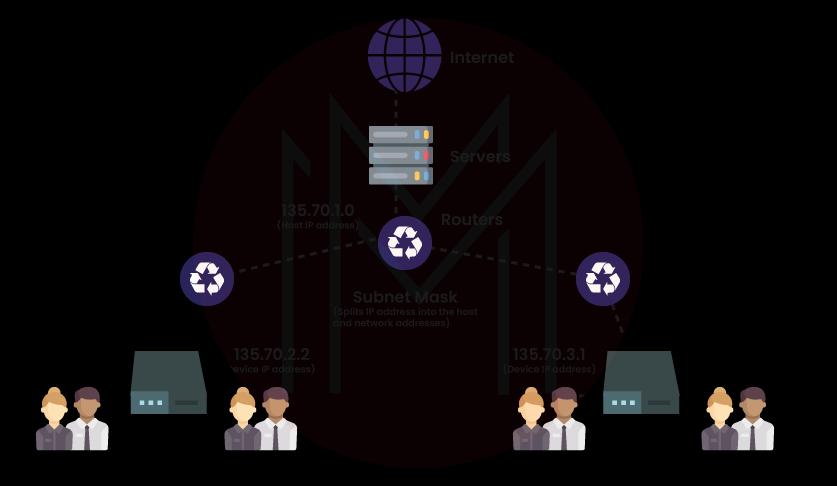
26) What Is a Subnet Mask?
Specifying a network's identity is known as the subnet mask.
For Example:
- For a class A address, a standard subnet mask is 255.0.0.0,
- For a class B address, a common subnet mask is 255.255.0.0,
- For a class C address, a common subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
27) What is the maximum allowable length of a UTP cable?
The maximum length for a single section of UTP cable can be installed between 90 and 100 meters. By using repeaters and switches, it is possible to circumvent this limitation.
28) What are the main elements of a protocol?
A protocol consists of three essential parts:
- Syntax
- Semantics
- Timing
| Read More : Useful Iperf Commands for Network Troubleshooting |
Advanced-Level Network Troubleshooting Interview Questions
29) What is an APIPA IP address? Or, when the DHCP server isn't available, what IP address does the computer get?
Automatic private IP addressing is the acronym for this APIPA system.
Whenever a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server is not accessible, Windows clients automatically assign themselves IP addresses. IPv4 APIPA is the name given to this particular address. Hosts with IP addresses between 169.254.0.0 and 169.254.255.255

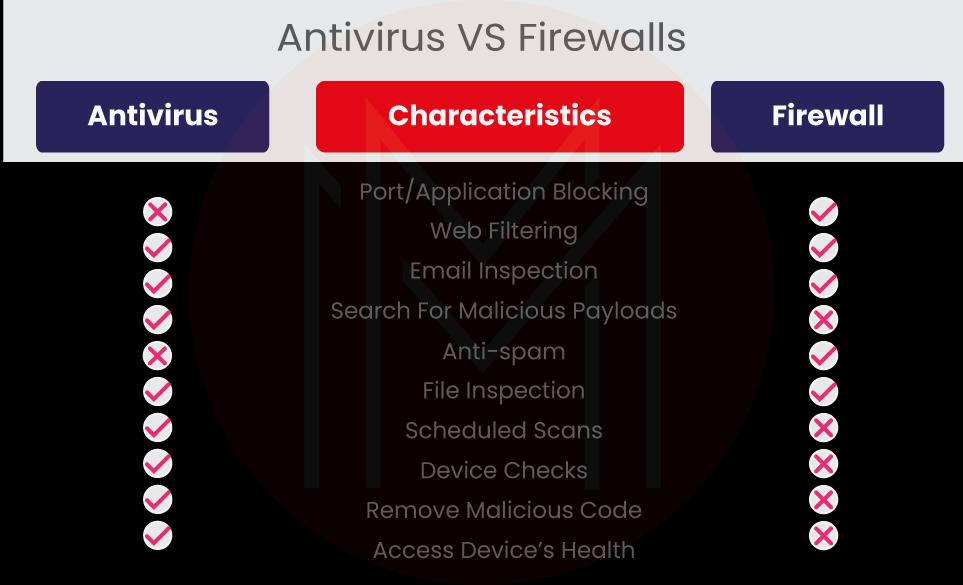
30) What is the difference between Firewall and Antivirus?
Firewall: A firewall prevents unauthorized users from entering a protected network. Malware such as viruses, spyware, and adware can easily be installed and has no defenses.
Antivirus: An antivirus program is designed to ward off any malware, adware, or viruses that might try to infiltrate your computer. These are both networking security applications.
31) How many different addresses are there in each class of Internet addresses?
Here are the five different ranges of Internet addresses:
- Class A: 0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
- Class B: 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255
- Class C: 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255
- Class D: 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
- Class E: 240.0.0.0 – 247.255.255.255
32) What is HTTPS, and what port is it used for?
Secure HTTP is HTTPS. HTTPS is used to send and receive information over a computer network safely. HTTPs give websites authentication, which keeps unwanted attacks from happening.
Port 443 is used by TCP for HTTP. When two people are conversing back and forth, the HTTPs protocol encrypts the discussion so that the data can't be modified. With the help of an SSL certificate, it checks to see if the connection to the server that was asked for is reasonable.
33) What is meant by 127.0.0.1 and localhost?
The localhost or loopback address is 127.0.0.1. These systems are often only accessible to the largest clients or the Internet's founding members. Pinging the server to see if it responds is the first step in diagnosing connection problems.
There could be many reasons why the server isn't responding, such as a malfunctioning network, faulty wiring, or a malfunctioning network card. Pinging 127.0.0.1 indicates that the hardware is functioning properly because it is a loopback connection on the NIC.
With most network operations, 127.0.0.1 and localhost refer to the same thing.
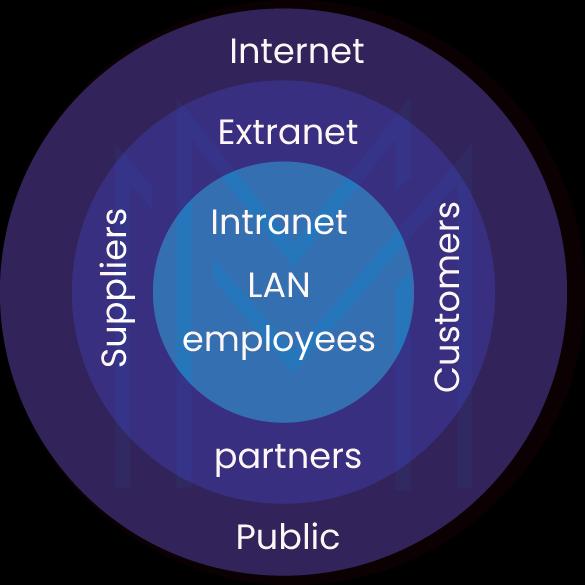
34) What is the difference between the Intranet, Internet, and Extranet?
They both use TCP/IP technology, but the level of access each user has inside and outside of the network is different.
- Intranet: It only lets people in the same organization use it.
- Internet: Anyone from anywhere can use the web to get to applications.
- Extranet: Users from outside the organization are allowed to use the network application or are given access to it.
35) What are different ways to send data through networks?
In computer networks, there are three different ways that data can be sent. Here is a list of them,
- Simplex: Simplex is one-way data transport. Simplex mode transfers data from sender to receiver or receiver to sender—radio signal, computer-to-printer signal, Etc.
- Half Duplex: Both directions can transfer data, but not simultaneously. Data is sent and received. In internet browsing, a user submits a request to the server, which then sends back the web page.
- Full Duplex: Simultaneous bidirectional data transfer. Two-way highways, phone calls, Etc.
36) What is Ghost Imaging?
Ghost Imaging is a software-driven backup method commonly referred to as cloning. The contents of a hard disc are copied to another server in the form of a single compressed file or an image, a collection of files. It can also return a ghost picture to its initial condition if required. It is typically applied while reinstalling an operating system.
37) Which counters are used for debugging VM CPU performance issues?
Memory, central processing unit (CPU), and network utilization can be evaluated using the ESXTOP tool. VMware administrators will find it a beneficial tool when dealing with performance difficulties.
To configure ESXTOP, you will require the vSphere Client and putty and SSH sessions. To evaluate the performance of the CPU, we utilize the counters percent MLMTD, RDY, and CSTP.
38) What are the various aspects that affect a network's performance?
A network's performance efficiency can be affected by the following:
- Transmission medium types
- A large number of users
- Software
- Hardware
39) What are the different types of networks?
There are two different types of networks available they are:
- Server-based network: It allows for the management and protection of a network to be centralized on a small number of computers known as "servers."
- Peer-to-peer network: Computers can function in two roles: the server providing access to shared resources and the client making use of those resources.
40) What's the difference between FTP and TFTP application layer protocols?
The simple file transfer protocol (TFTP) describes a local host retrieving data from a remote host. It takes advantage of the standard packet delivery features of UDP. However, it is unreliable and lacks security.
TCP/IP often provides the File Transfer Protocol to transfer data between hosts (FTP). Because it takes advantage of TCP's facilities, it is dependable and safe. Two connections are established between the hosts: one for command and control information and another for actual data transfer.
41) How can you tell what IP class a particular IP address belongs to?
Class A, B, and C, IP addresses can be determined by inspecting the address's first octet. Class A addresses have a leading zero bit in the first octet. Class B addresses start with the bit position 10. When the prefix is 110, you know you're dealing with a Class C system.

42) What are proxy servers, and how do they keep networks safe?
The primary purpose of proxy servers is to prevent users from the outside world from identifying the IP addresses of a private network. Even the physical location of the network can only be determined if the correct IP address can be provided. Proxy servers can render a network almost completely invisible to users outside it.
Most Common Network Troubleshooting FAQs
1) What is the basic troubleshooting in networking?
Network troubleshooting is a repeatable process, it can be broken down into simple steps that anyone can follow.
- Identify the Problem
- Develop a Theory
- Test the Theory
- Plan of Action
- Implement the Solution
- Verify System Functionality
- Document the Issue
2) Which tool is used for network troubleshooting?
The ICMP ping tool is a basic network troubleshooting tool that allows you to determine whether or not a device is reachable on the network. It logs errors such as packet loss, round-trip time, and so on.
3) What are the 10 common network problems?
The top 10 common network issues are as follows:
- High Bandwidth Usage
- Large Downloads
- IP Address Exhaustion
- File Sharing
- High CPU Usage
- DNS Issues
- Malfunctioning Devices
- Slow Internet Performance
- Physical Connectivity Issues
- Interference in the Wireless Network
4) How do I troubleshoot ping?
The ping command is frequently used to troubleshoot network problems. The command issues ICMP echo requests to the host or the destination. The system calculates the response time and displays the results after the host sends ICMP packets in response.
Simply enter the ping command in the command prompt on a Windows system, followed by the hostname or URL. Enter the same command in the terminal for Linux systems. Remember that the command syntax is as follows:
Syntax: ping hostname
5) How do I troubleshoot TCP IP?
The steps to troubleshoot TCP/IP issues are as follows.
Step 1: Check the configuration
Step 2: Networking traces
Step 3: Ping the computer's local IP address
Step 4: Troubleshoot error messages that appear during the ping or telnet test.
Step 5: Telnet or Ping to the default gateway
Step 6: Check issues that relate to the particular destination node
6) What are the causes of network failure?
Some of the causes of network failures are as follows.
- Traffic spikes
- Misconfiguration
- Sudden hardware failure
- Security breaches
- Incompatible changes
- Equipment Damage
7) What are the types of troubleshooting?
The three types of troubleshooting are
- Working with Hardware
- Working with software
- Working with the internet
Network Troubleshooting Interview Preparation Tips
- Lock in the fundamentals: A technical network troubleshooting interview will ask you about your knowledge of networking and more traditional questions about your behavior. Depending on the job, this could mean coding, networking, troubleshooting, solving, finding, fixing errors, etc.
- Research the job: You need to know what your interviewer wants before you can convince them to hire you. Fortunately, most companies list their requirements in the job posting. So review the description you saw before applying. What are their strengths? What issues must this hire address? Your interview should emphasize these.
- Brush up on your interview skills: Some things depend on how well you answer technical questions, but it is a lot. Interviewers also notice how well you use other interview skills, like small talk, active listening, and empathy, whether you are aware of it or not. These abilities will not only help you wow the interviewer but will also provide them with a notion of what it would be like to work with you.
- Get ready for interviews or tests of your technical skills: If you have been told there will be a skill test or a technical interview, start practicing as soon as possible. Going over this network troubleshooting interview questions will help you get ready to solve problems by giving you practice and putting you in the right frame of mind.
Conclusion
Start studying these essential network troubleshooting interview questions today and get one step closer to acing your next interview!
If you want to impress hiring managers that you are the best candidate for the position of network troubleshooter, you may sign up for the CCNA Training and Certification to get more prepared for the interview.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| CCNA Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| CCNA Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| CCNA Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| CCNA Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .









