Cisco Systems is the leading provider of services, systems, and products related to computer networking. Established in 1984 by two scientists coming from Stanford University, the objective of the firm was to connect different and multiple computer systems.
The brand sold its first product in 1986. Today, it operates as a Multinational Corporation (MNC) with thousands of employees residing in more than 115 nations. As of now, Cisco is providing networking solutions for several service providers, enterprise customers, small-scale customers, and medium-scale businesses.
Their clientele list comprises government organisations, educational institutions, large corporations, utilities, and more. The networking solutions of this company can connect computer networks, computing devices, and people, letting you transfer or access data without any differences in computer type, place, or time.
In contrast to other IT organisations, Cisco doesn’t believe in following a rigid approach as far as its interview processes are concerned. The brand focuses on listening and serving. Thus, if you can crack their expectations, you can easily become an employee in this firm. Jotted down below are some of the latest Cisco interview questions with answers to explore when preparing.
Cisco Recruitment Process
The Cisco recruitment process, for diverse roles, might comprise a set of technical questions, coding questions, and networking interview questions. They are designed to evaluate your competency and profoundness of knowledge for the role you have applied for. Generally, you will have to go through the below-mentioned process for the interview:
-
Online Test (Aptitude + Technical)
This online evaluation test comprises questions relevant to the technical and aptitude aspects. The technical part covers algorithms, operating systems, C language, Linux threads, computer networking, linked lists, data electronics, IPCs, mutex locks, and more. Contrarily, aptitude questions are more about profit & loss, simple and compound interest, probability, number series, algebra, percentage, permutation, and combination, etc.
-
Technical Interview
This is the second round that comprises questions related to networking, like manipulation algorithms, hub vs switch, routing a packet from one network to another, the importance of a gateway, building a packet, and more.
-
HR Interview
Once you have cleared the above-mentioned rounds, you will have to appear for an HR interview round, which lasts for 40-50 minutes. You will be asked questions related to the profile you have applied for, about the company, solving critical bugs, and more. You may also get asked questions from the resume.
Top 10 Cisco Frequently Asked Questions
- What do you mean by a link?
- What do you know about a node?
- Define routing.
- What is cut-through LAN switching?
- Define recovery testing.
- How can you establish the TCP connection?
- How do you use a linked list to activate 3 TCP/IP packets?
- Explain bridges in networking and its usage.
- In C, what is an auto keyword?
- How can you achieve multithreading in Python?
Cisco Technical Interview Questions
Now that you have understood the process of recruitment at Cisco, let’s move ahead with technical interview questions for freshers and experienced.
Cisco Technical Interview Questions for Freshers
If you are a fresher and appearing for a Cisco interview for the first time, here are the questions you should prepare for
1. What do you mean by a link?
A link is a physical or logical part of a network that helps interconnect nodes or devices. It is known as a communication channel, which is majorly used for transmitting data. For instance, when we join two ends of a chain with a lock, it forms a link.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in Cisco UCS then enroll in , then enroll in "Cisco UCS Training" - This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2. Define a firewall.
A firewall is used for filtering outgoing and incoming traffic on the basis of a company’s previously developed security policies. In simple words, it is a network security device that tracks and filters traffic. Basically, it is a barrier present between the public internet and a private internal network.
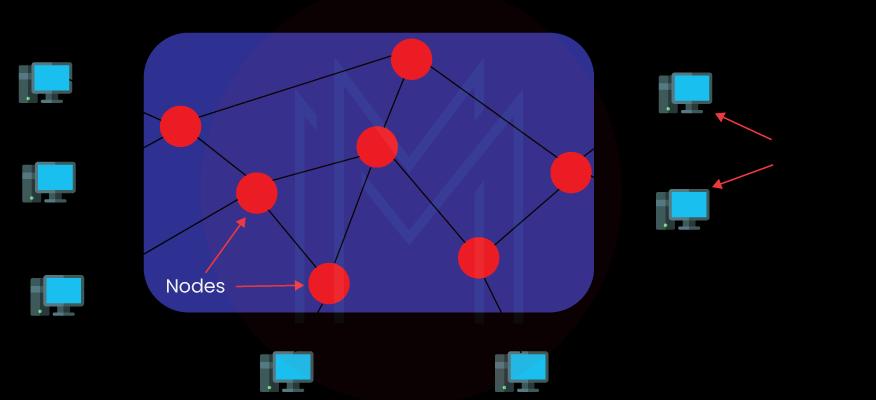
3. What do you know about a node?
A node is one computer network that is defined as the connecting point among varying network devices, such as printers, switches, routers, and more. It receives and sends data via a network.
4. Define the types of network nodes.
Here are the types of network nodes based on their function and application in a distributed network:
- Internet Network Nodes
They are the physical network nodes that act as a host computer in the internet network. They are generally defined by their distinct IP addresses. WAN access points don’t have any IP address.
- Data Communication Nodes
They either include communication devices, like modems, hubs, bridges, routers, switches, etc., or physical nodes. They are present between Data Terminal NodeS (DTE) and data communication circuits. One of the primary roles of data communication nodes is to execute signal conversion, line clocks, and coding.
- Telecommunications
With the help of telephone nodes in a computer, you get intelligent network services. These assist in exchanging information. Nodes in a cellular network carry base station controllers that work to regulate different base stations at once.
- LANs and WANs
These include devices or physical nodes. Furthermore, they comprise a different MAC address for Network Interface Card (NIC). LANs and WANs are computers, modems, wireless LAN access points, and more.
- Distributed Nodes
These nodes are involved in a distributed environment. There are generally two types of distributed nodes: virtual nodes and physical nodes. Mainly, they are used to maintain transparency in the network.
5. Do you know about the default TCP session timeout for Cisco?
Cisco's default TCP session timeout is one minute. After the completion of the normal connection sequence, the connection slots get closed for a minute. But you can configure it as well to match your requirements and needs.
6. Define a gateway.
A gateway is referred to as a node of a network. Meaning it is a computer that is placed between different applications or networks. A gateway can be used in the form of an entrance into another network. It is a hardware piece that converts information, data, and other communications from one format or protocol to another.
7. Define routing.
Routing is one process that builds routes for data packets to carry to a specific location. Routers, which are the devices used to choose a path for traffic across or between multiple networks, help perform routing. The topology of the network majorly depends on the hardware setup to transmit data effectively.
8. Do you know about the types of memories available in a Cisco router?

Different types of memories available in a Cisco router are
- NVRAM: It is used to store the startup configuration file.
- Flash Memory: It is used to store Cisco iOS.
- DRAM: It is used to store the executed configuration file.
9. What do you know about diskless workstations?
It refers to the client computers that are connected to a networked server. Such computers will require only a small amount of hardware to interact with the system through a user. Diskless workstations don’t carry a hard disk. Programs and data will get retrieved from the network. The server does all the hard work, such as performing calculations, booting, and data storage.
Furthermore, they are even helpful in decreasing the overall cost of LAN as a single disk drive. In addition to this, diskless workstations also simplify backups and security as all the files are stored in a single place, which is the file server.
10. Which protocol will you use to boot the diskless workstations?
Bootstrap Protocol or BootP will be used to boot the diskless workstations across the internet. The BootP is much similar to Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and lets a computer obtain the IP address of the server along with its own IP address.
11. What is cut-through LAN switching?
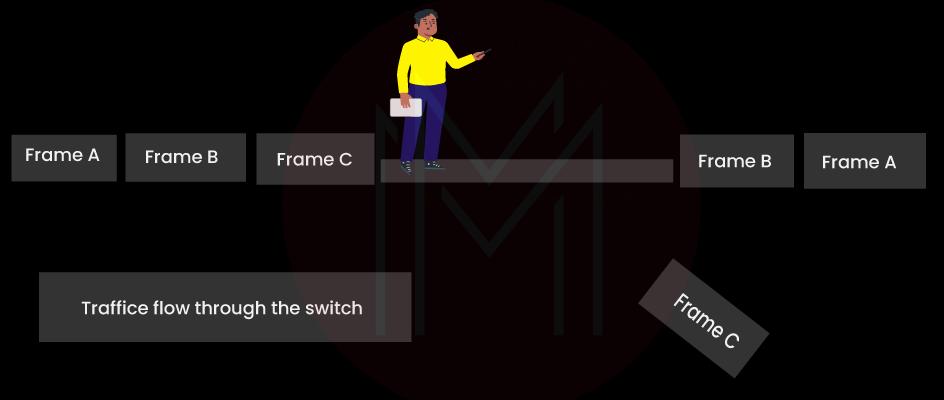
Also known as cut-through forwarding, cut-through LAN switching is a method for packet switching systems. It is executed when the router gets a data frame and sends it again instantly. Cut-through LAN switching reads the destination address and forwards the same to the next network.
12. Tell us the access-list range for extended VINES, extended XNS, and extended IP.
The access-list range of extended VINES extended XNS and extended IP is:
- Extended VINES: The range is 101 - 200
- Extended XNS: The range is 500 - 599
- Extended IP: The range is 100 - 199 and 2000 - 2699
13. Do you know about layers of the OSI model?
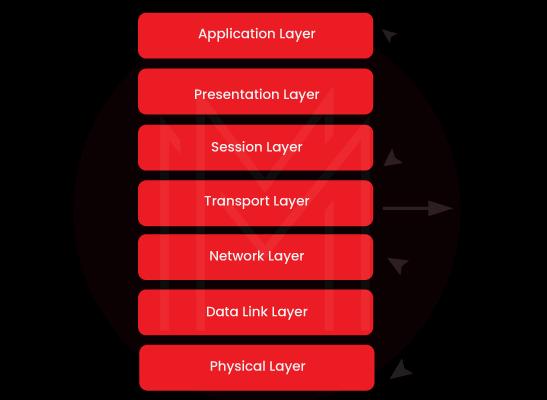
The OSI model has seven layers, such as:
- Physical Layer
- Application Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Network Layer
- Session Layer
- Transport Layer
14. Define recovery testing.
Recovery testing is a software testing technique that tells you how the software can recover from varying failures, like network failures, software or hardware crashes, etc. Generally, it forces the loss of software in different ways to evaluate whether the recovery has been performed correctly or not.
15. Which command will you use to enable failover in the ASA firewall?
The command is ‘Failover’ which will enable failover in the ASA firewall.
Cisco Technical Interview Questions for Experienced
| If you are a mid-level or experienced person, here are Cisco UCS technical interview questions to help you with the preparation. |
16. Can you write a program to reverse every word in a string?
Until a space is discovered in the given string, we will keep using a stack to push all letters. When the space is found, we will then empty the stack and the reversed word will get printed with space towards the end. This process will continue until the string has reached its end.
The program for the same is as follows:
// C++ program
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Reverses each word of a string
void reverseEachWords(string s)
{
stack<char> stk;
/* Traverses the given string and all the characters will be pushed to stack until a space is found. */
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (s[i] != ' ')
stk.push(s[i]);
else
{
// Contents of the stack will be printed when a space is found.
while (stk.empty() == false)
{
cout << stk.top();
stk.pop();
}
cout << " ";
}
}
// As there may not be space after last word.
while (stk.empty() == false)
{
cout << stk.top();
stk.pop();
}
}
int main()
{
string s = "Welcome To MindMajix";
reverseWords(s);
return 0;
}
The output of the above-mentioned program is:
emocleW oT nMxdjaMii 17. How can you establish the TCP connection?

A TCP connection can be established through these steps:
- Step 1
In the first step, the receiver or the host sends a packet along with an SYN flag to the server or the sender. Then, the server responds with an ACK flag (ACKnowledge) and an SYN flag to accept the connection. Next, the receiver sends the ACK flag to confirm this relation. At both ends, the OS is told about this new connection.
- Step 2
In the second step, the sender initiates the transmission of data and receives acknowledgments from the receiver. At the moment when the sender starts sending data, a timer begins.
- Step 3
The third step involves the sender transmitting the data once again, even if it didn’t get any acknowledgement after the limit of the timer has been exceeded.
- Step 4
In the case of windowing, when the receiver buffer gets full, the receiver stops sending signals to the sender. In return, this halts data transmission as well.
- Step 5
Once the processing of data is completed, the sender receives a go signal from the receiver. With this, the transmission of data begins again.
18. Can you write a program to find the first and last occurrences of a number in an array of a sorted method?
The program for the same is as mentioned below:
// C++ program
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void findFirstAndLastFunc(int a[], int n, int x)
{
int firstPos = -1, lastPos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (x != a[i])
continue;
if (firstPos == -1)
firstPos = i;
lastPos = i;
}
if (firstPos != -1)
cout << "First Occurrence = " << firstPos<< "\n Last Occurrence = " << lastPos;
else
cout << "Element not Found";
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 7, 7};
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(int);
int x = 7;
findFirstAndLastFunc(a, n, x);
return 0;
}
The output for the above-mentioned program is:
First Occurrence = 8
Last Occurrence = 919. How do you use a linked list to activate 3 TCP/IP packets?
First of all, every packet must have a destination IP, a source IP, and some data to use a linked list to activate 3 TCP/IP packets. And then, the steps mentioned below should be followed for the activation:
- Step 1: The packets should be searched one by one to discover suspicious IP (the one that begins with 000).
- Step 2: And then, the data should be checked for the cipher. Subtract 1 from ASCII of the first 8 to check the data.
- Step 3: Ideally, the program should activate the processing of six packets in two groups of three.
- Step 4: Next, check all the given three packets (nodes) and change the data and IP in each of the packets. Then, evaluate again. You can use a QUEUE instead of a linked list. However, keep in mind that the QUEUE should contain the same data.
20. Write a program to find the difference between two elements of one array that is in the increasing order of elements.
The program for the same is:
// Java program
class MaxDiffrence
{
/* The function will assume that there will be at least two elements
in an array. The function will return a negative value if the array
is in decreasing order of sorting. This function will return 0
if elements are equal. */
int maximumDiff(int x[], int size)
{
int res = x[1] - x[0];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for (j = i + 1; j < size; j++)
{
if (x[j] - x[i] > res)
res = x[j] - x[i];
}
}
return res;
}
// Driver program for testing above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
MaxDifference md = new MaxDifference();
int array[] = {2, 3, 90, 10, 120};
System.out.println("Maximum difference between two elements of an array is " + md.maximumDiff(array, 5));
}
}
The output for the above-mentioned program is:
Maximum difference between two elements of an array is 11821. Explain bridges in networking and its usage.

A bridge is referred to a networking device that connects several Local Area Networks (LANs) to create a bigger LAN. Moreover, it can connect LAN segments to create newer LAN segments. The bridge operates in the Data-Link layer of the OSI model. It is helpful when it comes to increasing the network capacity of a LAN by joining different LANs.
By connecting two or multiple LANs with same protocols, the bridge helps them communicate between nodes (devices) in them. It accepts all the data packets and they get amplified to the other side. In a way, a bridge is regarded to be an intelligent device as it allos the passing of merely chosen packets from it.
A bridge can pass only such packets that are addressed from one network’s node to other network’s node. This means, the bridge consults the database upon receiving the data frame to decide whether to discard, transmit or pass the frame.
- In case the frame has a destination Media Access Control (MAC) address in the same network, it will get passed to that node and will be discarded later by the bridge.
- In case the frame has a destination MAC address in the connected network, it will get forwarded to the respective network.
Uses of the Bridge
- The network’s capacity gets increased and multiplied as several small networks get combined to create a single network through the bridge.
- In the bridge, the database helps to decide whether the data frame should be discraded or transmitted.
- By deciding whether to discard or forward the data frame, a single faulty node will be averted from bringing the entire network down.
- A bridge helps with frame broadcasting to every node in case the destination address or MAC is not available.
- It is possible to connect the wireless networks with wireless segments through a wireless bridge.
22. Can you write a program to print all permutations of a string?
Here is the program to print all permutations of a string:
// C Program to print all permutations of a given string including duplicates
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// Function for swapping values at two pointers
void swap(char *a, char *b)
{
char temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
/* Function for printing permutations of a string. This function takes
three parameters: String, Starting index of the string, last index of
the string. */
void permute(char *a, int beg, int end)
{
int i;
if (beg == end)
printf("%s\n", a);
else
{
for (i = beg; i <= end; i++)
{
swap((a+beg), (a+i));
permute(a, beg+1, end);
//backtracking method
swap((a+beg), (a+i));
}
}
}
// Driver program for testing above defined functions
int main()
{
char string[] = "XYZ";
int n = strlen(string);
permute(string, 0, n-1);
return 0;
}
The output of the above-mentioned program is:
XYZ
XZY
YXZ
YZX
ZYX
ZXY23. In C, what is an auto keyword?
The auto keyword is majorly used to declare a variable that comes with a complex type. For instance, you can use it for variable declaration where the initialisation expression comprises pointers to functions, pointers to members or templates.
You can also use an auto keyword to declare and initialise a variable to the lambda expression. It is impossible to declare the type of variable on your own as only the compiler knows the lambda expression type.
You can access auto variables only in the function or block wherein they were declared and not outside them. By default, they come with garbage value whenever declared without any value assigned.
The syntax for auto keyword in C is:
auto <data_type> <variable_name>;For instance:
auto int x = 1;24. Write a program for creating a stack through a linked list in Java.
Here is the program for creating a stack through a linked list in Java:
// Java program
// Importing package
import static java.lang.System.exit;
// Creating Stack using Linked list
class StackLinkedlist
{
// A node of linked list
private class Node
{
// Integer data
int info;
// Reference variable of Node type
Node link;
}
// Creating a global top reference variable
Node top;
// Constructor
StackLinkedlist()
{
this.top = null;
}
// Function for adding an element i in the stack
public void push(int i) // Insert at the beginning
{
// Creating a new node t and allocate memory
Node t = new Node();
/* Checking if the stack is full, then inserting an
element would lead to stack overflow*/
if (t == null) {
System.out.print("\nStack Overflow");
return;
}
// Initializing data into info field of t node
t.info = i;
// Add top reference into link field of t node
t.link = top;
// Update top reference
top = t;
}
// Function for checking if the stack is empty or not
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return top == null;
}
// Function for returning topmost element of a stack
public int peek()
{
// Checking for empty stack
if (!isEmpty())
{
return top.info;
}
else
{
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
}
// Function to pop the topmost element from the stack
public void pop()
{
// Checking for stack underflow
if (top == null)
{
System.out.print("\nStack Underflow");
return;
}
// Updating the top pointer to point to the next node
top = (top).link;
}
public void show()
{
// Checking for stack underflow
if (top == null)
{
System.out.printf("\nStack Underflow");
exit(1);
}
else
{
Node tmp = top;
while (tmp != null)
{
// Printing node data
System.out.printf("%d->", tmp.info);
// Assigning tmp link to tmp node
tmp = tmp.link;
}
}
}
}
//Class with main() function
public class ImplementStack
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object for the StackLinkedList class
StackLinkedlist ob = new StackLinkedlist();
// Inserting values for stack
ob.push(15);
ob.push(20);
ob.push(25);
ob.push(30);
// Printing elements of Stack
ob.display();
// Printing Top element of Stack
System.out.printf("\nTop element of Stack is %d\n", ob.peek());
// Deleting top element of the Stack
ob.pop();
ob.pop();
// Printing Stack elements
ob.show();
// Printing Top element of Stack
System.out.printf("\nTop element of Stack is %d\n", ob.peek());
}
}
The output of the above-mentioned code is:
30->25->20->15->
Top element of Stack is 30
20->15->
Top element of Stack is 2025. How can you achieve multithreading in Python?
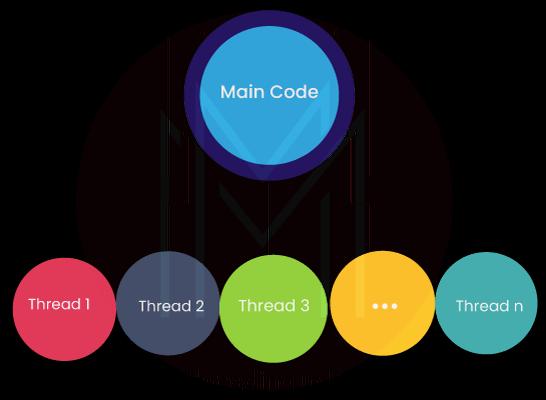
The Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) in Python ensures only one of the threads get executed at a time. A thread acquires the GIL, does some work, and the GIL gets passed onto the following thread. This process is executed quickly that it looks like the threads are getting executed in parallel. However, in reality, they are taking turns through the same CPU core. This entire process adds overhead to the thread execution, meaning that if you wish to speed up the code run, the threading package usage is not regarded as an appropriate idea.
26. In C, what is a void pointer? Can it be dereferenced without the awareness of its type?
In C, a void pointer is used in pointing to the memory location that has an undefined data type during the time of defining the variable. This means that it can be any data of any type. A void pointer can be dereferenced only once it has been explicitly casted. For instance:
int x = 10;
void *y = &x;
printf(“%d\n”, *((int*)y));In the code above, a normal variable ‘x’ has been declared with the integer data type. Also, the ‘x’ reference has been assigned into a void pointer ‘y.’ Through printf(), we get to display the value of ‘y’ by dereferencing it.
27. What is the difference between C and C++?
The below-mentioned table showcases the difference between C and C++.
|
C |
C++ |
|
C is a procedural programming wherein the code is in the form of a procedural set and is used to develop applications. |
C++ is a hybrid programming language considering that it supports both the object-oriented and procedural programming concepts. |
|
It doesn’t support OOPS features. |
It supports OOPS features. |
|
It doesn’t support data hiding. |
It supports data hiding via encapsulation. |
|
Function and operator overloading is not supported. |
Function and operator overloading is supported. |
|
It doesn’t have access to specifiers. |
It has access to specifiers. |
28. What do you know about virtual memory?
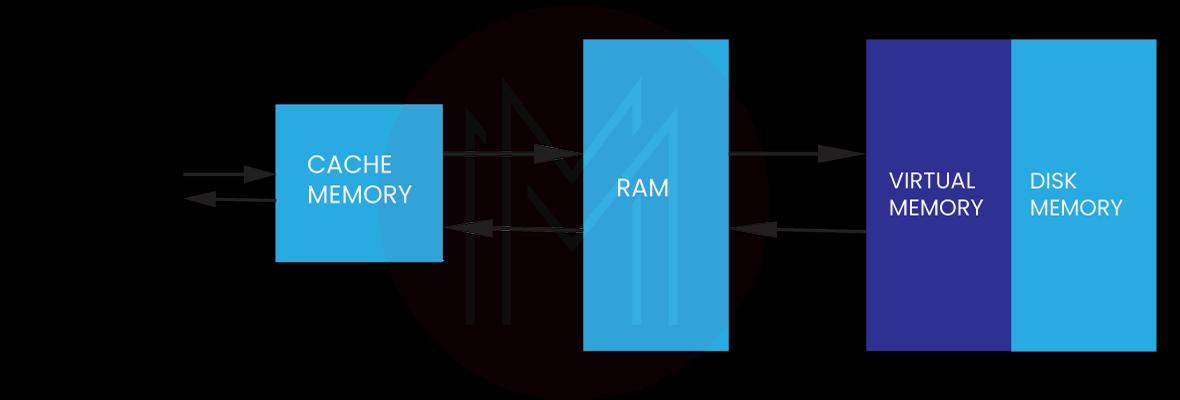
Virtual memory is a storage allocation method where a part of the secondary memory gets emulated as it is the primary memory of a computer. The virtual memory solves the problem of insufficient memory by converting a part of disk memory into virtual addresses; thus, creating a large size of RAM to accommodate the requirement of increased memory. It also gives an illusion that there is a lot of memory. The modern microprocessors come with an inbuilt Memory Management Unit (MMU) that translates the virtual addresses into physical ones.
The virtual storage’s size is restricted by the addressing scheme of the computer system. Moreover, the secondary memory’s available quantity is not dependent on any real number of the primary storage locations.
Commonly, virtual memory gets integrated in a segmentation system or through demand paging. We can also use demand segmentation to provide virtual memory.
29. What are terminal access controller access control system and remote authentication dial in user service in networking?
The Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) is a group of remote authenticated protocols that are used to control remote authentication and relevant services for the networked access control through a centralised server. It helps in determining whether we have access to the network and it permits the remote access server to communicate with authenticated servers.
The Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) is an Authentication, Authorisation, and Accounting (AAA) protocol that controls the access to network resources. It is used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) along with corporations to regulate access into the internal networks and internet across a group of access technologies, including VPNs, modem, DSL, and wireless.
30. Why is the layered model used by the networking industry?
The networking industry uses the layered model as it offers systematic troubleshooting in the network. Furthermore, it clarifies the task that needs to be done through general function. One of the best reasons is that the edits made to one layer doesn’t have any impact to other layers in the model.
Cisco Leadership Principles
Cisco follows these leadership principles:
- Conscious Culture: The brand believes in fostering a conscious culture within the company to empower an inclusive future for everyone. This conscious culture means acting with equity, fairness, respect, and dignity.
- Give Your Best: The employees at Cisco showcase an urge to be at their best and connect with others. They keep their minds open to gain ideas from anywhere and everywhere.
- Take Accountability: Regardless of come what may, they understand the situations and take personal accountability for success.
- Give Your Ego the Day Off: The team supports the best solution to fulfill their customers’ needs without making concerns about anything else.
- Take Difference to Heart: They value and respect their differences. Hence, they believe in personal differences and unique personalities.
Tips to Crack Cisco Interview
Basically, the Cisco interview is all about testing your competency to solve problems, code, and think. At first, the technical interview round might seem strenuous, however, with adequate preparation, you can crack it with ease. Here are some tips to crack Cisco interview:
- Explain with examples: Give relevant instances of what you have achieved in the past and explain how you managed to contribute in the context of your team.
- Prove yourself: Explain how you stay updated with the developments in your industry. Try to prove that you are capable of keeping up with the quick-paced Cisco culture.
- Be futuristic: Try and make some connections with the interviewers as it might be useful in the future. Ask them about career growth. Make them understand that you are interested in everything going on at Cisco. Show them that you are ready to learn and accept challenges.
- Learn everything about the company: Research about the company and connect with leaders on social media. This will help you engage with them and comprehend several things about the firm.
- Be passionate and genuine: Be yourself and authentic during the interview. Let them know that you are going to be a valuable asset to the company. Put your thoughts out positively and explain them everything about yourself passionately.
Most Commonly Asked Cisco FAQ
1. What programming languages are preferred at Cisco?
Cisco generally prefers the C programming language. Other than that, if you are fluent in Java, C#, Ruby or Python, you can still apply for a job at Cisco.
2. How to get Cisco Network Associate certification?
To get this certificate, you must pass some exams relevant to the certificate, such as ICDN1 (100 - 101) or the ICDN2 (200 - 101) exams. You can even take a combined CCNA (200 - 120) exam. You can register for these exams through Cisco. To pass the exam and get the certificate, you must get 80% or above.
3. What are the prerequisites for an entry-level job at Cisco?
If you are applying for an entry-level job at Cisco, you should have a Bachelor’s degree with 60% in 10th, 12th and graduation degree. Also, you should not have any backlogs to be cleared. Apart from this, you must possess some technical skills and soft skills, like reasoning, and good communication.
4. How do I prepare for a Cisco interview?
To prepare for your Cisco interview, make sure you are familiar with Cisco interview questions with answers. You must also be well prepared for the position you are applying for. Know everything about networking and coding. Also, be real, authentic and genuine with your answers.
5. Is Cisco interview hard?
The interview process at this company could be challenging as Cisco received hundreds of applications from competent people. It is also a popular employee-friendly firm to work at and attracts varying job applications. So, you must prepare well to beat others.
6. Is Cisco a good company to start your career?
Yes, Cisco is one of the best companies to begin your career if you are inclined towards the networking domain. Along with a good pay package, you can rest assured of getting plenty of perks and benefits at this firm.
7. What is the average salary of a Cisco employee in India?
Accordingly, Cisco Systems offers an average salary of Rs. 15,40,418 a year to its employees. Typically, the salaries at this company begins at Rs. 6,51,805 and go up to Rs. 29,81,928 a year. Software engineering managers get paid the most at this firm with an annual salary of Rs. 28,78,888 a year.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, getting a job at Cisco is not a breeze. That is why we are here to help you. Hopefully, this list of latest Cisco interview questions and answers will be helpful in preparation for the interview and will allow you to tackle questions with confidence. Navigate through them profoundly and learn as much about Cisco as possible.
If you would like to add more weight to your resume, try taking this Cisco UCS Training course by MindMajix. The course helps you learn everything about the components and architecture of UCS, its installation, server modules, director, and more.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco UCS Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| Cisco UCS Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Cisco UCS Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Cisco UCS Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .









