- Home
- Blog
- Quality Assurance
- Quality Analyst Job Description

A quality analyst's function is crucial in a software company from the beginning to the end of the project. Their primary task is to complete manual testing before moving on to the automation phase. They must guarantee that all testing functionalities are in good functioning order.
A quality analyst assists with project planning, design, and execution, which can range from simple to complicated tasks. In order to validate the test cases in light of the system requirements, they work together with the organization's development team.
Implementing quality assurance principles and practices throughout the SDLC is the responsibility of a quality analyst.
Quality Analyst Job Description - Table of Contents
- Who is a Quality Analyst?
- What Does a Quality Analyst Do?
- Job Description
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Skills
- Qualifications and Requirements
- Companies that Hire
- Salary Trends
- Take Quality Analyst skills To Next Level
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Who is a Quality Analyst?
A quality analyst is often a trained analyst who collaborates with management, design, and development teams. They remain involved in all phases of a product's development, from the beginning to the end. Quality analysts now hold a prominent position in the field of software development. They monitor quality assurance in regards to things like software usability and the broader SDLC, as well as validating test cases (software development life cycle).
These professionals in quality control are skilled in QA testing methods that identify a product or service's drawbacks. They are trained to spot these inconsistencies and get them fixed, whether it be a user-side issue that degrades their experience or a preventable hardware flaw that raises production costs.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in QA, then visit Mindmajix - a global online training platform: "QA Certification Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
What Does a Quality Analyst Do?
Analysts of quality control make sure that goods and services adhere to accepted standards. They perform this work as part of their duties in a variety of sectors, including technology, manufacturing, and healthcare. In order to increase and decrease quality, these analysts frequently collaborate closely with different teams from engineering, operations, and customer support.
A quality analyst needs to have a firm grasp of quality management principles and techniques in addition to being able to assess and solve problems. People in this position need to be able to analyse data and spot trends and patterns that point to quality problems or places where improvements may be made. The ability to create and implement quality management systems that adhere to industry laws is also essential for quality analysts.
Quality Analyst Job Description
You must comprehend the function of this position in order to create a strong analyst job description. The major objective of this position is to test all of the software's technical and functional features, which is crucial for producing a high-quality product. They pinpoint software flaws while collaborating closely with the IT department.
An effective quality analyst should have excellent problem-solving skills and attention to detail. They must be able to put quality control procedures into practise and give pertinent teams precise feedback.
Quality Analyst Roles and Responsibilities
The importance of quality analyst specialists has grown across several industries, including manufacturing, customer service, and software development.
Regardless of the field they choose to work in, a quality analyst has many tasks. This is an assortment of it.
- Planning should be a quality analyst's main priority, and they should check that the quality criteria are in line with the organization's policies.
- A quality analyst is accountable for putting a plan into action and fixing any faults. They must also determine whether the plan is appropriate in light of its functionality, performance, dependability, and compatibility.
- They should be familiar with quality assurance testing equipment.
- They determine the root cause analysis technique to find the fault and gather all the necessary statistics.
- Decreased employee churn rates
- Convey information to new hires and provide knowledge
- Creates a positive relationship between the management and the staff
- Managing a variety of resources at work
- Delivering effective responses to a range of problems.
Depending on the business and the domain you select, a QA's duties may become more precise. But the training and abilities of a good analyst are consistent.
Quality Analyst Skills
Because of increased company innovation and customer demand for technology, the skill set required to become a quality analyst is rising. Yet, the following skills are those necessary for a quality analyst:
Skill #1: Communication
They may deal with clients, partners, and different powerful people inside a business. To keep responsible authorities informed of the essential procedures, everything from reporting bugs to disclosing weaknesses must remain transparent. Any communication, whether informal or formal, oral or written, must be error-free, according to QAs.
Skill #2: Detail-oriented
Being specific ensures that supply chain disruptions don't happen, and it lowers the likelihood of reworking and adding extra time. The team's significant product innovations and even the smallest contributions must be carefully reviewed in order to achieve this competency. Good workplace etiquette, which is necessary in the corporate sector, is the result of paying such close attention to the details.
Skill #3: Collaboration and Teamwork
QAs may interact hierarchically with managers, corporate executives, programmers, and testers. Once all product uncertainties have been discussed and resolved with these specialists by the QA, the product is then launched onto the market. As a result, value-centric teamwork and the highest level of coordination are two qualities that enhance any QA's skill set.
Skill #4: Flexibility in Analytical Approaches
It is advantageous for QAs to be knowledgeable about production procedures, design techniques, and desired product attributes. This is especially true when adhering to detailed rules that protect a product's originality. QAs are a flexible resource for boosting a company's quality control system because they have a thorough understanding of a variety of analytical techniques.
Skill #5: Time Management
When it comes to deadlines, quality analysts are thinking about more than simply their own objectives. Their job is to work closely with other teams that have deadlines. In other words, a QA's efficiency increases in direct proportion to their time management skills.
Skill #6: Critical Thinking
By using critical thinking, there is a greater chance of seeing mistakes and fixing them before a product moves further in its development life cycle. Despite the situation, QAs must come up with solutions that either permanently fix the problem or replace an undesired trait with a more desirable one. QAs must have a firm knowledge of their problem-solving abilities because they can give other teams resolution-based targets.
Quality Analyst Qualifications and Requirements
Now that you are aware of what a quality analyst is responsible for and the skills required, let's look at the educational requirements to become one.
- Comprehensive familiarity with HTML, JavaScript, Scrum, project management, Python, Java, and SQL
- 2-4 years of demonstrable expertise in the field of software testing
- Bachelor's degree in management information, computer science, or a closely related discipline
- 3 years of technical quality analyst experience
- Comprehensive understanding of the QA's tools, concepts, and related processes
- Microsoft Office, QA programmes, and databases certifications such as quality engineer, quality auditor, and quality improvement associate
[ Related Article - Core Java Interview Questions ]
Companies That Hire Quality Analyst Engineers
QA engineers are hired by businesses in a range of sectors, such as software development, healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and gaming. As more businesses adopt digital transformation and create new software products, demand for QA engineers is anticipated to rise.
Companies frequently seek applicants with a solid technical background, familiarity with software development processes, and background in software testing and quality assurance when hiring QA engineers. Also, employers place a great importance on people with strong communication, problem-solving, and critical thinking abilities.
Quality Analyst Salary Trends
Thoughtworks, Inc.: 10,65,500/year
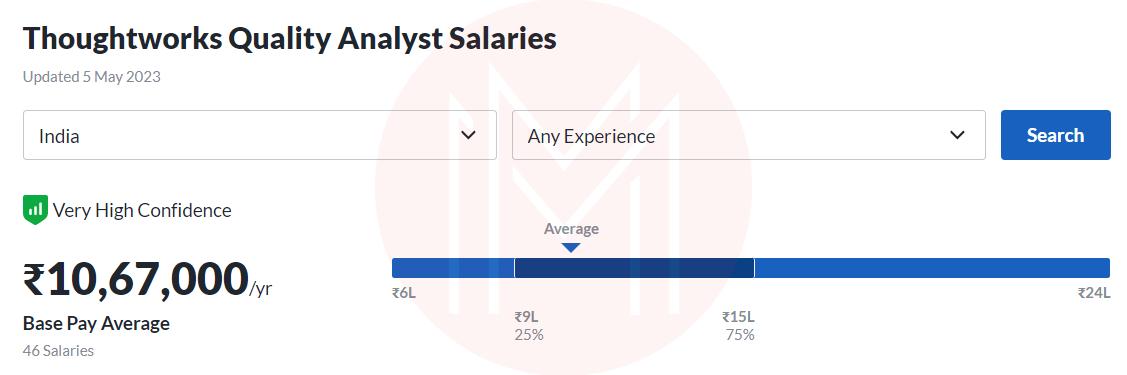
Accenture: Rs. 6,38,499 /year
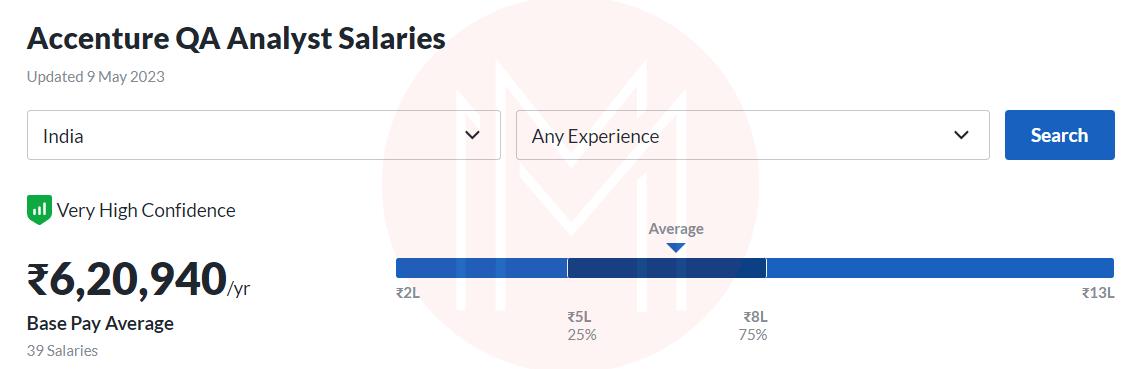
TCS: Rs. 6,00,000 /year
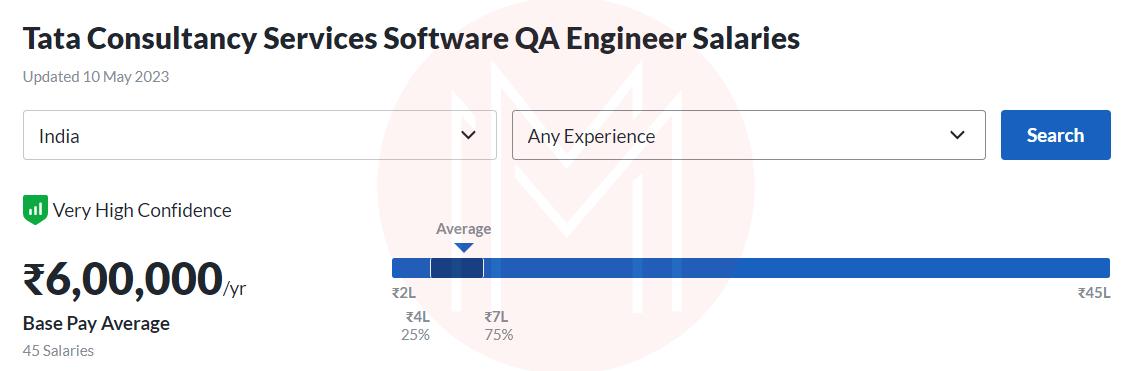
Cognizant: Rs. 5,83,447 /year
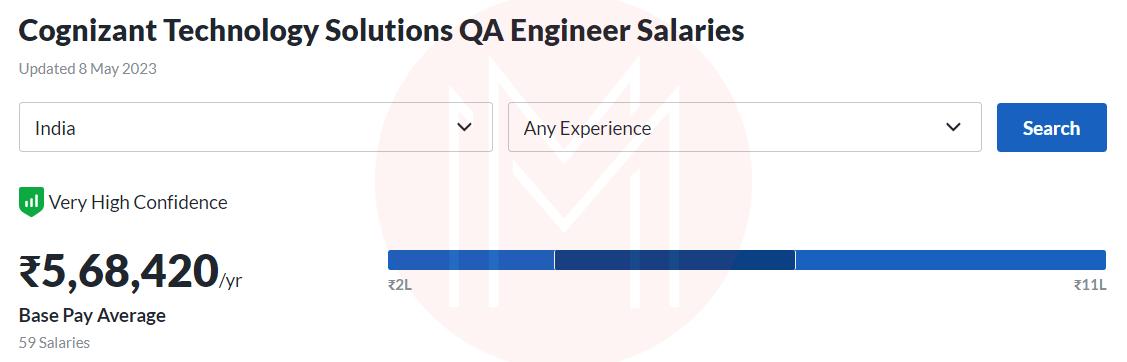
Deloitte: Rs. 6,00,000 /year
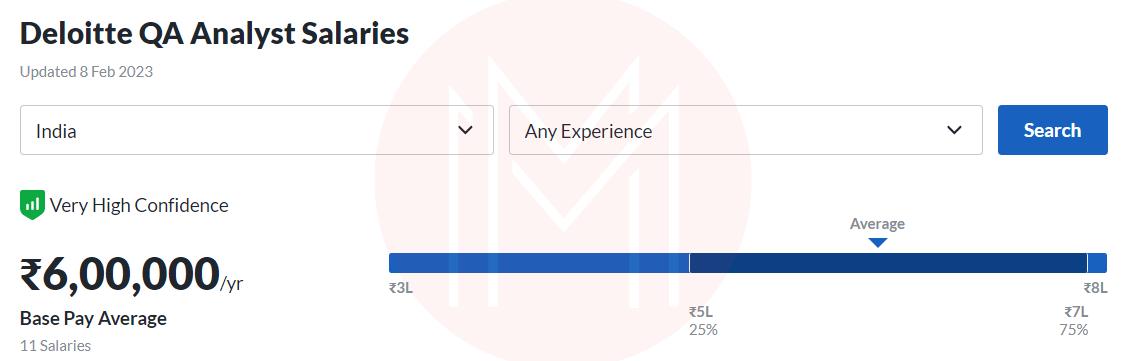
HCL Technologies Ltd.: Rs. 370,000 /year
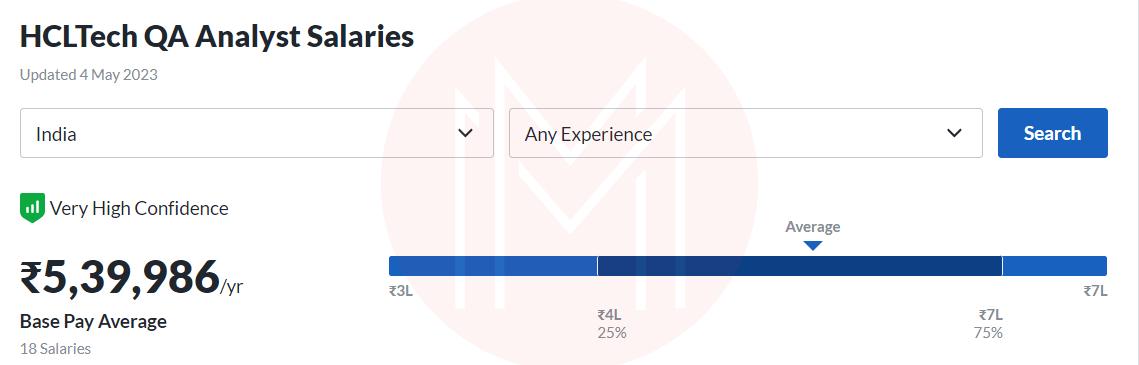
Wipro: Rs. 5,10,382 /year
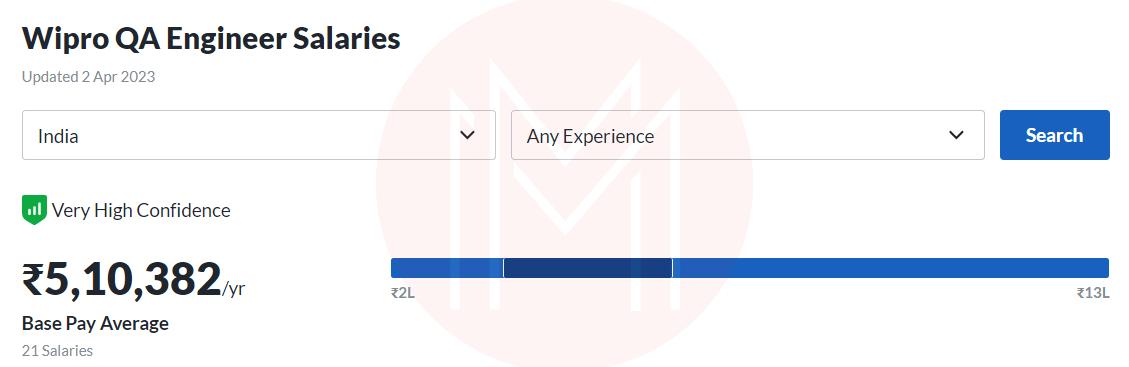
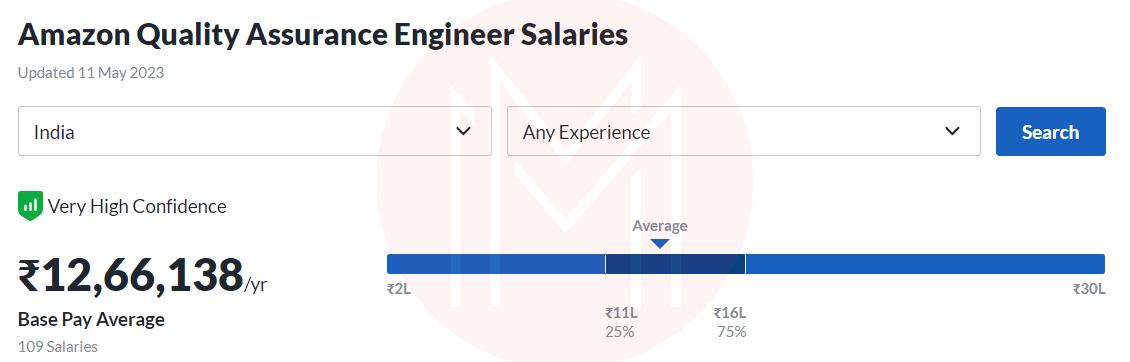
Amazon: Rs. 12,42,048 /year
How To Take Your Quality Analyst Skills To Next Level?
1. Look Into The Newest Trends
Any QA analyst who isn't given access to all the information may be losing out on simpler and more useful ways to teach, grade, and enhance your customer support team.
The newest trends are something you should be aware of and keep up with, but you don't have to follow them completely. Yet, it does keep you informed so you may use fresh, more effective strategies when they are called for.
Industry trends might change quickly, but a skilled quality assurance professional will be able to use the most recent trends to your advantage.
2. Deliver Coaching With a Goal in Mind
In order to help employees do better work, coaching is essential. The coach may be the customer service quality analyst themself, or they may offer suggestions to management. Role-playing may be a part of effective coaching; the agent should be forced to deal with a scenario that caters to their shortcomings.
As a result, they can experiment with various strategies and fixes without worrying about upsetting actual clients. A clear objective should be established, such as guiding the caller through a challenging technical issue or making them happy enough to recommend the business to others.
3. Track Personal Development
After coaching, QA analysts need to keep an eye on agents' development to assess how they're incorporating what they've learnt.
It might not be sufficient to only trust the employee to make improvements to their work. Effective quality assurance involves monitoring agents' personal growth and providing further, specialised training as required. In this regard, call monitoring and one-on-one feedback can be helpful.
4. Make Relevant Scorecards With Important Metrics
Scorecards are a quick and easy approach to evaluate the abilities of call centre personnel.
Customer service quality analysts should talk with management about the aforementioned attributes and KPIs before creating personalised scorecards based on this information.
5. Regular Data Analysis
Data should be the foundation for all decisions made on tools, technology, and processes.
Customer surveys, scorecards, changes in sales trends over specific time periods, customer referrals, and studying response times can all be used to gather data from customer encounters to track how agents are performing overall.
When providing agents with feedback and coaching them to improve their performance, this data can be utilised. Frequent customer surveys are a wonderful approach to track the effectiveness of training or adjustments because errors can be fixed before they do further harm if the feedback reveals a decline in the quality of their experience.
| Learn Quality Analyst Interview Questions and Answers that help you grab high paying jobs |
Quality Analyst FAQs
1. What does a Quality Analyst do?
Quality analysts make sure that goods and services adhere to specified criteria for quality. They perform this work as part of their duties in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and technology.
2. What makes a good Quality Analyst?
To be successful as a quality analyst, you must have excellent analytical abilities, attention to detail, and problem-solving capabilities.
3. What are the duties and responsibilities of a Quality Analyst?
Prior to the delivery of goods to customers, quality analysts are responsible for running quality tests and validating test cases. In the end, you'll collaborate with a small team to make sure our products live up to the standards of quality set by our company.
4. Who does a Quality Analyst work with?
In order to increase and decrease quality, these analysts frequently collaborate closely with different teams from engineering, operations, and customer support. A quality analyst needs to have a firm grasp of quality management principles and techniques in addition to being able to assess and solve problems.
5. What skills are required for a quality analyst?
The quality analyst is the finder if the developer is the fixer. In software development, the capacity to recognise and convey faults in an application is essential.
The quality analyst (QA) searches for application issues as well as process defects that may have contributed to these issues. The QA also works with a development team to find solutions to such issues, ensuring that a programme is debugged before going live.
6. Does quality analyst require coding?
Quality analysts (QA) assess the test's functionality and overall quality. Following the completion of the development process, these analysts test the software product. Because a QA's job is less technically oriented than a developer's, they might not need to learn how to code or write code.
Conclusion
Because of the intense rivalry in the IT industry, hiring a qualified analyst is not only prudent but also predictable. Considering what a quality analyst does, their duties, and the abilities needed, you can now decide if this career path is right for you.
The current situation calls for quality analyst professionals to concentrate on developing their abilities to deal with complex challenges by expanding their knowledge through a variety of industry-recognized certification training programmes in areas like Agile, DevOps, IT Service Management, Project Management, and Quality Management
They are essential in getting top-notch software onto the market. They are also responsible for finding and fixing software bugs. In spite of this, one of their job duties includes testing to support or facilitate comprehensive quality management. They not only guarantee the market release of a mistake-free product, but they also guarantee consumer satisfaction levels.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| QA Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| QA Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| QA Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| QA Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .















