- Linux Commands for Beginners
- Linux Environment Variables
- Linux File Permissions
- Linux Interview Questions
- Linux Kernel Tutorial
- Linux Networking Commands with Examples
- What is Linux? - A Complete Beginners Tutorial
- Linux vs Unix
- Linux Advanced Functions And Commands
- Introduction to Linux Operating System
- Monitoring Tools in Linux
- Top 10 Reasons Why You Should Learn Linux
- Shell Scripting Tutorial
- What is Kali Linux ?
- What is Linux Operating System?
- Parrot OS vs Kali Linux
- Network Administrator Interview Questions
- Linux Projects and Use Cases
- Linux Connect to MySQL
- Linux Networking Tutorial
Arch Linux and Ubuntu are nothing but the two Linux distributions widely used by home users and businesses. Undeniably, both operating systems are sound in terms of installation, use, and performance. Although they have many standard features, they also have a few differences. This blog will detail the differences between the two Linux distributions, key features, and pros and cons.
Arch Linux vs Ubuntu - Topics of Content:
Comparison Between Arch Linux vs Ubuntu
What is Arch Linux?
A Canadian scientist released Arch Linux in 2002. This Linux distribution was released to support advanced users who wish to control their systems completely. Basically, Arch Linux is a simple, general-purpose, lightweight Linux operating system. And it is a free, open-source Linux distribution with good customisation capabilities.
As Arch Linux is a lightweight operating system with good customisation features, it best suits small businesses. With the roll-release model, Arch Linux provides its users with the latest stable versions of the Linux distribution. Arch Linux encourages a Do-it-yourself (DIY) approach so that its users can make customisations easily. Unlike other distros, it is not software bloat but allows you to control the packages' installations. Furthermore, Arch Linux is the Linux distribution backed by Canonical and is one of the leading global software vendors.
| If you want to become a professional in Linux, then visit Mindmajix - a global online training platform: "Linux Training Course" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
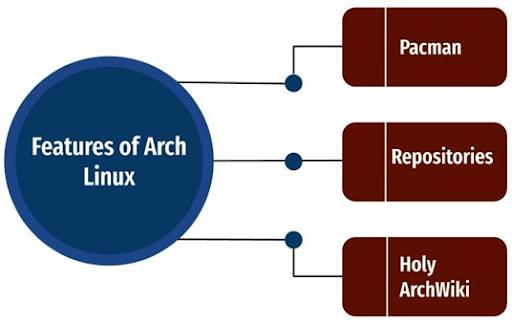
Features of Arch Linux:
Arch Linux offers many excellent features to its users. Here are a few features listed below:
- acman: Pacman manages all the packages in the repositories. It supports the installation of these packages from the repositories into your systems. Not only this, Pacman supports upgrades, removals of packages, and downgrades.
- Repositories: Arch Linux has two repositories: Arch package repositories and Arch User Repositories (AUR). In particular, they are massive libraries consisting of installation packages. Know that Arch Linux repositories are essentially community-based repositories where users can add new packages.
- The Holy Arch Wiki: It is the documentation wing of Arch Linux, which is large and organised. Here, you can get all you need to know about Arch Linux in the form of the latest changes, statistics, arch news, etc.
What are the Advantages of Arch Linux?
Here’s the list of the advantages of Arch Linux below:
Installation: With Arch Linux, you don’t require a desktop environment or Windows Manager, but the installation should have been done without any issues. Also, you can use patches when they are required.
Customisation: Arch Linux allows the Do-it-yourself (DIY) approach by which users can make customisations as they wish. No wonder that flexibility is one of the key advantages of Arch Linux.
Rolling Release Model: With this model, you need to install the operating system only once. Because of this, when there is an upgrade in the packages, you don't need to reinstall the software. Arch Linux allows continuous software upgrades without reinstalling the operating system.
What are the Drawbacks of Arch Linux?
Where there are pros, there might be cons as well. Let’s look at the drawbacks of Arch Linux below:
- Arch Linux community is small due to the limited number of users.
- Although Arch Linux encourages a DIY approach, beginners may still have difficulty working with this software. However, experts and experienced users can use this as smoothly as possible.
- While updating packages, if there are bugs, it will seriously affect the systems.
- Shifting operating systems from Arch Linux to any other Linux distribution is complicated.
- Package Manager or Pacman would work slowly at times.
| Related Article: "Top 10 Reasons Why You Should Learn Linux" |
What is Ubuntu?
A South African entrepreneur released Ubuntu in 2004. It is the modern, free, and open-source DEBIAN-based Linux distribution. And it is one of the popular distributions among other Linux distributions. Ubuntu is the desktop operating system developed by Linux. Mainly, it is intended for personal computer operating systems; however, it can be installed in public clouds and data centers. In short, Ubuntu is best suitable for home users and small businesses.
Know that security and release quality are the key features of Ubuntu. Besides, you can install Ubuntu in the systems where the latest versions of Windows are not compatible. Not only limited to this, but you can also install Ubuntu in other systems such as servers, Robots, IoT devices, mac computers, and so on. Note that the most recent release in Ubuntu is 16.04 Xenial Xerus.
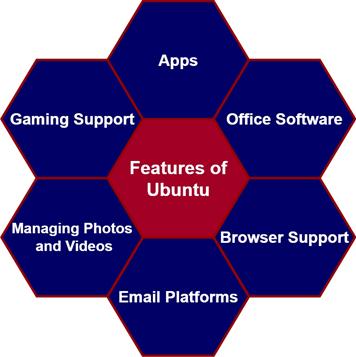
Features of Ubuntu:
Ubuntu comes with many good features. Let’s see how it works.
- Apps: You can install any app from the pool of apps offered by Ubuntu, which ranges from Spotify to Skype to Telegram. It’s not a surprise, they can be installed within a few clicks.
- Office Software: Ubuntu offers LibreOffice, which is no way less than MS office. You can create documents, PowerPoint presentations, and spreadsheets similar to MS office. Not only that, you can share these documents with others too. No wonder Ubuntu allows you to open google docs as well.
- Browser Support: Providing speed and security, Ubuntu simplifies the web browsing experience for its users. Ubuntu supports chrome and other popular browsers installed from 'Ubuntu Software'. Note that Ubuntu software is the app store of the Ubuntu operating system.
- Email Platforms: In addition to Ubuntu’s Thunderbird – an email platform, Ubuntu allows you to use other mail platforms such as – Gmail, Microsoft Exchange, Hotmail, and so on.
- Managing Photos and Videos: Without the support of any additional drivers, Ubuntu supports you in importing, viewing, organising, editing, managing, and sharing photos quickly. This way, the following tools play vital roles – Gimp, Shotwell, and Krita. You can watch HD videos in Ubuntu with a default movie player, OpenShot, or VLC. Besides, the tools such as Shotcut and Kdenlive support you in editing movies on Ubuntu.
- Gaming Support: Ubuntu undoubtedly offers its users thousands of gaming applications.
What are the advantages of Ubuntu?
The advantages of Ubuntu are many. Let’s discuss them as follows:
User-friendliness: Beginners who wish to work on Linux operating systems can choose Ubuntu without a doubt. This is because it provides the features such as – shared efforts, shared code, and shared principles. Moreover, Ubuntu comes with easy use, stylish, and beautiful GNOME desktop environment allowing its users to customise the desktop as they wish. What’s more! Ubuntu offers desktop environments in different flavors.

Privacy and Security: it’s no wonder that Ubuntu is stable and fast. Generally, Ubuntu is more secure than other platforms such as Windows, macOS, etc. It supports protecting systems against virus attacks.
Apps: You can install any application in Ubuntu as with operating systems like Windows and macOS. Know that ‘Ubuntu software’ is the app store offered by Ubuntu. Any application can be found from this Appstore, undoubtedly.
Accessibility: With Ubuntu, you can work with the Content Management System platforms of PHP such as Laravel, WordPress, and Magento quickly. Additionally, you can work with the tools such as Ruby, Python, Java, and many more.
Performance: Ubuntu achieves quick booting of computers. And it is less affected by viruses. Another important thing is that Ubuntu provides free-of-cost IDEs. As a result, Ubuntu has become highly reliable and increased the confidence among users.
Free Upgrades: it's not a wonder that all the upgrades are free in Ubuntu and will be automatically released every six months – on average.
What are the Drawbacks of Ubuntu?
In fact, Ubuntu has a few setbacks as well. Following is the list of the drawbacks.
- Ubuntu is not a lightweight operating system like Arch Linux
- Customisation is not so easy as Arch Linux
- GUI in Ubuntu is not as smooth as in Windows
- In Ubuntu, you can install apps in ‘snap form’ only. It demands large storage space when compared to other operating systems.
- Ubuntu is not suitable for old systems and low-power systems.
- Ubuntu demands a robust hardware support system since some of the software and hardware wouldn’t be compatible with Ubuntu.
What are the Key differences between Arch Linux and Ubuntu?
Let’s explore the key differences between Arch Linux and Ubuntu in detail. Here are the listicles.
Installation: With the help of driver manager and GUI, you can simplify Ubuntu installation. On the other hand, you have to use command lines in Arch Linux. Also, you can install a minimum set of packages with Arch Linux, whereas Ubuntu allows you to install many facilities. You can control the installation of packages in Arch Linux during installation. But, in Ubuntu, if you want to remove a few unwanted packages, you can do this only after the installation.
Customisation and User Experience: With DIY capabilities, users can make customisations in Arch Linux as they need. On the other side, the users who wish to make a one-time setup and no longer require customisations or changes can choose Ubuntu. In other terms, Ubuntu supports users who wish to make a hassle-free configuration setup.
File Systems: Ubuntu uses only the ext4 file system. At the same time, Arch Linux invariably uses different file systems such as – xfs, btrfs, and f2fs in addition to ext4.
Multimedia Support: With Arch Linux, you can choose any audio server such as PulseAudio or Pipewire – no matter what type. On the other hand, Ubuntu uses only PulseAudio as the default audio server.
Community Support: The user community in Ubuntu is massive, whereas it is small in Arch Linux. Therefore, you can take support from this vast community while working with Ubuntu, but chances are less with Arch Linux.
However, thanks to ArchWiki, the robust documentation setup compiled by Arch Linux supports users to get the information they need related to Arch Linux.
Releases: Arch Linux uses the ‘rolling release’ model for making upgrades with the support of Pacman. On the other hand, Ubuntu uses ‘point releases’ in which packages are tested against performance, compatibility, and security. In this regard, Ubuntu uses Advanced Package Tool (APT) for easy installation.
Repositories: Ubuntu has four repositories named – main, restricted, universe, and multiverse. On the other side, Arch Linux has two repositories named – supported and unsupported.
Performance and Scalability: Although both operating systems are sound in performance, Ubuntu faces hardware compatibility issues with older systems. Considering scaling, Arch Linux is better than Ubuntu due to its lightweight feature. On the contrary, Ubuntu demands little fine-tuning while scaling.
Conclusion:
Both Arch Linux as well as Ubuntu have long been used by all types of developers and users. Essentially, they provide the best support to them in all dimensions. In the simplest terms, Arch Linux provides simplicity and freedom, whereas Ubuntu offers excellent release quality and security. Also, Arch Linux is flexible, and you can customise as you wish, whereas Ubuntu is suitable for easy installation and use. Either way, both the distros have many pluses and few minuses. In the end, it is the users who have to choose the right distro that will best fit their requirements.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Linux Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| Linux Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |
| Linux Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Linux Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |











