Know that DB2 is the database product offered by IBM. DB2 is a relational database management system with which you can store, manage, and retrieve data in an organized way. Database servers play a vital role in the database management of DB2. As a whole, DB2 is one of the most secure, reliable, and efficient database systems.

With DB2, you can store large data arrays and retrieve the data faster. DB2 uses SQL queries to store, manage and retrieve data. Apart from all these, DB2 offers flexibility, independency, concurrency, and many more features to users.
In this blog, we compiled the IBM DB2 interview questions and answers in the following categories in greater detail.
Top 10 Frequently Asked IBM DB2 Interview Questions
- What is the IBM DB2 database?
- What is the Declarations Generator (DCLGEN)?
- What do you mean by a Buffer Pool?
- What is the response of DB2 if a program abends?
- What do you mean by the binding process in DB2?
- What is the use of DB2 optimizer, and how does it find the optimum access plan?
- Differentiate DELETE and DROP statements in DB2.
- How will you find the number of rows or values in a DB2 table?
- Why don't we prefer using SELECT statements in embedded SQL programs?
- Can you eliminate duplicate values from a table in DB2? If yes, how will you do this?
IBM DB2 Interview Questions For Freshers
1. What do you mean by database?
A database is nothing but an organized collection of information or data stored in tables. You can easily access, update, and manage the data in the tables. In every database, the information is stored in the rows and columns of one or more tables. We can use Database Management Systems (DBMS) to manage or control a database. Also, we can use Structured Query Language (SQL) to write as well as query data in a database.
2. What is the IBM DB2 database?
In its basic form, DB2 is a relational database management system. It is also a cloud-native database with which you can store, manage, and retrieve data effectively. Mainly, this database performs real-time data analytics and low-latency transactions. You can use DB2 for mission-critical applications since it offers a high level of security as well as continuous availability. With this database, you can manage both structured and unstructured data effortlessly.
| Do you want to get certified and build your career in IBM DB2? Then enroll in "IBM DB2 Online Training" this course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
3. What are the significant components of DB2?
There are totally four components in DB2 as follows:
- System Services Component: This component manages system operations, logging, communication, and so on.
- Locking Services Component: This component is also known as the Internal Resource Lock Manager. This component comes with the required controls to manage concurrent access to data. Mainly, it rectifies concurrency issues in addition to deadlocks.
- Database Services Component: This component manages to define, update, and retrieve users as well as system data. This component is prime in executing SQL statements and managing the buffer pool.
- Distributed Data facility Component: This component supports distributed database management.
4. What do you mean by an alias?
It is the substitute for a table or view. In other words, it is the alternative name of objects. The objects can be tables, sequences, views, etc. An alias is usually defined as a local server. It can also refer to a table or view at a remote server. We can use an alias if we want to refer to a table or view in an SQL statement. Another thing is that we can create and drop aliases like we create and drop tables and views.
5. What is a table space in DB2?
A tablespace is nothing but a set of volumes on disks. The disks contain the data sets where tables are usually stored. A table space will have linear VSAM datasets. Tables are generally divided into equal-sized units, known as pages. We can compress data in table spaces, which in turn saves space and allows for storing more data. DB2 creates two types of table spaces such as partition by growth and partition by range.
6. What is the language used in DB2?
Structured Query Language (SQL) is nothing but the language used in DB2 to access data from DB2. With this language, we can define and manipulate data in relational databases. We can modify data objects such as tables. We can insert, delete, and update data in tables. Not only that, we can use SQL to authorize users to access tables and views.
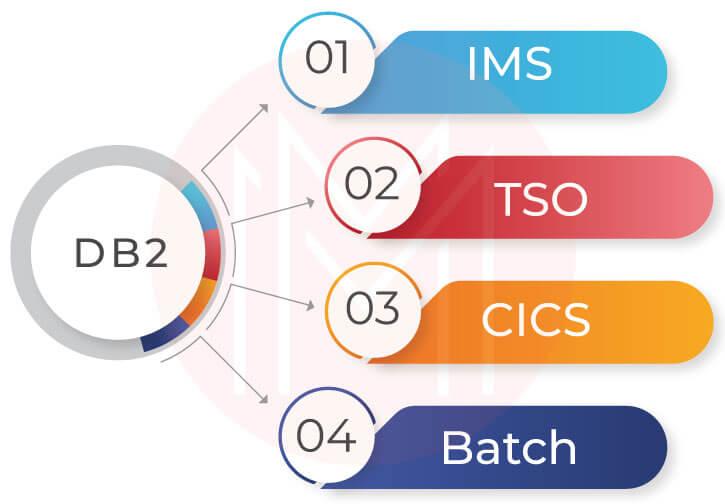
7. What do you mean by attachment facility?
An attachment facility is an interface that connects DB2 with other environments. Here, the environments can be WebSphere, Information Management System (IMS), Customer Information Control System (CICS), Time Sharing Option (TSO), and Batch. We can use ODBC, SQLJ, and JDBC interfaces to connect DB2 with other environments.
8. What do you mean by a BufferPool?
A Buffer pool is part of the main memory. You can store tables and indexes in a buffer pool. Generally, the buffer pool is managed by the database manager.
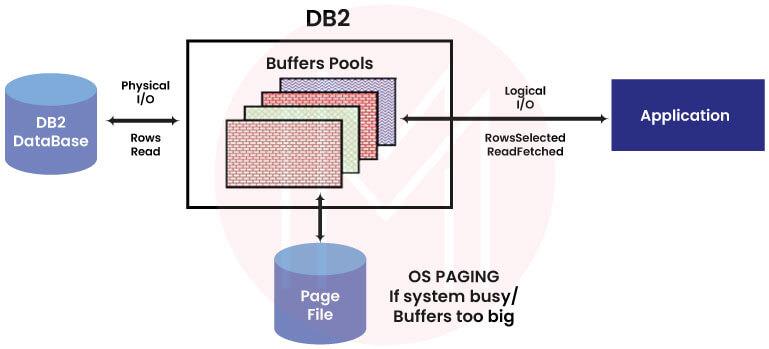
Every DB2 has a buffer pool. Every new database comes with a buffer pool known as IBMDEFAULTBP. You can create, drop or modify buffer pools with the help of the statements such as CREATE BUFFERPOOL, ALTER BUFFERPOOL, and DROP buffer pool.
9. What are isolation levels, and name their types?
The isolation level in DB2 denotes the degree of isolation between the data and other concurrent processes. There are four isolation levels in DB2: Repeatable Read (RR), Cursor Stability (CS), Read Stability (RS), and Uncommitted Read (UR).
10. What do you mean by Cursor Stability?
This is one of the isolation levels of IBM DB2. According to cursor stability, a row is locked when the cursor is pointed at the row. Note that the specific row is accessed during a transaction, and the lock remains locked until the transaction gets completed. Significantly, an application can only update the row once the lock is released.
11. What is the Declarations Generator (DCLGEN)?
Usually, it is essential to declare tables and views when you write codes. The declarations generator, or DCLGEN, generates DECLARE statements for programs written in C in addition to COBOL. As a result, you can avoid writing codes for statements. Along with that, DCLGEN generates respective host variable structures.
12. What is Lock Escalation?
It is the process of releasing any number of page locks, LOB, row locks, and XML locks. Applications on a single table or table space usually make these locks. Whenever a lock escalation occurs in the database, it releases a message like DSNI0311. Using this message, we can identify the tablespace where the lock escalation occurred.
13. What do you mean by Aggregate Function?
The function receives a set of inputs but returns only a single value. In other words, the argument of every aggregate function is a set of values.
ARRAY_AVG, COUNT, AVG, COUNT_BIG, MEDIAN, MAX (aggregate), and SUM are some examples of aggregate functions.
14. What is SQLCA?
SQLCA refers to SQL Communications Area. SQLCA is a set of variables updated at the end of every SQL statement execution. There will be only one SQLCA for every application with executable SQL statements. But at the same time, every multi-threaded application will have more than one SQLCA.
15. What do you mean by the binding process in DB2?
The binding process uses DB2 as well as DBRM. Here, DBRM is nothing but a database request module. During the binding process, the SQL statements in the DBRM switch to operational mode. The binding process builds access paths to the DB2 table. Also, the binding process supports authenticating users along with validating SQL statements in the DBRM.
16. What is the use of the host variable in DB2?
- You can use host variables to exchange data between applications and DB2.
- You can insert data into a host variable to load the data into a table.
- If you want to change the fields of rows in a table, you can use host variables.
- While evaluating the WHERE as well as HAVING clauses, we can use the data in the host variable.
- If you want to indicate a NULL value, then you can use the host variable.
17. Name the various authorities in DB2.
- Security Administration Authority – SECADM
- Access Control Administration Authority – ACCESSCTRL
- Database Administration Authority – DBADM
- Data Access Administration Authority – DATAACCESS
- Workload Administration Authority – WLMADM
- SQL Administration Authority – SQLADM
- Explain Administration Authority – EXPLAIN
- LOAD Authority
18. What are the four types of DB2 registry variables?
- Global level profile registry: This registry includes all server-wide environment variable settings.
- Instance level profile registry: This registry consists of all environment variable settings of instances
- Instance node-level profile registry: This registry has all the environment variable settings that belong to a Massively Parallel Processing (MPP)
- User-level profile registry: This registry includes the environment variable settings that belong to users.
19. What are the monitor elements in DB2, and brief them a bit?
Monitor elements are nothing but the data structures used to update the status of the DB2. Following are a few examples of monitoring elements in DB2.
- Counter: If any activity happens in DB2, counters record the number of times that activity occurred.
- Gauge: It represents the volume of activities that happen in DB2. For example, a gauge indicates how long an activity occurred if the activity is time-dependent.
- Watermark: They are the highest values of various measurements taken against the activities in DB2. This value is the maximum value of measurement up to this moment.
- Text: They are the text values. For instance, stmt_text returns the text of SQL statements.
- Timestamp: It indicates the time at which activities occurred in DB2.
20. What is CHECK Constraint?
In its basic form, it is a rule that ensures data integrity in DB2. Only based on this rule, values are allowed to store in one or more columns of a base table. This means that values are stored in a base table after being verified by the check constraint. When you create a table in DB2, you can also create the CHECK constraint.
21. What is the Clustering Index?
The clustering index decides how the rows must be physically ordered in a table space. Know that every table in DB2 comes with a clustering index. We can define clustering index on both partitioned tablespaces as well as segmented table space. Also, Clustering indexes are highly helpful in ordering operations, grouping operations, etc.
22. What is the security model of DB2?
Two modes of security control are available in DB2, such as authentication and authorization.
Authentication is the security control used to allow users to access the DB2. It is managed by external systems.
The authorization is the security control that allows users to access data within the DB2. A database manager manages it.
IBM DB2 Interview Questions For Experienced
23. Mention the characteristics of the Resource Control Table (RCT).
- The RCT table defines the connection between DB2 as well as CICS. More to the point, it defines the relationship between CICS transactions as well as DB2 plans.
- RCT contains the elements collected through macros of DSNCRCT
- This table matches the CICS transaction ID to the respective DB2 authorization ID as well as to the plan ID.
- All the DB2 plans must be registered in the RCT
24. List out the different fields of SQLCA.
- SQLCAID
- SQLCODE
- SQLCABC
- SQLERRML
- SQLERRP
- SQLERRMC
- SQLERRD
- SQLWARNA
- SQLWARN
- SQLSTATE
25. Brief about the Storage Groups (STOGROUP) in DB2.
Essentially, storage groups in DB2 represent a set of volumes on disks. This is where tables and indexes are stored in datasets. Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) catalog stores the datasets. With storage groups, DB2 defines, deletes, extends, and modifies VSAM datasets.
We can assign table spaces for storage groups. However, it is essential to note that table space is usually associated with only one storage group, whereas one storage group may be associated with many tablespaces.
| Related Article: VSAM Interview Questions |
26. What are the significant differences between Cursor Stability (CS) and Repeated Read (RR) isolation levels?
|
Cursor Stability (CS) |
Repeated Read (RR) |
|
It is the default isolation level and is used if you want maximum concurrency |
It is one of the isolation levels. |
|
It locks only the current row on which the cursor is positioned |
It and locks all the rows specified by the SQL statement |
|
Locks are released once the program moves to the next row |
All locks are held until a commit or rollback releases them |
|
CS offers good consistency and data integrity |
RR offers high-level data integrity due to its locking strategy |
27. Can you list out the advantages of using DB2 Packages?
Below is the list of DB2 advantages:
- DB2 packages reduce plan outage time
- They reduce processor execution time
- They reduce CICS starts or exits
- They avoid cloning CICS as well as DB2ENTRY definitions
- They allow specifying collection at execution time.
28. How does DB2 physically store a NULL value?
DB2 physically stores the NULL value by adding an extra byte in prefix to the column value.
29. How can we retrieve rows from the DB2 table in Embedded SQL?
We can use the SELECT statement if we want to retrieve rows from the DB2 table. When more than one row is returned, you can use the cursor to fetch a single row out of the multiple rows.
30. What are the two types of database logging used in DB2?
- Circular logging: It is a default behavior when you create a new database.
- Archive logging: It is used for roll-forward recovery. The log files are copied from the current log path. It can be copied from the mirror log path.
31. Can you differentiate INTEGER and SMALLINT data types in DB2?
|
INTEGER |
SMALLINT |
|
It is used to store large binary integers with 31 bits |
It is used to store small binary integers with 15 bits |
|
The range of integers varies from -2147483648 up to +2147483647 |
The range of small integers varies from -32,768 up to +32,767 |
32. List out the advantages and disadvantages of INTEGER and SMALLINT data types.
Advantages:
- Both INTEGER and SMALLINT types need tiny spaces for values.
- Using these data types, you can perform arithmetic and sorting operations such as SUM and MAX.
Disadvantages:
- They can store values only within a limit.
- The database server cannot store values that exceed the capacity of integers.
33. Differentiate DELETE and DROP statements in DB2.
|
DELETE Statement |
DROP statement |
|
It deletes a row from a table or view |
It removes an object or table from the database |
|
Only the rows are deleted. No other associated entities are deleted. |
If an object is removed, the objects associated with the dropped object also get removed. It doesn’t matter whether they are associated directly or indirectly with the object. |
|
You can restore the rows using the ROLLBACK function |
You cannot restore the table or object. |
34. Can you compare QMF and SPUFI in DB2?
|
QMF |
SPUFI |
|
QMF stands for Query Management Facility |
SPUFI stands for SQL Processor Using File Input |
|
It is a query or reporting environment. You can format reports with QMF. |
It is a SQL execution engine. |
|
You can store your queries in tables and reports in QMF |
It needs datasets to store SQL statements as well as move them to DB2. |
|
It is an add-on product that comes with a cost |
It is absolutely a free product |
|
There is no need that all the DB2 users should have QMF |
Every DB2 customer will have SPUFI, undoubtedly. |
35. Mention the functionalities of the Buffer Manager in DB2.
- Buffer Manager (BM) accesses data for other DB2 components
- BM uses pools of memory for storing frequently accessed data
- It transfers data between external devices and storage.
- It reduces the number of physical I/O operations with the help of advanced buffering techniques such as read-ahead buffering in addition to look-aside buffering.
36. Differentiate Simple, Partitioned, and Segmented Table Spaces.
|
Simple |
Segmented |
Partitioned |
|
It contains one or more tables and stores rows for all tables |
It contains one or more tables |
It contains only one table rows |
|
Rows from multiple tables can be interleaved |
A tablespace is divided into multiple equal-sized segments. This is where tables are stored. |
A tablespace is divided into multiple parts. Here, rows are stored in all the parts. |
37. Mention the four environments that access DB2.
IMS, TSO, CICS, and BATCH are the four environments that can access DB2 seamlessly.
38. What is the use of DB2 optimizer, and how does it find the optimum access plan?
DB2 optimizer processes every SQL statement and selects a query access plan. It estimates the execution costs of multiple access plans and selects the access plan with the minimum cost.
When selecting the optimum access plan, the DB optimizer achieves it in the following way.
- It verifies the syntax of SQL statements
- It determines the table to be accessed
- It identifies the columns that must be returned and the columns in the predicate
- It identifies the indexes for this combination of tables and columns
- Then, it collects the statistics provided in the catalog tables.
39. What are the Advantages of MDC Tables?
- MDC tables use block-based indexes. They are smaller, so they occupy less space and allow quick scanning.
- They are physically clustered with more than one key or dimension
- Query performance is improved significantly
- MDC tables can maintain their clustering over all dimensions automatically as well as continuously
40. What are the Pros and Cons of DB2?
Pros:
- You can quickly access data in DB2, especially when the file size is small
- You can easily share data with DB2. This is because it comes with AI capabilities that simplify sharing structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data with other systems.
- DB2 has compression capabilities with which you can save space significantly without compromising performance
- You can make hybrid transaction analytical processing with DB2
Cons:
- DB2 responds slowly when the file size is large
- It will only be suitable for modern development if it requires a rigid schema.
IBM DB2 Interview Questions For Advanced
41. How will you find the number of rows or values in a DB2 table?
We can use the COUNT function to get the number of rows in a set of rows or values. The argument can be of any data type, such as BLOB, DBCLOB, CLOB, and XML.
It is essential to note that the result of this function will be an integer. And it cannot be a null value.
The argument of the COUNT (*) function is a set of rows. This function returns the number of rows in a set of rows.
The argument of the COUNT (expression) function is a set of values. This function will return the number of non-null values in the set. Note that this function includes duplicate values for counting.
The argument of the COUNT (DISTINCT expression) function is a set of values. This function will return the number of non-null values in the set. Note that this function removes duplicate values.
42. How can you move a table space to another DASD volume?
We can move the table space by using ALTER STOGROUP statement. This is possible only when the tablespace is allocated to that storage group.
43. What is the response of DB2 if a program abends?
When there is a program abend, DB2 performs the auto rollback function.
44. Why don't we prefer using SELECT statements in embedded SQL programs?
If we change the structure of a table, then we need to change the program. The change can be adding or deleting a field in the table.
Sometimes, it leads to I/O overhead due to the retrieval of columns that is not required for the users.
45. Why do you need to create MQT, and how will you create it?
We create Materialized Query Table (MQT) to improve the performance of SQL applications.
If we want to create an MQT, we need to write a CREATE TABLE statement. We need to specify a full selection too. Then we need to include the DATA INITIALLY DEFERRED as well as REFRESH DEFERRED clauses to define an MQT.
46. Can you eliminate duplicate values from a table in DB2? If yes, how will you do this?
Yes. We can remove many identical rows from the result table of a query. You need to use the DISTINCT keyword in the query to achieve this. This is because the DISTINCT keyword eliminates the duplicate rows from the query result table. As a result, every result table will contain only the unique data.
47. If you drop the index of a PLAN, what would be the response?
If this case, it will impact PLANS negatively. The PLANS may contain the SQLs using that dropped index. Simply put, the PLAN will be marked as invalid.
48. What are the contention situations created by locks in DB2?
Know that locks are essential to achieve concurrency in DB2. Timeout, Suspension, and Deadlock are the contention situations created by locks. And they will degrade the performance of DB2, undoubtedly.
- Suspension: This situation occurs when an application requests a lock already held by another. The requested application must stop its operation until the application releases the lock. The application resumes its operation only when the lock is released.
- Timeout: This situation occurs when the suspension of an application exceeds the defined preset level. In that case, DB2 terminates the application and returns error codes.
- Deadlock: This situation occurs when two or more applications lock specific resources and not allows other applications to access the resources. The main thing is that the other applications can only proceed with their operations if they access the locked resources.
49. Compare: PLAN and a Package?
|
PLAN |
Package |
|
A plan contains many packages or DBRMs |
A package contains a single DBRM |
|
It is an executable unit since it has access path |
It is not an executable unit since it doesn’t have any access path |
|
Less preferred |
Highly preferred |
50. What is the maximum number of volumes that you can add in a STOGROUP?
You can add a maximum of 133 volumes in a storage group.
Conclusion
It’s a wrap! We hope you have thoroughly learned the top IBM DB2 interview questions in one place. You will now be able to attend the IBM DB2 interviews with your polished knowledge and enhanced confidence. Keep in mind that hard work never fails. We advise you to read the blog periodically to keep the knowledge fresh. We wish you all great success and bag your dream job soon.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| IBM DB2 Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| IBM DB2 Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| IBM DB2 Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| IBM DB2 Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















