- Home
- Blog
- UI Developer
- Full Stack Developer Interview Questions and Answers

In this tech-driven world, the demand for full-stack developers is increasing every day. That's because companies focus on delivering software applications with improved user experience.
According to a recent US Bureau of Labor Statistics survey, the demand for full-stack developers is expected to grow over 16% from 2022 to 2032. So, it's undoubtedly a great choice if you aspire to make a career in full-stack development.
In this blog, I have crafted the crucial full-stack interview questions and answers. The Q&A will increase your knowledge of client-side and server-side technologies.
Let’s jump in!
Frequently Asked Full Stack Developer Interview Questions
- What is Full-stack development?
- What do Full Stack Web Developers do?
- Name a few full-stack developer tools.
- What is pair programming?
- What is multithreading, and how is it used?
- What is an application server?
- What are the types of design patterns?
- What are the popular Full-stack technologies?
- How does SDLC work?
- What are the key features of MongoDB
Here Are Skills and Responsibilities of Full Stack Developers
In this section, I have outlined the primary and secondary skills required for full-stack developers. Also, I have listed the job responsibilities of full-stack developers at various expertise levels. Yes! We will take a glance before jumping into full-stack interview questions and answers.
Primary skills:
Below are the essential skills required for a full-stack developer.
- Proficiency in programming languages such as typescript, ruby, python, PHP, etc.
- Proficiency in front-end technologies such as CSS, HTML, and JavaScript.
- Exposure to various operating systems such as Linux and Windows.
- Good knowledge of front-end frameworks such as Bootstrap, VueJS, AngularJS, ReactJS, etc.
- Expertise in back-end frameworks such as expressJS, NodeJS, Django, etc.
- Familiar with database design principles.
- Proficiency in troubleshooting and solving complex issues.
- Familiar with MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, MongoDB, etc.
Secondary skills:
The following are the secondary skills required for full-stack developers.
- Familiar with SQL queries
- Knowledge of CI/CD deployment
- Knowledge of REST APIs and microservices architecture
- Exposure to version control systems like Git
- Familiar with agile project management concepts
- Excellent analytical and problem-solving skills
- Exceptional time management and collaboration skills
Job responsibilities of full stack developers with 1-2 years of experience
Below are the job responsibilities of entry-level full-stack developers.
- Developing applications using the front-end and back-end technologies
- Design server-side and client-side scalable architecture
- Developing and managing databases
- Creating unit and integration tests to examine the quality of codes
- Creating test plans, test cases, and testing applications
- Designing monitoring systems for tracking development progress
Job responsibilities of full stack developers with 3-5 years of experience
Here are the job responsibilities of middle-level full-stack developers.
- Understanding business requirements from stakeholders
- Participating in the ideation, design, and development of products
- Organizing project review meetings and updating stakeholders about the project's progress.
- Analyzing user requirements and specifications based on business needs.
- Developing high-quality software products that meet the specifications precisely.
- Developing dynamic user interfaces using front-end frameworks
- Storing and managing codes in repositories efficiently.
- Designing databases and managing them
- Developing documentation for codes, APIs, etc.
Job responsibilities of full-stack developers with more than five years of experience
Let’s go through the job responsibilities of senior-level full-stack developers.
- Leading a team of core developers
- Reviewing the codes of team members
- Resolving issues that arise during the development process
- Developing the back-end side using Jakarta and EE Spring Boot frameworks
- Implementing business logic, data validation, authorization, and authentication on the Java back-end
- Leveraging Angular CLI to generate services, components, and modules
- Designing the database schema to store application data efficiently
- Deploying applications on a web server such as Jetty or Apache Tomcat for the back-end.
- Hosting the Angular front-end on a static file server.
Well! I hope that you have understood the full-stack developer skills and job responsibilities. I am sure that it will help you prepare effectively for your interviews.
Here Are Full Stack Developer Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is Full Stack development?
Full stack development is a process of developing the front-end and back-end of web applications or websites. Simply put, it is end-to-end software application development.
Full stack development has three layers, as shown below:
- The presentation layer or user interface that deals with the front-end
- Business logic layer or application workflows that deal with the server-side
- Database layer that deals with databases.
We use CSS, HTML, and JavaScript for front-end development. We also use Python, Ruby, Java, Node.js, and PHP for back-end development.
|
If you have questions about interviews and the hiring process, particularly in relation to full-stack development, our training experts can provide valuable insights. Feel free to reach out to our Full-Stack Training expert for more details. |
2. What do Full Stack Web Developers do?
A full-stack developer mainly creates code for both the client and server sides. They also code for databases, browsers, and servers.
Moreover, a full-stack developer performs the following tasks.
- Understand the client's requirements accurately
- Perform data modeling to build robust databases
- Integrate front-end and back-end codes
- Testing and debugging codes
- Develop APIs and RESTful services
- Create delightful user experiences.
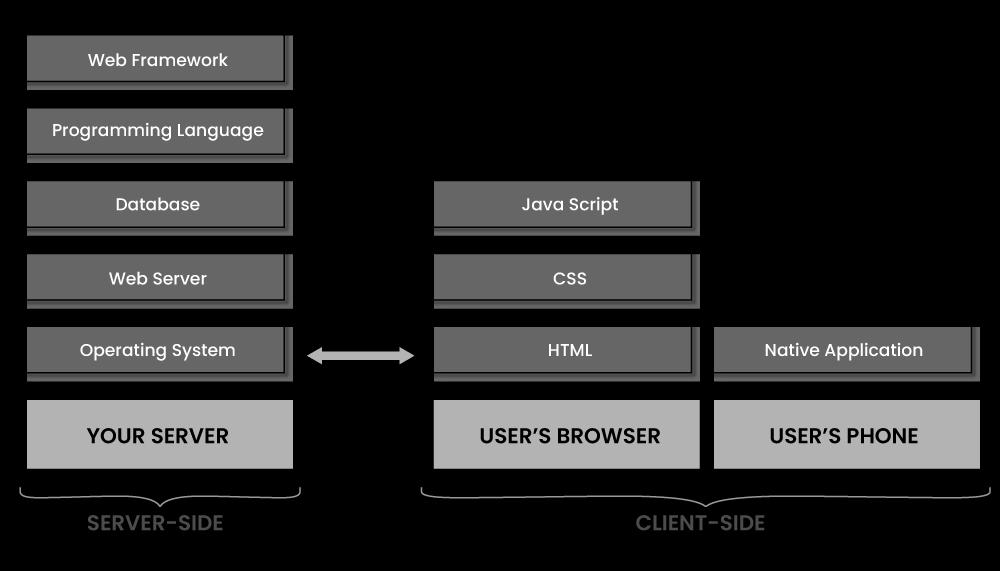
3. Name the different full-stack developer tools.
Front-end developer tools:
- AngularJS
- JavaScript
- Python
- Bootstrap
- SQL
Back-end developer tools:
- Ruby on rails
- Django
- NodeJS
- ASP.net
- MySQL
- MongoDB
4. What is CORS?
CORS stands for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing. It is a robust mechanism for integrating applications. It allows client applications in a domain to interact with resources in other domains. We can incorporate CORS with web scripts when connecting with an external domain, protocol, or port is needed.
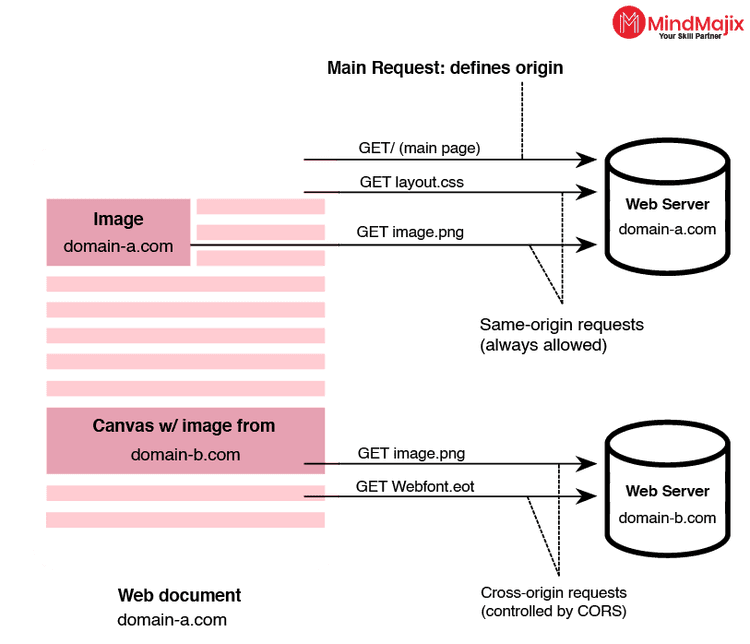
CORS acts as a mechanism when complex application client codes refer to third-party APIs and resources. For example, an application may use a browser to pull videos from a video platform, use a font from a public library, and so on.
5. What is pair programming?
Pair programming is an agile methodology in which two programmers work together on a single machine. They design, develop, and test codes together. They are equally skilled and spend equal time on the machine. Pair programming is a collaborative method that needs strong communication between the two programmers. In pair programming, one programmer is known as the driver, who writes codes. Another programmer is the navigator, who reviews codes. Above all, the programmers can swap their roles.
6. What is the Inversion of Control?
We widely use the IoC concept in object-oriented programming. IoC allows a framework to control the flow of a program. To achieve this, IoC uses abstractions with some additional behaviours. We must extend the framework's classes to add new behavior.
We use the inversion of control (IoC) mechanism to decouple task execution from implementation. Various mechanisms, such as strategy design patterns, service locator patterns, and dependency injection, play a key role in achieving IoC.
7. What is Dependency Injection?
Dependency injection is a process of providing resources for a code piece. We leverage dependency injection to create loosely coupled programs. Dependency injection helps improve code usability and reduce the need for frequent class changes.
On the other hand, dependency injection is essentially a design pattern supporting executing control inversion. Dependency injection has four roles: clients, interfaces, services, and injectors. Below is a summary of the roles.
Clients: It is a class that uses services
Interfaces: It breaks dependencies between lower and higher classes
Services: It is a class that has functionality
Injectors: They insert services into a client.
8. What is continuous integration?
Continuous Integration (CI) is an automation practice in which developers regularly integrate code changes into a central repository. Automation tools help integrate bug-free codes into the repository.
Continuous Integration helps address bugs earlier, reduce manual efforts, improve software quality, and reduce the time to release new updates. A version control system like Git is a crucial part of continuous integration.

9. What is RESTful API?
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. A RESTful API is an interface with which two computers can exchange information over the Internet. It complies with reliable and efficient communication standards. That's why it exchanges information securely. A REST API uses HTTP requests to exchange information.
REST optimizes client-server interactions, so systems implementing RESTful APIs provide higher scalability. RESTful APIs can decouple server components, providing high flexibility. We can develop front-end and back-end applications in any programming language with an REST API.
10. What is a callback in JavaScript?
A callback in JavaScript is typically a function passed as an argument into another function. A callback function runs after a function completes its execution. We can use callback functions synchronously or asynchronously.
For example, we can call the calculator function (myCalculator) using a callback function (myCallback). Once the calculation is over, the calculator function runs the callback function.
main.js
1 - function myDisplayer (something) {
2 document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = something;
3 }
4- function myCalculator (num1, num2, myCallback) {
5 let sum = num1 + num2;
6 myCallback(sum);
7 }
8 myCalculator (2, 2, myDisplayer);
Okay! I hope the knowledge you gained in this section will help you effortlessly ace your interviews.
Here Are Full Stack Developer Interview Questions for Freshers
In this section, I have compiled beginner-friendly full-stack interview questions and answers. It will provide you with comprehensive knowledge of full-stack technologies.
Let’s dive in!
11. What is multithreading, and how is it used?
Multithreading is the concurrent use of multiple execution threads. In other words, multithreading is the ability of a processor to manage various user requests at a time with the maximum utilization of the CPU. In multithreading, a single program is broken into many pieces. They run on different threads of execution concurrently. The main thing about multithreading is that all the threads share common resources like memory. If any exception occurs in any thread, it won’t affect other threads. Hence, multithreading optimizes thread execution, reduces time, and improves performance.
12. What do you mean by ACID in database systems?
ACID is the acronym for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. ACID is a standard set of properties. It ensures that database transactions take place reliably. If a database operation satisfies these properties, it is known as an ACID transaction. Database systems that apply these properties are known as transactional systems.
- Atomicity – It ensures that the entire transaction happens as a single unit.
- Consistency – The database remains consistent because of a transaction.
- Isolation – multiple transactions can happen independently without any interference.
- Durability – Even if a system fails, the committed transaction remains unchanged.
13. What is an application server?
An application server handles business logic. So, we can create dynamic content by integrating various databases and other resources. It also provides a runtime environment for running application codes.
An application server has a comprehensive service layer. It supports various protocols and APIs. For example, it allows protocols such as Remote Method Invocation (RMI) and Remote Procedural Call (RPC).
14. What is referential transparency?
Referential transparency is essentially a function property. According to this property, if we call a function with the same arguments, we should get the same returning values without changing codes.
We use Referential transparency in functional programming. It provides many properties, such as self-sufficiency, determinism, safe operation, and device independence.
15. What are the types of design patterns?
A design pattern is essentially a repeatable solution for common issues in software design. It reveals the interactions and relationships between classes and objects.
There are three types of design patterns as follows:
- Creational – It deals with object creation and class instantiation. We can classify them into object-creational patterns and class-creational patterns.
- Behavioral – It deals with identifying common communication patterns between objects.
- Structural – It involves organizing different objects and classes. They help create new and extensive functionality.
16. What are the strategies to optimize a website to be as efficient and scalable?
We can employ the following strategies to make a website efficient and scalable.
- Optimising all assets of a website
- Avoid inline CSS, JavaScript, and duplicate codes.
- Specifying image dimensions
- Reducing DNS lookups
- Minimizing request size
- Using browser caching.
17. What are the popular Full-stack technologies?
The popular full-stack technologies are:
- MEAN Tech Stack: MEAN stands for MongoDB, Express.js, Angular.js, and Node.js. This tech stack is handy for developing dynamic JavaScript-based web applications.
- MEVN Tech Stack: MEVN stands for MongoDB, Express.js, Vue.js and Node.js
- MERN Tech Stack: MERN stands for MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js. This tech stack helps develop robust web applications.
- LAMP Tech Stack: LAMP stands for Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP.
18. What are the seven best practices of database design?
The following are the seven steps of database design.
- Selecting the right database type
- Building a consistent database system across the development and production environment
- Selecting the right tool for database modeling
- Understanding the data completely
- Designing the database based on project requirements
- Removing data redundancy
- Using stored procedures for optimization
19. What is a Flask web framework?
Flask web framework is a Python module for developing web applications. It is a microframework that allows developers to build applications. They don’t need to worry about protocol, thread management, etc.
The learning curve for Flask is low. Flask comes with less base code and develops a simple web application. Flask works based on the Jinja2 template engine and WSGI toolkit. Here, WSGI is a standard for web application development. Jinja2 is a template system that unites a data source with a template to develop a dynamic web application.
20. What are the key features of MongoDB?
MongoDB is a non-relational database. It is typically a document database that stores JSON-like documents. MongoDB's flexible model stores unstructured data and provides full indexing support.
The key features of MongoDB are:
Ad-hoc queries: MongoDB supports different queries, such as field, range, and regular-expression queries. We can use these queries to return parts of documents or entire documents.
Replication: MongoDB offers a high availability of replica sets.
Indexing: We can use primary and secondary indices to index the fields of a document stored in a MongoDB database.
21. What is the 'use strict' mode in JavaScript?
Enabling the ‘use strict’ mode conveys to the JavaScript engine that we will develop reliable and maintainable code. Once we allow the ‘use strict’ mode, the engine will throw more errors.
By tapping into the ‘use strict’ mode, we can identify common coding mistakes and avoid using complex JavaScript features. We can also make your code easy to understand. However, some disadvantages exist in using the 'use strict' mode since not all browsers support it. Also, if we add any other script with the script in 'use strict' mode, the new script automatically gets into the 'use strict' mode.
22. What is short polling and long polling?
In short polling, clients send requests to servers and await responses. A server may receive several requests, causing response time to increase. Short polling is inefficient because it creates latency and network overhead.
On the other hand, Long polling supports near-instantaneous communication between clients and web servers in web applications. We use long polling in chat and messaging applications. That's because real-time updates are crucial in these applications.
23. What is the event loop in Node.js?
The event loop in Node.js supports non-blocking operations, though Node.js is single-threaded.
The event loop is initiated when Node.js starts. First, Node.js processes the input script and then processes the event loop. The below diagram shows the order of operations of the event loop.Great! I hope this section has given a strong foundation on full-stack technologies.

Here Are Full stack developer interview questions and answers for experienced
In this section, I have prepared the high-level full-stack developer questions and answers to help crack challenging full-stack interviews.
Let’s check out them!
24. Is GraphQL faster than REST?
Yes, graphQL is faster than the REST API. That’s because graphQL provides a single endpoint to access multiple resources. On the other hand, RESTful APIs provide various endpoints, which result in network latency.
25. How to make web pages load faster?
We can follow the strategies below to speed up the loading of web pages.
- Minimizing HTTP requests
- Using CDNs and removing unused files/scripts
- Compressing images
- Optimizing files
- Caching on browsers
- Applying CSS3 and HTML5
26. How is rolling deployment different from blue-green deployment?
Regarding rolling deployment, an application’s new version gradually replaces the previous version. However, upgrading to the latest version takes time. The main thing is that both old and new versions will exist without affecting the user experience or functionalities.
On the other hand, blue-green deployment allows two identical production environments to work simultaneously. The production environments are the blue environment and the green environment. The blue environment receives all user traffic and runs the environment. The green environment is the one that we need to upgrade. The main thing is that both environments use the same database back-end and application configuration.
27. What are the differences between Server-side Scripting and Client-side Scripting?
| Features | Server-side scripting | Client-side scripting |
| Area of focus |
It works in the back end. |
It works in the front end |
| Processing |
Server interaction is required. |
No server interaction |
| Languages |
It supports Ruby, ASP.net, PHP, and Python. |
It supports CSS, JavaScript, HTML, etc. |
| Security |
Security is high |
Security is low. |
| Visibility |
Users cannot view source codes. |
The source code is visible to users |
| Function |
It provides the requested output to end-users |
It manipulates and allows access to databases. |
28. What’s the difference between Normalization and Denormalization?
| Features | Normalization | Denormalisation |
| Data redundancy | Normalization divides data into tables. It reduces Data redundancy and inconsistency. | Denormalisation combines data into a single table. We add Redundancy to execute queries quickly. |
| Data integrity | Normalization supports data integrity | It doesn’t support data integrity |
| Scalability | The number of tables and joins is increased. | The number of tables and joins is decreased. |
| Optimization | Normalization optimizes the use of disk storage. | It doesn’t optimize the use of disk storage. |
| Data processing | We apply normalization in OLTP systems to insert, delete, and update. | We apply denormalization in OLAP systems to perform search and analysis. |
29. When to use the observer pattern?
We can use observer patterns to define a one-to-many dependency between objects. The object that monitors the state of another object is known as the observer. On the other hand, the object being watched is known as the subject.
30. What is the difference between GET and POST methods?
| GET Method | POST Method |
| GET method helps to request data from a specified resource. | The POST method sends data to servers to create or update a resource. |
| We can bookmark a GET request. | We cannot bookmark a POST request. |
| We can cache a GET request. | We cannot cache a POST request. |
| GET request parameters remain in the browser history. | POST request parameters don’t remain in the browser history. |
| We can view data through the URL. | URL doesn’t contain data using the POST method. |
| This method supports only ASCII characters. | This method supports only binary data. |
31. What are the differences between an abstract class and an interface class?
| Abstract | Interface |
| An abstract class may have abstract as well as non-abstract methods. | An interface class will have only abstract methods |
| It has static, non-static, final, and non-final variables. | It has only static and final variables. |
| It can provide the implementation of the interface. | It cannot provide the implementation of an abstract class. |
| We use the 'extends' keyword to extend the abstract class. | We use the 'implements' keyword to create an interface. |
| We use abstract keywords to declare an abstract class. | We use interface keywords to declare an interface class. |
| It supports multiple inheritance. | It doesn’t support multiple inheritance. |
32. How can you prevent a bot from scraping a publicly accessible API?
If the data of an API is publicly available, we cannot prevent a bot from scraping the data. However, we can employ the throttling or rate-limiting method to overcome this issue.
Throttling is a method that prevents a device from performing a defined number of requests within a defined time. When the number of requests exceeds the specified number, an HTTP error is thrown.
Alternatively, we can use the following techniques.
- By blocking requests based on the user agent string.
- By generating temporary session tokens at the front end.
33. What is the difference between the ‘resetting’ and ‘normalizing’ CSS?
| Resetting | Normalizing |
| It is a set of styles applied to the default styles of HTML elements | It normalizes the styles of HTML elements across browsers |
| This method removes all the built-in browser styling. We can format paddings, margins, and font sizes for this type. | This method ensures consistent built-in browser styling across multiple browsers. |
| It is a non-modular method. | It is a modular type. |
| This method uses a big chain of selectors, which creates redundant overrides. | This method doesn’t use many CSS selectors. |
| Debugging is not easy in resetting. | Debugging is easy to normalize. |
34. How does SDLC work?
The software development lifecycle has many phases: planning, designing, implementing, testing, deploying, and maintaining.
- Plan: This stage includes collecting software requirements and specifications from stakeholders. It also consists of the cost-benefit analysis, resource estimation and allocation, etc.
- Design: In this phase, developers analyze the requirements. Then, they create designs to develop the best software application.
- Implement: In this phase, developers build codes for the required application.
- Test: Developers and testers leverage manual and automation testing to find bugs in codes
- Deploy: This phase includes moving the build environment into a production environment. It includes packaging, environment configuration, and installation.
- Maintain: In this phase, developers resolve customer issues, remove bugs, and manage software changes and upgrades.
35. Can you tell us the latest trends in full-stack development?
Yes, many trends are emerging in full-stack development nowadays. Let's take a look at them.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-based solutions are booming as companies lean towards automated processes and systems.
- Languages: We leverage JavaScript to develop web applications. Developers use angularJS for front-end and node.js for back-end development.
- Low-code Development: Software development companies simplify development processes with simple drag-and-drag options.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology is growing like never before. So, gaining some good knowledge of this technology will be beneficial.
- IoT: It is a cutting-edge technology that is spreading everywhere nowadays. IoT creates an IT ecosystem of sensors, hardware, and the internet. It enables efficient communication across devices.
36. How do you stay up-to-date with the latest trends in web development?
It is a crucial question. Interviewers want to know how you keep tapping with the latest trends in the web development domain. So, you should mention the various knowledge sources you follow for continuous learning. Here are some tips.
- You can mention the blogs, newsletters, and podcasts you read and listen to regularly.
- You can discuss the recent webinar, workshop, or conference attended for web development.
- You can refer to the online communities where you are part of. It can be a forum, social media group, or chat platform.
- You can talk about the recent online course that you have gone through recently.
Celebrate! You have completed learning the crucial full-stack interview questions. Now, you are ready to face your full-stack interviews boldly.
Watch this video on “Top 10 Highest Paying IT Jobs in 2021” and learn how to get into these job roles.
FAQS
1. Is full-stack development easy?
Of course! Full-stack development is easy to learn. The more you practice coding, the more expertise you gain in full-stack development. MindMajix offers full-stack development training for learners of all levels. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced learner, the training will help you master full-stack development. The industry-designed course curriculum will elevate your skills and make you job-ready.
2. Are full-stack developers in demand?
Yes, full-stack developers are in high demand worldwide. Companies prefer to hire candidates who master both front-end and back-end development. According to Glassdoor, the salary for a full-stack developer in India is around 8.5 LPA on average. Companies like TCS, IBM, CTS, Accenture, Virtusa, etc., recruit full-stack developers for high salary packages. Glassdoor says they earn over 120k USD per year on average. In the USA,
3. What new skills should I learn to become a better full-stack developer?
Acquiring the below skills will keep you up-to-date with the latest trends in full-stack development.
- Knowledge of cloud computing and DevOps concepts
- Expertise in secure shell protocol (SSH)
- Excellent collaboration skills
- Data analysis and visualization skills
4. How long does it take to learn full-stack development?
MindMajix offers full-stack training in live online and self-paced modes. If you choose the live online method, you can learn full-stack within 50 hours. On the other hand, if you select the self-paced mode and watch two videos per day, you will complete the training within 25 days. Above all, your commitment to learning and interest in practice make you a competent full-stack developer.
5. Will AI replace full-stack developers?
No, AI is replacing full-stack developers as of now. In the future, things may change. AI has the potential to change the way we develop applications right now. But I would be in a positive direction. AI tools may simplify full-stack application development. It may help to build super-performing software applications in the future.
Conclusion
Let’s wrap it up! I am sure that reading this article has supercharged your knowledge of full-stack technologies. I hope this blog has boosted your confidence and helped you crack your full-stack developer interviews. However, if you go through professional training on full-stack development, it will be beneficial to gain comprehensive knowledge and breeze through your interviews.
MindMajix is a leading eLearning provider that offers top-class full-stack web development training with expert trainers. You can sign up for the full stack development course in MindMajix and advance your career.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Full Stack Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Full Stack Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| Full Stack Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| Full Stack Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .















