SAP is one Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software that features a huge number of integrated modules, and SAP Sales & Distribution (SD) is one of those modules. SAP helps companies create a centralized system for every process while helping different departments of the company in recording and evaluating the data, allowing them to create an appropriate working environment for employees.
If you are planning to curate your career in SAD SD, it would be appropriate to know about varying concepts. Through this article, let’s dive deeper into understanding SAP SD, its features, and key components.
| Table of Contents - What is SAP SD? |
What is SAP SD?
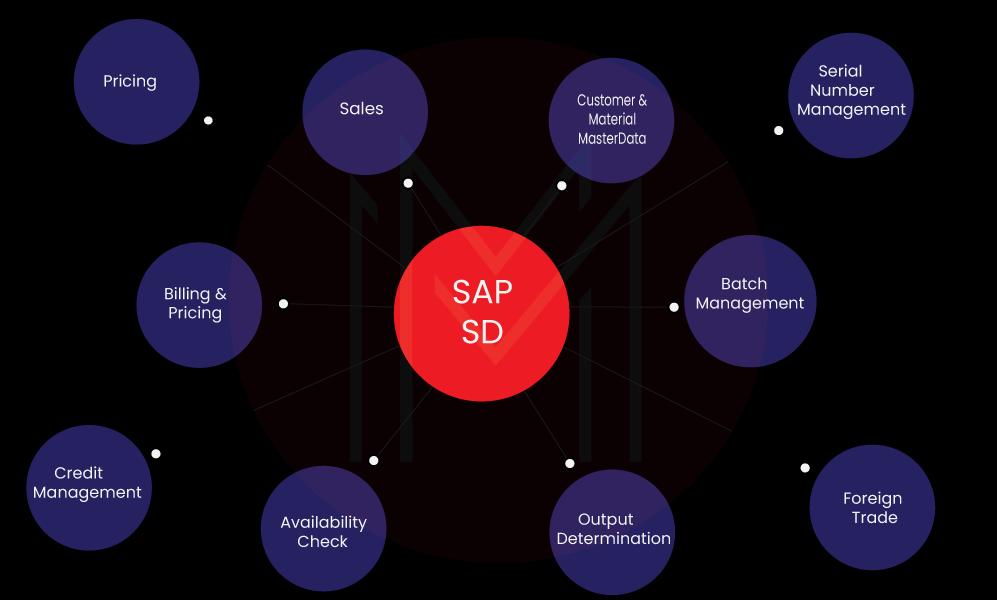
SAP SD is one of the modules in the SAP software. You can use this module to store product-related and customer-related data. It is an integral part of the SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) Logistics function and is integrated with SAP Production Planning (PP) and SAP Material Management (MMP). This module further has sub-modules, like:
- Invoicing
- Credit management
- Delivery
- Billing
- Customer and vendor management
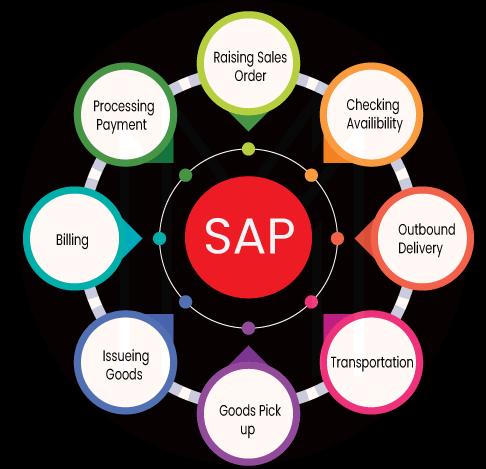
When working closely with diverse modules, SAP SD begins the cycle of the order-to-cash business procedure. Sales and distribution help manage details that are a part of this cycle. In a normal cycle, SD helps create the sales quote, and customers place their orders.
Once the order has been confirmed, products get dispatched from the warehouse or the production facility to the location of the customer. An invoice is also forwarded with the order, and the accounts team begins processing the payment. In this step, every step records transactions that lead to more transactions in some other modules.
| If you want to enrich your career and become an SAP SD professional, enroll in "SAP SD Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
Features of SAP SD Module
Jotted down below are some important features of SAD SD:
- Pricing and Taxation: This one helps calculate the cost of the products or services for the client based on their needs and other factors, such as rebates or discounts that they wish to give to the customer. Moreover, it helps calculate the tax considering every region might have different taxes.
- Availability Check: It helps check in case the product is available in the warehouse or the facility. It might calculate the number of available pieces of a specific product.
- Billing and Invoicing: The billing and invoicing feature helps create bills and invoices for customers.
- Material Determination: This one offers information on the product’s material.
- Credit Management: It helps manage the credit limits that you have assigned to customers. This figure offers two different methods to maintain credit, such as simple credit checks and automatic credit checks.
- Account Determination: Account determination is a feature that assists you in understanding the account type on the basis of the provided condition.
[Related Article: SAP SD Interview Questions]
Key Components in SAP SD
This sales and distribution module is a crucial ERP module created by SAP. It helps manage customers and sales distribution while processing the data in an appropriate way. Here are some key components you can find in SAP SD:
SAP-SD-MD: Master Data
Master data is helpful in maintaining the record of each activity in the existing data. The master data has credit management, customer data, pricing conditions, output records, and material data. It also comprises all the processes right from the order to the cash flow. This function also stores customer master data, pricing condition data, and material master data.
SAP-SD-BF: Basic Functions
This component is useful in looking after basic functions that occur in sales and distribution. It calculates as well as processes the pricing amount needed for a certain sale. SAP SD BF also helps to process the resultant output of the sale.
SAP-SD-SLS: Sales
This module is helpful in maintaining the small details of every sale. Right from the details regarding the products that were sold to the price at which they were sold, customer details, and customer feedback, everything is recorded through this module. Some of the major functions of this module are:
- Sales orders
- Backorders and rush orders
- Inquiries and quotes
- Debit and credit memo requests
- Scheduling agreements
- Consignment
SAP-SD-SHP: Shipping
This one helps record the shipping of products along with their delivery to the right address. Moreover, it helps track all the shipping methods that are used for the product’s delivery. Alongside the shipment, it helps track the return of the shipment. Some of the key functions of this module are:
- Picking, packing, and managing the inventory
- Creating shipment documents
- Management of scheduling and transportation
- Stock transferring
- Scheduling of delivery and return
SAP-SD-TBA: Transportation
This module works with the shipping module. Considering that each product’s transport mode might vary, this module tracks the data related to the products’ transportation. This module is flexible and something you can use to compile, consolidate and use data from the process. The transportation module lets you collect information on logistics through the LIS.
SAP-SD-FTT: Foreign Trade
This foreign trade module allows you to maintain foreign trade data. It helps record products that you have imported and exported for customers. Companies that use foreign trade might benefit from this module.
SAP-SD-BIL: Billing
The billing module is one of the important aspects of the SD process. Herein, customers have a choice to pay either through an online platform, such as credit cards, debit cards, or net banking or pay cash on delivery. This module helps track the whole billing data for any future reference. Some integral functions of this module are:
- Automatic or manual invoice creation
- Updated, real-time finance details
- A collection of varying billing functions
- Detailed pricing information
SAP-SD-CAS: Sales Support
Right from selling the product or service to its maintenance, the sales team is an integral part of a company when it comes to building relations with customers. This module helps maintain the customers’ records. Sales teams can exchange information among themselves so as to give support to customers at the time of delivery. This module further provides a feature to support the sales staff as well. Some of the key features of this module are:
- Contact persons
- Direct marketing to customers
- Sales prospects
- Products of competitors
- Sales activities
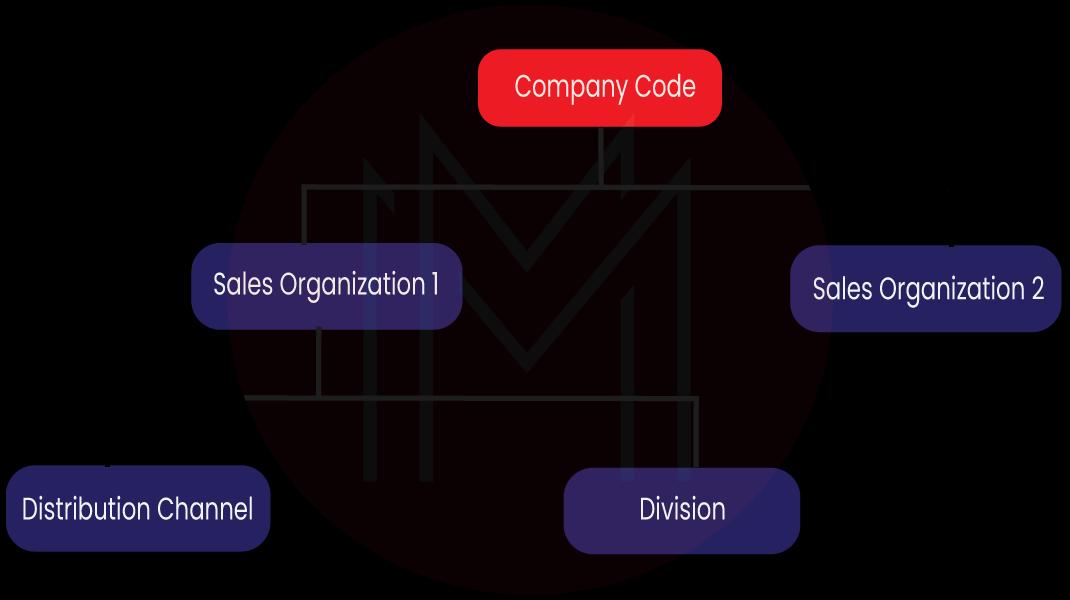
SAP SD - Organisational Structure
SAP offers several components to complete the entire Sales and Distribution organizational structure, such as Divisions, Distribution Channels, Sales Areas, and more. This organizational structure primarily comprises two steps:
- Creating organization elements in the SAP system
- Linking every element as needed
At the top of this organizational structure, the sales organization is at the highest position and is liable for the distribution of products and services. As per the SAP, the number of the sales organization, in an organizational structure should be minimum. This will make the entire reporting process much easier.
The next level in the organization structure is the distribution channel which tells the medium that should be used to distribute the products and services to the end users. In an organizational structure, a division represents a product or a service line in a single organization.
Also known as an entity, a sales area is needed to process the orders in a company. It has a sales organization, a distribution channel, and a division.
In the SAP SD organizational structure, every sales organization is given a company code. And then, the divisions and the distribution channel get assigned to the sales organization, and together, they create a sales area.
This diagram represents the organizational structure of the SAP SD module:
-
Material Management
Material management is one of the essential modules in the SAP ERP System and can cover daily business operations relevant to procurement and inventory. This one is closely linked to other modules of the R/3 systems, such as Product Planning, Quality Management, Sales and Distribution, and Finance Accounting and Controlling.
Integrating with SAP SD Module
Let’s create an example of how to create a sales order in this module. It comprises copying the items’ details from Material Management. You can also take availability checks of the products and price details from here, but they can be regulated in the SD module. To create outbound and inbound product delivery for a sales order, loading point, shipping details, and more also come from the Material Master.
The product that is placed through a Sales order should be extended to the sales area of the company to the sales customer/order. If not, transacting with the material will be impossible. This leads to the confirmation of a link between the MM and SAP SD modules whenever a sales order is created and completed. In the same way, there are several other links between these two modules.
-
Finance and Accounting
SAP FI is known for Financial Accounting, and it is one of the crucial modules of the SAP ERP system. This one is used to store a company’s financial data. SAP FI assists in analyzing the financial condition of an organization in the market. It can be easily integrated with other SAP modules, such as SAP SCM, SAP MM, PP, SD, and more.
-
Document Flow
This displays how a transaction in one system can impact the details available in the other system of the SAP module.
Let’s consider this transaction:
For SAP FI-MM, you must use T-code: OBYC
Whenever you create a delivery with reference to a sales order, product movement takes place in the system.
-
Process Chain
SD module is integrated closely with other SAP modules. The below-mentioned tables will give you an idea regarding how SD can be linked to other modules:
Sales Order
| Link Points | Module Involved |
| Availability Check | MM |
| Credit Check | FI |
| Costing | CO/MM |
| Tax Determination | FI |
| Transfer of Requirements | PP/MM |
Billing
| Integration Point | Module |
| Debit A/R | FI/CO |
| Credit Revenue | FI/CO |
| Updates G/I (Tax, discounts, surcharges, and more) | FI/CO |
| Milestone Billing | PS |
Goods Delivery and Issue of Goods
| Integration | Module |
| Availability Check | MM |
| Credit Check | FI |
| Reduces Stock | MM |
| Reduces Inventory | FI/CO |
| Reduces Eliminated | PP/MM |
Characteristics of SAP SD
Here are the characteristics of SAP SD:
- Implementing business processes used in billing and selling of products and services
- Integrating data flow to the remaining SAP modules
- Different languages can be used
- Automatic conversion between currencies
- Adaptable functionality and product customization through the function of IMG
- Creation of complicated pricing schemes dependent on sold products, customers, special promotions, and more
- Comprehensive and sophisticated rebate processing options
Advantages of Using SAP SD
Below-mentioned are some major benefits of SAP SD:
- Helps track sales transactions
- Offers efficient management of sales documents in a certain system
- Helps track sales data with team performance
- Helps categorize diverse sales and processes
- Records pre-and-post sale process
- Defines the process for sales and distribution
| Visit here to learn SAP SD Training In Banglore |
SAP SD FAQs
1. What does SAP SD contain?
SAP Sales and Distribution (SAP SD) is an integral functional module in the SAP ERP ECC that lets companies store and handle customer-related data and product-related data. Companies use this data to regulate sales orders, invoicing, shipping, and billing of their services and products.
[Related Article: SAP ERP Interview Questions]
2. Who uses SAP SD?
There are plenty of companies using SAP SD, such as Reliance Industries, Jindal Steel, Tata Steel, BPCL, and more.
3. What are the skills required for SAP SD?
An understanding of business processes is one of the crucial skills that you must possess if you wish to form a career in SAP SD. Apart from this, you should also have analytical skills, creativity, and communication skills.
4. Why do you choose SAP SD?
SAP SD is one such module that consists of a part of the larger SAP system. It helps companies strategize for distribution and sales by centralizing the data management processes.
5. What is the scope of the SAP SD course?
Once you have completed the SAP SD course, you will become skillful at various tasks, such as managing the sales, shipping, delivery, and billing aspects of a business. You will also learn how to map out customer business processes in SAP ERP.
6. What are the roles of SAP SD?
An SAP SD professional designs integrates and deploys SAP ERP solutions for sales, specifically the management cycle of sales-order and post-sales activities. The professional handles all business transactions in SAP SD.
7. Who can learn the SAP SD module?
If you are from a consultation, marketing, or sales background, you can learn SAP SD. Other than that, if you are a beginner and wish to create a career in this field, you can learn the SAP SD module.
8. Does SAP SD have coding?
No, SAP SD does not have coding.
Conclusion
For many companies, SAP SD has been nothing but a boon to improve sales and distribution. Considering that the software provides real-time data on inventories and customers, companies can evaluate their sales performance with ease. The software helps in comprehending major key performance indicators. This will help measure return on investment effortlessly. Furthermore, it also assists in evaluating the performances of the sales teams. All-in-all, SAP SD is an inclusive solution for the sales department of any company. you can also enroll in "SAP SD Training" and get a certification.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP SD Course | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| SAP SD Course | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| SAP SD Course | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |
| SAP SD Course | Mar 28 to Apr 12 | View Details |

















