- Home
- Blog
- Cloud Computing
- What is Cloud Security - Why is Cloud Security Important?

Changing your company's computing needs from on-premises hardware to the cloud is the first step in positioning it for future success. The cloud facilitates access to more apps, enhances data accessibility, facilitates team collaboration, and simplifies content administration. Due to security concerns, some individuals may be hesitant to adopt Cloud Security. However, a dependable cloud service provider (CSP) can alleviate your concerns and safeguard your company's data with high-quality cloud services.
Meanwhile, Cloud security refers to the technologies and best practices to safeguard data and information within a cloud infrastructure. It is a crucial component of any cloud-based IT infrastructure plan to protect the confidentiality and compliance of cloud-stored data.
Learn more about cloud security, the fundamental cloud environments for which it is necessary, their significance, and their main advantages below.
| What is Cloud Security - Tables of Content |
What is Cloud Computing?
The "cloud," or more precisely, "cloud computing," is the delivery of various services via the Internet.
These resources include servers, data storage, networking, databases, and software. This technology allows organizations to scale their operations more easily by offloading a portion, or the majority, of infrastructure management to third-party hosting providers.
Cloud computing is on-demand Internet access to computer resources hosted at a remote data center and managed by a cloud services provider, including applications, servers (virtual servers and physical servers), development tools, data storage, and networking capabilities, among others (or CSP).
The following are the most popular and widely used cloud computing services:
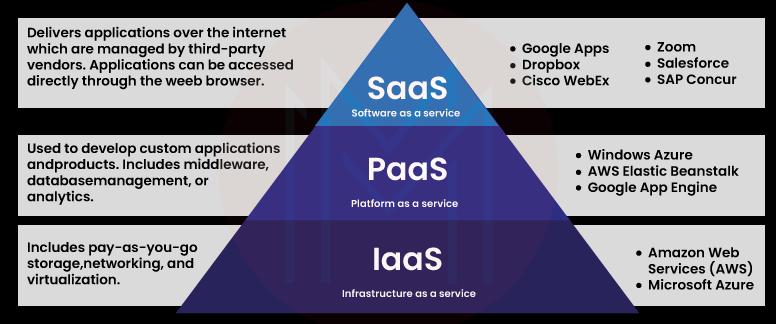
- Software as a service (SaaS): Full software solutions are available in the cloud for free to use.
- Platform as a service (PaaS): Developers can use tools that are delivered from the cloud to test, build, and deploy apps in a scalable environment.
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS): A third party manages a virtualized infrastructure on which an organization can install software
- Functions as a service (FaaS): FaaS is also called serverless computing. Similar to Platform as a Service, but with granular app features.
| Related Article: Top 10 Cloud Computing Tools |
What is Cloud Security?
Cloud security, also called cloud computing security, is a group of security measures meant to protect infrastructure, applications, and data stored in the cloud. These safeguards protect the user and device authentication, data and resource access control, and privacy. They also aid in the compliance of regulatory data. Cloud security is used in cloud environments to protect a company's data from DDoS attacks, malware, hackers, and unauthorized user access or use.
The most important parts of cloud security are the following:
- Data security
- Data retention (DR)
- Legal compliance
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Business continuity (BC) planning
- Governance (policies on detection, threat prevention, and mitigation)
| Do you want to get certified and build your career in Cloud Security? Then enroll in "Online Cloud Security Certification" this course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
Why Cloud security?
Ironically, many businesses cite security concerns as a primary reason for not migrating to the cloud.
Today, however, in a complex economy driven by innovation and overshadowed by the expanding cybercrime industry, organizations require the adaptability and scalability of cloud services, which can only be effectively secured by cloud security solutions that rise to meet the cloud's specific requirements. For this reason, it is crucial to partner with a cloud service provider that offers customized cloud security for your infrastructure.
Cloud security necessitates the modification of some past IT practices, although its importance has increased for two primary reasons:
- Multi-storage enhancement: Every component, from core infrastructure to small data such as emails and documents, can now be located and accessed remotely via web-based connections that are available 24/7. All of this data collection on the servers of a small number of large service providers could be very dangerous. Threat actors can now go after large data centers that are used by more than one organization. This can lead to massive data breaches.
- Convenience over safety: Cloud computing is becoming increasingly popular as a primary method of communication in the workplace and among individuals. Innovation has made it possible to use new technology faster than industry security standards can keep up with. This means that users and providers have to think more about the risks of accessibility.
| Related Article: Cloud Security Interview Questions |
What are Cloud-Based Security Concepts?
There are three primary cloud environments to consider when searching for cloud-based security. The leading solutions on the market include public, private, and hybrid clouds. Each of these environments has unique security issues and benefits; therefore, it is essential to understand their distinctions.
# Public Cloud
- Everything in a public cloud is stored and accessed via the internet.
- Anyone with the necessary permissions can access some of the applications and resources through this deployment system.
- The most exciting aspect of the public cloud is that you do not own any components, whether hardware, software, or applications. The provider manages all of the components in this case.
Examples: Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure are two prominent public cloud examples.
# Private Cloud
- A private cloud is used solely by businesses, which can run it locally or outsource it to other cloud service providers.
- Private cloud infrastructure operates solely on a private network, which means that it is only accessible to those present on the network.
Examples: Some private clouds include the VMware cloud and some AWS products.
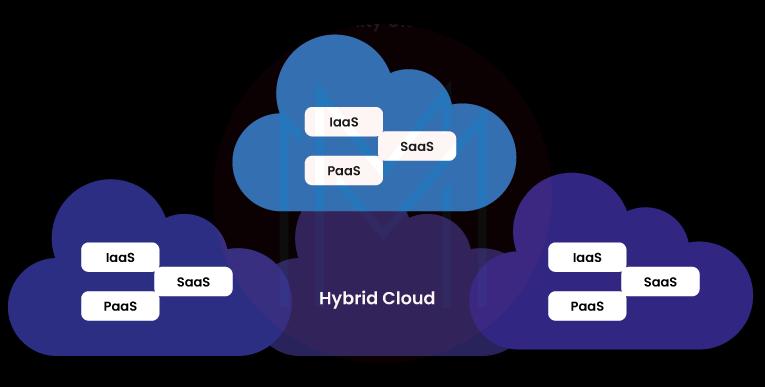
# Hybrid Cloud
- It is the most exciting cloud computing type because it combines public and private cloud features.
- Organizations that use the hybrid cloud can choose to keep some of their data locally and some in the cloud.
- It uses a private cloud to hold sensitive data and a public cloud to store and exchange data that the public may view worldwide.
Example: NASA is the most well-known organization that uses a hybrid cloud.
Every cloud model is susceptible to threats. IT businesses are naturally apprehensive to deploy mission-critical systems to the cloud. It is crucial to have the appropriate security precautions in place regardless of whether you are operating in a native cloud, hybrid cloud, or on-premises environment.
Why is Cloud Security Important?
Businesses can take advantage of next-level features made possible by cloud security computing, such as improved customer service thanks to increased data collecting and storage, remote work opportunities, rapid scalability, and the ease of transferring information between systems on time.
Protecting your digital assets and lowering the possibility of a costly loss due to an unnecessary breach are both possible with cloud security. However, every company's cloud infrastructure needs to be safe to stay effective due to the hazards of misconfiguration and the ever-present danger of cyber thieves. This is where cloud-based safety measures come in.
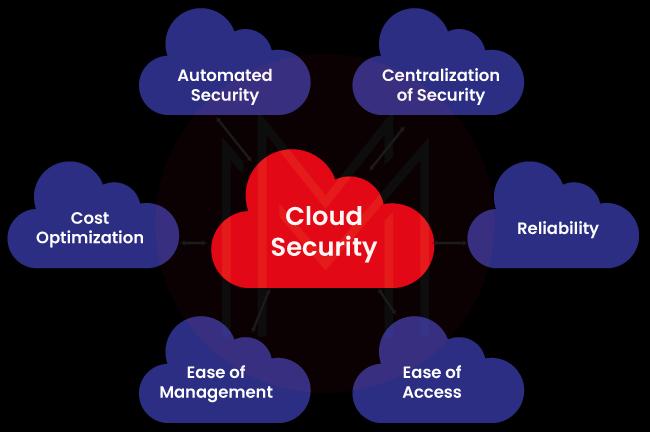
Check out the list below to see why cloud security is important:
- Centralized security
- Reliability
- Reduced Administration
- Reduced costs
1. Centralized security
Aiding in making more information available, establishing rules, and bolstering security against threats. As with cloud computing, cloud security concentrates defenses in a single location. Having everything in one location also helps with disaster recovery and maintaining business operations.
2. Reliability
Cloud computing security services provide the highest level of dependability. With the proper cloud security measures in place, users can securely access cloud-based data and applications regardless of location or device.
3. Reduced Administration
By using the cloud, a shared responsibility model for security is introduced. The cloud security service provider and you will be accountable for the physical infrastructure, networking, computing, and storage security. As a result, there may be a significant reduction in the time and resources required to administer security.
4. Reduced costs
One benefit of using cloud security for storage and security is that you don't have to buy any extra hardware. This not only cuts down on capital costs but also cuts down on administrative costs. IT teams used to respond to security problems by putting out fires. Cloud security offers proactive security features that provide protection 24/7 with little or no help from people.
Cloud security provides all the features of traditional IT security. It enables companies to use the many benefits of cloud computing security while remaining secure and meeting data privacy and compliance requirements.
| Related Article: Cloud Computing Interview Questions |
How does Cloud Security Work?
Cloud security is made up of a lot of different technologies, controls, processes, and policies that all work together. A practice that is highly customized to meet the needs of your organization.
A cloud environment is only as safe as its weakest point, so adequate cloud security requires the collaboration of numerous technologies to protect data and applications from every viewpoint. This typically consists of firewalls, identity and access management (IAM), segmentation, and encryption, although security requirements can vary by cloud deployment type.
Because of this, there is no single way to explain how cloud security "works."
Fortunately, you can build a robust cloud security configuration by employing a well-established set of tactics and technologies. Any security measure implemented in the cloud security will do one or more of the following:
- Safeguard the Server
- Data Encryption
- Data Retention
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Legal compliance

1. Safeguard the Server
Cloud data security encompasses the technological component of threat prevention.
Tools and technology enable providers and clients to place barriers between sensitive data's accessibility and visibility. Encryption is among the most potent of these techniques. Encryption scrambles your data so that only someone with the encryption key can decipher it. If your information is lost or stolen, it will be illegible and meaningless.
Data transit protections such as virtual private networks (VPNs) are also stressed in cloud networks.
2. Data Encryption
You upload and download information to and from the cloud service provider's servers when you use cloud computing security.
To further safeguard your data in the cloud, you can encrypt it at rest and in transit. This makes it extremely difficult for anyone to read the data without your private decryption key.
3. Data retention (DR)
Planning for data retention (DR) and business continuity (BC) involves taking technical steps to recover data in case it is lost.
Data redundancy plans, like backups, are at the heart of any DR and BC plan. Having technical systems to make certain operations don't stop can also help.
For a complete BC plan, it's just as important to have cloud security frameworks for testing the reliability of backups and clear instructions for employees on how to recover.
4. Identity and access management (IAM)
Managing who can see what is within an organization's network is the responsibility of an Identity and Access Management (IAM) system.
You can choose to have your cloud service provider work with your existing IAM or use their proprietary solution.
Using an IAM, you can manage who has access to your applications and data, what they can do with that data, and how often they can do it by combining multi-factor authentication with user access controls.
5. Legal compliance
Legal compliance is about protecting user privacy, which the law says needs to happen.
Governments have realized how important it is to keep private information from being used to make money. Because of this, organizations must follow the rules to keep these policies in place.
One way is to use data masking, which uses encryption to hide who is behind the data.
How can I keep my data safe in the Cloud?
Data security in the cloud may necessitate a wide variety of measures. Cloud architecture, the availability of in-house and third-party technologies, the quantity and nature of authorized users, and the sensitivity of the data to be safeguarded are all essential considerations.
The following are some examples of recommended practices for securing cloud-based corporate data:
- Encrypt data while it is at rest, in use, and in motion.
- Log and track all data access, additions, and changes.
- To avoid ransomware attacks, isolate cloud data backups.
- Adopt cloud-edge security measures such as firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and anti-malware.
- Before granting access, use multifactor authentication (MFA) or two-factor authentication (2FA) to verify the user's identity.
- Ensure visibility and control over data location to identify where data resides and to implement restrictions on whether data can be copied to other locations inside or outside the cloud.
| Related Article: Cloud Security Architecture |
Cloud Security Benefits
There are many advantages to using cloud security. Some of them are:
- Lower Upfront Costs: Since businesses are renting services from the data center of their cloud provider rather than building, equipping, and managing their own data center, the cost of cloud-based security is lower than that of on-premise security.
- Greater ease of scaling: Cloud providers' data centers make it simple and quick to increase or decrease the resources dedicated to security applications and systems.
- Reduced Time to Market: Cloud providers are more careful about implementing new, cutting-edge cloud security tools and systems because that's what they do best. Cloud providers hire experienced security experts who have already done the research and analysis so that customers don't have to waste time and can move forward faster.
- Lower Ongoing Costs: When a company has its own data center, it pays for its security resources whether or not it uses them. When using a cloud provider, a business only pays for security based on how much it uses.
- Protection against DDoS attacks: Protecting businesses from online threats like hackers and DDoS attacks is a top priority for cloud security services.
- Improved availability: In addition to fixing cloud security issues, many cloud security services offer real-time monitoring and help.
- Increased reliability: A deliberate approach to cloud security will have built-in redundancy, resulting in a more reliable experience.
- Improved Scalability: If you have a secure cloud architecture, your most important resources, and data can be backed up and running faster after a disaster.
- Regulatory compliance: Complex cloud architectures can make it difficult to guarantee compliance with industry regulations. By offering protection and assistance, cloud providers aid in maintaining cloud security.
Things to look for when choosing a CSP
It can be challenging to find a reliable Cloud Service Provider (CSP) that can meet all of your company's needs. It is because no two CSPs can provide you with similar services and pricing plans, even though the essential benefits are consistent across all of them. Suppose you're just starting in the business world. In that case, you'll want to start with an essential cloud subscription so that you may create, configure, and personalize your company applications virtually from anywhere with an internet connection. The intricacy of your business processes may prompt you to consider switching to a more advanced cloud service.
Here are some features to ask your cloud service provider (CSP) to look for in a cloud security solution:
- Controls designed to prevent data leakage
- Integrated Security
- IT Complexity
- Ease of change management
- Visibility and threat detection
- Intelligence
- User Experience
- Strong authentication
- Data encryption
- Continuous compliance
#1. Controls designed to prevent data leakage
To avoid problems like hacking, data loss, and theft, it's important to find a cloud service provider with security measures built right in. They should have built-in security mechanisms, such as classifications, that allow you to protect your most private and valuable information better.
#2. Integrated Security
With appliance-based security, combining data from many point appliances from multiple vendors is impossible because they all operate independently. With cloud-based security, you get a holistic view of your network thanks to the correlation of data from integrated security controls and cloud services.
#3. IT Complexity
Deploying and maintaining appliances from numerous security suppliers is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and costly, necessitating constant patching, updates, and hardware upgrades. With cloud-based security, you don't have to worry about buying or maintaining any specialized gear or software because all the necessary components are hosted remotely.
#4. Ease of change management
You do not want to collaborate with a CSP that is resistant to change. As a result, you should look for a vendor with change management certification. This will guarantee that the CSP you select has clear change management procedures, making applying modifications to your cloud-based information systems easier. These procedures should incorporate controls for requesting, evaluating, authorizing, and enforcing new system modifications. Before deployment, a policy should be subject to formal review if you or your CSP need to make emergency changes.
#5. Visibility and threat detection
Good CSPs provide administrators with a single pane of glass to monitor all user actions and material sharing, both inside and outside the organization. A trustworthy service should also employ machine learning to recognize malicious activities, spot potential dangers, and send out warnings to your staff. Algorithms that use machine learning for security first examine data to identify standard behavior patterns and actively seek out anomalies. Data behavior analysis could detect, for instance, a questionable attempt by a member of your sales staff to download proprietary product blueprints.
#6. Intelligence
The Zscaler cloud receives more than just security upgrades daily. When it comes to cloud security, appliances often use a singular method to flag potential dangers and relay that information to the next device in the chain. When a patch is released, it is installed immediately. When a threat is recognized in one part of the cloud, protection is immediately activated in every other part. This is made possible by the cloud's ability to aggregate intelligence from several sources.
#7. User Experience
Any security appliances placed between your end customers and the internet will increase response times. Using a virtual private network (VPN) to access the data center only makes things worse for the end user. Zscaler's cloud-based security allows for quick local exits, and our single-scan multi-action technology allows our security services to scan simultaneously, improving overall performance.
#8. Strong authentication
Your CSP must provide robust authentication controls, such as strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, to guarantee proper access (MFA). The CSP should support single sign-on and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for internal and external users.
#9. Data encryption
Make sure it's possible to encrypt data wherever it is stored or travels. Data transmitted over a wireless or wired network is encrypted using Transport Layer Security before being sent over the web. When information is written to storage, it is encrypted using a symmetric key while at rest.
#10. Continuous compliance
Look for things like document retention and disposal, eDiscovery, and legal holds that are part of content lifecycle management. Determine whether the service has been independently audited and certified to meet the most stringent global standards. A CSP provider focusing on continuous compliance can keep your business from trouble with the law and ensure you're using the latest security methods.
Cloud Security FAQs
1. What is Cloud Security, and how does it work?
To put it simply, cloud security is a set of protocols and tools developed to safeguard information and files stored in a cloud environment. Protecting sensitive data in the cloud is essential for any cloud-based IT infrastructure strategy. Cloud security ensures that data stored in the cloud is kept private and follows the rules.
2. How do I start Cloud Security?
To get started with cloud security, do the following:
- Develop technical skills by taking courses, attending boot camps, or earning a degree.
- Improve your cloud and security knowledge.
- Begin with an entry-level IT position.
- Learn how to get an entry-level IT or cloud certification.
3. Does Cloud Security require coding?
No, To learn cloud systems, you don't need to know a single tag or line of code.
4. Why is Cloud Security important?
Cloud security ensures that your data and apps are easy for authorized users to access. You'll always have a reliable way to get to your cloud apps and data, which will help you respond quickly to any possible security issues.
5. Can Cloud Security be hacked?
Cloud security is good but not perfect. Hackers can get into the files stored in the cloud using automation and brute force attacks. Still, privacy is one of the biggest risks of storing data in the cloud. Even if this information isn't stolen, it can still be seen or used.
6. Is Cloud Security easy to learn?
Learning cloud security computing can be difficult depending on the individual and their prior experience with technology. However, it is widely regarded as difficult because it requires understanding and working with diverse technologies and concepts.
7. Is Cloud Security in demand?
Yes, to keep up with business innovation, several organizations have increased their demand for cloud security. As more businesses migrate to the cloud, cybersecurity is evolving into cloud security.
8. What is the future of Cloud Security?
Machine learning has the ability to not only aid organizations in detecting dangers but also in mitigating them before their impact on operations. Machine learning (ML) and Artificial intelligence (AI) are the future of cloud security.
9. How does Cloud Security work?
A shared responsibility model is used for cloud security. This means that the cloud provider is responsible for hardware and software security. At the same time, the customer is responsible for the security of their own assets, such as virtual machines, applications, and data.
10. Is coding required for Cloud Security?
To begin learning any of these systems, you need not be familiar with any tags or lines of code. Many certification programmes teach the principles of these platforms without focusing on coding.
Conclusion
Choose the right cloud security provider to ensure that your assets hosted in the cloud are safer. Cloud security is a broad term for the steps taken to protect digital assets and data stored online using cloud services. The benefits of cloud security make it clear that it is better than security kept on-site.
Take advantage of the growing demand for Cloud computing experts with our Cloud security training course, designed to help you move up in this exciting field.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Security Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Cloud Security Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Cloud Security Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| Cloud Security Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .















