- Home
- Blog
- ServiceNow
- ServiceNow Data Model

- ServiceNow Interview Questions and Answers
- What is ServiceNow Ticketing Tool
- ServiceNow Tutorial
- Top 10 IT Management Tools
- What is Servicenow Workflow
- ServiceNow Admin Interview Questions and Answers
- What is ServiceNow - A Complete Guide for Beginners
- What is ServiceNow GRC
- ServiceNow Reporting
- What is ServiceNow Orchestration
- What is ServiceNow ITIL - A Complete Overview
- ServiceNow vs Jira Service Management
- ServiceNow Architecture
- SLA ServiceNow
- ServiceNow Webassessor
- ServiceNow Integration With Jira
- ServiceNow Scripting Interview Questions
Companies who want to operate IT will find ServiceNow extremely valuable when the ServiceNow data model and the Now Platform, a standard design for automated and integrated IT services, are created. The Now Platform automates the workflows on a large scale, allowing you to improve your business processes' productivity, agility, and resiliency. With streamlined supporting activities and value streams wholly integrated on the Now Platform, you may achieve full-value chain alignment, more outstanding quality, transparency, better insights, automation, and lower costs.
This ServiceNow data model blog will explore the Common Service Data Model (CSDM) and its benefits in detail.
| ServiceNow Data Model - Table of Contents |
What is CSDM (Common Service Data Model)?
The Common Service Data Model (CSDM) is a framework for mapping your IT services based on the ServiceNow Configuration Management Database (CMDB). It’s an industry-standard framework for CMDB data modelling and management. It provides advice on service modelling and includes a standard set of terms and definitions. It serves as the foundation for service configuration, connecting your CMDB from a business and technical standpoint with recommended mappings and relationships.
CMDB real-world challenges
We see that our clients are dealing with several CMDB-related issues:
- Customizations to tackle CMDB data issues, such as classifying CIs and connecting them to company capabilities, goods, and services.
- CMDB architectural alignment is poor to non-existent.
- Working in silos prevents stakeholder collaboration and ownership of data.
- IT Infrastructure Library Service Management Principles aren't in place.
- There are no formally defined services.
- Low CMDB visibility and awareness results in a lack of ownership, an incomplete CMDB, and a danger to fundamental ITSM processes.
Key Benefits of the CSDM
We'll look at some of CSDM's most important benefits to see how it might help your company achieve more success.

1. Aids in the optimization of the CMDB
The CSDM improves your CMDB, making it easier to use and manage in the long run. Many ServiceNow users underestimate the time and work it takes to keep a CMDB up to date. The CMDB could not immediately map initial business outcomes before CSDM. On the other hand, the CSDM must overcome this lag by connecting the site to the technical underpinning clearly and concisely. The CMDB's core tables contain information on business capabilities, business applications, service portfolios, technical services, and more.
As a result, the CSDM analyses your business models’ technological and physical implications and redesigns how they interact, maximizing their potential. ServiceNow’s standardized tables ensure that accurate and rigorous reporting satisfies standards.
| Do you want to build your career in ServiceNow, then Visit Mindmajix - a global online training platform: "ServiceNow Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain |
2. A more solid link to a unified data model
Having a single, consistent data model is beneficial whether you employ numerous ServiceNow modules or just its popular Information Technology Service Management (ITSM). All customer-facing services and internal processes are covered by creating a CMDB basic table that all other base tables can extend. This feature makes it easier to manage similar data types, creating a more efficient single source of truth that connects customer-facing and internal technical services.
It allows for better decision-making because it integrates both business and service data. This is beneficial to both business and technical teams. Following the CSDM framework enables service teams to have a holistic view of their operations, including upstream and downstream functions.
3. Improved services and lower costs
A unified data model with a broad viewpoint improves services by delivering higher-quality output when appropriately used. This opens the door to a plethora of improvements, including:
Collaboration between business and IT has improved.
- IT accountability has improved.
- From start to finish, the service is visible.
- Customers will have a better experience, and business operations will be more straightforward.
As a result, your ServiceNow instance will have a higher return on investment. Improved workflows identify chances for higher productivity and cost reductions, which aids in cost reduction. Improved visibility also helps you to do a more extensive examination of the costs of running your firm, allowing you to identify cost-cutting options.
4. Possibilities for better agility and innovation
ServiceNow's CSDM best practices increase operations and business outcomes across the enterprise, allowing for greater agility and creativity. It also enables businesses to boost their agility and innovation capabilities. Faster decision-making and adaptation to new opportunities are made possible by enhanced visibility.
Following the achievement of improved customer outcomes through the use of the CSDM, the next step in ensuring long-term success is to pursue innovation with an agile mindset that allows you to improve across the board – from increasing productivity to simplifying workflows and processes for your teams and lowering costs.
How to get started with CSDM
It's preferable not to implement all of the Common Source DataBase (CSDB) features at once but rather to follow the ServiceNow crawl, walk, run, and fly stages. Your apps or services must pass through these four steps to be successful. We'll talk about how to make your ServiceNow cawl stages a success here.
1. To begin, make a list of business applications
Especially in large organizations, a thorough overview of all applications is sometimes unavailable. This is the initial step in using CSDM. As a result, make sure ServiceNow has all of your Business Applications and Application Services.
| Also Read: ServiceNow ITIL |
2. Examining the roles and duties associated with business applications
It's crucial to know who's responsible for a Business Application (who owns it) and who's in charge of the quality and operations of the Application Service. External suppliers to whom you've delegated responsibility for an Application Service may host the services in their own (cloud) data center, so don't forget about them.
3. Identifying the importance of the business
Working with the Business Application Owners to undertake a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) and assess your services will help you establish business criticality. If you haven't already, you might use the custom tables that come with your ITSM bundle to aid in this process of getting information from your service owners.
4. Prioritize the most important CIs
Significant aspects such as load balancers, application servers, database servers, essential network equipment, and other essential components should be given specific attention during the CSDM Crawl phase. Make simple connections between these Critical CIs. Ensure they're linked to the exemplary Application Service, and the Application Services are connected to the proper Business Application.
5. Expand
This is where you'll find the new round of business apps to fill out.
Why should we follow the CSDM?
To map your IT services to ServiceNow, you can utilize the CSDM as a blueprint. The CSDM is a CMDB-based framework for determining where data for your products should be stored. In addition, all ServiceNow products that use the CMDB use the CSDM as a standard. The CSDM framework ensures that your ServiceNow application needs maps to the correct CMDB tables.
You may not get the most out of the ServiceNow platform if you don't follow this standard.
| Also Read: ServiceNow Developer Instance |
What is the ServiceNow data model?
The ServiceNow data model is a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) framework that will enable and support diverse configuration methodologies across ServiceNow products and platforms. The Common Service Data Model (CSDM) is a standard and common set of service-related definitions that will enable and support genuine service level reporting while offering prescriptive guidance on service modeling within the CMDB across our products and platform. These service-related definitions apply across the whole ServiceNow product line.
ServiceNow data model diagram
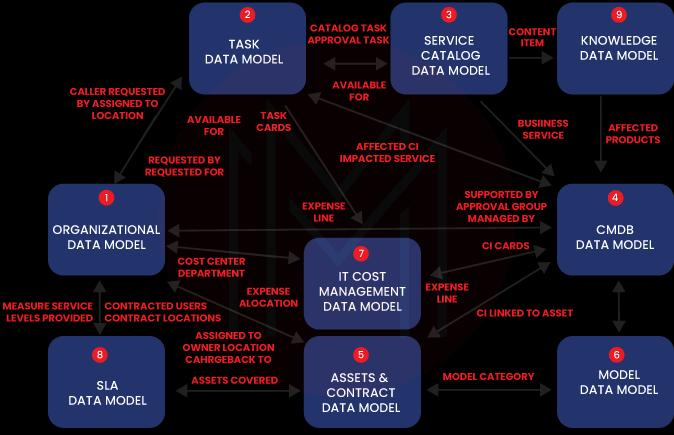
ServiceNow Mid Server
The MID Server is a Java application that runs on a server in your local network as a Windows service or UNIX daemon. The ServiceNow MID Server connects a ServiceNow instance to external applications, data sources, and services, allowing data to flow between them.
The MID Server initiates all communication between the MID Server and the ServiceNow instance. The ECC Queue, which serves as a communication log between the representative and the MID Server, keeps this communication as record. The MID Server retrieves any work from the ECC Queue that it needs to complete and returns the results to the queue.
| ServiceNow Interview Questions and Answers |
Conclusion
This draws us to the conclusion of this ServiceNow data model blog. We hope this has provided you with a precise grasp of its advantages. CSDM can also drive uniformity and enhance the value proposition of ServiceNow products and services.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly

Vinod M is a Big data expert writer at Mindmajix and contributes in-depth articles on various Big Data Technologies. He also has experience in writing for Docker, Hadoop, Microservices, Commvault, and few BI tools. You can be in touch with him via LinkedIn and Twitter.
