- SAP HANA Administration Tutorial
- SAP HANA Interview Questions
- SAP HANA Tutorial
- Application Programming Interfaces for SAP HANA
- Dell Introduces New Solutions for SAP HANA Environments
- Different Types of SAP HANA Modeling Views
- Fujitsu Services and Solutions SAP HANA Environments
- SAP HANA General Principles of Data Modeling
- SAP HANA Co-innovation for Real-Time Computing
- SAP HANA Data Modeling Tools Overview
- SAP HANA Database – SQL Script Guide
- SAP HANA Implementation and Useful Scenarios
- How to Build A SAP HANA Business Case for Your Investment
- How to Install SAP HANA Studio
- HP ConvergedSystem Solutions for SAP HANA
- Huawei SAP HANA Solutions Overview
- Introducing SAP HANA Extended Application Services (XS)
- Introduction to Application Development with SAP HANA
- Learn SAP HANA Use Cases for Your Industry
- Learn SAP HANA Studio Overview
- Making Big Data Real with SAP HANA
- NEC High-Performance Appliance for SAP HANA
- SAP’s Big Data Ecosystem Overview
- SAP Business Suite Powered by SAP HANA — Business Scenarios
- SAP Business Suite Powered by SAP HANA
- Learn SAP Business Warehouse Powered by SAP HANA
- SAP BW on HANA Implementation and Migration
- SAP BW on SAP HANA Administration
- SAP HANA Features and Building Blocks
- SAP HANA Integration with Microsoft Excel
- SAP HANA Introduction and Architectural Overview
- SAP HANA as a Primary ABAP Database
- SAP HANA Roadmap and Its Applications
- SAP S/4 HANA In Memory Basics and Projects
- Scoping Sizing Topics for SAP BW on HANA
- SAP HANA Specific Enhancements for SAP BW
- Steps to Create SAP HANA Application
- Steps to Create SAP HANA Business Case – Methodology
- System Landscape Options for SAP BW On HANA
- Using SAP HANA as a Secondary Database from ABAP
- VCE Vblock Specialized System for SAP HANA Architecture Overview
- What are the General Specifications of SAP HANA Hardware
- What are the HANA Skills Needed for Successful Projects
- SAP HANA Architecture Overview
- What is SAP HANA’s Big Data Strategy?
- What is SAP HANA Hardware?
- What is SAP HANA Rapid Deployment Solutions (SAP RDS)
- What is SAP HANA Starter
- What is SAP Hana Studio | Definitive Guide
SAP HANA is a popular in-memory database platform used by many organizations for managing their data. As a result, there is a high demand for professionals with SAP HANA administration skills. These positions are often well-paid and offer a chance for career growth.
If you are looking for a career in SAP HANA administration, knowing the interview questions can give you an edge over other candidates. By demonstrating your knowledge and expertise, you can increase your chances of being selected for the job.
This article covers the most commonly asked SAP HANA Administration interview questions for both beginners and experienced.
We have categorized SAP Hana Admin Interview Questions into 3 levels they are:
Top 10 SAP Hana Administration Interview Questions
- What is SAP HANA architecture?
- How does SAP HANA work?
- What is SAP HANA Multi-Tenancy?
- What is SAP HANA Cockpit?
- What is SAP HANA XS?
- What is an index in SAP HANA?
- What is a tenant database in SAP HANA?
- What is the high availability in SAP HANA?
- What is data replication in SAP HANA?
- How do you troubleshoot and resolve issues with SAP HANA?
SAP Hana Admin Interview Questions For Freshers
1. What is SAP HANA, and what are its key features?
SAP HANA is a popular relational database management platform developed by SAP. Data storage and retrieval are the primary functions of SAP HANA. Some of the key features include in-memory processing, multi-tenancy, real-time analytics, advanced analytics, integration with SAP systems, high availability and disaster recovery, scalability, and security.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in SAP HANA Admin, then enroll in "SAP HANA Administration Course". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2. What is SAP HANA architecture?
SAP HANA (High-Performance Analytic Appliance) is a relational database management system developed by SAP. SAP HANA's architecture is created to deliver real-time processing and high-speed capabilities, with the ability to manage large volumes of data from different sources.
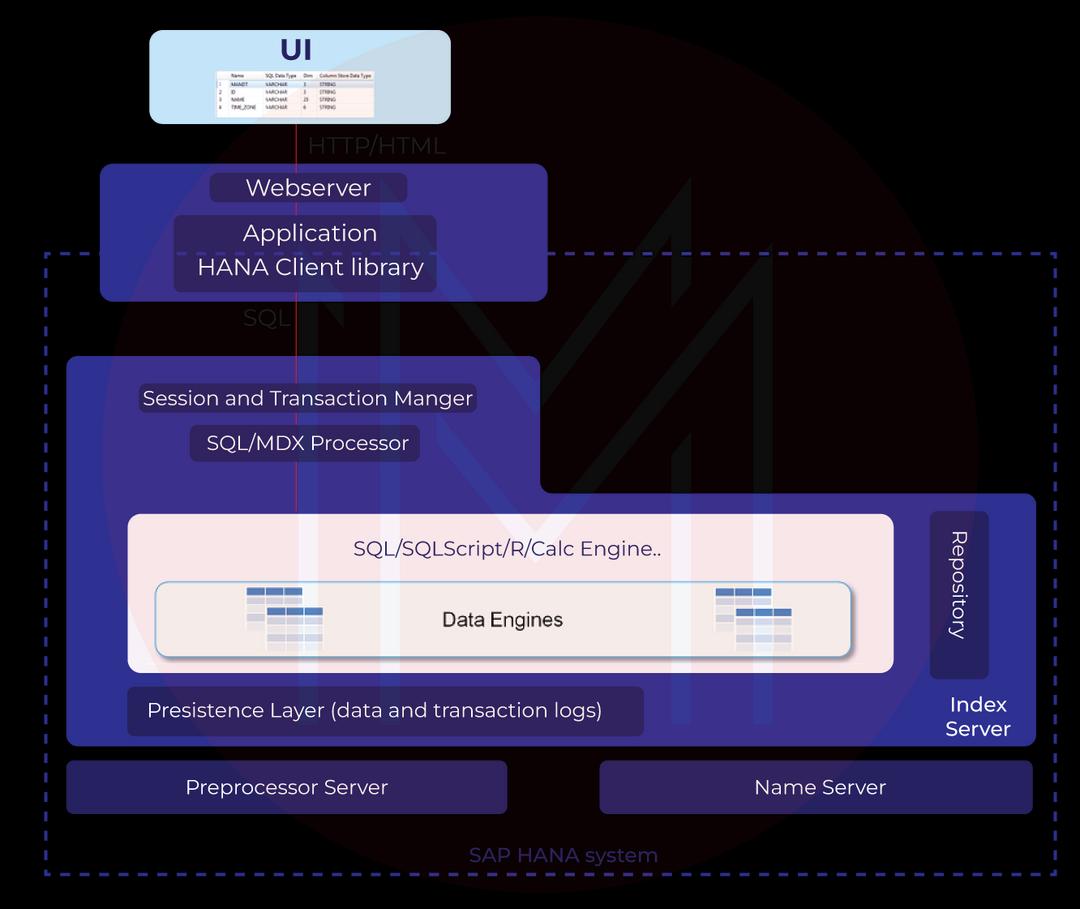
- In-Memory Computing Engine: SAP HANA's core component. It stores data in memory to deliver high-speed processing, with the ability to handle complex queries in real time.
- Row Store and Column Store: SAP HANA provides row- and column-based data storage options optimized for different types of operations. The row store is suitable for transactional processing, while the column store is more efficient for analytical processing.
- Data Services: SAP HANA also includes data integration and replication services, enabling users to extract data from different sources and load it into the system.
- Calculation Engine: This SAP HANA component performs complex calculations and aggregations on large volumes of data.
- Application Services: Various tools support application development, including SAP HANA XS, SQL Script, and more.
3. How is SAP HANA installed and configured?
The following are the common steps involved in SAP HANA installation and configuration:
- First, make sure the system satisfies SAP HANA's hardware and software requirements.
- From the SAP support portal, download the SAP HANA software.
- Following installation, SAP HANA must be configured according to your needs.
- After configuring SAP HANA, you must test it to make sure it is operating properly.
4. How does SAP HANA work?
Here is how SAP HANA works:
- SAP HANA uses in-memory computing, which speeds up data access and processing by storing data in memory rather than on a disc. By removing the need to transfer data between the disc and memory, it allows real-time data processing.
- Data is saved using a columnar format, which means that information is kept in columns rather than rows. Data processing and analytics speed up by only loading the columns needed for a particular query into memory.
- In order to benefit from parallel processing, SAP HANA was designed. Data processing and analytics are sped up by its ability to distribute data and queries over numerous processors.
- SAP HANA utilizes compression to minimize the amount of data that needs to be kept in memory. This improves performance and lowers the amount of memory used.
5. How do you ensure the security of data in SAP HANA?
SAP HANA offers a number of techniques to ensure data security, including
- The use of secure communication protocols.
- The implementation of role-based access control.
- Activation of data encryption.
6. What backup and recovery options are available in SAP HANA?
The backup and recovery options provided by SAP HANA include incremental, database, and log backups. Additionally, SAP HANA offers disaster recovery options such as system replication and storage replication.
7. How do you monitor the performance of SAP HANA?
You can use a variety of monitoring tools, including SAP HANA Studio, SAP Solution Manager, and SAP EarlyWatch Alert, to monitor the SAP HANA's performance. You may uncover performance issues and improve system performance with the aid of these tools, which offer real-time system monitoring.
8. What is SAP HANA Multi-Tenancy?
SAP HANA Multi-Tenancy is a feature that allows multiple organizations or tenants to share a single SAP HANA system. Each tenant has an isolated database schema and may access only the data belonging to that tenancy. This feature enhances system scalability and lowers hardware and maintenance expenses.
9. How do you perform system updates and upgrades in SAP HANA?
To perform system updates and upgrades in SAP HANA, you need to follow a defined upgrade path and ensure that all requirements are met. This involves creating backups, applying support packages, and testing the system before and after the upgrade.
10. What is SAP HANA Cockpit?
To manage, monitor, and operate SAP HANA database systems, a web-based tool called SAP HANA Cockpit was created. Its standard interface allows database administrators and IT staff to administer and monitor numerous SAP HANA databases from a single location.
Using SAP HANA Cockpit, users may configure backups, manage users and authorizations, manage system configurations, monitor alerts and failures, and monitor performance. Thanks to its robust analytics and reporting features, administrators may gather data on system performance, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize system resources.
One of its key benefits is the user-friendly and intuitive interface that SAP HANA Cockpit provides, which simplifies managing and administering SAP HANA.
11. What is SAP HANA Studio?
The SAP HANA Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) for the SAP HANA in-memory database and platform, which allows for the real-time management of massive volumes of data. Thanks to a number of offered tools and interfaces, developers, administrators, and data analysts can interact with HANA databases and applications.
The Studio was developed using the Eclipse IDE framework and includes a variety of tools for managing the HANA database, modeling data, and developing applications.
[ Learn More About SAP HANA Studio ]
12. What are the key features of SAP HANA Cockpit?
The SAP HANA Cockpit is a web-based management tool for SAP HANA databases. It provides a central location for monitoring, directing, and overseeing several HANA databases simultaneously.
Some of SAP HANA Cockpit's key features include the following:
- Monitoring: Along with the HANA database and its components, it provides real-time monitoring of the CPU, RAM, disc I/O, network activities, and other components. Additionally, it offers performance indicators that can be used to identify and analyze performance issues.
- Administration: Users can configure the system's preferences, notifications, backups, and users, roles, and rights for the database.
- Analytics: It offers reporting and data visualization capabilities to aid in the analysis of data stored in the HANA database.
13. What is SAP HANA XS?
Web-based apps can be developed and deployed by programmers from within the SAP HANA database using the SAP HANA XS (Extended Application Services) feature. This lightweight application server allows developers to build apps on top of the HANA database using common web development tools like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
With SAP HANA XS, developers can quickly and easily create and deploy apps without setting up and maintaining separate application servers. The apps made with XS are accessible through any web browser and can benefit from SAP HANA's powerful in-memory processing capabilities, enabling real-time data analysis and processing.
14. What is the difference between a row store and a column store?
Data is stored in columns in a column store, whereas in a row store, it is stored in rows. Column stores are optimized for analytical queries, including aggregations, whereas row stores are optimized for transactional queries involving single rows.
15. What is the difference between OLTP and OLAP?
The terms "online transaction processing" (OLTP) and "online analytical processing" (OLAP) refer to different types of processing, such as transactional processing (processing sales orders) and analytical processing (analyzing sales data).
[ Related Blog: OLTP vs OLAP ]
SAP Hana Admin Interview Questions For Experienced
16. What is an index in SAP HANA?
An index, which stores a sorted copy of the data in those columns, is created using one or more columns from database tables. When a query containing the indexed columns is executed, SAP HANA can quickly locate the relevant data and create the results by using the index.
Indexes can be created for both single columns and groups of several columns.
With indexes, SAP HANA queries may be executed much more quickly, especially for large databases with lots of rows. Indexes have certain drawbacks, though, including increasing database size and slowing down insert, update, and delete operations.
17. What is a calculation view in SAP HANA?
A Calculation View in SAP HANA is a sort of modeling artifact that enables you to combine data from many tables or other views to construct complicated analytical views.
On substantial amounts of data kept in SAP HANA, calculation views are used to carry out sophisticated data processing and analytical operations like aggregations, filters, and calculations. They can be used to create complex analytical apps and reports that give instantaneous insights into how well businesses are performing.
18. What is a schema in SAP HANA?
A schema is a container for SAP HANA database objects such as tables, views, procedures, functions, and sequences. It functions as a logical container to help organize and manage database objects.
With the help of SAP HANA, it is possible to divide database objects based on logical categories or security requirements by allowing the establishment of many schemas inside of a single database instance. This is especially useful when multiple users or programs are sharing a single SAP HANA instance in multi-tenant configurations.
19. What is the maximum size of a database in SAP HANA?
The maximum size of a database in SAP HANA is influenced by a number of factors, including the license agreement with SAP, the hardware setup, and the version and edition of HANA being used.
20. What is an instance in SAP HANA?
An instance in SAP HANA is an independent copy of the SAP HANA system that is installed on a single server or node. Each instance has unique resources and procedures.
Multiple instances of an SAP HANA system may be spread over various servers or nodes. These instances can cooperate to offer SAP HANA applications and databases excellent availability and scalability.
21. What is a tenant database in SAP HANA?
A tenant database in SAP HANA is a feature that enables the operation of numerous separate databases on a single HANA system. Each tenant database in the same system is totally isolated from the other databases and has its unique collection of tables, views, and other database objects.
This feature is especially helpful when many organizations or departments must share the same HANA system but need their own separate databases to preserve data separation and security. Tenant databases allow for the pooling of hardware resources while allowing each organization or department to have its own database with its own set of users, roles, and security policies.
22. What is the difference between a single-container and a multi-container architecture in SAP HANA?
A single-container architecture in SAP HANA is a configuration in which the database, application server, and web server are all deployed and operated within a single container or instance. This indicates that all services and applications operate in the same environment and utilize the same resources, including CPU and memory.
Contrarily, a multi-container architecture in SAP HANA describes a configuration in which various system parts are installed and run in independent containers or instances. For instance, the web server, application server, and database might all operate in different containers.
The key difference between these two architectures is that the single-container architecture is simpler and easier to manage, but it has limitations in terms of scalability and flexibility. In contrast, the multi-container architecture is more complex, but it allows for greater scalability and flexibility, as different components can be scaled independently, and new components can be added or removed as needed.
23. What is the high availability in SAP HANA?
High availability defines a system's ability to continue operating and being reachable despite hardware or software malfunctions. High availability in the context of SAP HANA ensures that customers always have access to crucial data and apps without any interruptions in service.
There are several methods that can be utilized in SAP HANA to ensure high availability, including:
- System Replication: With this technique, multiple copies of the SAP HANA system are made, and data is replicated between them in real-time. The system immediately changes to another copy if one copy fails, guaranteeing that the data is still accessible.
- Disaster Recovery: A backup SAP HANA system is set up at a different site in this method.
- Cluster Configuration: In a cluster configuration, several servers are installed, each of which is assigned a specific amount of workload. The other servers can take over a failing server's functions, ensuring the system's availability.
24. What is a scale-out system in SAP HANA?
A scale-out system in SAP HANA is a distributed system architecture that permits the scalability of SAP HANA databases on a horizontal basis. An SAP HANA system's processing power and capacity can be increased by adding additional servers, also known as nodes.
The burden is split across several SAP HANA nodes in a scale-out system, enabling quicker processing of big data sets. A single logical perspective of the data is provided by the system's individual nodes, each of which has memory and processing capacity of its own.
Scale-out solutions are appropriate for businesses that need great performance and scalability and have huge data collections.
25. What is a scale-up system in SAP HANA?
A scale-up system in SAP HANA is a sort of hardware design where the SAP HANA database is run on a single large server. As opposed to a scale-out system, which uses numerous smaller servers to run the database in a distributed manner.
In comparison to a scale-out system, a scale-up system can offer greater performance and capacity, but it may also be more expensive and have a single point of failure. When high performance and reliability are crucial, scale-up systems are frequently utilized for mission-critical applications and large-scale data processing.
26. What is the difference between a delta merge and a full merge in SAP HANA?
Data is stored in a columnar format in SAP HANA, enabling effective data processing and analysis. Two distinct methods are utilized in HANA to transfer data from delta storage to main storage: delta merge and full merge.
A delta merge transfers new data from the delta store to the main storage since the last merge. It is a gradual process that only refreshes the data that has changed. Because it simply analyzes the changes that have occurred since the last merging, which may be significantly smaller than the entire dataset, this method is efficient.
On the other hand, a full merge is a method used to transfer all data from HANA's delta storage to the main storage. It is frequently used when query performance needs to be optimized or when the amount of data in the delta storage gets too enormous to manage effectively. Due to the fact that a full merging includes processing all of the data in the delta storage, it might be resource-intensive.
In summary, a full merge transfers all data from the delta storage to the main storage, whereas a delta merge merely updates the data that has changed since the last merging. The individual use case and the amount of data involved determine which technique should be used.
27. What is data replication in SAP HANA?
Data replication in SAP HANA is the process of transferring data from external systems to the HANA database. This is required to enable the data for HANA's real-time processing and analysis.
28. How do you ensure data security in SAP HANA?
Implementing access controls, encrypting data, and using data masking and anonymization methods are all ways to ensure data security in SAP HANA. System audits and vulnerability assessments on a regular basis can also aid in identifying and reducing security risks.
29. What is a system replication in SAP HANA? How is it different from the SAP HANA scale-out?
System replication is a feature of SAP HANA that makes it possible to build a secondary system that is constantly in sync with the primary system. This synchronization ensures that the secondary system can take over effortlessly in the case of a primary system breakdown, minimizing downtime or data loss.
On the other hand, SAP HANA scale-out is a technology that enables horizontal scaling of SAP HANA systems by dividing the workload among several servers. With scale-out, a single SAP HANA system is divided into numerous nodes, each of which runs on a different server and handles a specific amount of data and workload.
The main difference is that scale-out is primarily concerned with increasing performance and scalability by distributing the workload across several nodes, whereas system replication is mostly concerned with ensuring high availability and disaster recovery.
30. How do you troubleshoot and resolve issues with SAP HANA?
SAP HANA troubleshooting and resolving issues require a combination of technical know-how and tools. You can follow the following steps to troubleshoot and fix issues with SAP HANA:
- Finding the issue is the first step in solving an SAP HANA problem. If errors are found, system logs may need to be examined, and monitoring tools may be used to keep tabs on system performance.
- The next step is to isolate the issue once the issue has been found. This could entail turning off specific system functions or parts, or restoring the system to a previous setting.
- The next step after isolating the problem is to investigate it thoroughly. This could entail looking through system logs, utilizing tracing tools to monitor system behavior, or doing tests to duplicate the problem.
Most Common SAP Hana Admin FAQs
1. What is SAP HANA Administration?
SAP HANA is an in-memory database platform used for processing massive amounts of data in real time. SAP HANA Administration involves managing and maintaining the SAP HANA database and related components.
2. Which tool is used for SAP HANA?
There are many tools used for SAP HANA, depending on specific tasks from data modeling to analytics. Some of the most commonly used tools are SAP Lumira, SAP HANA Studio, SAP Data Services, and more.
3. What is the purpose of the SAP HANA Administration?
SAP HANA administration involves configuring and managing the SAP HANA database effectively to support the effective operation of business applications.
4. What is the role of the SAP HANA administrator?
SAP HANA Administration needs a solid understanding of the SAP HANA database and knowledge of network protocols and security practices. In order to make sure that the SAP HANA system satisfies business requirements, SAP HANA administrators may collaborate closely with developers, business users, and other IT personnel.
5. What are some of the main benefits of SAP HANA?
The benefits of using SAP HANA include faster processing times, real-time analytics, decreased data redundancy, enhanced data quality, and greater decision-making abilities.
6. What are the different types of HANA?
Here are the most common ones:
- SAP HANA Platform Edition
- SAP HANA Cloud
- SAP HANA Express Edition.
7. What are the 3 main components of SAP HANA?
The different components of SAP HANA include the SAP HANA database, SAP HANA Studio, SAP HANA client, SAP HANA application server, and SAP HANA XS engine.
8. What are the skills required for SAP HANA?
Some key skills required for SAP HANA include:
- Deep understanding of SAP HANA's architecture and development.
- Knowledge of SAP Business Intelligence (BI) tools.
- Experience with database management concepts and technologies.
- Proficiency in programming languages.
- Strong analytical skills.
9. Does SAP HANA require coding?
Yes, SAP HANA does require coding. SAP HANA is a database management system that uses programming languages to perform data processing and analytics operations.
Tips to Clear SAP HANA Administration Interview
Here are a few steps to clear the SAP HANA administration interview:
Tip #1. Review Job Description
Review the job description to understand the specific requirements and responsibilities of the SAP HANA role you're applying for. Make sure you're ready to talk about your relevant experience and talents.
Tip #2. Practice With SAP HANA System
Get some hands-on experience with an SAP HANA system.
Tip #3. Prepare For Common Interview Questions
Research common SAP HANA interview questions and practice your answers to help you feel more confident during the interview.
Tip #4. Stay up-to-date
Keep up with the latest SAP HANA trends, technologies, and best practices.
Tip #5. Come Ready With a Few Questions
This shows how committed you were to learn about the company and the job you're applying for.
Conclusion
These are just a few of the many possible SAP HANA administration interview questions and answers. It is important to have a good understanding of the software and its various components to succeed in this role.
Your learning journey to become SAP HANA certified is easier with MindMajix’s SAP HANA Admin Training program. Enroll now to get started!
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP HANA Administration Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| SAP HANA Administration Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |
| SAP HANA Administration Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| SAP HANA Administration Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















