- Lean Interview Questions
- Lean Manufacturing Tools
- Lean vs Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Interview Question and Answers
- What is Lean Management? - A Complete Tutorial
- What is Six Sigma Green Belt?
- Six Sigma Tools
- What is Lean Six Sigma - The Definitive Guide
- Six Sigma Companies
- Six Sigma Techniques
- Six Sigma Methodology
- Six Sigma Projects and Use Cases
As the world becomes more competitive, almost every company and organization is beginning to implement various management development methodologies. Many training programs are available worldwide to assist organizations in improving their existing processes. Specifically, Six Sigma and Kaizen are two programs focusing on real-world scenarios to improve various business models consistently.
Six Sigma and Kaizen are both approaches to process improvement, with Six Sigma focusing on achieving near-perfect levels of quality through statistical analysis and structured problem-solving, while Kaizen emphasizes continuous improvement through incremental changes and employee involvement. Both aim to enhance organizational performance by reducing waste, improving efficiency, and increasing customer satisfaction. Both refer to lean principles that aim to eliminate waste, but there are clear differences in how each method is used. Know more below to know the importance and principles of each methodology!
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a collection of tools and strategies designed to reduce variability and defects.
It is a set of quality-control-based methodologies aiming to identify and eliminate errors. It is utilized for the detection, management, and control of variance. 6 sigma aims for six standard deviations between the mean and its nearest limit for detail.
Due to the intense competition, businesses are using the Six Sigma methodology to boost productivity and achieve continuous performance improvement. The number of faults per million opportunities and the number of standard deviations discovered in a process specification is related to Six Sigma.
There are two Project Techniques for Six Sigma
- DMADV (Define-Measure-Analyze-Design-Verify)
- DMAIC (Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control)
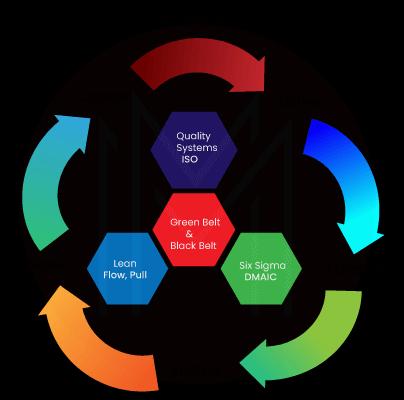
As we've already discussed, these two project methods are based on Deming's Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, which has become the basis for continuous quality improvement.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in Six Sigma, then enroll in "Six Sigma Green Belt Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
What are the Examples of Six Sigma?
Examples of Six Sigma are an excellent approach to comprehending the characteristics and benefits of its implementation techniques.
Some prominent six sigma examples include the following
1. General Electric(GE): GE has had problems with its products' quality and overall service, even though it hires the best specialists and uses the latest technology. It tried out Six Sigma and streamlined its product assurance process, leading to more money.
2. Wipro: Customer service and the creation of consumer goods were inadequate for a company that led the software development sector. With the help of putting Six Sigma concepts into the workplace, its problems were quickly fixed.
3. Microsoft: Their exceptional product line and customer service are made possible through Six Sigma. The market leader in software and goods is now cited as a Six Sigma best practices.
4. Motorola: As one of the first major corporations to implement Six Sigma, it attempted to improve the quality of its products and services and generate more revenue. The results were quite positive and contributed to the company's overall improvement.
Six Sigma Techniques
The following methods and tools are used by the Lean Six Sigma strategy to reach its most important goals
- 5S Tool: A method for making the workplace more profitable, secure, productive, and efficient.
- Kanban: Workflow management techniques, such as displaying the process and restricting the number of concurrent jobs, increase productivity and motivate ongoing enhancements.
- Kaizen: Workplace habits that inspire employees to better themselves and advance their careers.
- Value Stream Mapping: Evaluate areas for waste reduction and process improvement.
| Related Article: Six Sigma Techniques |
What is Kaizen?
The Japanese term kaizen refers to "development by way of modification." Kaizen is based on the principle of continuous improvement (CI), which means that as time goes on, a company's goods and services get better and more efficient.
Kaizen aims to improve the workplace, eliminate overly difficult tasks, and train employees how to identify and eliminate waste in company operations. Kaizen can be used to improve and eliminate waste in all areas and aspects of a business, including the manufacturing line.
In particular, Kaizen is the idea that everything can be changed and made better. When an organization has a Kaizen culture, people use their own ideas to find and solve problems. The goal of the strategy is to make small, regular improvements by using the knowledge of all employees in an organization.
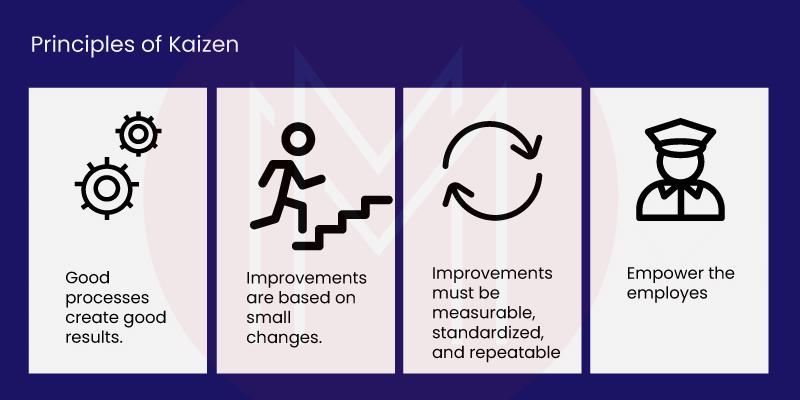
Kaizen is founded on several guiding concepts, including
- Work together.
- Go look for yourself to understand what's going on.
- Do something to stop and fix the problems' root causes.
- Use data to talk and facts to run things.
- Good results come from good processes.
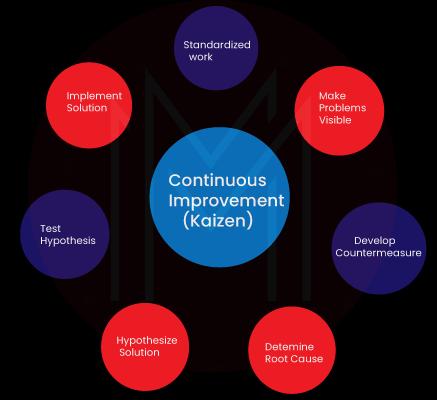
What are the Examples of Kaizen?
Kaizen is a tool for training the next generation of business leaders. Employee participation in creative activities is one of these means.
Some of the Kaizen examples include the following:
- Nestle is the world's largest food corporation and a company that employs Lean principles, specifically Kaizen. Nestle Waters utilized value stream mapping, a tool commonly linked with Kaizen. Nestlé has endeavored to make ongoing improvements to reduce waste and lessen the amount of time and resources squandered in their processes.
- A company that makes electronic circuit boards finds out that their customer, the final assembler, sends back 1.5% of their products because they are broken. After looking at each circuit board for a certain amount of time, the plant manager realizes that a certain capacitor is often missed. This capacitor is in a bin with other parts, and the way the process works makes it easy for the worker to miss it. To use Kaizen, the manager puts a sensor on the parts bin. The sensor would trigger a warning light if an operator moved a product to the next station without reaching into the container.
- Kaizen isn't just suitable for manufacturing companies and facilities. It can also help other types of businesses. The Mayo Clinic is a charitable medical practice and research organization that has applied the Kaizen philosophy to healthcare. Mayo wanted to apply the principles of Kaizen that Toyota used in their complex manufacturing process to the complex world of healthcare. Kaizen can significantly improve wait times and the handling of patient records, and the Mayo Clinic has successfully implemented it in their work areas.
Kaizen Techniques
Kaizen provides several continuous improvement techniques that businesses can use. Here are a few techniques that will help with Kaizen implementation:
1. Jishuken
Jishuken is the same as a self-study group or a group of people who study independently. This idea encourages managers to be more hands-on and learn about the processes they are in charge of and how they can be improved.
2. Gemba
Gemba is a Japanese word for "the actual location." Going down to the assembly line and talking to workers can provide managers and supervisors with invaluable insight. Scheduled walks where managers and supervisors can see procedures firsthand and have conversations with frontline workers are a common application of Gemba.
3. Value Stream Mapping
A Kaizen business can get a lot out of mapping out the processes and flows in a building. Most of the time, these maps are drawn by hand, and they show how materials move through the different parts of the workplace.
Value stream maps aim to find wastes in the manufacturing process and places where an approach could be improved. These possible improvements can be the focus of future Kaizen events and activities.
4. PDCA Cycle
PDCA cycles are frequently utilized while implementing Kaizen techniques. This cycle can be used by personnel at all organizational levels and is a great introduction to Lean manufacturing.
The PDCA cycle consists of four phases: Plan > Do > Check > Act is a kaizen strategy implementation and evaluation structure that provides a foundation for continuous improvement.
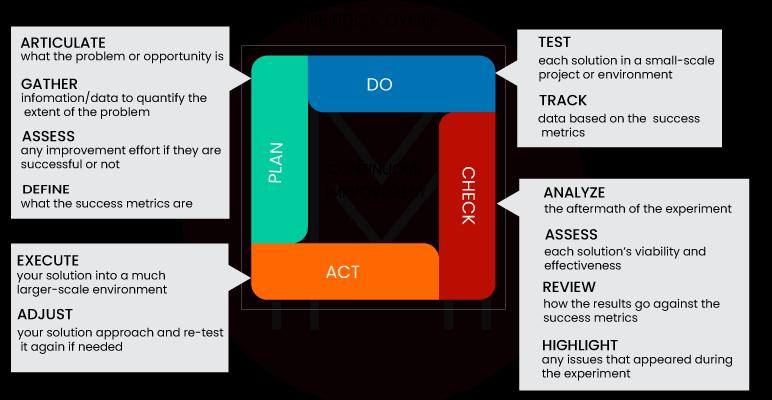
5. 5 Whys
As the name suggests, the 5 Whys is a problem-solving method that entails repeatedly asking "why?" This is a useful resource when trying to pin down the origin of a problem. If the underlying problem is ignored, it will be difficult to implement lasting change in the workplace.
What Are the Principles of Six Sigma?
Six Sigma has a simple goal to make sure that products and services are almost perfect so that businesses can change and customers are happy. Many companies have used each of the following Six Sigma principles to keep making their products and services better.
Most Six Sigma projects are successful because they follow five primary rules.
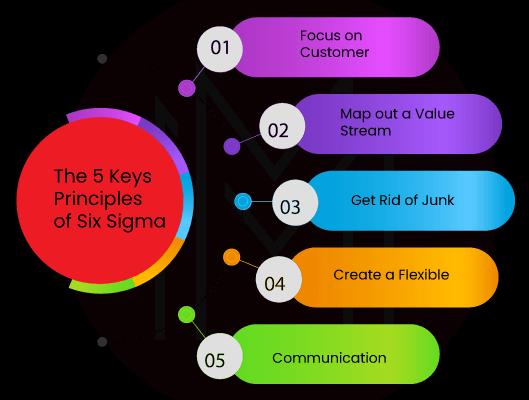
1. Focus on the Customer
"The customer is king" is a common saying that this is based on. Any change you want to make should be to help the customer as much as possible. Set a precise quality standard based on what the market or customer wants early.
2. Determine Your Problem by Measuring the Value Stream.
To identify waste areas
- Map the steps in a given process.
- Collect information to identify the specific problem area that needs to be transformed or addressed.
- Have clear goals for collecting data, like figuring out what data needs to be collected, why it needs to be collected, what insights are expected, making sure measurements are accurate, and setting up a standard system for collecting data.
Determine whether the data helps you achieve your goals, if it needs to be refined, or if more information is needed.
3. Get rid of variations and bottlenecks.
Once the problem is found, the process needs to be changed to eliminate the variation, which will eliminate the defects.
Streamline tasks so that quality control and efficiency can be achieved. Take out the steps in the process that don't add value for the customer. Tools are used to find outliers and problem areas if the value stream doesn't show where the problem is.
In the end, bottlenecks are taken care of by getting rid of the above waste.
4. Keep things rolling
Adopt a clear process in which everyone on your team can contribute and work together to solve problems using their different kinds of knowledge.
Six Sigma methods can have a big effect on a business, so the team needs to know the methods and principles behind them.
So, you need specialized training and knowledge to reduce the risk of a project or re-design failures and make sure that the process works at its best.
5. Make sure the ecosystem is responsive and flexible.
Six Sigma is all about changing and transforming businesses.
When an inadequate or ineffective process is taken away, work habits and the way employees do their jobs need to change. Project implementation can go smoothly if there is a strong culture of being flexible and open to changes in procedures. People and departments should be able to respond quickly to changes.
To make this easier, you should set up quick and easy ways for this to happen. Ultimately, a company can acquire a competitive advantage if it monitors the data, examines the bottom line frequently, and makes any required modifications to its procedures.
What are the Principles of Kaizen?
Unlike Six Sigma projects, which result in significant changes, Kaizen's methods produce minor improvements because the emphasis is on continuous improvement by all company employees.
To get the most out of Kaizen, ensure you understand the following elements and Kaizen principles before implementing them.
The Kaizen principles are divided into several stages
1. Teamwork
Kaizen can only be successful if the emphasis is placed on teamwork. Companies using Kaizen must instruct employees at all levels and in all departments on how they can participate in creating improvements to their own work or area.
2. Continuous Improvement
Continuous Improvement, which is at the heart of Kaizen, should also be at the heart of every Kaizen activity and event. Continuous improvement is an idea that needs to be done often and doesn't really have an endpoint.
3. Standardization
People often say that Kaizen is based on standardizing work. The idea is that once a department or area of a facility has solved a problem and found the best way to do it, that way of doing things is spread to other departments and regions.
4. Quality Circles
Both effective teamwork and Kaizen as a whole rely heavily on quality circles. Workers and others in the same line of employment form the backbone of quality circles. They hold regular meetings to discuss and resolve work-related problems, which is a crucial part of the Kaizen methodology.
5. Observe and follow the action for yourself.
Management engagement is a fundamental component of Kaizen. Supervisors, managers, and even executives need to visit the production line to observe the real job being carried out there.
6. Empowering people
Not only is it important to involve individuals of all levels in the kaizen process, but also to give them more responsibility. It is ideal for employees to feel at ease approaching their managers or supervisors with ideas and concerns when they are working.
Comparing Six Sigma and Kaizen
- Both systems are extremely helpful in finding solutions to issues, but they take very different approaches. Six Sigma's use of technical data focused on addressing product deviations is where it diverges most sharply from Kaizen's emphasis on continuous improvement.
- On the other hand, Kaizen is centered on enhancing existing workplace conditions to boost productivity. While Six Sigma relies on numbers to make adjustments, Kaizen looks to people's feelings to find answers to workplace issues.
- While Six Sigma relies on a statistical analysis of business processes, Kaizen tends to rely less on numbers. Instead of focusing on percentile success rates, as Six Sigma does, Kaizen strives for perfection by constantly improving the work environment, the systems in place, and the methods implemented.
- Kaizen's method helps the company as a whole, and it doesn't think that just using charts will be enough in the long run. Different Six Sigma concepts guide toward measurable objectives. In the case of Kaizen, the primary goal has never been to achieve so many purposes within the first month or year. However, they always attempt to focus on areas where they can improve. The main goal of Kaizen is to make each person's life better and more refined.
- Despite their differences, Six Sigma and Kaizen share a common goal: boosting corporate efficiency and effectiveness by eliminating waste. This demonstrates that the two ideologies are compatible with one another and may be applied together. In reality, enterprises across various sectors may adopt a synchronous strategy incorporating Six Sigma and Kaizen ideas.
- Still, both Six Sigma and Kaizen are excellent concepts that save a great deal of time and money.
Six Sigma vs Kaizen: Differences
| Six Sigma | Kaizen | |
| Developed by | Bill Smith and Mikel Harry | Masaaki Imai |
| Origin | Western Origin | Japanese TQC and toyota production System |
| Definition | Six Sigma is a methodology that is based on data and statistics. | Kaizen is a Japanese business philosophy focusing on continually improving operations and involving all personnel. |
| Widely used | Methodology | Technique |
| Theory | Reducing Variation and Defects | Mistakes as Possibility for Improvement |
| Program or activities driven by | Top down approach (top to bottom) | Bottom up approach (Bottom to top) |
| Perfection | Immediate | continuous |
| Results | Short term results | Long term results |
| Elements |
|
|
| Principles |
|
|
| Tools used for the approach | DMAIC | Use QC 7 & New QC 7 tools |
| Types/ Methodologies |
|
|
| Implementation structure | Black, green, yellow belts | Small group activities (QC circle/QIT/WIT) |
| Companies use | Motorola, GE, Ford, Sony, ABB, Lockheed Martin, KodaK | Nestlé |
| Focus on |
|
|
| Data-Driven | Statistical | Observational |
| Quantitative | Technical Approach | Common sense approach |
| Techniques | Advanced statistical and analytical tools | Quality tools and suggestion |
| Projects | Larger/Longer | Smaller/shooter |
When Should You Choose One or the Other?
Kaizen may be the best option if you're trying to improve an entire department or an entire corporation. It gives you more freedom in how you complete tasks. The development of strict statistical methods or other scientific criteria is also not required. Kaizen places a strong emphasis on involving everyone in making these improvements. The aim is to make modest advancements rather than perfection.
Six Sigma might be better for projects that have to do with problems with products. It can get rid of mistakes that slow down the process of getting a final product to the customer. It also makes workflows simpler by using logic to come up with a solution that will work and last. Six Sigma also helps build customer relationships by making it a top priority to solve their problems.
Six Sigma vs Kaizen FAQs
1. Who is the best example of Six Sigma?
Wipro is the greatest example of Six Sigma. As an industry leader in software development, consumer goods production and customer service were deficient. Its flaws were quickly eliminated with the aid of Six Sigma implementation.
2. Is Six Sigma still used?
Six Sigma experts are still used by businesses worldwide that want to streamline operations, cut costs, and reduce waste.
3. What are Kaizen Skills?
The five skills that make up the Kaizen method are
- Teamwork
- Improved morale
- Personal discipline
- Suggestions for improvement.
- Quality circles
4. What is the best Kaizen?
Kaizen is best for reducing waste because it gets rid of overproduction, improves quality, makes people more efficient, cuts down on idle time, and gets rid of activities that aren't needed. All of these things save money and can turn losses into profits.
5. Is Kaizen better than Six Sigma?
Six Sigma could be a better way to handle projects that deal with product failures. It can eliminate mistakes that slow down the process and keep a finished product from getting to the customer. Kaizen puts a lot of weight on getting everyone involved in making these changes.
6. Is Kaizen still used?
Yes, business leaders usually use Kaizen because it offers consistent, incremental gains in productivity and efficiency. Teams are urged to seek out ways to increase value continuously.
7. Which software is used in Six Sigma?
Minitab and SigmaXL are two of the most popular statistical software packages used in Six Sigma programs.
8. How many types of Six Sigma are there?
Six Sigma has different levels of certification, such as Yellow Belt, White Belt, Black Belt, Master Black Belt, Green Belt, and Champion.
| Related Article: Six Sigma Interview Question and Answers |
Conclusion
The choice between Six Sigma and Kaizen depends on the specific needs and goals of the organization. If the goal is to achieve near-perfect levels of quality, Six Sigma may be the best approach. However, if the goal is to create a culture of continuous improvement with a focus on efficiency and waste reduction, then Kaizen may be a better fit. Ultimately, both approaches can lead to significant improvements in organizational performance and should be considered valuable tools in the process improvement toolkit. We hope this essay on Six Sigma vs. Kaizen has broadened your understanding of these methodologies.
"If you wish to learn about Six Sigma, you may enroll in a Six Sigma Course and achieve certification."
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .




