- Django Interview Questions
- Python Array Examples
- Python enum
- Python Enumerate with Example
- Python Flask Tutorial For Beginners
- Python For Beginners - Way To Success
- Python For Data Science Tutorial For Beginners
- Python for loop
- Python GET and POST Requests
- Python IDEs for Python Programmers
- Python Interview Questions
- Python Lists with Examples
- Python Partial Function Using Functools
- Python Print
- How to generate random numbers in python
- Python Regular Expression (RegEx) Cheatsheet
- Python Sleep Method
- Python List Methods
- Python Split Method with Example
- Python String Functions
- Python Tutorial
- Python Variable Types
- Python vs Java
- Python vs SAS vs R
- Python Operators
- Code Introspection in Python
- Comprehensions in Python
- Python Exception Handling
- Defining Functions - Python
- Generators & Iterators in python
- Install Python on Windows and Linux
- Introduction to Python Programming
- Lists concepts in Python
- Loops in Python
- Regular Expression Operations in Python
- Python Serialization
- String Formatting - Python
- R vs Python: Which is better R or Python?
- Six Digit Salary With Python
- Top 20 Python Frameworks List
- Why Learn Python
- Python Substring
- Career Shift To Python : Success Guaranteed
- Face Recognition with Python
- Go vs Python
- Pyspark Interview Questions
- Python Pandas Interview Questions
- OpenCV Interview Questions
- Python Project Ideas
- Flask Interview Questions and Answers
- Array Interview Questions
- What is PyCharm?
- What is Seaborn in Python?
- What is Anaconda Navigator
- Numpy Broadcasting - Detailed Explanation
- Python Data Science Interview Questions
- Genpact Interview Questions
- Python Developer Job Description
- Pandas Projects and Use Cases
- DataFrame Tutorial
- How to install Python on Windows
- Pyspark DataFrame
Object-oriented programming has become an essential part of software development. Most of today’s top programming languages are OOPs compatible. Professionals aiming for a lucrative career in the IT world should possess a strong understanding of OOP concepts.
We have compiled these top 50 frequently asked OOPs interview questions and answers in this blog, covering basic to advanced concepts to help you out. We hope these interview questions will definitely help you to clear your interview with flying colors.
So let’s get started.
- OOPs Interview Questions and Answers
- OOPs Basic Interview Questions
- OOPs Advanced Interview Questions
- OOPs Interview Questions for Experienced
- Python OOPs Interview Questions
Top 10 Frequently Asked OOPs Interview Questions
- What are OOPs?
- Who invented OOPs?
- What are the principles of OOPs?
- What are the benefits of OOPs?
- What are the disadvantages of OOPs?
- Define Single and multiple inheritances?
- What are access modifiers in OOPs?
- Why do you use an abstract class in oops?
- What is an exception in object-oriented programming?
- What’s the difference between error and exception?
OOPs Interview Questions And Answers
Here are the most frequently asked OOPs Interview Questions and Answers for freshers and experienced for getting programming jobs.
1) What are OOPs?
OOPs(Object Oriented Programming) is a programming concept that creates objects for data and methods. It works on the principles of encapsulation, classes, abstraction, aggregation, polymorphism, and inheritance. OOPs aims to create, re-use, and manipulate objects throughout the program to get results.
OOPs, are popularly used in modern programming languages like Java.
| If you would like to Enrich your career with a Python-certified professional, then visit Mindmajix - A Global online training platform: “Python Training” Course. This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2) What are the four basics of OOPs?
The four main basics of OOPs in Java are:
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
Abstraction - It means using simple things to represent complexity.
Encapsulation - It’s a practice of keeping fields in a private class, then accessing through public methods.
Inheritance - It’s a unique feature of OOPs that lets users create new classes sharing some of the existing classes’ attributes.
Polymorphism - It lets you use the same word to mean different things in different contexts. Method overriding and Method overloading are the two forms of Polymorphism. Method overloading occurs when the code itself implies different meanings. Method Overriding occurs when the values of the supplied variables indicate different meanings.
3) What are the benefits of OOPs?
OOPs is a core development approach used in modern programming languages. Let’s see the advantages of OOPs that it offers:
- Code reusability through inheritance
- Data redundancy
- Security
- Code maintenance
- Easy troubleshooting
- Better productivity
- Polymorphism flexibility
- Effective problem solving
4) What are the principles of OOPs?
The five concepts that make up solid principles of OOPs:
- Single Responsibility Principle.
- Liskov Substitution principle.
- Open/Closed principle.
- Dependency Inversion principle.
- Interface Segregation Principle.
5) Who invented OOPs?
Alan Kay put the idea of object orientation in the early 1970s. The concept includes classes, multiple instances of classes, and the message passing between the objects of one class and another.
6) What is a class and object in OOPs?
- A class is a set of instructions or a blueprint to build a specific type of object. It determines what an object will contain and how it behaves.
Syntax:
class <class_name>{
field;
method;
} - An object is an instance of the class. It’s nothing but a self-contained component consisting of properties and methods to make a particular type of data useful.
Syntax:
ClassName ReferenceVariable = new ClassName();7) What’s the difference between class and Object?
The following table lists the differences between object and class:
| Class | Object |
| Class is a template or blueprint from which objects are created. | The object is a class instance. |
| It’s a group of similar objects. | It’s a real-world entity. |
| Logical entity | Physical entity |
| Declared once | It can be declared many times based on the requirement. |
| It does not allocate memory when its created | Allocates memory when created. |
| The class keyword is the only way used to create a class. | There are many ways to create the object, such as a new keyword, clone() method, newInstance(), factory method, and deserialization. |
8) Explain the use of abstraction in OOPs?
- One of the main concepts of OOPs is Abstraction. It handles the program complexity and improves efficiency by hiding unnecessary information from the user, showing only essential attributes.
- Abstraction is selecting data from a large pool to show only relevant data of the object to the user.
- For example, you want to create a bank app and collect all your customer details.
- The customer details you come up with might include full name, address, contact, tax information, favorite place, etc. But only a few of them are required to create a bank app.
- Relevant data like name, address, etc., make sense for a banking application.
- Since we have fetched/selected/removed the customer information from a larger pool, the process is called abstraction in OOPs.
However, the same information, once extracted, can be used for a wide range of applications. For instance, you can use the same data for job portal applications, hospital applications, a Government database, etc., with little or no modifications. Hence, it becomes your Master Data. That is an advantage of Abstraction in OOPs.
9) What is encapsulation?
- Encapsulation in object-oriented programming is referred to as the bundling of data, along with the methods that operate on that data in a single unit.
- Many programming languages use encapsulation in the form of classes. A class is a program code template that allows you to create objects that contain both variables (data) and behaviors (methods or functions).
- A class consists of data and its methods bundled into a single unit.
- Encapsulation can also hide the internal representation or state of an object from the outside. It can hide both data functions and data members associated with instantiated class or object.
10) Explain the concept of inheritance in OOPs.
- Inheritance is one of the core concepts of OOPs, in which one class acquires the property of another class in the same way, as a child inherits some attributes from its parents.
- With inheritance, we can reuse the methods and fields of the existing class and facilitate reusability.
- It declares different kinds of exceptions, adds custom logic to the existing framework, and even maps the database’s domain model.
- For example, consider a group of vehicles. For that, you need to create classes for Bike, Car, and Truck. The methods fuelAmount(), capacity(), applyBrakes() will be the same for all of the three classes.
If these classes are created avoiding inheritance, then all these functions are written in each of the classes as shown below:
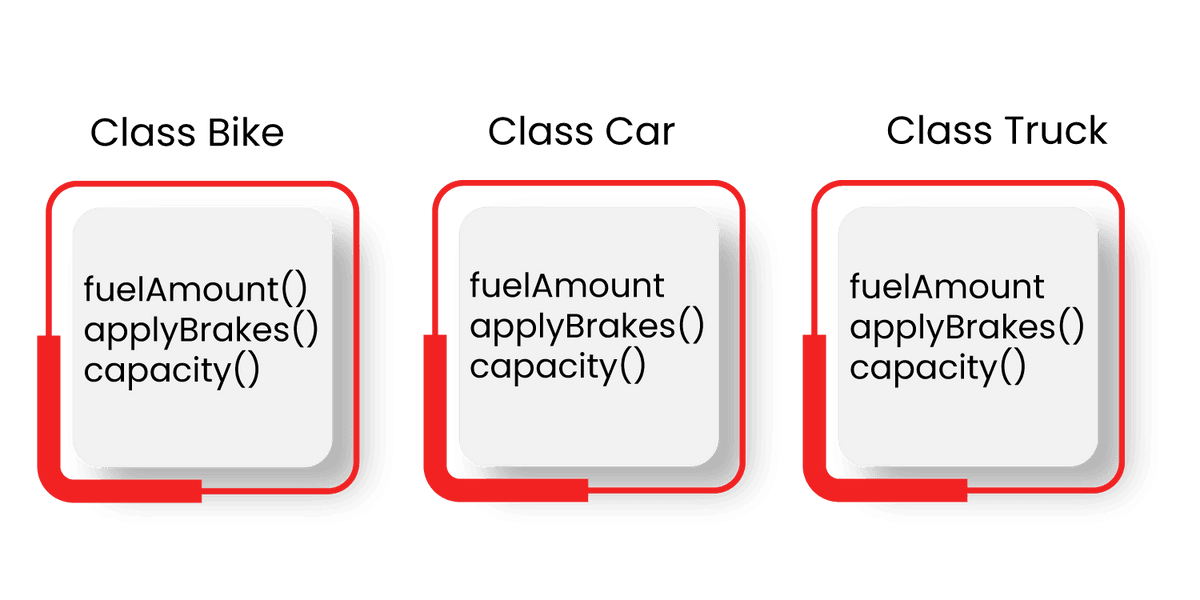
This creates deduplication of the same code three times. This increases data redundancy and the chances of errors. To avoid this, inheritance is used. If you create a class named Vehicle and write these functions in it and inherit the rest of the classes, we can avoid data duplication and improve reusability.
Look at the below diagram to understand how three classes inherited from vehicle class:
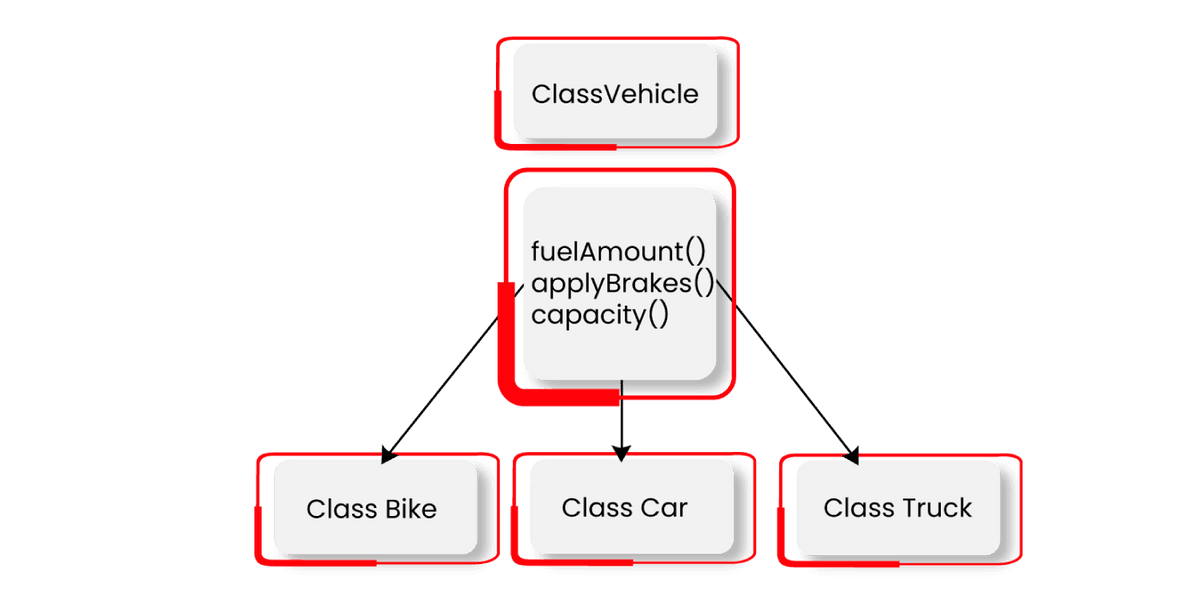
OOPs supports different types of inheritance as given below:
- Single inheritance.
- Multiple inheritances.
- Multi-level inheritance.
- Hierarchical Inheritance.
- Multipath inheritance.
- Hybrid Inheritance.
OOPs Basic Interview Questions
This section covers Basic OOPs interview questions which will help you with different expertise levels to reap maximum benefit.
11) What are the limitations of Inheritance?
- The main disadvantage of using inheritance is two classes get tightly coupled. That means one cannot be used independently of the other. If a method or aggregate is deleted in the Super Class, we have to refactor using that method in SubClass.
- Inherited functions work slower compared to normal functions.
- Need careful implementation otherwise leads to improper solutions.
12) Define Single and multiple inheritances?
- Single inheritance allows a derived class to inherit properties from a single parent class ().
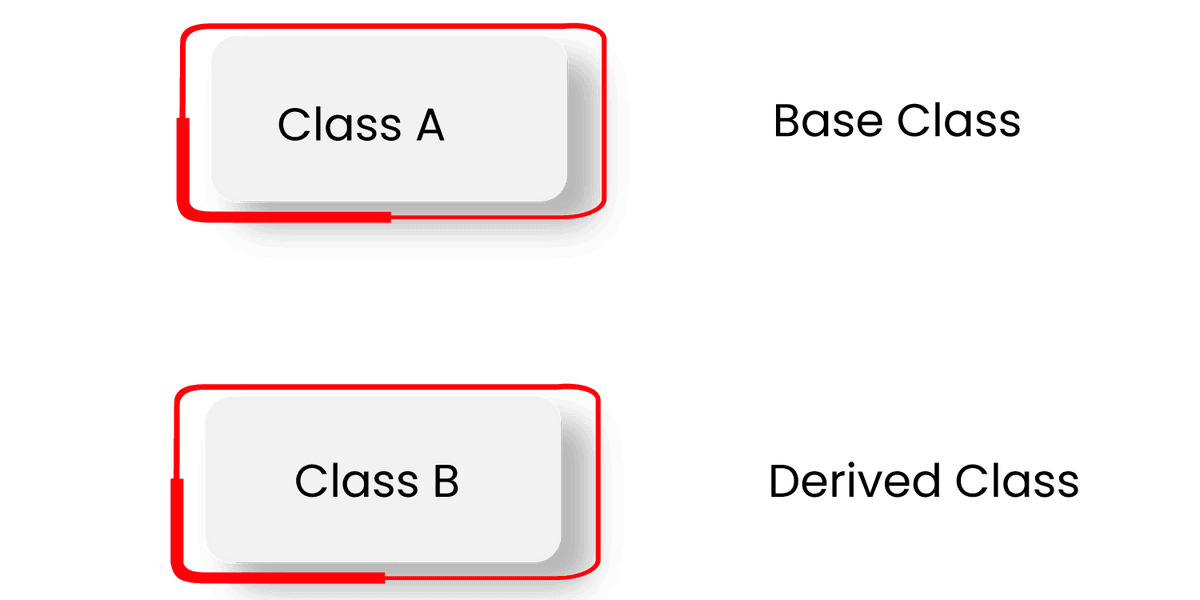
In the above diagram, Class B (subclass) extends only Class A(superclass).
Syntax:
class subclass_name : access_mode base_class
{
//body of subclass
};- Multiple Inheritance is where a class can inherit from more than one class.
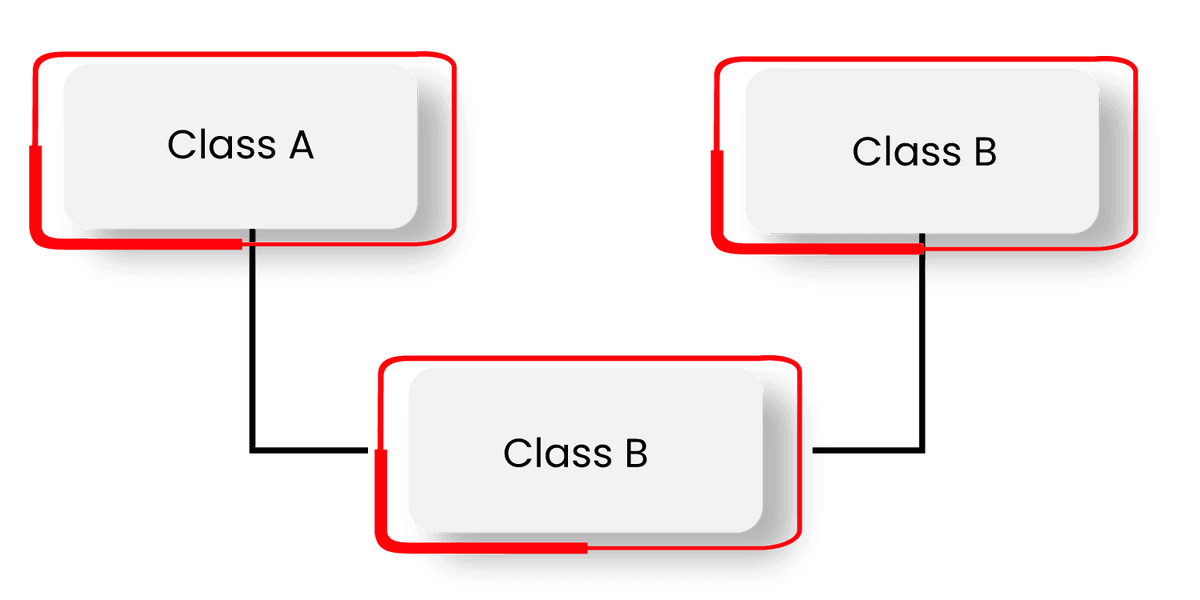
Syntax:
class subclass_name : access_mode base_class1, access_mode base_class2, ....
{
//body of subclass
};13) What is the difference between multiple and multilevel inheritances? Give suitable examples to illustrate both.
| Multiple Inheritance | Multilevel Inheritance |
| Multiple inheritances come into the picture when one class extends more than one class. | Multilevel inheritance comes into the picture when we create a derived from another derived class. |
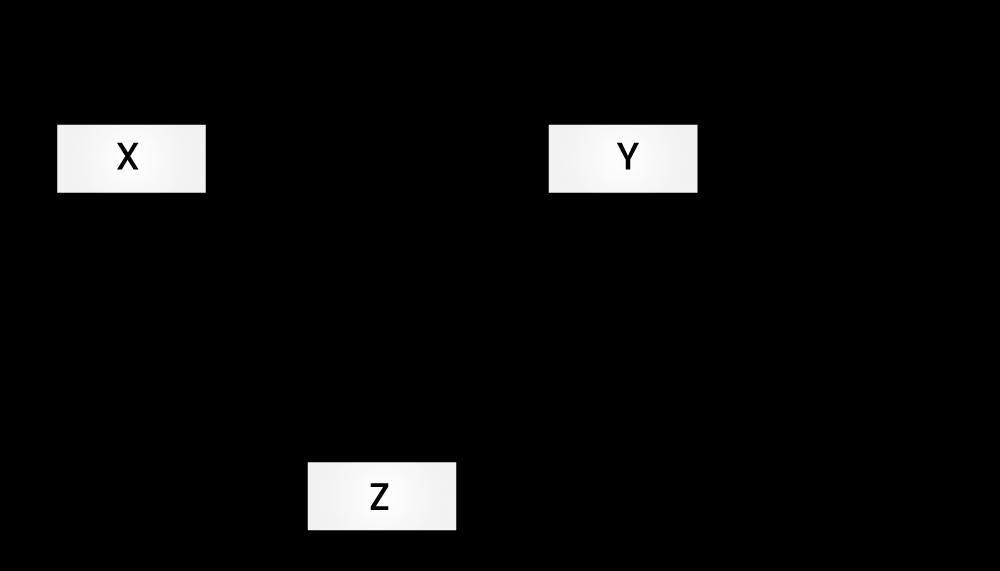 | 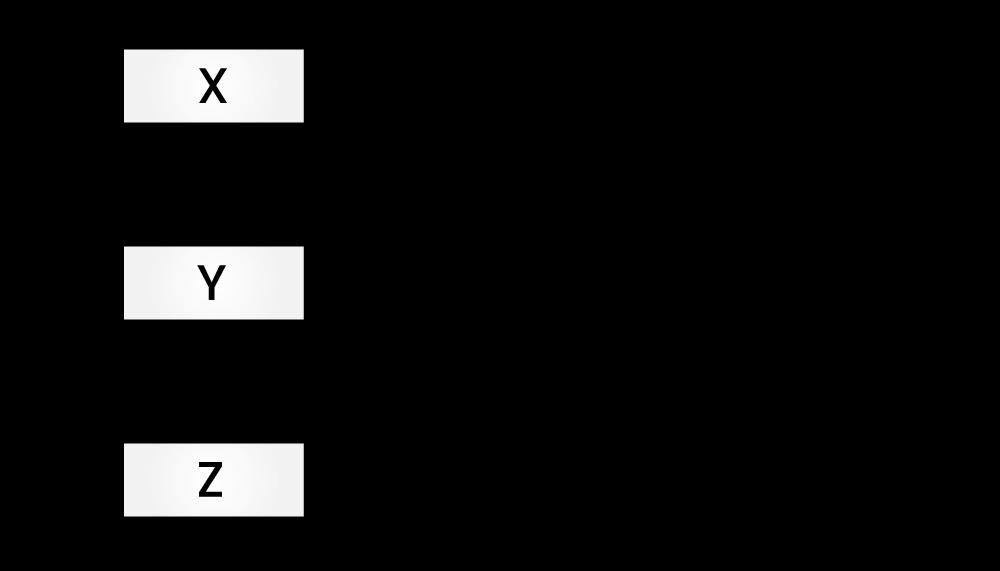 |
14) What’s the difference between hybrid and hierarchical inheritances?
| Hybrid Inheritance | Hierarchical Inheritance |
| It’s a combination of both single and multiple inheritances. | More than one sub-class inherited from the base class in this type of inheritance means more than one derived class from a single base class. |
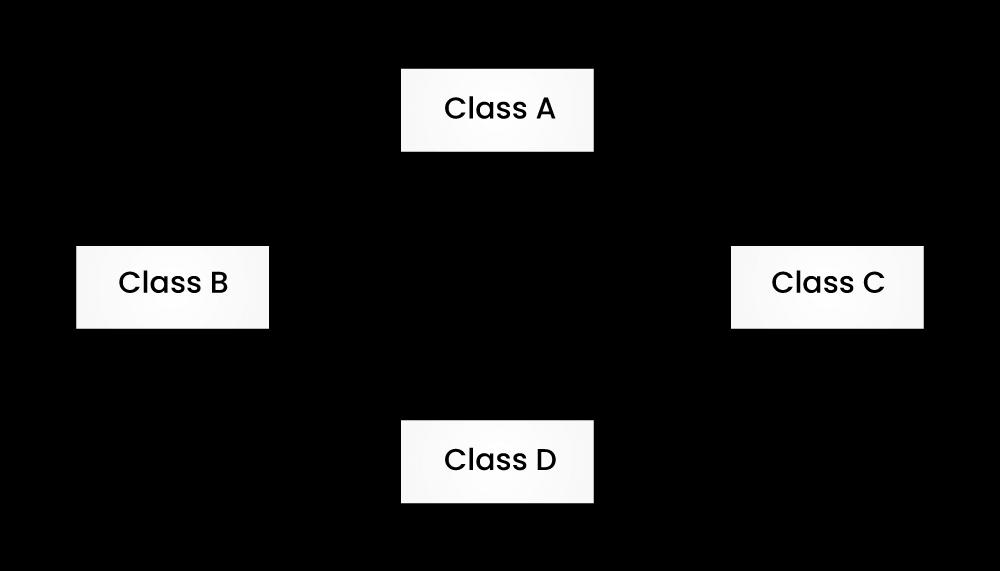 | 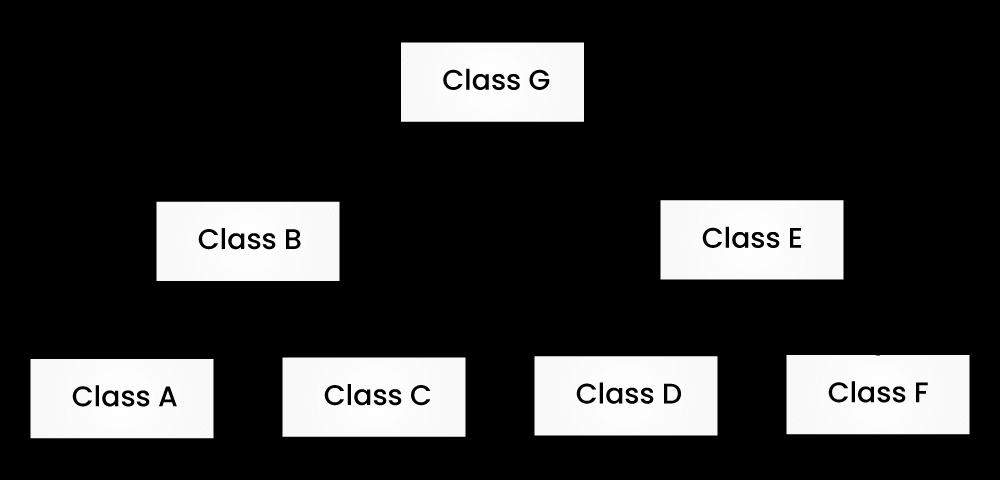 |
15) What does Polymorphism in OOPs mean?
As the word suggests, poly means ‘many’ and morph points at ‘forms’. On the whole, it means property of many forms. In OOPs, polymorphism processes objects of different types and classes through a single, uniform interface. It allows us to perform a single action in different ways. It implements the concept of overriding, overloading, and virtual functions. Also, it can be used for inheritance in programming.
For example, if you define a class called Vehicle, it can have a speed method but cannot be defined as different vehicles with different speeds. We define this method in the subclasses with different definitions for different vehicles.
16) What are the different types of Polymorphism?
OOPs supports two different types of Polymorphism as below:
- Static Binding (or Compile time) Polymorphism
- Dynamic Binding (or Runtime) Polymorphism
Static Binding or Compile time polymorphism
This polymorphism type uses method overloading or function overloading. Certain conditions are conducive for static polymorphism as below:
- Parameter types should be different.
- The sequence of parameters can be different.
- A number of parameters for one method should be different from another method.
- The matching type and number of arguments of static polymorphism invoke the overloaded functions.
- Dynamic Binding or Runtime polymorphism
- This polymorphism type uses method overriding. Through pointers and virtual functions, we can achieve overriding.
- When a derived class has a definition for one of the base class’s member functions, that base class is method overridden.
17) Describe method overloading.
In OOPs, method overloading is a feature that allows a class to have one or more methods that have the same name with different arguments lists. Overloading is related to compile-time (or static) polymorphism.
Method Overloading is achieved either through:
- Changing the number of arguments
Or
- By changing the data type of parameters
Following operators cannot be overloaded:
- Member selection through a pointer to function (.*)
- Scope Resolution (::)
- Member Selection (.)
18) What is method overriding?
Method Overriding in OOPs is a feature that allows a child class or subclass to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of its parent class or superclass. Method overriding is related to runtime polymorphism.
Conditions for method overriding:
- The method must have the same name as in the parent class.
- There must be an IS-A relationship (inheritance).
19) Abstraction vs. encapsulation: What are the differences between both of them?
| Abstraction | Encapsulation |
| Abstraction shows only useful data by providing required details. | Encapsulation wraps code and data for required information. |
| It solves problems at the design or interface level. | It solves problems at the implementation level. |
| It’s a method to hide unwanted information. | It’s a method to hide and protect data from inside and outside. |
| Abstract classes and interfaces implement abstraction. | You can implement encapsulation using access modifiers: public, private, and protected. |
| Objects that perform abstraction can encapsulate. | Objects that perform encapsulation cannot perform abstraction. |
| In abstraction, the implementation complexities hide using abstract classes and interfaces. | While in encapsulation, the data hides using methods of getters and setters. |
20) Can you have polymorphism without inheritance?
- Both inheritance and polymorphism are independent of each other but are related entities.
- If you use a language (Java, C++, C#) that requires variables to have a specific type, then the concepts of inheritance and polymorphism are linked.
- If you use a language (javascript, python, ruby, vb.net ) with a generic type of declaration, then the concepts of polymorphism and inheritance are separated.
| Explore Frequency Asked Core Java Interview Questions |
OOPs Advanced Interview Questions
The following section discusses the most advanced OOPs interview questions that you should absolutely know to crack the OOPs-related interviews.
21) Inheritance vs. Polymorphism: What are the differences between inheritance and polymorphism?
| Inheritance | Polymorphism |
| Inheritance is one in which a derived class inherits the already existing class’s features. | Polymorphism is one that you can define in different forms. |
| Applied to classes | Applied to functions or methods |
| Used for pattern designing | Used for pattern designing |
| Inheritance can be single, hybrid, multiple, hierarchical, multipath, and multilevel inheritances. | Polymorphism can be compiled-time (overload) and run-time polymorphism (overriding). |
| Reduces code length and supports code reusability | Allows the object to decide which form of the function to implement at run-time (overriding) and compile-time (overloading). |
22) What’s the difference between association and aggregation?
| Association | Aggregation |
| Association refers to "has a" relationship between two classes that use each other. | Aggregation "has a"+ relationship between two classes where one contains the collection of other class objects. |
| Linkage is needed to maintain the association. | The linkage between objects is not mandatory. |
| Lines represent the association. | Diamond shape next to assembly class is used to represent the aggregation relationship. |
| Inflexible in nature | Flexible in nature |
23) What are access modifiers in OOPs?
In OOPs, access modifiers are keywords that set the accessibility of methods, classes, constructors, and other members. You can change the access level of fields, methods, class, and constructor by applying the access modifier on it.
Access modifiers can also be called access specifiers.
24) What are the different types of access modifiers?
OOPs supports four types of access modifiers:
- Public: You can access this modifier from everywhere. This modifier’s access level is within the package, outside the package, within, and outside the class.
- Private: You can access this modifier outside the class. The access level of this modifier is only within the class.
- Protected: This modifier’s access level is within the package, through the child class, and outside the package. If you don’t define child class, you cannot access it from outside the package.
- Default: This modifier’s access level is only within the package, and you cannot access it outside the package. If the access level is not specified, it will be the default.
25) What is a constructor?
A constructor is a particular type of subroutine called to create a project in object-oriented programming. It resembles an instance method but differs as it has no explicit return type.
A constructor is different from regular functions in the following ways:
- Constructors don’t have a return type.
- The constructor has the same name as the class itself.
- A constructor is called when you create an object.
26) Do we require a parameter for constructors?
No, you don’t require a parameter for constructors.
27) What are the different types of constructors?
- Parameterized constructors
- Default constructors
- Copy constructors
- Conversion constructors
- Move constructors
28) Can the constructor be private?
Yes, you can declare a constructor as private. Once a constructor is declared private, you cannot create an object of a class. We use private constructors in the Singleton Design Patterns.
Rules for private constructors:
- The private constructor does not allow object creation outside the class and a class to be subclassed.
- We can use a private constructor when all the methods are static.
- If we extend a class containing a private constructor, then a compile-time error will occur.
29) Why is the constructor not overridden?
You cannot override the constructor because it looks like a method, but it is not. It doesn’t have the return type, and the name is the same as the class name. If you treat it as a method and write a super class's constructor in the sub-class compiler expecting a return type, it will generate a compile-time error.
30) Can you use this () and super () both in a constructor?
- Both super() and this() functions are used to make constructor calls. this() is used to call the current class constructor, while super() is used to call the base class’s constructor.
- But we can’t use both this() and super() together in a constructor, as it will give a compile-time error.
- Because super() and this() must be the first executable statement, if anyone is written first, the other will become the second statement and vice-versa. That's why we can't use this() and super() together.
OOP's Interview Questions For Experienced
In this section, we introduce you to the most commonly asked questions for experienced professionals in OOPs interviews for the year 2021.
31) Can the constructor be static or final?
No, the constructor can’t be made static or final.
32) Why do you use an abstract class in oops?
Declaring a class as an abstract means that it cannot be directly instantiated, which means the object cannot be created from it. It protects the code from being misused. Abstract classes need subclasses to define attributes for individual instantiation further.
33) How do you access an abstract class?
The only way to access the non-static method of an abstract class is to extend it, implement the abstract methods in it (if any), and then use the subclass object you need to invoke the required methods.
34) Why do you need a virtual function?
A virtual function is a member function declared within a base class and redefined by a derived class. When a class containing a virtual function is inherited, the derived class can redefine the virtual function to satisfy its requirements.
35) What are the final variables or methods?
We use a final keyword for declaring an entity. A variable declared with the final keyword means its value can't be changed, essentially, a constant. A method declared with the final keyword cannot? be overridden or hidden by subclasses.
36) What is the difference between virtual and pure virtual functions?
A virtual function is a member function of a base class that a derived class can redefine. A pure virtual function is a member function of a base class whose declaration is provided only in the base class and defined in the derived class, or else the derived class can also become abstract.
37) What is the purpose of a virtual destructor?
Virtual destructor helps to destruct the resources correctly when you delete a base class pointer pointing to the derived class object.
38) Can you override a final method?
No, you can’t override the final method.
39) Can you inherit a final class?
If you make a class final, then no class can inherit the final class feature. You cannot extend a final class.
40) Explain Garbage collections
Garbage collection(GC) is reclaiming unused runtime memory automatically. The GC frees up the space occupied by the objects that are no longer in existence.
Different types of Garbage collectors are:
- CMS Garbage Collector.
- Serial Garbage Collector.
- Parallel Garbage Collector.
- G1 Garbage Collector.
Python OOP's Interview Questions
Following are the most frequently asked OOPs interview questions in Python for both freshers as well as experienced professionals.
41) What is an Interface?
The interface is an essential concept of OOPs that allows you to declare methods without defining them. Unlike classes, interfaces are not blueprints because they don’t contain specific instructions or actions to be performed. Any class that implements an interface defines the methods of the interface.
42) What is an exception in object-oriented programming?
An exception is a type of notification that interrupts the usual program execution. Exceptions help you to detect and react to unexpected events. The program’s state is saved when an exception arises, and control is passed to an exception handler. The exceptions are thrown or raised by programming code that must send a signal to the executing program about an error or an unusual situation.
For example, when you want to open a file that doesn’t exist, the code responsible for opening the file will detect this and throw an exception with a proper error message. Exceptions are of two types in OOPs, such as checked exceptions and unchecked exceptions.
- Checked exception - The classes which inherit compile-time exceptions are known as checked exceptions.
- Unchecked exception - The classes which inherit Runtime exceptions are known as unchecked exceptions.
43) What’s the difference between error and exception?
| Error | Exception |
| Classified as an unchecked type | Classified as a checked and unchecked type |
| Error recovery is not possible. | Exception recovery is possible using a try-catch block or throwing exceptions back to the caller. |
| Errors are caused by the program's running environment. | The program itself causes exceptions. |
| It occurs at runtime and is not known to the compiler. | It occurs at runtime but checked exceptions are known to the compiler while unchecked is not. |
44) What is exception handling?
In OOPs, exception handling is used to handle errors. It allows errors to be thrown and caught and implements a mechanism to resolve them.
| Read Top Python Interview Questions and Answers |
45) Can a base class be called without creating an instance?
Yes, you can call a base call without instantiating it if:
- Base class instantiated by some other subclass.
- It’s a static method.
46) What is the use of try/ catch block?
You can use the try/ catch block to handle exceptions. Try statements define the statements that lead to error. Catch block catches the exception.
47) What is a ternary operator?
The ternary operator is also called a conditional operator. It’s an operator that takes three arguments. Results and arguments are of different data types depending on the function.
| Explore Python Sample Resumes Download & Edit, Get Noticed by Top Employers! |
48) What is early and late Binding?
Early binding refers to the assignment of values during design time to variables. On the other hand, late binding refers to the assignment of values during run time to variables.
49) What is the difference between override and new?
The override modifier overrides the base class function. Simultaneously, a new modifier instructs the compiler to use a new implementation instead of the base class function.
50) What are the disadvantages of OOPs?
The disadvantages of object-oriented programming are:
- Steep learning curve - The concepts involved with OOPs are challenging to comprehend initially and can take a long time to get used to them.
- Slower programs - OOPs are typically slower than procedure-based programs as it requires more instructions for execution.
- Larger program size - OOPs programs are much larger than other programs. It involves more lines of code.
- Not suitable for all types of problems - Some problems lend themselves well to logic-programming style, functional-programming style, or procedure-based programming style, and applying OOPs in those situations will result in inefficient programs.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Python Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Python Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| Python Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| Python Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















