SAP Materials Management (MM) is one of the modules in SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) that offers organizations with inventory, warehouse, and materials management capabilities. The primary objective of SAP MM is to ensure materials are always available in adequate quantities and there are no gaps or shortages in the company’s supply chain.
It also assists supply chain professionals, along with other SAP users, in completing the purchase of products in a cost-effective and timely method. SAP MM also accommodates daily changes taking place in processes. Being one of the crucial modules, SAP MM plays an important role in the supply chain of a manufacturer. It can be easily integrated with other components of ECC, such as Production Planning (PP), Human Capital Management (HCM), Sales and Distribution (SD), Finance and Controlling (FICO), Plant Maintenance (PM), and Quality Management (QM).
In this post by MindMajix, let’s dive deeper into SAP MM and find out more about it.
| What is SAP MM - Table of Contents |
What is SAP MM?
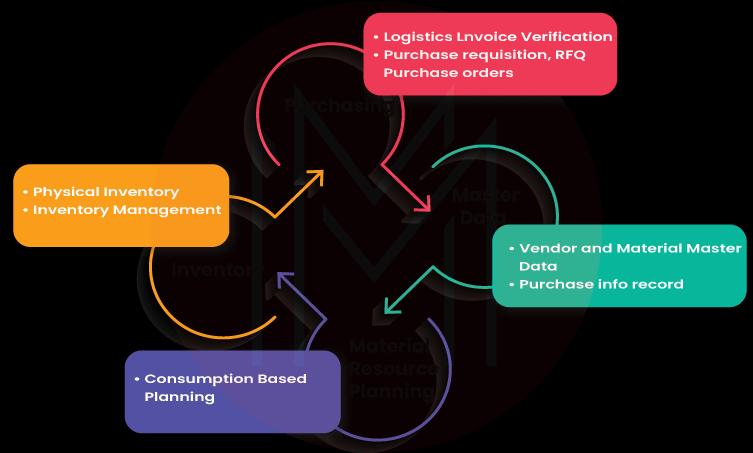
As mentioned above, SAP Material Management is a module of the SAP ERP component that helps companies with the management of material, inventory, and warehouse in the supply chain process. It is an integral part of the logistics functions of SAP ECC that comprises a variety of components and sub-components. Herein, some of the extensively used components are Master Data, Inventory and Purchasing.
All these components have subcomponents that are important in certain business processes and all such processes have been executed through transactions in the SAP MM process flow.
In SAP, the transaction means processing specific information to complete business process needs. For instance, if you have bought 10 pieces of buckets, you can perform a specific transaction code (t-code) that will reflect such changes in SAP.
Most business processes comprise different SAP transactions to be achieved and are generally spread over one, two, or multiple modules.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in SAP Material Management, then enroll in the "SAP MM Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
Organizational Structure
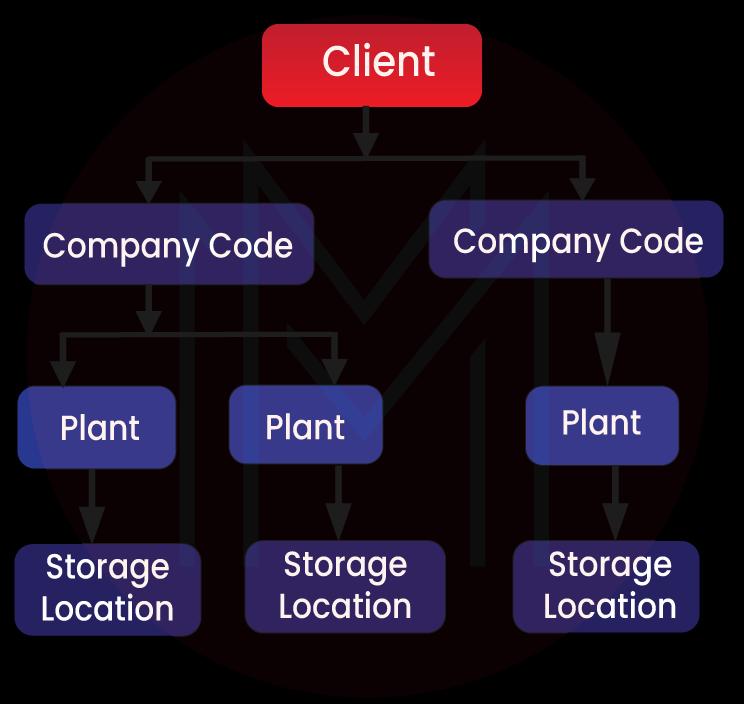
The organizational structure is referred to as the framework of an organization as per the business it is conducted. This structure comprises several levels that have either indirect or direct relations with each other. Furthermore, the organization structure is also known as the enterprise structure, which is created of several organizational units that have relations with each other.
-
Plant
A plant is referred to as an operational facility that is within an organization code, such as a production facility, a branch office, or a regional office. As a company unit within logistics, the plant helps to subdivide the enterprise from the viewpoints of materials planning, maintenance, procurement, and production.
-
Valuation Area
Materials could be valued at either the company code level or the plant level. Generally, the level at which materials get valued is referred to as the valuation area.
-
Storage Locations
A storage location is another organizational unit that, in reality, differentiates between the varying material stocks in the plant. The storage location is one such place where stock is placed physically. A plant can comprise several storage locations. All the data gets stored at a storage level for a specific storage location.
-
Purchasing Organisations
This one is within logistics and helps to subdivide the enterprise as per the requirements of purchasing. It procures services and materials, negotiates terms and conditions of purchase with vendors and takes responsibility for transactions.
-
Purchasing Groups
A purchasing group is key for the customer(s) in SAP MM. It is liable for procuring a class of materials or materials and is the main channel for the dealings of a company with its suppliers.
Features of SAP MM
Jotted down below are some key features of SAP MM
- It is capable of handling both inventory management and raw material management
- SAP MM takes care of several business aspects, such as invoice verification, warehouse management, material validation, procurement, vendor evaluation, material requirement planning and more
- It makes sure there is no shortage or lack of materials in the supply chain.
- It helps accelerate productivity while decreasing the overall costs of procurement.
- SAP MM assists in enhancing the efficiency of procurement activities.
Components of SAP MM
The SAP MM system comprises many components that are integrated with one another. This integration helps make it easier for every department to share information with other departments. This way, the data gets updated in real-time. SAP MM is further divided into five major components, each one of them comprising different sub-modules. Here are the fundamental components of this suite:
1. MM - CBP (Consumption-Based Planning)
Consumption-based planning generally uses previous consumption values to foresee future needs through statistical procedures. The main role of this component is to keep track of stocks and create procurement proposals automatically for production and purchasing. The proposal triggers whenever the stock levels go down a set reorder point or by foreseeing needs through previous consumption values.
2. MM - PUR (Purchasing)
This component makes sure streamlined communication among everybody in the procurement process, thus, ensuring that the purchasing unit functions with smoothness. The major tasks of this unit are:
- Taking care of external procurement of services and materials
- Comprehending potential sources of supply for a need
- Tracking deliveries from vendors
- Tracking payments to vendors
3. MM - SRV (External Services Management)
This component is helpful in supporting bid invitations, acceptance of services, aware/order placements, and invoice verification. It offers a platform for handling and coordinating external services. Basically, MM SRV supports two different types of external services, such as
- Unplanned services where the required scope is unavailable, and the procurement is dependent on the value limit
- Planned services where the scope and nature of requirement are known at the beginning of the procurement phase
4. MM - IV (Inventory Management)
This specific component deals with the below-mentioned tasks:
- Managing and tracking physical material stocks on the basis of their value and quantity
- Documenting, entering, and planning the movement of products
- Maintaining the physical inventory of products
5. MM - IV (Logistics Invoice Verification)
The MM - IV is a procedure that comes towards the end of the logistics supply chain. It comprises varying tasks, such as purchasing, invoice verification, inventory management, and more. This component is helpful in verifying incoming invoices on the basis of quantity, content, and prices. The moment the vendor sends an invoice, the logistics invoice verification adds the same to the system and passes it to the financial account and other elements in the materials management.
Benefits of SAP MM
With evolving customer expectations and demand, the efficiency of a company is related to its competency to cater to market demands in a short time. To make sure product delivery is as seamless as possible, the business must maintain the correct stock quantity at the right time.
Having an effective material management process in place helps avert supply gaps and lack of raw materials and inventory while enhancing the overall efficiency of the supply chain. With SAP MM, you can easily automate material management and activities of procurement; thus, making the process more suitable.
Keeping that in mind, here are some benefits of SAP MM that you must keep in mind before using this module:
- It improves the overall management of inventory.
- It increases the transparency when it comes to inventory management.
- SAP MM decreases and eliminates the losses of inventory.
- It enhances the delivery time of a product.
- It decreases expenses on storing unnecessary materials.
- You can decrease the labor and time spent on inventory management with SAP MM.
- It also decreases manufacturing cycle time.
- SAP MM helps reduce material wastage by avoiding stocking unnecessary and obsolete products.
- It decreases labor costs and optimizes the employment of labor.
SAP MM Module Components

Here are all the important SAP MM module components that you must know about:
1. Master Data
Master data is basically used for any type of transaction. Whether you are creating a physical inventory or transferring stock, everything needs master data. The end customer will be able to track each transaction with master data. There are different types of master data, such as:
- Warehouse management data
- Material data
- Vendor data
- Pricing data
- Customer data
2. Material Requirement Planning
This gets processed according to the bills of different materials. The need for such materials is decided as per the bills.
3. Purchasing
The primary goal of this task is to get services and materials. Purchasing comprises buying materials, monitoring payments of vendors, and deciding supply sources. The tasks assist employees in fulfilling the needs of the material planning department.
4. Inventory Management
This component deals majorly with the management of the inventory of products. It comprises several key processes, like issuing products, definition, movement of products, product receipt, and more.
5. Material Valuation
Material valuation helps to determine the stock value of a specific material. The stock quantity and material price comprehends the stock value. Valuation activities, like FIFO, LIFO and material price range, are also linked to material valuation.
6. Invoice Verification
Whenever an invoice is posted in the SAP system, the invoice data available in the MM Module gets updated. Post evaluating the details of the invoice, it is forwarded for processing. This component covers invoice receipts from vendors, automatic invoices, and more such activities.
7. Physical Inventory
There are different activities that get covered under physical inventory, such as:
- Inventory creation
- Count area
- Post difference
- Inventory session
- Cycle count
8. Service Management
Under the component of service management, activities like service master and service entry sheet are covered.
| Visit here to learn SAP MM Training in Pune |
Types of Procurement Process
Let’s put an eye on two different types of procurements available in the SAP MM module
1. Basic Procurement
Herein, the procedure of purchasing adequate materials and services in the correct quantities at the accurate time and at the lowest possible price is known as basic procurement. There are different steps here, such as:
- Gathering Information: The process of procurement begins with acquiring details regarding a product and quantity. On the basis of the number of needed products, the module gets in touch with the supplier(s) accordingly.
- Contacting Suppliers: On the basis of the demand, the chosen suppliers meet the orders.
- Rating Products and Services: The team of materials management rates products and services on the basis of their performance. Then, depending on the rating of the product, the team will contact the supplier for repeat orders or will get in touch with new suppliers.
2. Special Procurement
Products that don’t belong to the company are known as special procurement. Some of the regular types of special procurement are:
- Consignment Stocks: These are materials available at the store premises. However, to use these products, the seller will have to pay the vendor.
- Third-Party Processing: The seller gives the orders to the vendor, who in turn, delivers the product directly to the consumer.
- Pipeline Handling: Whenever somebody places an order, the seller gets the material from the supplier and delivers it to the consumer.
Career Scope for SAP MM
If you are planning to form a career in SAP MM, you can choose to go with the SAP MM certification, which is one of the considerable professional certificates available in the entire IT industry. Having this certificate makes it easier for you to secure a high-paying job in the ERP market. Also, by having this certificate, you can open up a gamut of career paths, such as:
1. SAP MM Consultant
If you are an SAP MM Consultant, you will be a store manager with the responsibility of making sure that the store contains the right products in stock, at the right price and at the right time. Apart from this, your roles and responsibilities will include:
- Implementing SAP MM
- Configuring SAP MM
- Testing and training
- Providing support and maintenance
- Integrating with other SAP modules
- Documenting
- Consistent improvement
2. SAP Team Lead
Being a team lead, you will be responsible for planning, assigning and supervising the work of the given team that is involved in performing varying SAP MM functions and tasks. You will also have to perform difficult system analysis and programming to help the team. Apart from this, your roles and responsibilities will include:
- Planning, assigning and supervising the work of the given team
- Reviewing products to ensure accuracy, completeness, and functionality
- Connecting with functional and management teams to make sure processes and procedures are integrated properly
- Advising management on cost, efficiency, operations and material resources
- Planning detailed workflow, information sources, manpower distribution, and more
- Consulting with other SAP teams to discover and resolve problems
3. Material Manager
Being a manager, you will have to deal with materials, inventory, and the warehouse. Your responsibility will be to ensure materials are stored in proper quantities and there are no gaps or shortages in the supply chain. Apart from this, your roles and responsibilities will include:
- Supporting the current MM
- Analyzing and solving material management issues
- Conducting material management process configuration
- Updating and maintaining material management functional documentation
- Conducting unit tests, system integration security tests and integration tests
4. Purchase Executive
Just as the name suggests, being a purchase executive simply means that you will have to handle the communication with vendors and product purchasing. You will also have to monitor stock levels, place orders whenever required, coordinate with warehouse staff to make sure requirements are met, coordinate logistics, work within the given budgets, and more. Apart from this, your roles and responsibilities will include:
- Researching suppliers
- Comparing and assessing the offers of suppliers
- Negotiating contract pricing and terms
- Tracking orders and ensuring seamless delivery
- Evaluating and monitoring product quality
SAP MM Frequently Asked Questions
1. What type of work is SAP MM?
The functions of SAP MM include procurement process management, material management, master data management, material requirements planning, inventory management, and invoice verification.
2. What is the role of SAP MM?
If you are an SAP MM professional, you will be liable for delivering complex, large-scale programs that are integrated with technology to help achieve higher performance. You will be designing, implementing, and deploying SAP MM solutions to accomplish defined business objectives.
3. What are the key components of SAP MM?
SAP MM is divided into five major components, such as materials management, quality management, plant maintenance, production planning and control, and a project management system.
4. What is the role of the SAP MM Support Consultant?
An SAP MM support consultant plays an important role in assisting clients in optimizing their inventory management, procurement, and material planning processes. Their responsibilities also include business process analysis, testing, implementation, support, and training.
5. What are the key skills of SAP MM Consultants?
To become an SAP MM consultant, you must have technical domain knowledge, business domain knowledge, team coordination, testing and troubleshooting knowledge, analytical thinking, business analysis, problem-solving, and onsite management.
6. What is the highest level in SAP MM?
The client is at the highest level in SAP MM.
7. Which module is best after SAP MM?
SAP Warehouse Management (WM) and SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) are the best after SAP MM.
| Related Article - SAP MM Interview Questions |
Conclusion
Throughout the years, SAP Material Management has become popular among several organizations from across the world. Even new companies are adopting this module to improve their overall supply chain activities. SAP MM has helped businesses handle their transactions and regulate manufacturing processes with ease. All of this, in return, positively affects their process of business development. Enroll in the SAP MM Course to Upskill yourself.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP MM Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| SAP MM Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |
| SAP MM Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| SAP MM Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |

Ravi is an author, coach, and business leader with more than 25 years of experience in the IT industry. He had a long tenure at SAP Labs as Director for Engineering Services of SAP Technology Stack and gained a broader perspective and expertise in multiple SAP solutions. He wrote and managed multiple thousands of pages of knowledge material on various SAP solutions, and actively contributed to SAP events and forums. Besides SAP, he has been a technical mentor for various start-up companies that develop AI and Data Science based solutions. He helped multiple educational institutions in building IT functional-oriented educational programs and promoting industry connect initiatives.
















