Golang, an open-source, high-level programming language, is the go-to choice for companies like Google, Netflix, Meta, Uber, and many more. The widespread use of Go in developing secure and scalable applications has led to significant demand for Go developers in the job market. Mastering Go will position you for a promising and rewarding career.
It is an excellent choice if you plan to pursue your career in Go programming. To help you, I have included the hand-picked Go interview questions with answers in this blog. It will help to improve your knowledge of the Go language and gain a competitive edge in the job market.
Let’s go!
Critical Skills required for Go developers:
As the demand for Golang developers increases, the Go aspirants must cultivate essential technical and soft skills to stand out. This section lists the primary and secondary skills required for Go developers to prepare for your Gointeriews.
Primary Skills required for Go programmers:
- Complete knowledge of the software development lifecycle
- Deep understanding of the Go programming language
- Sound proficiency in data structures and algorithms
- Good exposure to system design and architecture
- Proficiency in database integration and ORM tools
- Comprehensive knowledge of Goroutines, channel patterns, Go modules, and package management
- Proficiency in concurrency patterns, memory management, multithreading, and interface design
- Familiarity with testing frameworks, unit testing, and test-driven development.
- Knowledge of cloud computing concepts, managing cloud resources, and cloud service providers such as Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure
- Strong exposure to Integrating Go applications with APIs
- Exposure to security best practices such as secure code principles, authentication, encryption, and authorization techniques.
Secondary skills required for Go developers:
- Knowledge of containerization tools such as Docker and Kubernetes
- Exposure to RESTful APIs
- Decent understanding of CI/CD pipelines
- Familiar with version control systems like Git
- Knowledge of performance optimization and benchmarking
- Excellent communication, problem-solving, and collaboration skills
- Exceptional project management and time-management skills
Job Responsibilities of Go Developers:
It is essential to know about the job responsibilities of Go developers. It helps you to become a job-ready Go developer and excel from day one in the workplace.
Entry-level (1-2 years of experience)
- Designing and developing high-quality, reliable, scalable, and secure Go applications
- Integrating Go applications with external systems and Microservices
- Developing quality codes by performing testing and debugging
- Up-to-date with the current technological trends and developments
- Working with version control tools like Bitbucket, GitHub, and Source Control
Middle-level (3-5 years of experience)
- Understanding the application requirements precisely by working with clients
- Writing clean, reusable, and well-documented Golang codes meeting the exact needs of clients
- Structuring codes and optimizing performance
- Storing data in databases and implementing network protocols
- Mentoring junior developers, reviewing their codes, and recommending suggestions to improve performance
- Implementing RESTful APIs to ensure security and performance.
Senior-level (More than five years of experience)
- Designing and developing high-quality codes for large-scale Go applications.
- Bridging the gap between internal teams and stakeholders to create applications meeting specifications accurately
- Driving technical innovation and delivering high-performance applications
- Troubleshooting issues and providing analytical and logical solutions
- Setting test environments, designing test plans, and testing applications
- Gathering feedback on the usability and serviceability of client applications, analyzing results, and improving quality.
- Demonstrating leadership and motivating teammates for excellence.
Good! We hope you have become familiar with the Go developers' job roles and responsibilities. Undoubtedly, it will smooth out your journey to become a skilled Go developer.
Golang Interview Questions:
Ready to dive into the crucial Go interview questions and answers? In this section, I have compiled a collection of key Go interview questions for beginners and experienced learners. From basics to advanced Go programming concepts, these questions cover many topics. So, let's get started and ace your Go interviews!
Sure! The above skills will help you meet real-time challenges as a Golang developer. Mastering these skills will pave the way for a bright career in Go programming.
Let’s find them below!
For ease of learning and understanding, we have divided these questions into 2 categories they are:
Top 10 Frequently Asked Go Interview Questions
- What is Go?
- What are pointers in Go?
- What are the methods in Golang?
- List out the advantages of Golang.
- What are the decision-making statements of Golang?
- Explain structures in Golang.
- What are rvalue and lvalue in Golang?
- How can you increase the performance of Golang programs?
- Explain the switch statement in Golang.
- Does Go have a runtime?
Golang Interview Questions For Freshers
1. What is Go?
Go is also known as GoLang, it is a general-purpose programming language designed at Google and developed by Robert Griesemer, ken Thomson and Rob Pike. It is a statistically typed programming language used for building fast and reliable applications.
| Inclined to build a profession as a GO Developer? Then here is the blog post on, explore GO Training |
Golang comes with a standard library and a built-in concurrency mechanism. The great thing about the language is that it has a large community of developers and a rich set of tools. We can build fast Command Line Interfaces (CLI) using the open source packages and standard library.
2. What are the key features of the Go language?
Go is the short form of Golang. It is an open-source as well as general-purpose programming language. Go is an easy-to-learn language with a built-in concurrency and standard library. It is also a statistically-typed language that helps to build reliable applications. It is the best language that we can use to develop scalable web applications, network services, and command-line tools.
3. What is dynamic type variable declaration in Golang?
Regarding dynamic variable declaration, the compiler interprets the variable type. The interpretation is usually done based on the value passed to the compiler.
In the below example, we declare the variable ‘y’ without any type. After the execution, we will get the following result.
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x float64 = 20.0
y = 42
fmt.Println(x)
fmt.Println(y)
fmt.Printf("x is of type %T\n", x)
fmt.Printf("y is of type %T\n", y)
}Output:
go run /tmp/uFSFVdmdBN.go
20
42
x is of type float64
y is of type int4. What are packages in Golang?
Managing a large number of codes takes a lot of work. That's why we split a large program into multiple packages. Each package contains a set of related codes. So it is easier to manage and use the codes.
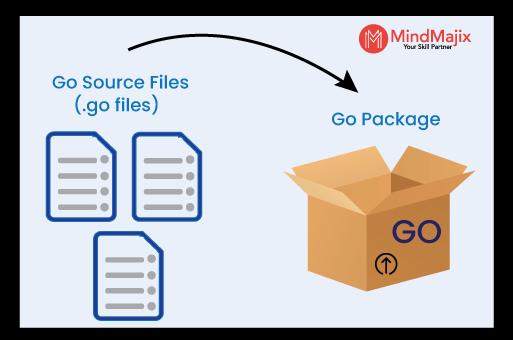
Go programs are usually made up of packages. A package is a group of files stored and compiled together. A file may have functions, variables, and constants.
Go programs start running with the main package. They use packages with import paths like 'fmt’ and ‘math/rand’. Generally, the package name is the last element of the import path. For example, the ‘math/rand’ is the package name of a Golang package that consists of files starting with the ‘package rand’ statement.
Below is an example Go program that uses the Golang package.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("My favorite number is rand. Intn(15))
}5. What is static type variable declaration in Go?
Static variable declaration ensures the compiler has a variable available for the given type and name. This type of declaration allows the compiler to continue with the compilation without requiring the variable details.
Know that static type variable declaration works only at the time of compilation. The following is the Go program that shows the static type variable declaration in Golang.
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x float64
X = 10.0
fmt.Println(x)
fmt.Printf("x is of type %T\n", x)
}Output:
go run /tmp/zxZUGTZFql.go
10
x is of type float646. What are the two crucial operators used in Golang?
The asterisk '*' and ampersand '&’ are the crucial operators used in Golang. Asterisk is the dereferencing operator that we can use to declare pointer variables. Also, we use this operator to access the value stored at the address. For example, var ptr *int declares a pointer variable pointer. This pointer holds the memory address of an integer value.
The '&' operator is known as the address operator. We use this operator to get the memory address of a variable. For example, if the variable is x, then ‘&x’ will return the memory address of the variable x.
Overall, these operators support accurate and efficient memory management and handling of data structures.
7. What are the constants in Golang?
Constants are declared using the ‘const’ keyword in the go programming. A constant can be a character, string, Boolean, or numeric value. A numeric constant is an untyped constant that consists of high-precision values.
We cannot declare a constant using the: = syntax. The following is the Go program that uses constants.
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
const Pi = 3.14
func main() {
const World = "MindMajix"
fmt.Println("Hello", World)
fmt.Println("Happy", Pi, "Day")
const Truth = true
fmt.Println("Go rules?", Truth)
}Output:
Hello MindMajix
Happy 3.14 Day
Go rules? true8. What are pointers in Go?
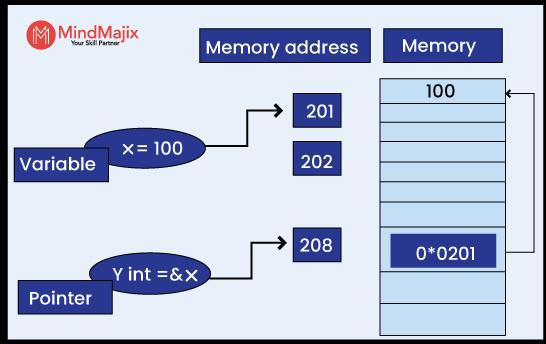
Pointers are typically variables that store the memory addresses of objects. In a way, pointers are the special variables. Pointers can have different data types like ‘int' and 'string'. Note that we use hexadecimal formats to store memory addresses in pointers.
As shown below, the ampersand operator '&' creates a pointer for its operand.
Similarly, the asterisk '*' symbol marks the pointer's underlying value.
9. Name the different Golang operators.
Jotted down are the different Golang operators.
Arithmetic operators: They perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, division operations and more.
Relational operators: They perform the equal to, not equal to, greater than, less than, greater than equal to, less than equal to operations and more.
Bitwise operators: They perform bitwise AND, bitwise OR, bitwise XOR, left shift, right shift, AND NOT operations.
Assignment operators: They perform simple assignments, add assignments, subtract assignments, multiply assignment operations and more.
Logical operators: They perform logical AND, logical OR, logical NOT operations and more.
Miscellaneous operators: They include the Ampersand and Asterisk operators.
10. What are the various data types used in Golang?
There are four data types in Golang.
- Integer data type – We use this data type to declare integer numbers
- String data type – It represents a sequence of characters
- Float data type – We use this data type to declare decimal numbers
- Boolean data type – This data type has either true or false value.
11. What is the scope of a variable in Golang?
The scope of a variable in Golang is a part of the code. That’s the place where we can access and modify variables. We define a Golang variable in a class, loop, method, etc.
There are variable scope categories, such as local variables and global variables. Local variables are usually declared inside a function or block of the code, whereas we declare global variables outside the code.
The code below shows the use of local variables in a Go program.
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var myvariable1, myvariable2 int = 25, 50
fmt.Printf("The value of myvariable1 is: %d\n",
myvariable1)
fmt.Printf("The value of myvariable2 is: %d\n",
myvariable2)
}Output:
go run /tmp/DLQojZzapk.go
The value of myvariable1 is: 25
The value of myvariable2 is: 50The code below shows the use of global variables in a Go program
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
var myvariable1 int = 10
func main() { // from here local level scope starts
var myvariable2 int = 20
fmt.Printf("The value of Global myvariable1 is %d\n",
myvariable1)
fmt Drintf("The value of local myvariable? is %d\n"Output:
go run /tmp/2000]SSEzd.go
The value of Global myvariable1 is : 10
The value of Local myvariable2 is : 20
The value of Global myvariable1 is : 1012. What are the methods in Golang?
A Golang method is typically a function but has a receiver argument. The receiver argument appears from the argument list between the method name and the 'func' keyword. A Golang method receives the properties of a receiver using the receiver argument. Note that the Golang receiver can be either a ‘struct’ type or a ‘non-struct’ type.
For example, this ‘area’ method has a receiver type of ‘rect’. Here, we defined the method with a value receiver type.
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
type rect struct {
width, height int
}
func (r *rect) area() int {
return r.width *r.height
}Output:
go run /tmp/rzcd8ce3no.go
area: 25
perim: 20
area: 25
perim: 2013. Is Go language case-sensitive?
Yes. Golang is a case-sensitive language.
14. What are the three directories of Go Workspace?
Golang workspace is a directory hierarchy of Go programs. A typical Go workspace consists of three subdirectories, as listed below.
src – This directory has source files as packages.
bin – This directory has the executable programs.
pkg – we can store Go package objects in this directory
15. What are the advantages of Golang?
Following are the key advantages of Golang.
- allows quick coding and compiling
- offers increased availability and reliability
- provides a garbage collector
- supports large-scale projects
- delivers high performance
- supports multi-core processors and concurrency
- Provides a low learning curve
| Related Article: Golang Tutorial for Beginners |
16. Why is Golang so popular?
Here are the reasons why Golang is so popular among developers community.
- Open-source and easy-to-learn language
- Interpreted and statically typed language
- Simple and compact syntax
- Quick compilation of codes
- Supports cross-platform application development
- Comes with a robust ecosystem of tools and APIs
- Enhanced memory performance and supports multiple IDEs
- Supports DevOps and site reliability engineering with the Automatic Formatter and doc generator
- It helps to build reliable, scalable web applications, network services, and command-line tools.
17. What is the use of the ‘init’ function Golang?
The ‘init’ function is usually called at the beginning of the execution time. We use the ‘init’ method to add initialization logic into the package.
18. What are Golang's different decision-making statements?
Below are Golang's different decision-making statements.
- If statement – It is a simple decision-making statement. A set of statements will be run if the given condition is true. Otherwise, no statement is run.
- If..else statement - A set of codes will be run if the given condition is true. Otherwise, another set of codes will be run.
- Nested if statement – When an If statement consists of another if statement inside of it, then it is known as the nested if statement.
- If…else…if ladder – We use this statement when there are many conditions. The program execution starts from the first if statement to the last statement one by one. A set of codes will be run when the condition in a particular if statement is true. Otherwise, the program execution continues to the next if statement. The final 'else' statement will be executed when no condition is satisfied.
19. What is the role of a slice in Golang?
Slices are more like arrays but support variable lengths of elements. In other words, slices are dynamically sized and flexible. Further, the slice is a lightweight data structure, so developers use slices more extensively than arrays.
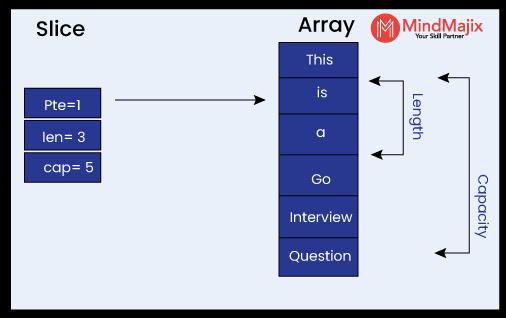
A slice in Golang has two indices - a lower and higher bound. The indices are separated by a colon, as shown below
a [low: high]
The following example shows the use of slices in a Golang program.
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
primes = [6]int{2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13}
var s []int = primes[1:5]
fmt.Println(s)
}Output:
[3 5 7 11]
20. What is the use of the GOROOT variable in Golang?
We use the GOROOT variable to find standard libraries. We also use this variable to locate the Go SDK. We also use this variable to determine the root of a workspace.
21. What are goroutines?
Goroutines are lightweight threads widely used in Go concurrent programming. A thread is a function that executes in parallel with the rest of the program. We use the ‘go’ keyword to invoke a function as a Goroutine.
Moreover, Gorountines are managed by the Go runtime. They run in the same address space. So, we need to synchronise the access to the shared memory.
The below example shows the use of Goroutine.
Code:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func say (s string) {
for i = 0; i < 5; i++ {
time.Sleep(100
fmt.Println(s)
}
}
func main() {
}
go say ("Mind")
say("Majix")Output:
Majix
Mind
Mind
Majix
Majix22. What is the latest version of the Go language?
Go 1.22.3 is the latest version of the Go language. It was released on May 7, 2024.
23. What are the new features of the latest version of Golang?
- Below are some of the critical features of the newest version of Golang - version 1.22.3.
- Security fixes included in the net package
- Bug fixes included in the compiler, the runtime, and the net/http package
- Changes are included in the ‘for’ loop of Golang. Each iteration in the loop creates new variables, which helps to avoid accidental sharing bugs
- The global functions in the math/rand package can be seeded to functions like int32. The random generator helps to achieve that.
- The vet tool is changed to match the new semantics of loop variables
- The web UI of the trace tool has been refreshed, improving the readability of various subpages.
- We can set HTTP methods in the net/http package while declaring a pattern for handlers
- The latest version includes the new version of wildcards.
24. What is the use of the ‘init’ function Golang?
We call the ‘init’ function at the beginning of the execution time. We use this function to add initialisation logic into the package.
25. What is CI/CD workflow?
CI/CD is the short form of Continuous Integration and Conditions Deployment. This methodology accelerates the software development lifecycle.
Continuous Integration supports integrating code changes into the repository automatically. Continuous integration supports integration, testing, and delivery of code changes in the repository.
What’s more! CI/CD avoids bugs, reduces code failures, streamlines workflows, decreases complexity, and increases efficiency.
26. What is the procedure involved in developing a RESTful API using Golang?
We can use the following procedure to develop a RESTful API in Golang.
- First, design API endpoints, which will help clients to get and add records,
- Create a folder to store codes,
- Design a data structure to manage data
- Write a handler to return all items. So when the client makes a GET request, it will return all records as JSON.
- Write a handler to include a new item. So when the client makes a POST request, we will add a record to the existing record.
- Finally, write a handler to return a specific item.
27. What are Bootstrap and material design?
Bootstrap and material design are popular front-end frameworks we use to develop web applications.
Bootstrap is a CSS framework that provides many pre-built components and styles. Similarly, material design is a design language that offers a set of guidelines to build user interfaces.
28. Name some crucial packages in Golang.
Jotted down are the crucial packages in Golang.
- main
- net/http
- log
- fmt
- Time
Super! We hope the Go interview questions have provided you with a solid foundational knowledge of the Go language. You are ready to explore advanced Go concepts in the following section.
Golang Interview Questions For Experienced
In this section, I have included the crucial Go interview questions and answers to deepen your knowledge of the Golang language. The section will enhance your expertise in the language to high levels.
Let’s get going!
29. Explain concurrency in Golang.
Golang supports concurrency using channels and Goroutines. A Goroutine is typically a function that can run concurrently with other functions. We use the go keyword to create a Goroutine. Goroutines are usually lightweight, so we can create numerous Goroutines.
Regarding channels, they allow Goroutines to communicate with each other and synchronise their execution.
30. Explain Structures in Golang.
A Golang structure or 'struct' is a collection of fields. We use the Golang struct to store several values of different data types into a single variable. Simply put, we use a 'struct' to group data to create records.
To store a player's details, we must create two variables with the player's name and age. If we store the details of an entire team, we can create a ‘struct’ to store the details of the whole team. Below is an example of a Golang structure.
type person sruct {
name string
age int
height int
}31. Why do you use the Goto statement in Golang?
The Goto statement jumps to a labelled statement within the same function. The labelled statement must be a valid Go statement. It shouldn't be a keyword. The label is visible only inside a function where it is declared.
Below is the syntax for the goto statement:
goto label;
label: statement;32. Why do you use break statements in Golang?
The break statement breaks a loop immediately after it is executed and continues to execute the statement next to the break statement. A break statement is also used to terminate a case in a switch statement.
The syntax for a break statement in Go is defined as below:
break;33. Why do you use the ‘goto’ statement in Golang?
We use the ‘goto’ statement to assign control to the labeled statement. In other words, this statement makes an unconditional jump from the goto to a labeled statement. It happens in the same function.
The syntax for the goto statement is given as follows:
goto label;
.
.
Label : statement;34.. What is the channel in Golang?
A channel is a medium through which a Goroutine effectively communicates with others. In other words, it is a pipeline through which Goroutines share values. Channels are usually bidirectional, allowing for the sending and receiving of values in the same channel. The important thing is that Goroutines can send and receive values only when the opposite end is ready.
35. What type of conversion is supported by Golang?
Golang supports only explicit type conversion. So, we need to specify the target data type explicitly.
Golang doesn’t support implicit conversion since Golang has a robust type system. For example, assigning an 'int' variable to a 'float' variable will throw errors.
36. What is the use of select statements in Golang?
In a way, the select statement in Golang is similar to the switch statement. This statement allows a Goroutine to wait on many communication operations.
The Golang's select statement is identical to the standard switch statement. However, the case statement in the select statement refers to communication.
37. Does Golang support inheritance property?
Golang doesn’t support inheritance property. At the same time, it provides embedding, composition, and interfaces to support code reuse and polymorphism.
38. How will you perform testing in Golang?
We use the ‘go test’ command to perform testing in Golang.
39. How do you check the variable type at runtime in Golang?
We use the type switch statement to check the variable type at runtime in Golang.
40. What is the use of CGo in Golang?
CGo enables the creation of Go packages that can call C language codes.
[ Related Article: Golang vs Java ]
41. How will you compare two structures in Go?
We use the ‘==’ operator to compare two structures in the go language. The main thing is that they shouldn’t contain any functions, maps, or slices.
42. Does Go support optional parameters?
Go doesn’t support optional parameters.
43. Does Golang have exceptions?
No. Golang doesn’t have exceptions. We use error-values to indicate the abnormal states in Golang.
44. Compare buffered and unbuffered channels in Golang.
| Buffered Channels | Unbuffered Channels |
| They make asynchronous communication | They support synchronous communication. |
| We cannot use these channels to send or receive data. | We can use these channels to send and receive data. |
45. What are rvalue and lvalue in Golang?
rvalue – This value appears on the right side of the assignment operator. It represents a value stored at some address in memory.
lvalue – This value appears on either the right-hand or left-hand side of the assignment operator.
46. What are function closures in Golang?
Anonymous functions are called function closures in Golang. We use them in dynamic programming.
47. Why do you use the Rune data type in Golang?
The Rune data type is also called a codepoint. It is an integer type that aliases for the int32 type. The Rune data type represents a single Unicode character. Rune literals can be represented by enclosing in single quotes.
48. Why don’t maps allow slices as keys?
Map lookup needs an equality operator that slices don’t use. Moreover, equality is not well-defined on slices.
49. How can you increase the performance of Golang programs?
We can increase the performance of Golang programs
- Managing goroutines using different cores
- Making input/output operations asynchronous
- Using predefined variables and sync pool
- Optimizing maps using integers instead of strings
50. Explain: Microservices architecture
In the Microservices architectural style, we develop applications as a collection of services. So it is easy to deploy and maintain the different applications' services. Each Microservice communicates with other services through interfaces. The main thing is that this architecture speeds up the development of applications.
With Microservices architecture, we can perform the following operations.
- migrating a complex website from a monolithic platform into a cloud-based microservices platform
- separating invoices and payment processing as independent units of services
- storing images and videos in a scalable object storage system
- providing cloud support to existing modular data processing services
51. Can you perform demand-driven design with Go?
We can perform Demand-Driven Design (DDD) with the Go language. DDD is a practical approach to modelling complex business domains as entities and their interactions. For instance, we can implement a customer service platform using the DDD principles in the Go language.
We can create maintainable and scalable Go applications by applying DDD principles in the Go programming. It helps to improve communication between developers, business stakeholders, and users.
52. Why do you build microservices with event sourcing or CQRS in Golng?
CQRS and Event sourcing are the two architectural designs. We leverage the architectural designs to rectify the challenges while dealing with transactions and data in the Microservices-based distribution systems.
53. How would you model a set in Golang?
We can model a set by using a map or struct. A map is a data structure that stores keys and values. Conversely, a struct is also a data structure that stores fields.
Selecting a map or 'struct' depends on the project requirements. Using maps is a good choice if we need a model set for adding and removing elements. On the other hand, if we need to model a set for iterating over elements, then using a struct is the best choice.
54. How will you manage logs in Go?
We can perform log management by using the following:
- Structured logging formats such as JSON or YAML
- Contextual information such as the User ID, request ID, and TimeStamp
- Log levels such as INFO, ERROR, DEBUG, etc.
- Centralised logs that support easy management and analysis
- The log management tool helps collect, store, and analyse logs.
Well done! You have completed learning the critical Go interview questions. We hope you have mastered Go concepts in the best way. Indeed, you will face your Go interviews confidently and stay ahead in the game.
55. Explain the switch statement in Golang.
The switch statement is essentially a multiway branch record. This statement helps to assign the execution to various parts of code based on the use of the expression. There are two types of switch statements: expression switch and type switch.
We apply an expression switch to dispatch execution to different parts of codes based on the phrase's value. We apply a type switch when match types are required.
Golang Frequently Asked Interview Questions:
1. Golang or Go – which one is the correct name of the language?
Go and Golang are used interchangeably. However, the Go is the commonly used name of the language.
2. Does Go have a runtime?
Yes! Go has a runtime system. Go’s runtime package supports interacting with Go’s runtime system and controlling its behaviour. For example, the package has functions to control Gortoutines, run garbage collection, and so on.
3. Can you link the Go and C/C++ codes?
Yes, we can link Go and C++ codes. However, linking is not advisable since it affects memory safety and stack management.
4. What is so great about Go?
Go language has a simple syntax. It has built-in support for concurrency through Goroutines. Besides, Go has a smaller standard library.
5. Is Go an object-oriented language?
Yes and No. Go comes with methods and types, which define go as an object-oriented language. At the same time, other object-oriented languages have no type hierarchy.
Conclusion:
It's time to wrap! We hope the top 50 Golang interview questions and answers have helped to boost your Golang knowledge significantly. Yes! This blog might have enhanced your expertise in the Go language to the next level.
If you want to explore the Go language more, sign up for the Golang course in MindMajix and gain certification. The practical and real-time projects of the training will boost your hard skills to greater heights. Eventually, you will become not only an industry-ready Go programmer but a top choice for employers.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Golang Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| Golang Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Golang Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Golang Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |

Ravindra Savaram is a Technical Lead at Mindmajix.com. His passion lies in writing articles on the most popular IT platforms including Machine learning, DevOps, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, RPA, Deep Learning, and so on. You can stay up to date on all these technologies by following him on LinkedIn and Twitter.
















