- Django Interview Questions
- Python Array Examples
- Python enum
- Python Enumerate with Example
- Python Flask Tutorial For Beginners
- Python For Beginners - Way To Success
- Python For Data Science Tutorial For Beginners
- Python for loop
- Python GET and POST Requests
- Python IDEs for Python Programmers
- Python Interview Questions
- Python Lists with Examples
- Python Partial Function Using Functools
- Python Print
- How to generate random numbers in python
- Python Regular Expression (RegEx) Cheatsheet
- Python Sleep Method
- Python List Methods
- Python Split Method with Example
- Python String Functions
- Python Tutorial
- Python Variable Types
- Python vs Java
- Python vs SAS vs R
- Python Operators
- Code Introspection in Python
- Comprehensions in Python
- Python Exception Handling
- Defining Functions - Python
- Generators & Iterators in python
- Install Python on Windows and Linux
- Introduction to Python Programming
- Lists concepts in Python
- Loops in Python
- Regular Expression Operations in Python
- Python Serialization
- String Formatting - Python
- R vs Python: Which is better R or Python?
- Six Digit Salary With Python
- Top 20 Python Frameworks List
- Why Learn Python
- Python Substring
- OOPs Interview Questions
- Career Shift To Python : Success Guaranteed
- Face Recognition with Python
- Go vs Python
- Pyspark Interview Questions
- Python Pandas Interview Questions
- OpenCV Interview Questions
- Python Project Ideas
- Flask Interview Questions and Answers
- What is PyCharm?
- What is Seaborn in Python?
- What is Anaconda Navigator
- Numpy Broadcasting - Detailed Explanation
- Python Data Science Interview Questions
- Genpact Interview Questions
- Python Developer Job Description
- Pandas Projects and Use Cases
- DataFrame Tutorial
- How to install Python on Windows
- Pyspark DataFrame
An array is the type of data structure that contains a set of elements in a tabular format. Each of its elements is associated with at least one key or index. Storing a few elements of data in multiple variables is no big problem. But consider storing, say 5,000 or 10,000 values. Can you still do it individually for each element? It's not at all an efficient way of storing values. There arises the dire need for arrays in programming where you can store the values in a single variable. Also, an array makes it super easy to sort as well as search any value of data. And the most important thing is that multiple values can be processed instantly in an array.
Almost every programming language supports arrays in the data structure. And the ones that don't have arrays support similar data structures with different names, such as lists.
We will explore Array Interview Questions- 2023 (updated) and answers separately for the given two categories:
Top 10 Array Interview Questions
- Differentiate between array and object.
- Mention the default value of the array.
- Differentiate between ArrayList and Array.
- Write a code to sort an Array.
- What do you mean by an anonymous array?
- Can the class name of an array be retrieved?
- Differentiate between an array and a dictionary.
- Differentiate between an indexed array and an associative array.
- How can you intersect two sorted arrays?
- Can the main() method of a class be called from another class?
Array Interview Questions for freshers:
1. What are the basic operations of arrays?
Traverse, Insertion, Deletion, Search, Search, and Update are the basic operations of arrays.
2. Differentiate between array and object.
A thing with characteristics is represented by an object. On the other hand, data is stored in an array in a single variable. Items can be accessed, changed, and deleted with dots and brackets from objects. In arrays, zero-based indexing and various built-in methods are used to access and modify items.
| If you would like to become a Python certified professional, then visit Mindmajix - A Global online training platform for “Python Training” Courses. This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
3. Can a negative number be passed in an array?
No, we can't pass a negative number as the size of an array. If we try to do so, NegativeArraySizeException will be obtained.
4. Mention the default value of the array.
The initiation of an array takes the default value in the given manner:
- For float, double- 0.0 is the default value
- For byte, int, short, and long- Zero is the default value.
- For object- Null is the default value.
- For Boolean- False is the default value.
5. When is the ArrayStoreException obtained?
This is an exception of runtime. For instance, only string elements can be stored in a String Array. And if we try inserting an integer element in it, ArrayStoreException will occur.
6. What is meant by a "jagged" array in Java?
Arrays having different lengths are contained in Jagged Arrays. They are also referred to as multi-dimensional arrays sometimes.
7. How can an array be copied into another array in Java?
We can copy any array into another using the given four methods:
- With “Arrays.copyOf()” method
- With "For loop."
- With “clone()” method
- With “System.arraycopy()” method
8. When does ArrayIndex OutOfBounds Exception occur?
This is an exception of run time. This occurs when an invalid index is tried to be accessed by the program. Usually, a negative index and an index higher than the array size fall under invalid indexes.
9. Differentiate between ArrayList and Array.
| Array | ArrayList |
| There is a fixed or static size of an array that can't be altered once declared. | The size of ArrayList is dynamic and not static. As we add elements, the size automatically increases. |
| Both objects of a class and primitive data are contained in it. | Object entries are contained in ArrayList but not primitive data types. |
| There is no Generics feature in an array. | There is a Generics feature in ArrayList. |
10. How can you print the element of an Array?
We can print element of an array as follows:
Int testmarks [] = {10, 40, 35, 20, 10};
System.out.printIn (Arrays.toAtring (testmarks));
Output-
[10, 40, 35, 20, 10]11. Write a code to sort an Array.
We can use Array.sort() method to sort an Array as given below-
Int Result [] = {15, 8, 10, 7}
Arrays.sort(Result);
System.out.printIn(Arrays.toString(Result));//[7, 8, 10, 15]12. How can two arrays be compared?
“Array.equal()” be used to compare 2 arrays of same data type and size:
Int [] A = {2, 4, 6};
Int [] B = {1, 3, 5};
System.out.printIn (Arrays.equal(A, B)); //false
Int [] C = {2, 4, 6};
System.out.printIn Arrays.equal(A, C)); //true
13. What do you mean by an anonymous array?
The array that is not stored on a variable is an anonymous array. We can construct other objects using it. There is a constructor in the polygon class of Java by which an anonymous array is passed as a parameter.
| Check out: Python Variable Types |
14. Which methods can you use for finding duplicate elements?
The following methods can be used to find duplicates:
- Brute Force method
- Using HashSet
- Using HashMap
Array Interview Questions for Experienced :
1. How does int array [] differ from int [] array?
There is no major difference between them both. Arrays can be declared using both methods. There is just a minor difference. Postfix [] should be used when we declare a single array in a line. On the other hand, prefix [] should be used when we declare multiple arrays in a line.
2. Can the class name of an array be retrieved?
An array is also an object, and the class name can be retrieved from the object. The getClass() and getName() methods are invoked for retrieving the class name of the array. The object's runtime class is returned by the getClass method. And the name of the array class is returned by the getName() method.
3. What is meant by left-rotation?
We can perform this operation over an array. Each element gets shifted 1 unit left when we use this operation. That means the value of the lowest index gets shifted to the highest index. Any number of rotations can be performed over an array. People also call it the circular array.

4. What do you mean by dynamic arrays?
Dynamic arrays are also known as the resizable arrays, growable arrays, ArrayLists, or mutable arrays in Java. That is because there is automatic resizing available in them.
5. Differentiate between an array and a dictionary.
| Array | Dictionary |
| This is a list of homogenous elements. | Key-value pairs are contained in a dictionary. |
| There can be a dynamic size of arrays. | There can be no dynamic size of dictionaries. |
| The size of an array has to be set before using it. | We don't have to set the size before in dictionaries. |
| The ReDim statement has to be used for increasing the size of the array. | We don't need any statement for adding an element in dictionaries. |
6. What is a Sparse array?
A sparse array is one with several elements having zero value. On the other hand, most elements are non-zero in a dense array. Integers are mapped to objects by Sparse array, and there can be gaps in indices. Their memory is better than that of a HashMap.
| Learn: Python Operators with Examples |
7. Differentiate between an indexed array and an associative array.
| Associative array | Indexed array |
| An associative array stores the key-value pairs in the form of string or numeric format. | There are numeric keys in an indexed array where each key has its specific value. |
| These are referred to as maps. | There are not referred to as maps. |
| Strings can act as strings here. | Integers are starting with 0 as keys here. |
| They act as tables of two columns. | They act as tables of a single column. |
8. What is meant by "Dimension" and "subscript"?
- Dimension is nothing but the count of subscripts or indices needed for specifying an individual element.
- Subscript is nothing but a number. And dimension describes the range of keys that are accepted.
For instance, in arr[10][5], the dimension is two. And we require 2 subscripts for addressing the elements. One will be between 0 and 9, while the other will be between 0 and 4.
9. How can a specific element be removed from an array?
While changing the size of the array is not allowed once defined, we can do either of the following:
- We will create a brand new array and omit the value which we want to remove.
- We will search the target element and then move all the elements one position back or to the target element's right side
10. How can you intersect two sorted arrays?
The element is printed if the element is there in both arrays
- Two index variables will be used- i and j. Both of them will be initialized to 0.
- There will be increment in i if arr01 [i] < arr02[j].
- There will be increment in j if arr01 [i] > arr02[j].
- Both will increment and get printed in case they are the same
11. How can zeros be separated from non-zeros?
We will follow the given steps:
- The counter will be initialized to 0.
- inputarray will be traversed from left to right.
- inputArray[i] will be assigned to inputArray[counter].
- The counter will be incremented to 1.
- The remaining values will be assigned zero.
12. Can you declare arrays in Java like- Int a[] = new int [4]{1,3,5,7}?
No, the size of the array should not be provided when we specify the elements.
13. Can you use the sizeof operator for telling an array size that is passed to a function?
Information about the number of elements in an array is not passed when we pass an array parameter in C or C++. Even though the size of the pointer and the type's size can be obtained by sizeof() but not the bytes of the array.
14. Can the main() method of a class be called from another class?
Yes, the main() method be called from another class with the help of Classname.main(). A string type array should be passed to it while calling the main() method.
Frequently Asked Array Interview Questions
1. What is an array?
An array is a collection of elements in the form of objects, numbers, or pictures arranged in rows and columns. It is a collection of data elements in contiguous memory locations in terms of programming. And this is called database systems. Multiple data pieces can be stored under a single variable.
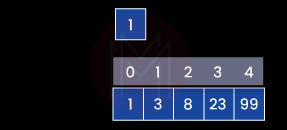
This enables easy operation of data using matrix properties. Just like in a book, every data element is assigned an index number. Therefore any element can be identified as well as located using this index number.
2. List some practical applications of the array in real life.
Some of the practical applications of an array in real life are as follows:
- Pages of book.
- Contact lists on our mobile phones.
- They are used in computer graphics, image processing, etc., through matrices.
- An array represents each speech signal in speech processing.
- Online ticket booking portals use arrays.
- Several IoT applications use arrays.
- The viewing screen of any system is also made up of pixels arranged in a multi-dimensional array.
3. Mention some advantages of an array data structure.
There are several advantages of using an array data structure, such as:
- Multiple data of the same kind are stored in an array with the same name.
- Random access is allowed to elements.
- Any type of data can be stored with a fixed size.
- The memory doesn't get short and doesn't overflow due to the fixed size and storage of the array in contiguous memory locations.
- Iteration is easy in this type of data structure due to the storage of array elements in contiguous memory locations. Also, the elements can be accessed in no time with the help of the index of the elements.
- Matrix operations can be performed on arrays to solve complex problems.
- Other kinds of data structures like heaps, hash tables, queues, and stacks can also be implemented by arrays.
4. Mention some disadvantages of an array data structure.
There are some disadvantages of array data structure as well, such as:
- We should know in advance the size of the given array.
- It costs a bit to insert and delete elements in an array since the elements are stored in contiguous memory.
- The array size can't be modified later during the runtime as it is a static type of data structure having a fixed size.
- Memory wastage can take place whenever the declared array's size is more than what is needed.
5. How are arrays classified- homogeneous or heterogeneous data structures?
Arrays are said to be homogeneous data structures since the same kind of elements is stored in arrays. Numerous types of data such as characters, Boolean values, strings, numbers, and objects can be stored in them. But the different types can't be mixed. Once the type is defined, all the elements should belong to that same category.
6. How does a linked list differ from an array?
| Array | Linked List |
| The elements of data are stored in a contiguous memory zone. | The elements are stored randomly in the memory zone. |
| The memory size can't be altered during the run time. | It is possible to change the memory size here. |
| There is no dependence among elements. | There is dependence among elements. |
| The elements can be accessed relatively faster and in an easier way. | It comparatively takes more time to access elements. |
| The memory is used ineffectively. | The memory is used effectively. |
| It assigns the memory during compilation. | It assigns the memory during run time. |
| Operations such as insertion and deletion are time-consuming here. | Operations such as insertion and deletion don't take much time here. |
7. When should a linked list be used over an array?
We can use linked lists over arrays in the following scenarios:
- Constant-time insertions or deletions are required from the list.
- Random access to any element is not required.
- The number of items on the list is unknown. The memory has to be re-declared and copied if there is an increase in array size like in basic arrays.
- We may need the insertion of elements in the middle of the list.
| Check out: Linked List Interview Questions |
8. What is the result of not initializing an array?
The default values will be taken up by the array based on the type of data.
9. Is it possible to declare an array without its size being assigned?
No, the declaration of an array is not possible without assigning its size. A compilation time error will pop up if we try to do so.
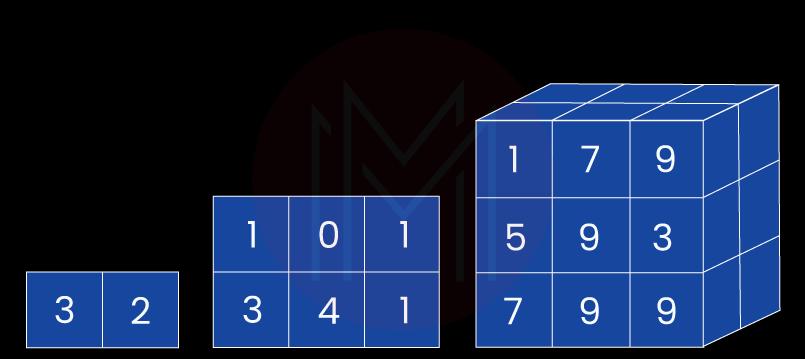
10. What are the types of arrays?
There are two types of arrays which are given below:
Linear or one-dimensional arrays:
It represents the elements linearly with a single subscript. It stores the data in consecutive memory locations like- A[1], A [2],……, A[N].
Multi-dimensional arrays:
- Matrix or two-dimensional arrays:
It represents elements with two subscripts. An m x n array signifies that there are m rows and n columns, and the total elements are m*n. An A [3] [4] array will have 3 rows and 4 columns with a total of 3*4 = 12 elements. - Three-dimensional arrays:
It represents elements with three subscripts. Therefore an m x n x l array will have m*n*l elements. An A [3] [4] [3] matrix will have 3*4*3 = 36 elements.
Conclusion
Arrays can be used to find solutions to even the most complex problems in no time. Handling data become very efficient with the use of arrays. That is why its knowledge is a must when it comes to computer programming. We have tried to provide you with the best Array Interview Questions. Now, it's your turn to practice as much as possible and converts your interview calls. We are sure that a little bit of practice can take you to the other side of this road.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Python Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Python Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| Python Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| Python Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

















