The International Business Machines Corporation, abbreviated as IBM, is an American multinational corporation that was founded in 1911 and has its headquarters in Armonk, New York. The company has its operations established in more than 175 countries. IBM holds expertise in computer hardware, software, and middleware while providing consulting and hosting services in varying areas. It is the largest industrial research organization in the whole world and has 19 research facilities in 12 countries.
The employees of this organization have received several recognitions for scientific inventions and research. It is one of the largest employers and has more than 297,900 people working from around the world. Undeniably, it is nothing less than a dream to have a job at IBM. However, the hiring process of this company is quite stringent; thus, you should be well-prepared before applying for a vacancy here.
To help you out with just that, MindMajix has brought some of the top IBM interview questions to make the preparation process a breeze for you.
Interview Interview Questions Table Of Content
- Interview Round and Process
- For Freshers
- For Experienced
- HR Interview Questions
- FAQs
- Tips
- Conclusion
Top 10 Frequently Asked IBM Interview Interview Questions
- What are the functions of an operating system?
- What do you mean by processes and threads?
- Explain arrays. State examples of array applications available in real life.
- What is an entry-controlled loop?
- Define the objective of the sudo command in the UNIX operating system.
- Is Python interpreter or compiled?
- Differentiate between abstract class and interface.
- Explain function overloading and overriding in the context of C++.
- Give the difference between merge sort and quick sort in the sorting algorithms.
- Write a program to convert uppercase characters to lowercase characters and vice versa.
IBM Interview Round and Process
As far as the interview and hiring process of IBM is concerned, the company has come up with two different rounds, wherein:
- Round 1: Online written test
- Round 2: Technical interview round and HR interview round
*Each of these rounds is an elimination round.*
Round 1:
This round is segregated into four different parts, including:
- Cognitive Ability Games: Includes 6 questions that should be completed in 30 minutes.
- English Language Test: Includes 10 questions that should be completed in 10 minutes.
- Learning Agility Assessment: Includes 50 questions that should be completed in 30 minutes.
- Coding Test: Includes 6 questions that should be completed in 30 minutes.
All in all, there will be 72 questions and you will get 100 minutes to complete them.
Round 2:
Once you have cleared the first round, you will get an email regarding the confirmation of the second round, which is the interview round. It is further divided into two parts:
- Technical Round: Herein, the concentration will be on your CV. You will be asked technical questions from your last project. If you have never worked on a project before, you might get asked something from your academic, such as on DBMS, operating system, data structures, algorithms, OOPs, networking, and a programming language.
- HR Round: In this round, your weakness, strength, and personality will be evaluated. An HR personnel will see whether you are confident enough or not.
IBM Selection Criteria
- If there is an education gap in your resume, it should not exceed one year.
- You must not have any backlogs at the time of interview.
- You have have an aggregate of 60% or above in 10th and 12th standards and 65% and above in graduation.
- You should submit correct documents, such as resume, government ID proof, marksheets, and anything related to work experience (if available)
| If you want to enrich your career in IBM, then visit Mindmajix - a global online training platform: "IBM Cognos Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
IBM Technical Interview Questions for Freshers
1. What are the major Object-Oriented Programming concepts in the context of C++ language?

There are four diverse but major concepts, such as:
- Inheritance
Being one of the essential features of Object-Oriented Programming, Inheritance is the ability of one class to derive traits and features from another class. Derived classes and subclasses are those classes that inherit properties from some other class. A base class or a superclass is one whose member functions and properties get inherited by other classes. Inheritance basically supports the reusability concept.
- Encapsulation
Encapsulation can be defined as the data binding and the functions that modify it. It means that the variables or data of a class are concealed from other classes and can be accessed only through the member function of that class wherein they are declared.
- Polymorphism
This one is used to describe the existence of several versions of anything. To put it simply, polymorphism is the ability of the message to be showcased in various ways. For instance, a person may play a gamut of roles simultaneously. They might be a father, a son, a husband, and a CEO - all at once. This results in the same person acting differently based on the situation. This is called polymorphism.
In C++, you have two different types of polymorphism, such as:
- Compile Time Polymorphism: It is accomplished by overloading operators and functions.
- Runtime Polymorphism: It is created with the help of function overriding.
- Abstraction
It gives just the essential elements and keeps the rest concealed. Data abstraction is referred to the process wherein only the most important parts of a dataset are revealed to the world, and the implementation details are hidden.
2. What are the functions of an operating system?
Following are the functions of an operating system:
- User Interface
Operating systems are a conduit between the users and the computer hardware. They let the user access the hardware in a completely structured manner.
- Maintenance of System Functionality
An operating system monitors the overall system health to help enhance performance. Along with that, it also tracks the time between service requests and system responses to get a detailed understanding of the system’s health. This helps with a performance by offering essential information for debugging.
- Security
Operating systems use password protection and varying other security features to safeguard the user data. They also avert unauthorized access to user data and other programs.
- Detection of Error
An operating system consistently monitors the entire system to discover errors and avoid situations that can lead to the machine's fall.
- Memory Management
The operating system is liable for managing main memory, which is also known as primary memory. It is made of many words or bytes, each having its own address. Such memory is fast storage that the CPU can directly access. Before getting executed, a program should be loaded into the primary memory first.
- File Management
To make usage and navigation more effective, a file system gets organized into varying directories. They might comprise additional files and directories. Besides everything else, an operating system has to track where data is getting stored, the condition of every file, and user access settings.
3. What is the difference between primary memory and secondary memory?

Primary Memory (Main Memory)
It is the computer memory that gets accessed by the CPU directly. It is made of Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) and offers a real working space to the processor. Primary memory tracks instructions and data that the processor is currently processing. Random Access Memory (RAM) is one example of primary memory.
Secondary Memory
The second memory’s contents should be transferred to the primary memory before the processor can access them. This is done because the processor is incapable of directly interacting with secondary memory. Some examples of secondary memory are hard discs, USB drives, and other such devices.
Here is a detailed differentiation between primary memory and secondary memory for a better understanding:
|
Primary Memory (Main Memory) |
Secondary Memory |
|
It is a temporary memory storage. |
It is a permanent memory storage. |
|
It is instantly accessible by the CPU/processor. |
It is not instantly accessible by the CPU/processor. |
|
It can either be volatile (requiring electricity to store the information) or non-volatile. |
It is non-volatile (it doesn’t need electricity to store the information). |
|
The devices used are semiconductor memories. |
The devices used comprise optical or magnetic memories. |
|
It has a higher cost. |
It has a lower cost. |
4. What do you mean by processes and threads?
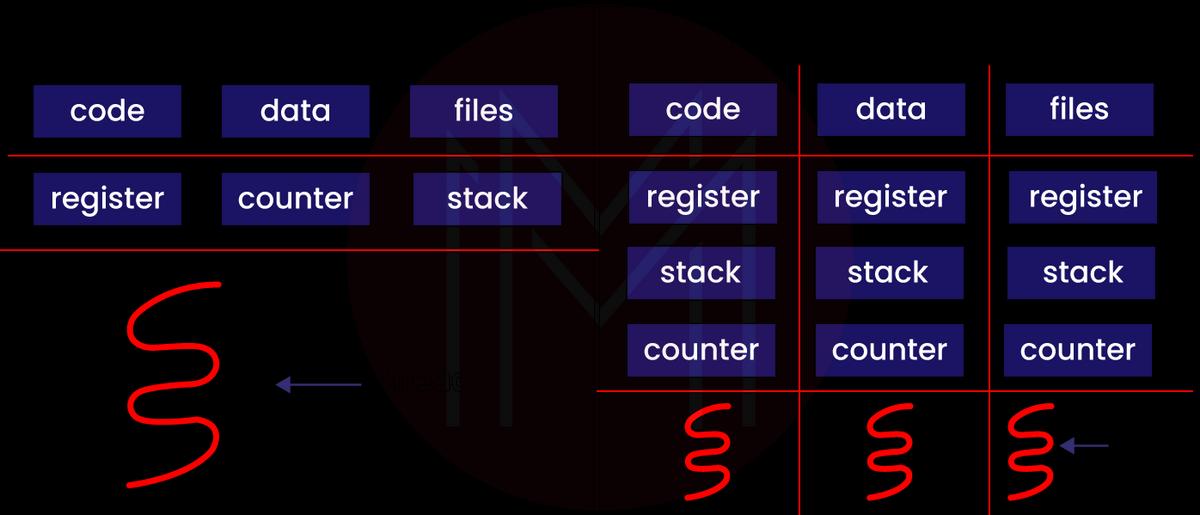
Processes
It is a program that is being executed currently. A process control block is responsible for controlling any type of process. This block also stores the register, process priority, CPU, process ID, process state, and other data. When one process generates another process, a new process is created. Generally, a process is isolated and takes a long time to complete; thus, it does not share a memory with any other processes.
Threads
It is referred to a segment of the process, meaning that a process can have several threads in it. For a thread, there are three states: running, ready, and blocked. Compared with processes, threads can terminate quickly, but they don’t get isolated.
Here is a detailed differentiation between processes and threads for a better understanding:
|
Processes |
Threads |
|
Takes a long time to create one process |
Takes less time to create |
|
Takes a long time to change contexts from one process to another |
Takes less time to change contexts from one thread to another |
|
As far as intercommunication is concerned, its method is not efficient |
As far as intercommunication is concerned, its method is more efficient |
|
Different processes use diverse memory locations and don’t have one recollection |
Memory gets shared among several threads in a single process |
|
Every process has an individual address space, process control block and stack |
All the threads share the same process control block but address space, thread control blocks, and stack are unique |
5. What is a database management system? What are its advantages over traditional file systems?

A Database Management System (DBMS) is a computerized system that stores data. Users of this system have the competency to execute several operations, such as database structure maintenance, data manipulation, and more.
Some benefits of a DBMS over traditional file systems are
- Users get to access efficiently managed data, courtesy of the database management. This results in end-users instantly reviewing their information and responding to changes accordingly.
- DBMS offers a sturdier platform for security standards and data privacy, thus, helping businesses enhance data security.
- It assists in the creation of quick responses to varying database queries, hence, allowing more accurate and faster data access.
6. Explain arrays. State examples of array applications available in real life.
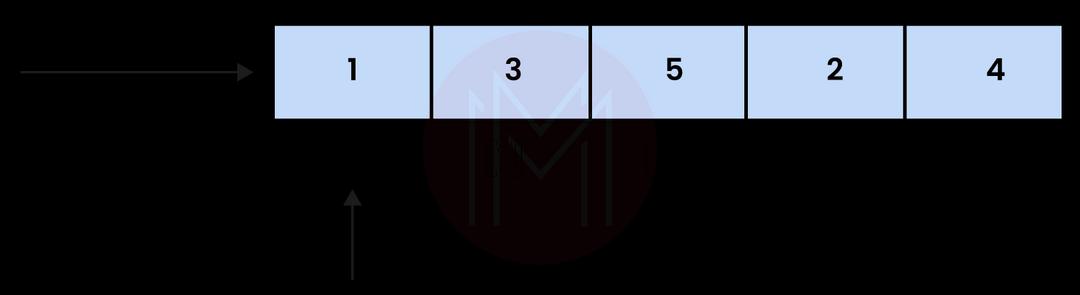
An accumulation of things stored in contiguous memory locations is an array. The objective here is to put those things together that are similar. By adding an offset to a base value, the position of every element can be calculated simply.
In the real world, the following are some array applications:
- In a simpler manner, you can use arrays to store data in a tabular format. For instance, if you wish to save contacts on your phone, the program will create an array comprising all of your contacts.
- A question paper is made of several numbered questions, each with an individual set of marks.
- An array is also used in speech recognition, demonstrating every spoken signal.
| Related Article - Array Interview Questions |
7. What do you mean by a deadlock? Mention some prerequisites of a deadlock.
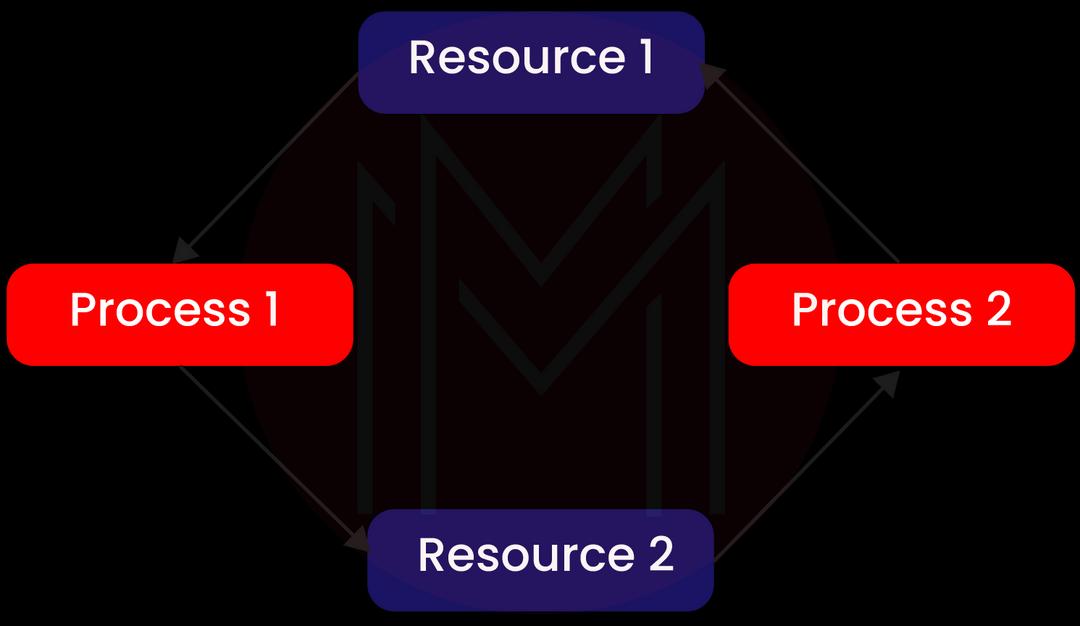
Let’s consider two sheep approaching each other on a log of wood hanging above a flowing river. Once both of them come in front, none can move. The same situation takes place in operating systems when two or multiple processes share resources while waiting for those resources that other processes hold. In this case, a deadlock is reached.
Here are some prerequisites for a deadlock:
- Mutual Exclusion: It occurs when one or multiple resources aren’t shared.
- No Preemption: A resource can be obtained from a process only if it has been released. There cannot be any forced obtaining.
- Hold and Wait: Herein, a process retains a minimum of one resource while waiting for more.
- Circular Wait: It is a collection of processes waiting for one another in a cyclic pattern.
8. What is an entry-controlled loop?
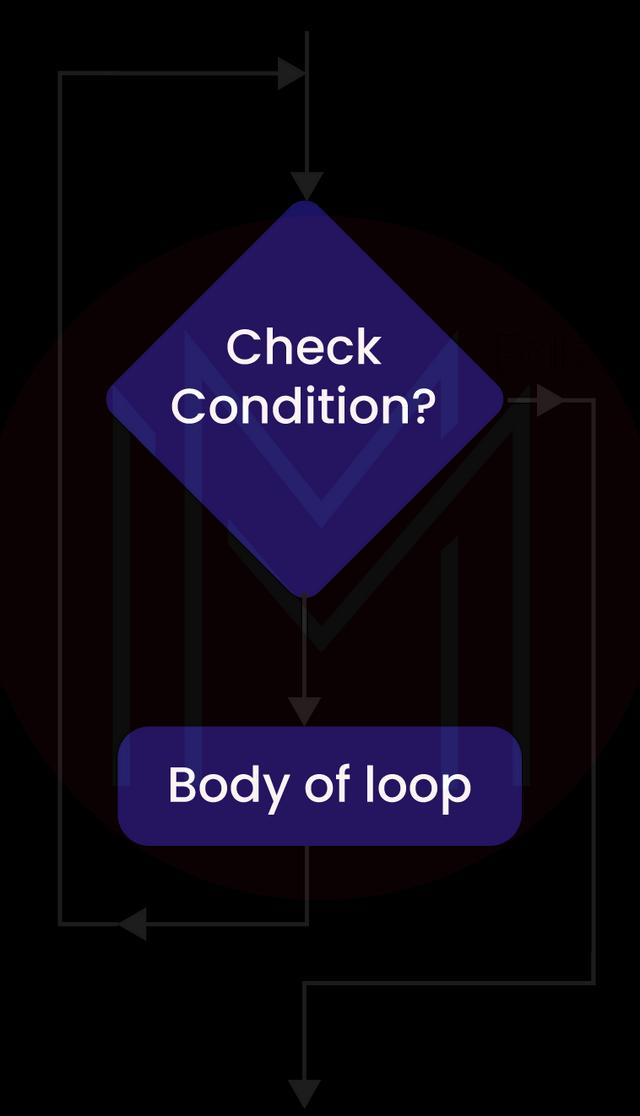
At the point of entry, if an expression or condition becomes true, control gets passed to the loop’s body. This loop type is called an entry control loop, as it regulates the entry of the loop. It comprises “for loops” and “while loops.”
9. What do you mean by procedural programming? How can you differentiate between procedural programming and object-oriented programming?

Procedural programming involves the concept of imploring processes, which came out from structured programming. Also known as functions, subroutines or routines, procedures are the collection of instructions that should be followed. In a program, any process can be called by other processes or programs at any point.
Here is the difference between procedural programming and object-oriented programming:
|
Procedural Programming |
Object-Oriented Programming |
|
Herein, a program gets divided into little modules, which are known as functions. |
Herein, a program gets divided into different components, known as objects. |
|
It uses the top-down methodology. |
It uses a bottom-up methodology. |
|
It is difficult to add new functions and data. |
It is simple to add new functions and data. |
|
It doesn’t allow overloading. |
It feasibly allows overloading. |
|
It is insecure as it doesn’t have an accurate way to conceal data. |
It is safe as it can hide data easily. |
10. Define the objective of the sudo command in the UNIX operating system.
sudo is referred to as Super Users DO. Often, this command is used in Linux as a prefix to a command that can be run only by superusers. Upon using “sudo” as a prefix to a command, you will find it running with enhanced privileges, letting you gain accurate permissions to run a command as a superuser. It is equivalent to the “run as administrator” option.
If you wish to use the sudo command, you must have an entry in the sudoers file, which can be found at “/etc/sudoers.” To investigate or change the sudoers file, you must use the sudo command. To edit this file, you must use the “visudo” command.
11. What do you think about virtual memory?
Virtual memory is a method to allocate storage that allows you to address the secondary memory as the main memory. Herein, addresses generated by a program get converted into machine addresses automatically. Also, they are different from those addresses that the memory system uses to designate physical places of storage.
12. Define three different categories of schedulers.
Schedulers are specialized computer programs that regulate the process scheduling in different ways. Their primary objective is to decide the jobs that should be entered into the system and the processes to execute.
The three types of schedulers are
- Long-Term Schedulers (LTS)
Also known as task scheduler, it helps determine the applications put into the system for processing. It chooses processes from the ready queue and loads them into memory for CPU scheduling before they can be executed. The main task of LTS is to provide a balanced mix of varying operations, such as CPU-bound workloads and I/O-bound workloads.
- Medium-Term Schedulers (MTS)
MTS is used to exchange processes in the primary memory. It frees the RAM that is used by the processes. This results in the minimization of the extent of multiprogramming. Thus, this scheduler is liable for swapped-out processes.
- Short-Term Schedulers (STS)
It is also known as CPU scheduler. The primary objective of STS is to enhance the system performance on the basis of pre-set criteria. The CPU scheduler chooses a process from the ones that are ready to be executed and provides it CPU time. And then, it selects the next process to execute.
13. Is Python interpreter or compiled?
Python is both interpreter and a compiled language. Herein, programs get compiled first, and then they are interpreted. However, Python deletes the compiled parts the moment you execute the code.
14. What is the difference between overloading and overriding?
Here are the major differences between overloading and overriding:
|
Overloading |
Overriding |
|
It is compile-time polymorphism. |
It is run-time polymorphism. |
|
It takes place within the class. |
It takes place in two classes along with inheritance relation. |
|
It may or may not need inheritance. |
It always requires inheritance. |
|
It must have a different signature and the same name. |
It must have the same signature and the same name. |
15. Differentiate between abstract class and interface.
The below-mentioned table clears the difference between abstract class and interface:
|
Abstract Class |
Interface |
|
It is designed to be a parent class. |
It is the class’s blueprint that contains abstract methods. |
|
It can be declared through “Abstract.” |
It can be declared through “Interface.” |
|
It does not support multiple inheritances. |
It supports multiple inheritances. |
|
It supports non-static, static, non-final and final variables. |
It supports static and final variables. |
IBM Technical Interview Questions for Experienced
16. Explain function overloading and overriding in the context of C++.
Function Overloading
There are multiple definitions of this function, including modifying the signature, i.e., the return type, the data type of parameters, and the number of parameters.
Here is a program showcasing an example of function overloading in this language:
using namespace std;
void overloadedMethod(int x)
{
cout << "Inside Overloaded Method 1" << endl;
}
void overloadedMethod(float x)
{
cout << "Inside Overloaded Method 2" << endl;
}
void overloadedMethod(int x1, float x2)
{
cout << "Inside Overloaded Method 3" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int x = 5;
float y = 5.5;
overloadedMethod(x);
overloadedMethod(y);
overloadedMethod(x, y);
return 0;
}
Output
Inside Overloaded Method 1
Inside Overloaded Method 2
Inside Overloaded Method 3Function Overriding
Function overriding is a process of overriding a base class function with the same signature in the derived class.
Here is a program showcasing an example of function overriding in this language:
class Test
{
public:
virtual void print(){ cout << "Testing Function"; }
};
class Sample: public Test
{
public:
void print(){ cout << "Inside a Sample Function";}
};
int main()
{
Test obj = new Sample();
obj.print();
return 0;
}
Output
Inside a Sample Function17. How will you define transaction ACID properties in the context of DBMS?
Each transaction in a DBMS has to follow a pre-set of guidelines. ACID attributes are related to such characteristics. They are defined as mentioned below:
- A = Atomicity
This showcases that a transaction either doesn’t occur at all or at once. There is no intermedia route, meaning you will not find any steps to transactions. Every transaction is seen as a single entity that is either incomplete or complete. It comprises these two steps:
- Abort: If a transaction aborts, database updates get lost.
- Commit: Upon committing, the changes within a translation become visible.
Atomicity is often known as the “all or nothing rule.”
- C = Consistency
To ensure the database’s consistency, integrity constraints must be satisfied before and after the transaction. It is related to the database’s accuracy.
- I = Isolation
This property ensures that varying transactions run concurrently without creating problems in the database. Here, non-interfering transactions get executed. Changes made in one transaction aren’t displayed in other transactions until the change is either committed or put to memory. With this feature, you can ensure that consequently running transactions offer the same situation as if they were running in order.
- D = Durability
This property makes sure that once a transaction is completed, the database modifications and updates get written and saved to memory and that they make it through the system failure. Such changes get stored in non-volatile memory permanently. Thus, the transactional results don’t ever get lost.
18. What is the difference between struct and union in C programming language?
Structure
Also known as a structure, it is a user-defined data type in the programming language that lets you mix data items of different types. It is used to signify a record.
The syntax for structure is
struct structureName
{
member definition;
member definition;
...
member definition;
};
Here is an example to understand it better:
struct student
{
int id;
char name[50];
string branch;
}; Union
It is a special data type that lets you store several data types in a single memory space. While a union can have several members, only one is worth it at a time.
The syntax for union is
union unionName
{
member definition;
member definition;
...
member definition;
};Here is an example to understand it better:
union student
{
string name;
string branch;
int phone;
}; Coming to the difference between a struct and a union, this below-mentioned table summarises it all:
|
Struct |
Union |
|
It is used to define a structure. |
It is used to define a union. |
|
The compiler assigns memory to every variable member once variables get declared in a structure. |
A structure’s size is comprehended based on the total size of every data element. |
|
When a variable gets declared in a union, the compiler assigns memory to such a variable member that has the biggest size. |
In a union, the largest data member gets to determine the union’s size. |
|
Change in one variable’s value doesn’t impact other variables. |
Change in one variable’s value will impact other variables in the union. |
|
Every variable member has its individual memory space. |
Members share the memory space with the largest variable in size. |
|
Multiple variables can get initialized simultaneously. |
Only the first data member can get initialized. |
19. What is the difference between function/variable definition and declaration in every OOPs programming language?

The definition of a variable assigns memory space for the variable and defines the place to keep it. On the other hand, the objective of a variable declaration is to let the compiler know the variable’s name, the value it comprises, and the starting value (if applicable). In simple words, a declaration provides information regarding the attributes of a variable.
Here is the summarised difference between function/variable definition and declaration:
|
Definition |
Declaration |
|
Herein, a function or variable can be defined only once. |
Herein, a function or variable can be declared infinitely. |
|
During this process, memory gets allocated. |
During this process, no memory gets allocated. |
|
Definition’s example is: void my_func() { cout << “something printed” << “\n”; } |
Declaration’s example is: void my_func(); |
20. Give the difference between merge sort and quick sort in the sorting algorithms.

The table below states a quick difference between merge and quick sort:
|
Quick Sort |
Merge Sort |
|
Herein, an array gets divided into any ratio. There is no need to divide the array into equal parts. |
Herein, an array is partitioned only into two halves (n/2) |
|
The worst-case complication is O(n^2). |
The average and worst instances have the same complications O (n log n). |
|
Large datasets don’t work well with quick sorting. |
Any type of dataset can work well with merge sorts. |
|
It doesn’t require additional storage; hence, it is in place. |
It is not implemented because the auxiliary arrays require additional storage. |
|
It is desirable for arrays. |
It is desirable for linked lists. |
21. A sorted array of 0s and 1s is given. The objective is to discover the index of the first ‘1’ in the sorted array. There are chances that the array could be made of either entirely 1s or 0s. If the array doesn’t have 1s, print ‘-1.’
In the given question, the array is sorted. You can use this array attribute and binary search to find the first ‘1’ in the array. You can start by searching through the entire array to look for the center element. When it is 0, it will mean that your response is located on the right side of the center element. However, if it is 1, the response can be on the left side.
Here is an example to understand it better:
Input
arr = {0, 0, 0, 0}
Output
-1
Input
arr = {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}
Output
4
The code here will be:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int searchIndex(int a[], int left, int right)
{
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (a[mid] == 1 && (mid == 0 || a[mid - 1] == 0))
return mid;
else if (a[mid] == 1)
left = mid - 1;
else
left = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = {0, 0, 0, 0};
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
cout << searchIndex(a, 0, n - 1);
return 0;
}
Output
-122. Write a program to convert uppercase characters to lowercase characters and vice versa.
For this, you will have to go over the string with each character. You remove 32 from the current character and convert it to uppercase if it is put in lowercase. Similarly, if it is in uppercase, add 32 and convert it to lowercase.
Here is an example to understand it better:
Input
“miNDmajIX”
Output
“MIndMAJix”
Here is the code for it:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void caseChange(string& str)
{
int len = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (str[i] >= 'a' && str[i] <= 'z')
{
str[i] = str[i] - 32;
}
else if (str[i] >= 'A' && str[i] <= 'Z')
{
str[i] = str[i] + 32;
}
}
}
int main()
{
string str = "miNDmajIX";
cout << "The Original String is: " << str << "\n";
caseChange(str);
cout << "The Changed String is: " << str << "\n";
return 0;
}
Output
The Original String is: miNDmajIX
The Changed String is: MIndMAJix23. Create a program to discover different ways that can be used to create a change for N cents, assuming you have an infinite supply of every C = C1, C2,...Cm coins.
To discover the total number of solutions, we will have to divide all the set solutions into two different sets.
- Solutions with no mth coin (or Cm)
- Solutions with a minimum of one mth coin (or Cm)
If the function solve(C[], m, n) has been used to count the number of ways, it can be written as the sum of solve(C[], m-1, n) and solve(C[], m, n) (C[], m, n-Cm). We will use dynamic programming to save the result for a certain n and m value. This decreases the temporal complication to O(nm).
Here is an example to understand it better:
Input
N = 5, C = {11, 23, 43, 7, 12}
Output
0
Input
N = 4, C = { 1, 2, 3}
Output
4
The code for it will be:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int solve(int C[], int m, int n)
{
int dp[n + 1][m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
dp[0][i] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
int x = (i-C[j] >= 0) ? dp[i - C[j]][j] : 0;
int y = (j >= 1) ? dp[i][j - 1] : 0;
dp[i][j] = x + y;
}
}
return dp[n][m - 1];
}
int main()
{
int C[] = {11, 23, 43, 7, 12};
int m = sizeof(C)/sizeof(C[0]);
int n = 5;
cout << solve(C, m, n);
return 0;
}
Output
0IBM HR Interview Questions
24. Tell us something about yourself.
I have recently completed my Bachelor’s in Computer Science and Engineering. Throughout my academic life, I have been highly focused on the contemporary side of technology, such as machine learning and data mining. C and Java are two of the programming languages that I am competent in.
25. What are your weak and strong points?
My weak point is that I won’t rest until I have completed the given task. On the other hand, I consider my strong points to be being responsible, open-minded and trustworthy.
26. Can you differentiate between confidence and overconfidence?
While confidence gives you the positive outlook of winning in different situations, overconfidence says there are no chances of failure - at least not in this life.
27. Why should you be hired?
Considering that I am a fresher in this stream, I don’t have any previous work experience to showcase. If you hire me, I will be able to sharpen my learnings, acquire new skills and accomplish my goals. This will also help me contribute to the success of your company.
28. Why do you want to work with us?
It will be a privilege for me to work with a globally recognised company like yours. Since it has its presence across the world, it can be said that the company is only going to soar high in the future. Thus, it is a good opportunity for me to grow tremendously.
29. How can you differentiate hard work and smart work?
Hard work is putting our sweat and blood into accomplishing a task well within the given deadline. On the contrary, smart work is finding an easier and quicker way to complete that task without compromising quality.
30. Can you work under pressure?
Sure, I can. In fact, I have enough experience working with a group and under tighter deadlines during my academic time.
31. Are you comfortable with working overtime?
If a project is urgent and my presence is required, I will be available whenever needed.
32. What are your objectives in life?
I aim to get this job and fit well in your company. My long-term aim is to succeed in every aspect of this company’s operations.
33. If required, would you lie for our organization?
Until it is not coming at the expense of my integrity or other people, I am fine with lying for the company’s sake.
34. Where do you see yourself in five years?
I see myself progressing in this company and accomplishing a higher position wherein I become an invaluable member of this firm.
35. Who is your inspiration?
My parents have been a great source of inspiration for me as they have been constantly on their toes to help you achieve my academic goals. They have been directing me towards the right direction and preventing me from experiencing downfalls.
36. What kind of person would you not like to work with?
I would not like to work with somebody who doesn’t respect their or others’ time. Additionally, I prefer staying away from lethargic people and the ones who constantly form excuses to not complete a task.
37. What has more value for you: the work or the money?
My work holds more value for me than money. In a way, I think both these factors are inter-related. The better I work, the more I make.
38. What are the most essential qualities of a team player?
Good communication skills, team bonding, listening traits, understanding skills, and empathy are some of the essential qualities of a team player.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How to prepare for an IBM interview?
One of the best ways to prepare for an IBM interview is by thoroughly researching the company. Once you have got the hang of it, know everything related to the role you are applying for, including the responsibilities and the types of tasks you will have to handle. And then sharpen your expertise in self-knowledge. Make sure you know enough about yourself so as not to fumble in front of the interviewer. Lastly, stay ready with all the possible IBM interview questions that can come your way.
2. How long is the IBM hiring process?
Basically, as per IBM, the process - from the opportunity to offer (start to end) - can take anywhere between a month and two.
3. Is IBM paying a good salary?
The average salary at IBM is between ₹1,68,000 to ₹13,84,843 a year. On average, the company pays anywhere between ₹10,000 to ₹55,000 a month, depending upon the role you have applied for.
4. Is IBM's job hard to get?
Yes, in a way, it is a bit challenging to get a job at this company. IBM is known for its rigorous hiring process. Also, the difficulty rating for the interview process at IBM is 2.9 out of 5.
5. What is the interview process at IBM?
The process of recruitment at IBM is conducted in two different rounds. The first round is an online written test wherein your cognitive abilities, English language, learning agility and coding skills are tested. The second round comprises a technical interview round and an HR interview round.
6. How many interview rounds are for IBM?
If you are applying for a job at IBM, you will have to go through two rounds of interviews.
7. How do I get selected for IBM?
Once you have found a role that matches your interest, complete the application process and apply for it. Next, your application will get read by experts at IBM. If selected, you will have to take an assessment test, which will be on the basis of the role you have applied for. The better you do on this test, the more will be your chances of getting selected.
Tips to Clear IBM Interview
- Conduct extensive research: To begin with, make sure you have as much information about the company, the role and the objectives, as well as the responsibilities as you can. Study the company’s history and understand the ongoing business initiatives. Learn about the competition and find out what is happening in the industry. Know about future trends as well.
- Find out more details about yourself: In a way, you should be ready to speak about whatever is there on your resume. You would obviously want to put your best self forward. Find out how you will be a good fit for the applied role and how you can demonstrate the skills needed. Think about whether you have done something the same in the past. If yes, don’t forget to point it out.
- Have a list of questions: When going for an interview, ensure you don’t end up only answering but asking too. Insightful and thoughtful questions show your interest in the role. It also tells the interviewer that you have done your research and that you are serious about this role.
- Be yourself: Out of all the things to remember, ensure you don’t leave your confidence behind. It shows who you truly are. Be genuine with your answers, and don’t try to bluff or fake around. Even if you don’t know an answer, accept it and move ahead with the interview.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we are definitely sure that these 38 IBM interview questions and answers would be helpful enough for you when it comes to sharpening your knowledge and expanding your skills. With a thorough understanding of the questions and answers mentioned above, you are sure to have an upperhand than your competitors. More so, if you would like to further enhance your knowledge and skills related to IBM, you can find a variety of IBM courses on MindMajix. You can learn a lot from these courses and ace your upcoming interviews like a pro.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| IBM Planning Analytics Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| IBM Planning Analytics Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| IBM Planning Analytics Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| IBM Planning Analytics Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















