- Docker Architecture
- Docker Commands with Examples for Container Operations
- Docker Interview Questions
- Docker Swarm Architecture
- Docker Container Security and Tools
- Basic Terminologies of Docker
- Docker Deployment Tools
- Docker Images and Containers
- Docker Security
- Getting Started with Docker
- Installing Docker to Mac, Windows, Oracle Linux 6 & 7 In Docker
- Isolated Development Environments with Docker
- Network Configuration in Docker
- Networking in Docker
- Running Docker with HTTP
- Software Development Tools and Virtual Machines VS Docker
- Why is Docker so Popular - Good and Bad of Docker
- What is Docker? How does Docker works?
- Vagrant Vs Docker
- Docker Projects and Use Cases
- What is Docker Kubernetes
Businesses are getting too complex nowadays because of their dynamic nature and scaling requirements. It's a simple but important note that you must choose smart tools to simplify complex processes. Software development with the right tools will result in quick delivery and deployment.
On that note, this blog compares LXD and Docker in terms of their features, pros and cons, similarities, and differences. It will help developers or operation engineers choose the right one for developing and managing their applications. Know that LXD and Docker are widely used as containerization tools that effectively manage containers for isolating applications, simplifying development processes, and providing robust security. Simply put, you can securely develop, run, control, and scale applications with these container management tools. Let’s start now!
LXD vs Docker - Table of Contents
- What is LXD?
- Features of LXD
- Advantages and Disadvantages of LXD
- What is Docker?
- Features of Docker
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Docker
- Similarities
- Differences
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in Docker, then enroll in "Docker Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
What is LXD?
LXD is nothing but an open-source Linux Container Hypervisor. With LXD, you can create system containers and Virtual Machines. In a way, LXD is the container management extension for Linux Containers – LXC. It uses LXC for running system containers. Actually, LXC divides systems into independent containers. At the same time, LXD acts as an interface to manage the containers. Note that a single container can run many applications.
Know that LXD is written in Go programming, and you can get the source code of LXD on GitHub. Also, LXD is image-based and offers many Linux distributions. LXD offers a template distribution system to create containers and operate them efficiently. With a single command, you can manage instances in system containers. Overall, LXD supports fine-grained control over applications and ensures high-scale operational security.
What are the Key Features of LXD?
The following features of LXD will let you know why it is being used as one of the effective container management tools.
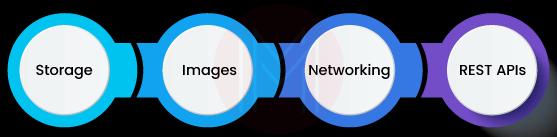
1. Storage: Generally, LXD stores data in storage pools. These storage pools are further divided into storage volumes based on different content types. With LXD, you can easily create any number of storage pools. Here, storage volumes are nothing but the parts of storage pools. Know that each storage volume can be used for a specific purpose. There are three types of storage volumes such as container/virtual machine, custom, and image. Besides, storage pools have storage buckets like Amazon S3.
2. Images: LXD has an in-built image store. It supports importing images from three sources: remote image server, file on a remote server, and direct pushing of the image files. LXD supports two image formats such as unified tarball and split tarball. Unified tarball uses a single file consisting of an instance root and the required metadata. On the contrary, split tarball uses two files where one file contains an instance root, and another file consists of the metadata.
3. Networking: LXD supports network types such as bridge network and OVN network. In the bridge network type, LXD creates a virtual L2 Ethernet in which you can connect instance NICs. A network device, NIC, is the short form of a Network Interface Card. Another one, the OVN network, is a software-defined networking system. It supports virtual network abstraction and building private clouds. Additionally, LXD supports external networks such as the Macvlan network, physical network, and SR-IOV network.
4. REST APIs: REST API is known as Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface. REST API communicates with LXC through the libLXC library. Also, this API helps communicate between LXD and clients over HTTPS. The data is encapsulated over a Unix socket for local operations and SSL for remote operations. Note that REST APIs have to return status information. For this, LXD uses three standard return types: background operation, standard return value, and error.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of LXD?
Advantages of LXD:
If you are still wondering why LXD is one of the powerful containerization tools, the following advantages of LXD make you clear:
- LXD comes with a powerful Command Line Interface (CLI).
- LXD easily integrates with cloud platforms such as Ansible, MAAS, Juju, Packer, Terraform, and Puppet Bolt.
- It is highly scalable but at the same time provides enhanced security.
- It has device pass capabilities for USB, Graphics Processors, Disks, NIC, and other hardware.
- It provides excellent control over compute resources.
- It creates snapshots of running containers.
- LXD has robust GIT repositories, application instances, and authentication servers.
- With LXD, you can create virtualized Linux environment where you can build reproducible software builds.
- No wonder LXD simplifies deployment with a few command lines.
Disadvantages of LXD:
Every coin has two sides. Likewise, every tool comes with pluses and minuses. No doubt LXD has a few shortcomings too. Let's see them below:
- LXD is not an easy-to-use tool.
- It doesn’t have an application delivery framework.
- Copying system containers from one machine to another is not easy in LXD
- Documentation can be improved.
- It isn't easy to run across different operating systems simultaneously while using LXD.
What is Docker?
Docker is one of the end-to-end and lightweight containerized platforms used to build, run, and share applications. Mainly, Docker allows applications to run on loosely-coupled environments known as containers. You can run applications in different containers, which will help to reduce the conflict between languages, frameworks, and binaries. With Docker, you can manage applications throughout their development lifecycle – no matter the size of the application. In short, you can build portable, fast, reliable applications by replacing mundane configuration tasks with Docker.
You can get Docker images from the Docker Hub repository. And you can use Docker images to develop applications on any platform – no matter whether it is a Desktop or Cloud. For example, you can run Docker in AWS ECS, Google GKE, Azure ACI, etc. Not only this, you can share applications across different platforms and environments. Docker is the best tool for developing stateless and microservices applications since it isolates applications effectively.
Administrators, Developers, and DevOps professionals use Docker for managing applications. Companies from mid-size to enterprises use Docker widely. Especially software development and IT companies widely use Docker. For example, JPMorgan, ThoughtWorks, Neudesic, SLALOM, and LLC use Docker extensively.
[ Related Article: Introduction to DevOps Docker ]
What are the Key Features of Docker?
There are a lot of features that make Docker one of the popular container management tools. Let’s discuss them below:
1. Docker Desktop: you can quickly install Docker Desktop on Windows and macOS desktops. Docker Desktop consists of Docker Engine, Docker content trust, Docker Compose, Docker CLI Client, and many more. Docker Desktop allows a simple interface to manage your machine's containers, applications, and images. Note that it can be done without using CLI. With Docker Desktop, you can build and share containerized applications. Moreover, Docker Desktop interacts with the Docker Hub and uses the images and templates to simplify the application development process.
[ Check out: Installing Docker on Windows and Mac ]
2. Docker Build: This tool helps build portable container images. In other words, you can create images for multiple operating systems. This tool also supports bundle images and sharing them anywhere – even with Docker Hub. You can use suitable build drivers to make builds and optimise them through effective cache management. Besides, you can customize, automate, and extend the builds seamlessly.
3. Docker Dashboard: Docker provides a quick view of containers running on a machine. It will help interact with containers and manage them effectively. It provides a quick view of container logs. So, you can easily manage container lifecycles, such as stopping or removing containers. Additionally, the dashboard provides ‘images view’ that displays the list of Docker images. You can view scanning reports of images in the dashboard, from which you can know the vulnerabilities in the images. Also, you can see the list of images shared with the Docker hub. What's more! ‘volumes view’ helps to see the list of volumes, which will support creating and deleting volumes quickly.
4. Docker Hub: It is one of the container image repositories. Here, we can find certified images and use them. You can pull high-quality images provided by vendors and Docker from this repository. Not just that, you can publish your own images in Docker Hub. Docker Hub comes with both private and public repositories. You can pull and push container images in private repositories when considering private repositories. Docker allows building images in GitHub and pushing them into the Docker Hub. As a whole, we can build, collaborate, and integrate using Docker Hub.
5. Docker Compose V2: Know that Docker comes with many developer tools. The tools help to build, run, and share applications efficiently. Mainly, Compose V2 helps to build multi-container applications and speeds up the development process. In other words, it helps to develop applications in a short development cycle. Further, Compose V2 simplifies cloud deployment.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Docker?
Advantages of Docker:
No wonder Docker has many advantages, like LXD. Let’s get to that:
- Docker is portable. Be it a virtual machine, cloud, or local machine, you can run Docker containers seamlessly.
- It easily integrates with development tools such as CircleCI, VSCode, and GitHub.
- Packaging and sharing applications are great things about Docker. As packages include all the dependencies, they can be quickly moved between environments.
- Creating and deploying images is a simple and less time-consuming process.
- Docker allows you to manage multiple versions of containers and images easily.
- With Docker, you can scale applications even for high-loads.
- It provides excellent security to applications running inside the containers since they are isolated from other applications.
- You can manage and share the images stored in the cloud effortlessly.
- With Docker, you can make quick configurations, resulting in rapid development and application deployment.
- Containers isolate applications from their infrastructure, which speeds up the delivery of applications.
[ Check out: Docker Deployment Tools ]
Disadvantages of Docker:
Undeniably, where there are pros, there can also be a few cons. Let’s now look at the cons of Docker:
- Docker lacks supporting enterprise-level applications.
- Container networking is not appreciable in Docker.
- It is challenging to manage the unused images in Docker.
- The retention policy of Docker Hub is a bit complicated and is not developer-friendly.
- Data storage and volume management can be simplified.
LXD vs Docker - Similarities
Some similarities exist between LXD and Docker. Let’s have a look at the following:
- Both LXD and Docker share a Linux kernel with the host Operating system for creating isolated processes.
- LXD and Docker have many tools for storage, interfaces, networking, and managing containers.
- They use daemon-based runtime for managing containers.
- They offer a robust documentation.
LXD vs Docker - Differences
Many differences exist between LXD and Docker. The following will talk through the same in detail.
- Ease of use: Docker is an easy-to-use platform. Mainly, documentation will help to be familiar with Docker. On the other hand, LXD is not a container option for beginners. Companies that are already working with virtual machines can leverage LXD.
- Containers: LXD uses system containers, whereas Docker uses application containers. System containers will have many applications, whereas application containers will have only one. System containers are usually long-lasting, whereas application containers are temporary. You can easily create, delete, and replace containers in application containers. Thatswhy, Docker creates stateless and ephemeral containers using minimum resources.
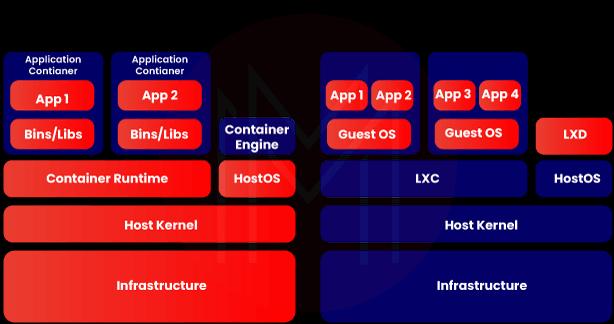
- Platform: LXD is the virtualization and container management tool. Basically, LXD is an interface. LXD provides virtualization with a full operating system. In a way, LXD increases the capabilities of LXC. On the other side, Docker is a container management platform. Moreover, LXD uses LXC to communicate with the kernel, whereas Docker uses its own library container.
- Operating System: Docker can host a single operating system container in a single host, whereas LXD is capable of hosting multiple Operating system containers. Also, LXD heavily depends on the features of an operating system for storage and networking, whereas Docker doesn’t depend on them.
- Ecosystem: LXD has a hypervisor that helps to integrate with OpenStack and other Linux distributions through REST API. On the other side, the Docker ecosystem is more extensive than LXD. To name a few – it has Docker Swarm, Docker trusted registry, Docker Machine, Docker Compose, and Docker Hub.
- Speed of Operation: Docker is faster than LXD in terms of CPU performance only when a single processor is used. On the contrary, LXD is faster than Docker in executing applications using multiple processors.
- Memory and Storage Performance: If you consider memory performance, memory or RAM speed is higher in Docker than in LXD. It is valid only when performing operations such as adding and copying integers. At the same time, memory speed is almost the same in LXD and Docker while making operations such as integer scaling and floating-point addition. If you consider I/O performance, LXD is slightly better than Docker.
- Community: Docker community is large and growing when compared with LXD. This is because Docker has good scaling and isolation capabilities.
[ Also Check out Vagrant vs Docker ]
Conclusion
It’s a short but important note that LXD is a fast, secure, lightweight, full operating system container management tool. As you know, Docker is a lightweight container management platform suitable for container isolation, running microservices and stateless applications, and much more. It's no wonder you can run Docker inside LXD containers. But the ultimate question is - which one is better? The answer is that it depends on the requirements. This is because LXD is good in certain features, whereas Docker is good in certain features. Thus, the selection of the right tool must be made based on the requirements of the applications.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Docker Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| Docker Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Docker Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Docker Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |

Viswanath is a passionate content writer of Mindmajix. He has expertise in Trending Domains like Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Blockchain, etc. His articles help the learners to get insights about the Domain. You can reach him on Linkedin






