- Linux Commands for Beginners
- Linux Environment Variables
- Linux File Permissions
- Linux Kernel Tutorial
- Linux Networking Commands with Examples
- What is Linux? - A Complete Beginners Tutorial
- Linux vs Unix
- Linux Advanced Functions And Commands
- Introduction to Linux Operating System
- Monitoring Tools in Linux
- Top 10 Reasons Why You Should Learn Linux
- Shell Scripting Tutorial
- What is Kali Linux ?
- What is Linux Operating System?
- Arch Linux Vs Ubuntu
- Parrot OS vs Kali Linux
- Network Administrator Interview Questions
- Linux Projects and Use Cases
- Linux Connect to MySQL
- Linux Networking Tutorial
In today’s world, which is more about automation, microservices, and advanced deployment methods, Linux plays a crucial role. Almost all organizations across the globe use the Linux Operating System for managing their system. Also, by 2032, the Linux Operating System market is expected to reach around USD 24 billion as stated in the report by Allied Market Research. Therefore, it is evident that the industry is full of opportunities in Linux development. So why not take advantage of these?
If you want to become a Linux developer in a reputed organization, this blog will help you. We will cover all the topics from basic Linux commands to advanced concepts like File Management so that you can easily crack your Linux Interview Round.
Table of Contents
Top 10 Frequently Asked Linux Interview Questions
- What is Linux?
- What is the History of Linux?
- What is the difference between Linux and Unix?
- What is the Linux Kernel?
- What is BASH?
- What is LILO?
- What are the Basic Components of Linux?
- What are the Features of the Linux Operating System?
- What is a Swap Space?
- What is LVM? Its a requirement in Linux?
Overview of Linux
Before moving straight to the interview questions, it is important to know its overview and history so that we can understand its use in a better way!
Linux is a Unix-like operating system. It was developed as an open-source project to provide users with a stable, customizable, and cost-effective platform for computing. It has been used as an alternative to operating systems like Windows and macOS which are not open source. It has a modular design due to which it can extend the software packages available for Linux. Thus, we can easily customize according to our own requirements.
Linus Torvalds, who was a Finnish computer science student developed Linux as an open-source project. It was developed as an Operating System similar to Unix. After development, its initial version 0.01 was released as open-source software under the GNU General Public License (GPL). Thus, it got huge contributions, bug fixes, and improvements from the global community of developers. It has a wide range of applications like server administration and network management. With these benefits, Linux has become a crucial part of the modern software development environment.
Skills and Responsibilities of Linux Engineers
Primary skills:
- Proficiency in programming languages such as C, C++, Python, Shell scripting, etc., for Linux development.
- Deep understanding of Linux operating system internals and kernel programming.
- Expertise in Linux system administration, including package management, file systems, and network configuration.
- Familiarity with Linux development tools and libraries, such as GNU toolchain, glibc, and systemd.
- Proficiency in troubleshooting and debugging Linux systems and applications.
- Experience with Linux-based development environments, including Docker and virtualization technologies.
- Knowledge of open-source licensing and community collaboration practices.
Secondary skills:
- Familiarity with SQL databases and basic database administration on Linux systems.
- Understanding of continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines and automation tools like Jenkins.
- Knowledge of RESTful APIs and microservices architecture for developing Linux-based applications.
- Proficiency in version control systems like Git for managing source code.
- Understanding of agile software development methodologies and project management concepts.
What are the job responsibilities of Linux Developers with 1-2 years of Experience?
The Linux Developers with 1-2 years of Experience are expected to deliver the strong fundamental skills such as:
- Understanding of Linux, its distributions, and applications.
- Knowledge of the Operating Systems, Process Management, and Networking to manage the Linux-based system.
- Writing scripts for automation tasks using shell scripting languages like Bash.
- Collaborating with the system administrators in configuring and maintaining Linux servers
- Knowing the above role would help you to easily adapt to the work environment within the project team.
What are the job responsibilities of Linux Developers with 3-5 years of Experience?
- As the 3-5 years of experience professional in Linux Development, you will have the following roles and responsibilities:
- Knowing the design principles and fundamentals of architecture.
- Understand performance engineering and Knowledge of quality processes and estimation techniques.
- Optimizing performance and scalability of Linux applications.
- Collaborating with cross-functional teams to integrate Linux solutions into larger projects.
What are the job responsibilities of Linux Developers with more than 5 years of Experience?
With more than 5 years of Experience, you are expected to deliver the following skills and responsibilities:
- In-depth knowledge of popular Linux Distributions like RedHat, CentOS, Debian, etc.
- Knowledge of VMWare and SAN management and concepts, and protocols such as Solid knowledge of network services and protocols such as DNS, HTTP, LDAP, SMTP, and SNMP.
- Collaborate with the team to develop automation strategies and deployment processes.
- Knowledge of SAN (Storage Area Network) Management and VMware concepts of virtualization.
- Managing, coordinating, and implementing software upgrades, patches, and bug-fixes on servers, workstations, and network hardware.
Linux Interview Questions for Beginners
1. What is Linux?
Ans: Linux is an operating system, which is based on the Linux Kernel. It is an open-source operating system that can be used with different hardware platforms. As it is an open-source OS, it provides a free and low-cost operating system for users. It is a user-friendly environment where they can easily modify and create variations in the source code.
| Delve into the fascinating world of operating systems with enriching educational materials, including valuable insights into Linux Training and a diverse array of related topics. |
2. What are the key features of Linux OS?
Ans: The key feature of Linux is that it is open source, which allows users to access, modify, and distribute the source code freely. Also, it has a modular architecture, security features like user permissions and access controls, networking support, and a command-line interface.
3. Who invented Linux? Explain the history of Linux.
Ans: Linus Torvalds created Linux. Linus Torvalds was a student at the University of Helsinki, Finland in 1991. He started writing code on his own to get the academic version of Unix for free. Later on, it became popular as Linux Kernel.
| Explore a rich array of educational content covering various operating systems, including an in-depth Linux tutorial designed to enhance your understanding of this powerful platform. |
4. What is the difference between Linux and Unix?
Ans: Here is the difference between Linux and Unix - mentioned below
|
Linux
|
Unix
|
| Both paid and free distributions are available. | Different paid structures for different levels of Unix. |
| Linux primarily uses GUI with an optional command-line interface | Unix uses the command-line interface |
| Linux OS is portable and can be executed on different hard drives | Unix OS is not portable. |
| Linux is developed by a worldwide Linux community. | Unix is developed by AT&T developers. |
| Linux is free. It is downloaded through the internet under GNU licenses. | Most Unix-like operating Systems are not free. |
| Linux is used at home-based PCs, phones, etc. | Unix is used in server systems. |
5. What is Root User in Linux?
Ans: The Root user is the superuser or administrator who has unrestricted access to all system resources and commands. Root privileges allow this user to execute administrative tasks, install software, modify system configurations, and manage user accounts.
| Discover the nuanced differences between Linux Vs Unix through an insightful comparison, shedding light on the unique characteristics of each operating system. |
6. What is Linux Kernel?
Ans: Linux kernel is the heart of the operating system. It acts as a bridge between software and hardware. If Software requests the hardware, then the kernel delivers the data between software and hardware. In other words, the hardware and software components communicate with each other through the Kernal. .
7. What is BASH?
Ans: Bash is a Unix shell and command processor written by Brian Fox for the GNU project. It is free software and acts as a replacement for Bourne Shell. It is an interpreted and not compiled process which can also be run in the terminal window. Bash is capable of reading commands from shell scripts.
8. What is LILO?
Ans: LILO means Linux Loader is a boot loader that is used for the Linux operating system. Most of the Linux Operating systems use LILO, to boot the operating system into the main memory to start the operations.
9. What is CLI?
Ans: CLI means Command language Interpreter. It interacts with the computer program, where the user issues commands in the form of text lines. It Interacts with the computer terminals also, the interface accepts the text lines and converts them as a command to the operating system.
10. What is a Linux Distribution?
Ans: Linux Distribution means the complete operating system containing the Linux Kernel and collection of the software applications, utilities, libraries, and system tools. Each distribution includes a package management system for installing, updating, and removing software packages. Therefore, every Linux Distribution has a unique set of configuration tools and documentation for specific requirements.
11. What is the latest version of Linux?
Ans: The Latest version of Linux is the Linux Mint 21.3 "Virginia." It was released on January 12, 2024, as the LTS (Long Term Support) release. Linux Mint is one of the most popular distributions that provides the desktop computing experience. We can select the pre-installed software applications, including web browsers, office suites, multimedia players, and system utilities, due to which it is considered as user-friendly.
12. What is the advantage of Open Source?
Ans: Linux was one of the first open-source technologies, many programmers added software that completely open to the users, which means you can download the file and change the code as you like. It has a wide range of options for users and increased security.
13. What is the disadvantage of Open Source?
Ans: Disadvantages of Open Source Operating System mentioned below
- Difficulty of use
- Compatibility Issues
- Liabilities and warranties
- Hidden costs
14. What is Shell?
Ans: Shell is a computer program that acts as an interface between the user and the kernel. Users can communicate with the kernel by writing programs, commands, and scripts on the shell. It accepts human-readable commands and converts them into kernel-understandable language.
15. How many types of Shells are there in Linux?
Ans: They are five Shells in Linux:
- C Shell (csh): It is like C syntax and provides spelling checking and job control.
- Korn Shell (ksh): This is a high-level programming language shell.
- Z Shell (Zsh): It provides some unique nature like it observes login/logout watching, file name generating, startup files, and closing comments.
- Bourne Again Shell (bash): It is the default to Linux distributions.
- Friendly Interactive Shell (Fish): It provides web-based configuration, auto-suggestions, etc. .
| Explore a diverse array of Linux monitoring tools designed to optimize system performance and enhance operational efficiency, offering invaluable insights into system health and resource utilization. |
16. What are the basic components of Linux?
Ans: Basic components of Linux
- Kernel: It is the core component of Linux, it acts as an interface between software and hardware.
- Shell: It acts as an interface between the user and the Kernel.
- GUI: It stands for Graphic User Interface, which is another way for the user to interact with the system. But it is unlike images, buttons, and text boxes for interaction.
- System Utilities: These are the software functions that allow users to manage the computer.
- Application Programs: A set of functions designed to perform a set of tasks.
17. How do you open a command prompt when issuing a command?
Ans:
Launch your terminal by pressing CTRL+ALT+T or by giving terminal in the menu search bar.18. What is a swap space?
Ans: Swap Space is used when the physical RAM memory is running out. It will move the RAM inactive pages to the swap space. It can be considered in the form of a dedicated swap partition or swap files.
19. What is the GUI?
Ans: GUI means Graphical User Interface. It is a human-computer interface that uses windows, images, icons, and menus which can be manipulated by using a mouse. Most of the modern applications in electronic gadgets communicate with the user through GUI. GUI is a combination of graphical and textual interaction that uses buttons, menus, message boxes, etc.
20. Explain File Permissions types in Linux?
Ans: Linux file permissions - Each file or directory has 3 permissions
They are
- Read: It refers to only they can read the file.
- Write: It refers that they can write the file or modify the file of a directory.
- Execute: It affects the user’s capability to execute the file or to view the file of a directory.
| Explore the intricacies of Linux file permissions, gaining a comprehensive understanding of how they regulate access to files and directories within the operating system's filesystem. |
21. What are the environmental variables?
Ans: In Linux, environmental variables are dynamic values that define the operating environment for processes and applications. They include system-wide settings such as PATH, HOME, and LANG, influencing how programs behave and interact with the system. These variables can be viewed, modified, and exported using commands like export and echo.
22. What are the symbolic links?
Ans: Symbolic links, also known as symlinks or soft links, are filesystem objects that act as pointers or references to other files or directories. Unlike hard links, which directly reference the inode of the target file, symbolic links store the path to the target file or directory.
Syntax:
ln -s <target> <link_name>
For example, if you want to create a symbolic link named docs in your home directory that points to a directory named documents located in /mnt/data, you would use the following command:
ln -s /mnt/data/documents ~/docs
22. What are the hard links?
Ans: Hard links are directory entries that directly point to the inode of a file or directory on a filesystem. They share the same inode as the target file. This means that changes to the original file are reflected in all hard links pointing to it, and vice versa.
Syntax:
ln <target> <link_name>
Suppose you have a file named file1.txt in your home directory and you want to create a hard link named file2.txt in the same directory that points to file1.txt, you would use the following command:
ln ~/file1.txt ~/file2.txt
23. What is redirection?
Ans: Redirection can be defined as changing the standard input and output devices. To redirect metacharacters are used, you can redirect the file or program. We can various types of redirection in Linux Like:
-
Standard Input (stdin) Redirection (<): Redirects input from a file to a command. You take data from a file and pour it into a command.
Syntax: command < input.txt -
Standard Output (stdout) Redirection (>): Redirects output from a command to a file, overwriting existing content. It means that you take the output from a command and pour it into a file, replacing any existing content.
Syntax: command > output.txt -
Appending Output (>>): Take data from the command to a file without removing the existing content. It just appends to existing content.
Syntax: command >> output.txt -
Piping (|): Redirects output from one command as input to another command. Thus, You take the output from one command and connect it to the input of another command.
Syntax: command1 | command2 -
Standard Error (stderr) Redirection (2>): Redirects error messages from a command to a file. Using this, we can take error messages from a command and pour them into a file.
Syntax: command 2> error.txt - Combining stdout and stderr (&> or 2>&1): Redirects both standard output and error messages to a file. Thus, you can take the output and error message and put them into the file.
Syntax: command &> output_and_error.txt or command > output_and_error.txt 2>&1
24. What are Daemons?
Ans: Daemons are background processes in Unix-like systems. They perform tasks independently of user interaction. Examples of the Daemons include sshd for secure remote access and cron for scheduled tasks. Thus, Daemons ensure system functionality and handle essential operations.
25. How to become a superuser in Linux?
Ans: The root is the user name, which by default has access to all files and commands. The root user can do many things, but an ordinary user cannot do things like installing software, changing file permissions, etc. To change the root user, you can use the command ‘sudo su ’ and enter the password as shown below:
26. Describe the root account?
Ans: The root is the user name, which default has access to all files and commands. The root user can do many things, but an ordinary user cannot do like installing software, changing file permissions, etc.
27. Explain the virtual desktop?
Ans: Virtual Desktop is a user interface when you are facing the problem of how to manage multiple windows on your desktop, virtual desktop serves as an alternative. Virtual desktops store remote servers and allow you to use one or more programs on a clean slate.
28. What are the different modes when using the vi editor?
Ans: There are three kinds of modes in vi editors. They are
- Command Mode/ Regular Mode: Use the command Esc to enter Command Mode from any other mode.
- Insertion Mode/Edit Mode: You have to press i to enter Insertion Mode from Command Mode.
- Ex Mode/ Replacement Mode: You have to press the “:” (colon) to enter Ex Mode from Command Mode.
29. What are inode and process id?
Ans: The inode (index node) is a data structure that stores metadata about a file or directory, excluding its name and actual data content. On the other hand, the process ID (PID) is a unique numerical identifier assigned to each running process.
When a program is executed, the operating system assigns it a PID, which serves as a reference point for identifying and managing the process. To view the inode content of a file or directory in Linux, you can use the ls command with the -i option.
Syntax:
ls -i <filename_or_directory>
30. What are the Process states in Linux?
Ans: Five process states in Linux. They are
- New/ Ready: A new process is created and ready to run.
- Running: The process is being executed.
- Blocked/ Wait: The process is waiting for input from the user.
- Terminated/ Completed: The process completed the execution or terminated by the operating system.
- Zombie: The process is deleted, but still the information regarding the process exists in the process table.
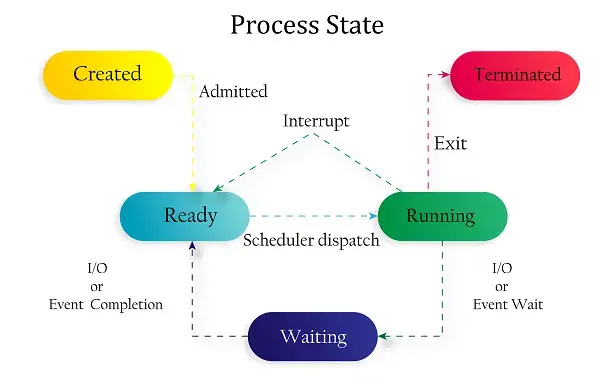
31. Explain Process Management System Calls in Linux?
Ans: Process management system calls in Linux are a set of functions that enable the creation, termination, and manipulation of processes, as well as facilitate communication and synchronization between processes.
- fork(): Used to create a new process.
- exec(): Execute new process.
- wait(): wait until process execution.
- exit(): exit from the process.
- System calls to get the Process ID.
- getpid(): to find the unique process ID.
- getppid(): to find the unique parent process id.
32. Explain File Permission groups in Linux?
Ans: The File Permissions define the access rights for different categories of users: the file owner, the group associated with the file, and others. There are three user-based permission groups for each file and directory. They are:
- Owner: Owners only will have to access the file or directory, they will not impact the actions of other users.
- Group: These permissions apply only to the group that has been assigned to the file or directory. They will not impact the actions of other users.
- All Users: These permissions are applied to all users on the system.
| Gain a deeper understanding of the Linux operating system with comprehensive educational resources that delve into its architecture, functionality, and versatility. |
33. What Is a File system in Linux?
Ans: Linux file system stores and handles the data. Without a file system, it cannot know where the file starts from and where the file ends. In simpler words, the file system in Linux defines how data is organized and accessed, including the hierarchy of directories, file naming conventions, permissions, and metadata associated with each file and directory.
34. Explain different file system types in Linux?
Ans: The different types of file systems in Linux are:
- ext4: It manages files with improved performance and reliability.
- XFS: It scales for large storage systems with high throughput.
- Btrfs: It provides features like snapshots and RAID support.
- FAT32: It facilitates compatibility with various operating systems and devices.
- NTFS: It allows accessing files in dual-boot setups or external drives.
- ZFS: It offers advanced functionalities such as data compression and deduplication.
Linux Admin Interview Questions
35. Why LVM is required?
Ans: LVM stands for Large Volume Management, it is a storage management device. Users can create, resize, and delete LVM partitions. It increases abstraction, flexibility, and control. LVM is used to gather existing storage devices into the group and allocate logical units.
36. Use of the screen command
Ans: The purpose of the screen command in Linux is to create and manage multiple terminal sessions within a single terminal window or SSH session. It allows users to create "screens" or virtual terminal windows that can run independently of each other, even if the original terminal session is disconnected.
37. What is umask?
Ans: unmask stands for user file creation mode. When the user creates any file, it has default file permissions. So unmask will specify a few restrictions to the newly created file (it controls the file permissions). To implement umask, you have to use the command
umask [-S] [mask]For example, to set the umask to 022, which removes write permissions for group and others, we can use the following commands:
umask 026
38. How to set the mask permanently for a user?
Ans: If the unmask command invoked without any arguments, it means it will display the current mask.
To set the unmask permanently, we have two types.
They are:
- Ocotal representation.
- Symbolic representation.
39. What is network bonding in Linux?
Ans: Network Bonding is a process of combining more than two network interfaces to form a single network interface. It offers performance improvement and redundancy by increasing network throughput and bandwidth.
40. What are the different modes of Network bonding in Linux?
Ans: Different modes of Linux network bonding
- Mode-0(balance-rr): It is a default mode and is based on the Round-Robin policy. It offers fault tolerance and load-balancing features. It used a round-robin fashion to transmit the packets.
- Mode-1(active-backup): It is based on the Active Backup policy and only one slave will act in the band and another one will act when the others fail in the band. It also provides fault tolerance.
- Mode-2(balance-xor): It sets an xor mode between the source Mac address and the destination Mac address to provide fault tolerance.
- Mode-3(broadcast): It is based on broadcast policy and transmits everything in the slave interface. It also provides fault tolerance and can be used only for a particular purpose.
- Mode-4(802.3ad): It is a dynamic aggregation mode, it creates aggregation groups having the same speed. It uses the transmit hashing method to select the slaves for outgoing traffic.
- Mode-5 (balance-tlb): The outgoing traffic depends on the current load on the slave, and the incoming traffic is received by the slave. It is called an adaptive transmit load balancing mode.
- Mode-6(balance-alb): It is an adaptive load-balancing mode. It does not require any switch support.
41. How to check the default route and routing table?
Ans: To display the default route and routing table, we use the following commands.
$ route-n
$ nestat-rn
$ ip 42. How to check which ports are listening in my Linux Server?
Ans: Here are several commands using which we can check on the open ports in the Linux Server. They are:
- netstat --listen: Displays all listening sockets for TCP and UDP protocols.
- netstat -tuln: Displays listening TCP and UDP sockets with numerical addresses.
- netstat -lt: Displays listening TCP sockets with numerical addresses.
- netstat -vatn: Displays all active TCP and UDP connections, including listening sockets, with verbose output and numerical addresses.
43. Where the kernel modules are located?
Ans: The location of the directory that stores the kernel modules is “lib/modules/kernel-version/” It stores all the information about the compiled drives under the Linux system. Using the ‘lsmod’ command also we can see the installed kernel modules
44. Explain the distinctions between the init and systemd initialization systems. When would you use each one?
Ans: The init is a traditional initialization system used in older Unix-like systems, executing startup scripts sequentially. An example command to restart a service using init is "service <service_name> restart".
On the other hand, systemd is a modern initialization system designed for faster boot times and advanced service management. An example command to restart a service using systemd is "systemctl restart <service_name>".
We should use the init for simple environments and systemd for the parallel startup and dependency management in modern Linux distributions.
45. What is the role of a Linux firewall and how to configure it?
Ans: The role of a Linux firewall is to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. It acts as a barrier between the internal network and external networks, such as the Internet, to protect against unauthorized access, malware, and other security threats.
We have to follow the below steps for its configuration:
- Select a firewall like the iptables or ufw.
- Install the firewall whatever you have chosen for your system like the iptables or firewalld package.
- Define firewall rules to allow or deny traffic.
- Apply rules to the firewall.
- Save the configuration rules to persist across reboots.
- Verify firewall configuration using appropriate commands.
46. How to change the default run level in Linux?
Ans: To change the default run level in Linux use the init command.
47. How to share a directory using NFS?
Ans: To share a directory using NFS, first edit the configuration file and ‘/etc/exports’ and add an entry like directory name ‘/<directory-name>’. Now restart the NFS service.
48. What are the default ports used for SMTP, DNS, FTP, DHCP, SSH, and squid?
Ans: Details mentioned below
|
Service
|
Port
|
|
SMTP
|
25
|
|
DNS
|
53
|
|
FTP
|
20(Data Transfer) 21(Connections Established)
|
|
DHCP
|
68(dhcp client), 67(DHCP server)
|
|
SSH
|
22
|
|
Squid
|
3128
|
49. How to lock a user account in Linux?
Ans: Locking user accounts is done for security purposes so that unauthorized users cannot log in. So, we have a few ways to lock the user account. Some of them are below
- Lock or disable the password using passwd command.
- Expire the user account using usermod command or chage command.
- Changing the shell using nologin command ( /sbin/nologin ).
Linux Commands Interview Questions
50. What is the 'ls' command and what it does?
Ans: It is one of the basic commands in Linux. It is used to list all the files and directories in the file system.zom
Syntax:
ls [OPTIONS] [FILES]We can use it without passing the arguments, then it will list all the files in the current working directory. Files will be displayed in alphabetical order.
Is
To list the specific directory files use the directory name in the syntax, follow as shown in the below syntax.
ls /etc
We can also pass multiple directories names in the syntax, but separated by space.
ls /etc /var /etc/passwd
51. What is the tail command in Linux?
Ans: The Tail command print the last N number of lines of the given data, it prints 10 lines by default.
Syntax:
tail [OPTION]... [FILE]Example:
$ cat names.txt
Tableau
sql server
linux administration
Now, check the syntax without giving any option or input.
$ tail state.txt
52. What is grep command in Linux?
Ans: The grep searches file patterns. If you are looking for a specific pattern in the output of another command, grep highlights the relevant lines. Use this grep command for searching log files, specific processes, and more
Syntax:
grep [options] pattern [files]For example, to search for the specified "pattern" within the file "filename.txt" and display all lines containing that pattern, you can use the following command.
grep "pattern" filename.txt
53. What is ps command in Linux?
Ans: The ps command displays the current process status of the system. And it displays the process id’s with some other related data also
Syntax:
Ps [options]
Output:
[root@rhe17~]# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
12330 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
21621 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
Example: This command displays a detailed list of all processes running on the system, including user, PID, %CPU, %MEM, and command.
ps -aux
| Explore a comprehensive collection of Linux commands with practical examples, enabling you to deepen your understanding and proficiency in navigating and managing the Linux operating system efficiently. |
54. What is the env command in Linux?
Ans: env is a shell command is used to print a list of current environmental variables and it can run another process in another environment without any modification of the current environment.
env [OPTION]... [-] [NAME=VALUE]... [COMMAND [ARG]...]Example: The ‘env’ command will print all the environment variables currently set in the shell.
Options
|
Tag
|
Description
|
|
-i, --ignore-environment
|
Start with an empty environment.
|
|
-0, --null
|
output line End with a 0 (null) byte rather than a newline.
|
|
-u, --unset=NAME
|
removes variable NAME from the environment
|
|
--help
|
Display a help message and exit.
|
55. What is the top Command in Linux?
Ans: The top command is used to show the system process and it displays and updates the sorted process information.
Syntax:
top [options]
Example:
top -n 1
Here, the ‘-n 1’ option specifies that the top should only run once and then exit, displaying system information once.
56. What is netstat command in Linux?
Ans: The netstat command gives various information about the network and routing tables, interface statics, and more about the system.
Syntax:
netstat [options]
Example:
The ‘netstat -tuln’ command will display all listening TCP and UDP sockets along with their respective numerical addresses and port numbers.
57. What is lsof command in Linux?
Ans: lsof means List of files, we can know which file is opened by which process.
lsof [options]Example:
The below command lists all open files and network connections, including those associated with port 80.
lsof -i :80
58. Explain about chmod command?
Ans: This command is used to change the permission of files and directories. Therefore, on the whole, there are three types of permission, read, write, and execute, and are represented by numbers as shown below.
- 4 - read permission
- 2 - write permission
- 1- execute permission
syntax:
$ chmod options permissions file name
$ chmod [OPTION]... MODE[,MODE]... FILE...
$ chmod [OPTION]... OCTAL-MODE FILE...
$ chmod [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE…For example, to give read and write permissions to the owner of a file named "example.txt" while allowing only read permission to the group and others, you would use the following command:
chmod 644 example.txt
Here, the first digit (6) represents the permissions for the file owner (read + write = 4 + 2).
The second and third digits (4) represent the permissions for the group and others. Thus, both are set to read-only.
59. Explain about chown command?
Ans: Chown command: The command “chown” stands for change file owner and Group. This command is used to change the ownership of one or more files or folders for a specified user or group.
syntax:
$ chown [OPTION]… [OWNER][:[GROUP]] FILE…
Or
$ chown [OPTION]… –reference=RFILE FILE…Suppose you want to change the ownership of a file named "example.txt" to a user named "john" and a group named "users", you would use the following command:
chown john:users example.txt
60. What is the cp command in Linux?
Ans: The cp command is used to copy files and directories. It is also used to backup files or directories.
Syntax:
$ cp filename
Example: The command “cp file1.txt file2.txt” copies the contents of file1.txt into file2.txt, creating file2.txt if it does not exist, or overwriting it if it does.
61. How to remove a file or directory from the system in Linux?
Ans: rm command: The rm command is used to remove the directory or file specified on the command line. You need to be careful while removing any file or directory.
Syntax:
rm filename---
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
rm filename
|
Removes single file.
|
|
rm filename1, filename2, filename 3
|
Removes multiple files.
|
|
rm * .pdf
|
Removes all pdf files in the current directory.
|
|
rm -i filename(s)
|
-i mean to confirm before deleting the file
|
|
rm -f filename(s)
|
Removes files without prompting
|
|
rm -fv *.txt
|
Remove all .txt files in the current directory without prompting
|
62. What is mkdir in Linux?
Ans: mkdir, command allows users to create directories in Linux. Users can create multiple directories at once and can set the permissions to the directories.
Syntax:
mkdir [options...] [directories ...]|
Option
|
Description
|
|
Directory
|
name of the directory to be created
|
|
-m=mode, --mode=mode
|
to set a file mode (permissions, etc.) for the created directories
|
|
-p, --parents
|
create parent directories
|
|
--v, --verbose
|
Verbose output. Print a message for the created directory.
|
|
--Z= context, --context=context
|
If you are using SELinux, this option sets the security context of each created directory to context.
|
|
--help
|
shows help message and exit
|
|
--version
|
It shows version information and exit
|
63. Explain rmdir command in Linux?
Ans: The rmdir command in Linux is used to remove empty directories from the filesystem.
Syntax:
rmdir [-p] [-v | –verbose] [–ignore-fail-on-non-empty] directoriesWhere:
- -p: Remove the specified directory and its parent directories if they are empty.
- -v, --verbose: Display a message for each directory removed.
- --ignore-fail-on-non-empty: Do not display an error message if a directory is non-empty.
Example:
rmdir -p -v --ignore-fail-on-non-empty mydirectory
The above command removes the specified directory named "mydirectory" and its parent directories if they are empty. It displays a message for each directory removed and ignores any error messages if a directory is non-empty.
64. How to exit from vi editors?
Ans: We can use two commands to exit from the vi editor. They are
- Wq: wq command saves the current work and exits from the vi editor.
- q!: q! The command does not save the current work, but it exits from the vi editor.
65. How to delete information from a file in vi?
Ans: The following commands are used to delete information from a file in vi editors.
- Command x: Deletes the current character. For example, to delete the character under the cursor, simply press "x".
- Command dd: Deletes the current line. For example, to delete the entire current line, type "dd".
66. Enlist some Linux to file content commands?
Ans: File content commands
- head: Display top lines of the file.
- tail: Display the last lines of the file.
- cat: Concatenate more than 2 files.
- more: Displays the content in pager form to view in the terminal.
Linux Technical Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
67. Tell the types of Linux distributions and name some popular distributions.
Ans: We have three types of Linux Distributions namely:
- Desktop Linux: Designed for personal computers with GUIs and a wide range of applications.
- Embedded Linux: Customized for resource-constrained embedded systems like IoT devices.
- Server Linux: Optimized for stability, reliability, and performance in server environments.
If we talk about the Linux Distributions, the most popular ones are:
- Linux Mint: It is stable and robust. Linux Mint uses mate desktop and cinnamon.
- Debian: It stands for robustness, stability, and a well-oiled release cycle. It is user-friendly. Debian version 8 will be replaced by version 9.
- Ubuntu: It is available for both desktop and server editions and is based on Debian.
- openSUSE: It is a good choice for new users and existing users.
- Manjaro: It gives a pleasant experience for new and experienced users
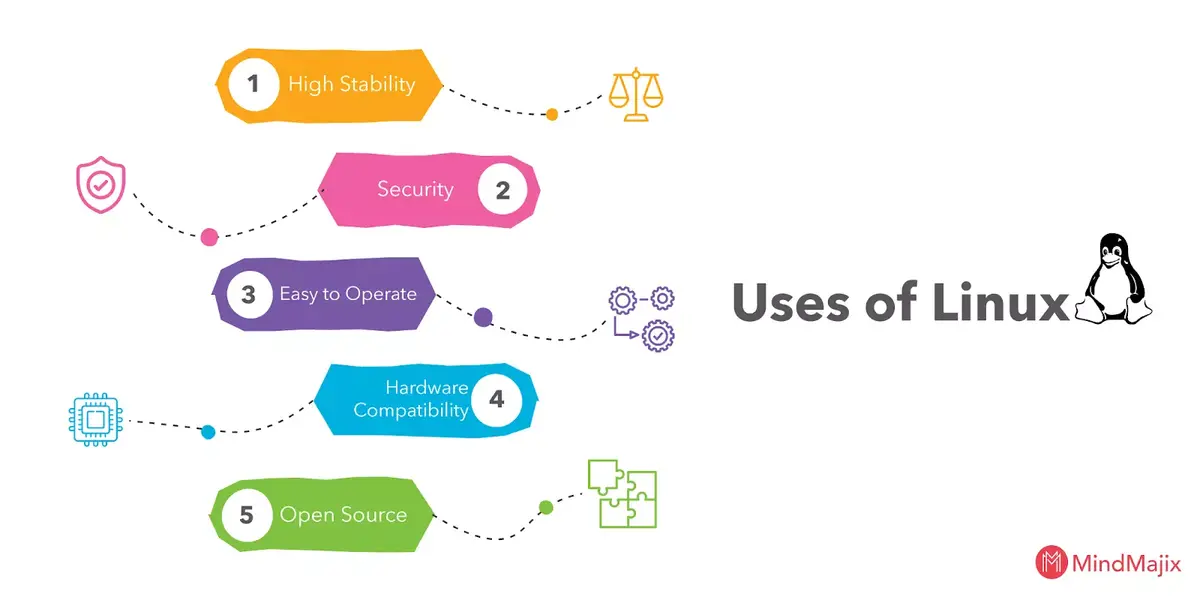
68. Why we use LINUX?
Ans: We are many reasons, in that few important reasons are listed out. Following are
- High Stability: It is very stable and does not lead to crashes, it runs fastly as it is when it installed first.
- Security: It is a dependable server, that offers high security to the user. Using Linux on your system it is easy to avoid viruses and malware. The attacker cannot change any changes in the system until the user logged in as the root user.
- Easy to Operate: Linux is easy to operate and we can install it easily onto the system because all the variants of Linux have their own software repositories. You can update the system periodically with just a few clicks or you can set automatic updation.
- Hardware Compatibility: Linux can use on any hardware, it doesn’t have any hardware restrictions. It uses efficiently all system resources.
- Open Source: The source code is available as it is under Free and Open Source Software(FOSS).
69. What are the features of the Linux operating system?
Ans: Following are the features of the Linux Operating System
- Portable: Software can work on different types of hardware in the same way. It can carry easily in pen drives and memory cards.
- Open Source: Source code available for free, and its community-based development project.
- Multi-User: Multiple users can use ram, applications and run programs at the same time.
- Multiprogramming: Multiple programs or applications can run at the same time.
- Shell: It has a special interpreter program where you can execute programs and commands of the system.
- Security: It provides authentication, authorization, and encryption to provide security to the data.
70. Differentiate between BASH and DOS?
Ans: Difference between Bash and Dos
| Bash | Dos |
| Commands are case sensitive | Commands are not case-sensitive |
| Backward slash(/) represents directories separator | ‘/’ represents command arguments |
| Forward slash ‘’ represents the escape character | ‘’ represents directories separator |
| Does not follow conventions naming in files | Follow naming convention in files |
71. What is meant by internal commands and external commands?
Ans: Internal Commands are the Commands directly run by the shell known as internal commands and there is no separate process to run the commands. Examples include cd, echo, pwd, and history.
On the other hand, the External Commands are the Commands which are run by the kernel and are known as external commands and every single command has its unique process id. ls, grep, cat, and rm.
Linux Networking Interview Questions
72. What is meant by PIPE in Linux?
Ans: It is a form of redirection that is used in Linux, it is used to combine more than two commands and the output of one command can take as input to the next command.
Syntax:
command_1 | command_2 | command_3 | .... | command_NExample:
ls | grep example
This command first executes ls to list all files and directories in the current directory, and then pipes the output to grep, which filters the output to display only the lines containing the word "example".
73. Describe how a parent and child process communicates with each other?
Ans: Communication between a parent process and its child process in Linux can be achieved through various inter-process communication (IPC) mechanisms. These mechanisms allow processes to exchange data, synchronize their actions, and coordinate their execution. The types of IPC mechanism in Linux are:
- Pipes: Allow communication by connecting the output of one process to the input of another.
- Sockets: Enable communication between processes over a network.
- Message Queues: Facilitate asynchronous message passing between processes.
- Shared Memory: Allows multiple processes to access the same memory region concurrently.
- Signals: Software interrupts used to notify processes of events or conditions.
74. What is a Stateless Linux Server?
Ans: It is a centralized server that does not have any exists states on the working station. It may have scenarios when a state of a particular system takes a snapshot then, the user wants all other machines to be in that particular state.
75. Explain the features of Stateless Linux Server?
Ans: Features of Stateless Linux Server
- Stores the prototype of every system.
- Stores the snapshot was taken.
- Stores the home directories.
- Uses LDAP, which contains the information about which snapshot should run on which system.
76. What is Zombie Process?
Ans: It is a process whose execution is completed but even the information exists in the process table. It occurs for the child process because the parent process needs to read the child process status. Once it is completed using the wait system call, then the zombie process is removed from the process table.
77. Explain the work of the Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination on the Linux operating system?
Ans: In Linux, the Ctrl+Alt+Del key is used to restart the computer, and it does not display any confirmation message before rebooting the system.
| Discover reputable institutions offering top-notch Linux training in Bangalore, providing aspiring professionals with the knowledge and skills essential for success in the tech industry. |
78. Why is Linux considered more secure than other operating systems?
Ans: Linux is an open-source operating system, nowadays it is rapidly growing in the technology market. We have a few reasons why Linux is more secure than other OS.
- The perk of accounts: Linux allows only a few users to access the system. Thus, the virus cannot attack the whole system, it may cause only a few files in the system.
- Strong Community: Linux users first accomplished the files before they open. So they can save their systems from vulnerabilities.
- Iptables: Iptables are used by the Linux because it checks the security circle of the system.
- Different Working Environment: Linux system has different working environments like Linux Mint, Debian, Arch, and many more, these working environments protect from the virus.
- Recording in Linux: It maintains log history because later it can view the details of the system files easily.
- Few User: Linux users are less compared to others, due to this security will be more.
79. What is the tail command in Linux?
Ans: The tail command displays the last part of a file. Generally, users don't need every logline to troubleshoot. Instead, you want to check what your logs say about the most recent request to your application.
tail Example:
$ tail -n 100 /var/log/httpd/access_log
80. What is the cat command in Linux?
Ans: In Linux cat command concatenates and prints files. Users might issue cat to check the contents of your dependencies file or to confirm the version of the application that you have already built locally.
cat Example:
$ cat requirements.txt
flask
flask_pymongo81. What is the grep command in Linux?
Ans: grep searches file patterns. If you are looking for a specific pattern in the output of another command, grep highlights the relevant lines. Use this grep command for searching log files, specific processes, and more.
grep Example:
$ cat tomcat.log | grep org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina.start
12-Jan-2018 17:08:35.542 INFO [main] org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina.start Server startup in 681 ms82. What is ps command in Linux?
Ans: ps command displays process status. Use this ps command to determine a running application or confirm an expected process.
ps Command Example:
$ ps -ef
$ ps -ef | grep tomcat83. What is the env command in Linux?
Ans: env command allows users to set or print the environment variables. During troubleshooting, users can find it useful for checking if the wrong environment variable prevents your application from starting.
env Command Example:
$ env
PYTHON_PIP_VERSION=9.0.1
HOME=/root
DB_NAME=test
PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin
LANG=C.UTF-8
PYTHON_VERSION=3.4.6
PWD=/
DB_URI=mongodb://database:27017/test84. What is the top Command in Linux?
Ans: top command displays and updates sorted process information. Use this top command to determine which processes are running and how much memory and CPU they are consuming.
85. What is the netstat command in Linux?
Ans: netstat command in Linux shows the network status. This netstat command shows network ports in use and their incoming connections.
86. What is the lsof command in Linux?
Ans: ls of command lists the open files associated with your application.
87. What is the df command in Linux?
Ans: Users can use the df command to troubleshoot disk space issues. Here df stands for display free disk space.
Syntax:
df [options] [file|directory]
df Command Example:
df -h
Here, the -h option is used to display the output in a human-readable format like kilobytes (K), megabytes (M), gigabytes (G), etc.
88. What is a du command in Linux?
Ans: The du command in Linux is used to retrieve more detailed information about which files use the disk space in a directory.
Syntax:
du [options] [file|directory]
du Command Example:
$ du -sh /var/log/*
1.8M /var/log/anaconda
384K /var/log/audit
4.0K /var/log/boot.log
0 /var/log/chrony
4.0K /var/log/cron
4.0K /var/log/maillog
64K /var/log/messagesHere, the -s displays only a summary of total disk usage for each specified directory, and the -h: Displays output in a human-readable format (e.g., kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes).
89. What is the iptables command in Linux?
Ans: iptables command blocks or allow traffic on a Linux host, similar to a network firewall. This iptables command may prevent certain applications from receiving or transmitting requests
Syntax:
iptables [options] [chain] [rule]
The following options are available for the iptables:
- -A: Append a rule to a chain.
- -D: Delete a rule from a chain.
- -P: Set the default policy for a chain.
- -I: Insert a rule into a chain at a specific position.
For example, the following command adds a rule to the INPUT chain to drop all incoming traffic from the IP range 192.168.1.0/24.
iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j DROP
90. What is the difference between Linux and Windows?
Ans:
| Linux | Windows |
| Linux is available for FREE | It is paid software |
| It is an Open-Source operating system | It is not an open-source OS |
| Linux customization is possible | No customizations are available |
| It provides high-level security | Can't defend against virus and malware attacks unless it is paid |
| Primary partitioning and logical partitioning available for boot | Booting is available while primary partitioning only |
| BackSlash separates directories | The forward slash separates directories |
| File names are case-particular | Irrespective of the case while naming files |
91. What does the cd - command do?
Ans: cd- command go to the previous directory.
92. What does cd command do?
Ans: Go to $HOME directory
93. What does (cd dir && command) do?
Ans: The command (cd /var/log && ls -l) changes the directory to /var/log, lists the contents of the directory using ls -l, and then returns to the original directory
Example:
(cd /var/log && ls -l)
In this example, the command first changes the directory to /var/log, lists the contents of the directory using ls -l, and then returns to the original directory (/home/user).
94. What does pushd command do?
Ans: The pushd command in Linux puts the current directory on the directory stack, allowing you to navigate between directories efficiently.
Syntax:
pushd [directory]
Example:
pushd /var/log
95. What is ls -lSr command?
Ans: The ls -lSr command in Linux is used to list files and directories in the current directory in long format (detailed listing) sorted by size in descending order (largest size first).
- ls: Command to list directory contents.
- -l: Option to use long listing format.
- -S: Option to sort files by size.
- -r: Option to reverse the sort order, making it descending (largest size first).
96. What is du -s * | sort -k1,1rn | head command used for?
Ans: This command is used to display the top disk space users in the current directory. Let us understand it's working in the following way:
- du -s *: Command to calculate the disk usage (in kilobytes) of each file and directory in the current directory.
- sort -k1,1rn: Command to sort the output based on the first column (disk usage) in reverse numerical order.
- head: Command to display only the first few lines of the sorted output, which represent the top disk space consumers.
97. What does this du -hs /home/* | sort -k1,1h command do?
Ans: This command sort path by easy to interpret disk usage.
98. What is df -h command?
Ans: This command shows free space on mounted file systems. The df -h command in Linux is used to display free space on mounted file systems in a human-readable format. It provides information about the total disk space, used space, available space, and usage percentage for each mounted file system.
99. What is df -T command?
Ans: The df -T command in Linux is used to display information about disk space usage in the system along with the filesystem type for each mounted filesystem
100. What is fdisk -l command used for?
Ans: The fdisk -l command in Linux is used to display the sizes and types of disk partitions on the system. It lists information about all available disk partitions, including their sizes, types, and start and end sectors. This command must be run as root (sudo fdisk -l) to display partition information.
101. How do you kill the program using one port in Linux?
Ans: To kill a program using a specific port in Linux, you can use the fuser command with the -k option followed by the port number and protocol (TCP or UDP). For example, to kill a program using port 8000, you would use:
sudo fuser -k 8000/tcp
102. How do you limit memory usage for commands?
Ans: The ulimit command allows us to limit memory usage for commands in Linux. By setting the virtual memory size (in kilobytes), you can restrict the memory usage of a command.
Syntax:
ulimit -Sv [memory_limit]
Example:
ulimit -Sv 1000
This command limits the memory to 1000 KBs (1 MB)
103. How do you get the full path of a file in Linux?
Ans: You can use the following commands to get the full path:
- The realpath command gives the absolute path of a file or directory.
realpath [file_path] - The readlink command with the -f option also gives the absolute path of a file or directory.
Syntax:
readlink -f [file_path]
104. How do you list the contents of tar.gz and extract only one file?
Ans: We can use the below commands to view and extract single file for tar file
-
tar tf file.tgz
-
tar xf file.tgz filename
105. How do you find who is logged in?
Ans: To find out who is currently logged in to the system, you can use the w command which displays the users as shown below:
106. How do you check the permissions of each directory to a file?
Ans: It is useful to detect permissions errors, for example when configuring a web server. So, to check the permissions of each directory leading to a file, you can use the namei command with the -l option followed by the path to the file.
namei -l /path/to/file.txt107. How do you run the command every time a file is modified?
Ans: To run a command every time a file is modified, you can use a combination of the inotifywait command and a loop.
Example:
while inotifywait -e close_write document.tex
do
make
done108. How to copy text to the clipboard?
Ans: we can use the command ‘cat file.txt | xclip -selection clipboard’ to copy the text to the clipboard.
109. How do you check resources usage?
Ans: This is an important Linux Interview Question to test your understanding of the Linux Development Environment. We can use the command /usr/bin/time -v ls to check the resource usage in the Linux File System.
110. How do you run a command for a limited time?
Ans: To run a command for a limited time, you can use the timeout command followed by the duration and the command you want to run. An example of this command is given below
timeout 10s ./script.sh111. How do you combine two lines from two sorted files in Linux?
Ans: Use this command: comm file1 file2.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much time will it take to Learn the Linux?
Well, the time to learn Linux depends on the individual's learning capacity. However, MindMajix offers a Linux Networking Course that can help you learn Linux Networking within 30 hrs of the session, and 25 hrs of Lab Access to do hands-on practice on the Linux commands. With continuous practice on a daily basis, you can easily complete the Linux course by MindMajix.
2. How do I acquire knowledge to become a Linux System Admin?
It is obvious that acquiring the knowledge to become a lot of Linux System Admin requires practice. So, create a roadmap and stick to it. Try to learn and practice at least 3-4 commands every day. And, if you are stuck somewhere, reach out to the Linux Community for support. Also, RHSA(Red Hat Certified System Administrator) certification can also help you to gain strong expertise in Linux administration.
3. What are the roles and responsibilities of the Linux Administrator?
The basic roles and responsibilities of the Linux Administrator:
- Install, configure, and manage the Linux Operating systems and other software, packages, etc.
- Monitoring the system’s performance, and troubleshooting the issues within the Linux Systems.
- Implementing security measures to protect the Linux System from unauthorized access.
- Installing and managing the network services like DNS, DHCP, and LDAP.
- Apart from this, Linux Administrators also have to collaborate with the other teams (cross-functional collaboration) to ensure the compatibility of the Linux System with the others.
The above insights are sufficient for you to understand the importance of the Linux administrator so that you can deliver your best work as the Linux Admin.
4. What secondary skills are needed to make a career in Linux Development?
Since the Linux System is often integrated with other platforms and systems, you should have a good understanding of scripting languages like Python or Perl for automation and tooling. You should also have Knowledge of version control systems such as Git for managing codebase changes. Also, Docker and Kubernetes, as they are widely used in modern Linux-based environments, can help you to achieve higher growth over Linux development.
5. What is L1, L2 and L3 in Linux Administration?
Knowing about the L1(Level 1) , L2(Level 2) and L3((Level 3) in the Linux Administration will help you to clearly understand your roles and responsibilities in the team. L1, L2 and L3 are the support levels in Linux that allows us to provide the technical assistance provided to users according to requirement.
L1 Support is the First-line support or helpdesk support in which we handle basic user inquiries and technical issues. L2 Support deals with more complex technical issues that require deeper understanding of systems and infrastructure. Finally, L3 provides fixes for highly complex technical issues like kernel debugging, performance optimization, and security hardening.
Conclusion
Wrapping up what we learned, Linux has become an important component of most modern Infrastructures, system administration, cloud computing, cybersecurity, software development, etc. Hence, you can explore multiple career opportunities in the IT Industry. The above most asked Linux Interview Questions would help you to gain expertise in Linux Kernel Development. So, you can easily gain expertise on Linux through this blog by MindMajix and grow your career as a Linux Developer.
Explore Linux Sample Resumes! Download & Edit, Get Noticed by Top Employers!
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Linux Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| Linux Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Linux Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Linux Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |

Usha Sri Mendi is a Senior Content writer with more than three years of experience in writing for Mindmajix on various IT platforms such as Tableau, Linux, and Cloud Computing. She spends her precious time on researching various technologies, and startups. Reach out to her via LinkedIn and Twitter.










