- Home
- Blog
- AI and Machine Learning
- What is Cognitive Computing and How Does it Work?

- Challenges Faced While Executing Real Life Scenarios With AI
- What is ACUMOS AI
- Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions
- Artificial Intelligence In Education
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution
- Top 10 Artificial Intelligence Technologies
- What Is Artificial Neural Network And How It Works?
- Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
- Genetic Algorithm in Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence Neural Network
- Top 5 Reasons why you should learn Artificial Intelligence
- Skill Demands in Artificial Intelligence Job Market
- Whats new in SQL Server 2016
- Why is Artificial Intelligence Important
- The Ultimate Guide to Chatbots
- AI Framework
- Artificial Intelligence Tutorial
- Machine Learning (ML) Frameworks
- What is LSTM?
- Best Software Development Courses
- What is AIOps - The Beginner's Guide
- What Is ChatGPT
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Projects and Use Cases
- How to Install TensorFlow?
- n8n Tutorial
AI is at the forefront of the new computing era, Cognitive Computing. It is a totally new sort of computing, unlike the programmed systems that came before it, similar to how those systems differed from tabulating machines a century ago. However, because of today’s big data and the need for complicated evidence-based decisions, traditional systems frequently fail or are unable to keep up with the information.
Cognitive computing enables humans to create a fundamentally new type of value by allowing them to find answers and insights locked in massive amounts of data. This article will teach you everything about cognitive computing, its advantages, and more.
What is Cognitive Computing?
The term "cognitive computing" refers to technology platforms that simulate human thought processes under the guidance of cognitive science. Artificial intelligence and signal processing are included in this area. This may involve attributes like artificial intelligence (AI), natural language processing (NLP), audio and image recognition, human-computer interface (HCI), and more.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in Cognitive Computing, then enroll in the "Artificial Intelligence Certification Course". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
How does Cognitive Computing Work?
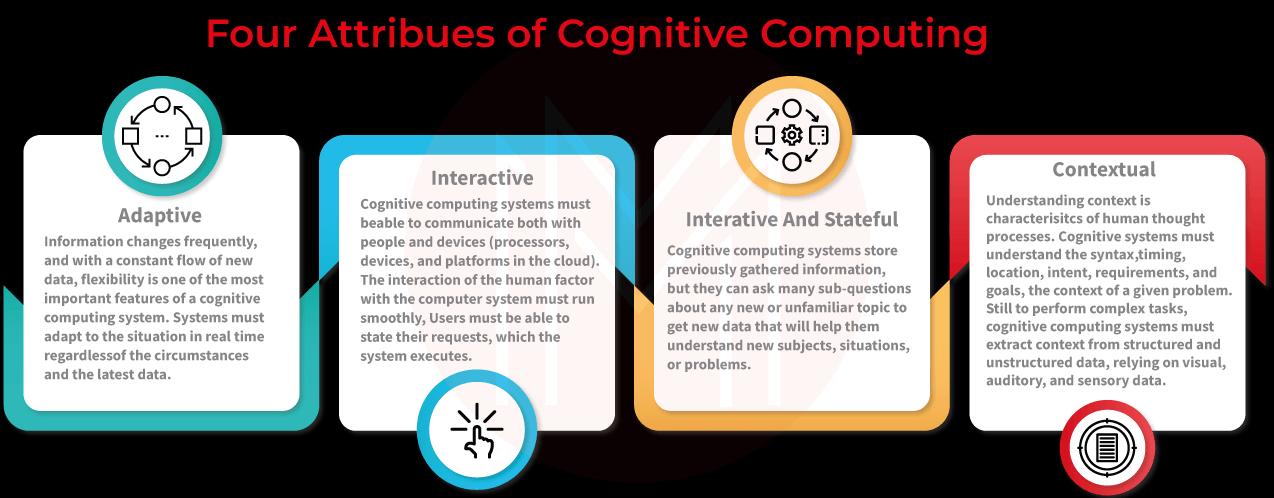
Cognitive computing has made it possible for computers to replicate how the human brain works. Self-learning algorithms based on data mining and pattern recognition are used by cognitive computing to identify solutions to a wide range of problems. But according to the Cognitive Computing Consortium, these tasks require adaptive, interactive, iterative, stateful, and contextual cognitive computing systems. All of these elements must be present for a system to be cognitively computing.
key attributes of Cognitive Computing
1. Adaptive
In order to achieve a shifting set of objectives, cognitive systems must be able to handle an input of information and data that is changing quickly. The platforms respond in real-time to changing data requirements and environmental conditions by processing dynamic data.
2. Interactive
Cognitive machines require human-computer interaction (HCI), which is a crucial component. Users engage with cognitive processes and set the parameters even as the parameters vary. The technology communicates with various hardware, CPUs, and cloud computing platforms.
3. Iterative and Stateful
In the event that a preset query is insufficient or ambiguous, cognitive computing systems identify issues by presenting questions or requesting additional information. The technology enables this by keeping records of relevant circumstances and future events.
4. Contextual
Contextual information such as time, syntax, domain, location, requirements, or a specific user's tasks, profile, or goals must be recognized, understood, and mined by cognitive computing systems. They may use a variety of information sources, such as sensor, auditory, visual, or visual data, along with structured or unstructured data.
Examples and Applications of Cognitive Computing
Systems for cognitive computing are frequently employed to complete tasks that call for the analysis of enormous volumes of data. For instance, cognitive computing in computer science helps with large data analytics, seeing trends and patterns, comprehending human language, and connecting with clients.
The following are some instances of how Cognitive Computing is utilized across many sectors.
1. Retail
These technologies examine both the customer's basic characteristics and the specifics of the goods they are considering in retail settings. The system then offers the customer customized recommendations.
2. Logistics
IoT devices, networking, and warehouse management are all made easier by cognitive computing.
3. Banking and Finance
In the banking and finance sector, cognitive computing analyses unstructured data from many sources to learn more about consumers. Chatbots that interact with customers are made using NLP. Customer engagement and operational effectiveness both increase as a result.
4. HealthCare
To provide advice to medical professionals, cognitive computing can handle huge volumes of unstructured healthcare data, including patient histories, diagnoses, ailments, and journal research articles. This is done to assist physicians in choosing the best course of treatment. A doctor's powers are increased by cognitive technology, which also aids in decision-making.
A prime example of a cognitive computing system is IBM's Watson for Oncology. It offers cancer patients' oncologists at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York evidence-based therapy alternatives. Watson creates a list of hypotheses and presents therapy alternatives for clinicians to evaluate in response to inquiries entered by medical professionals. Another IBM technology that aids clients in medical and clinical research is Watson Health.
What Value does Cognitive Computing Provide?
The ability of cognitive computing to extract usable information from complex data is a useful quality. In order to remain competitive, practically every organization must deal with an expanding volume of data, making BI solutions like Sisense more crucial than ever. These platforms make use of cognitive computing techniques to generate data analyses that are simpler for non-technical staff to understand. The tools from Sisense use natural language processing (NLP) capabilities to convey insights in conversational language. This minimizes unintentional misunderstandings and gives everyone access to an unbiased study of the data's facts.
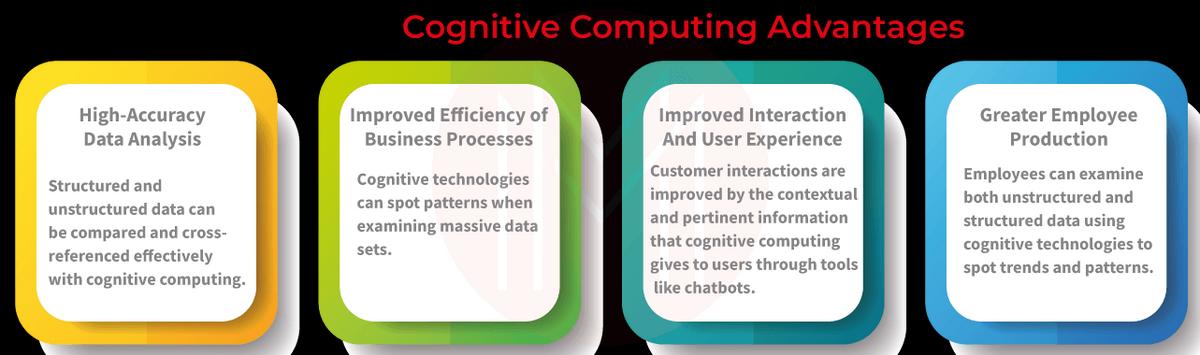
Advantages of Cognitive Computing
Positive outcomes in the following domains are among cognitive computing's benefits:
- Analytical accuracy: Structured and unstructured data can be compared and cross-referenced effectively with cognitive computing.
- Business Process Efficiency: Cognitive technologies can spot patterns when examining massive data sets.
- Customer Experience and Interaction: Customer interactions are improved by the contextual and pertinent information that cognitive computing gives to users through tools like chatbots. The client experience is improved by combining cognitive assistants, personalized recommendations, and behavioral predictions.
- Employee Service Quality and Productivity: Employees can examine both unstructured and structured data using cognitive technologies to spot trends and patterns.
Disadvantages of Cognitive Computing
Negative aspects of cognitive technology include the following:
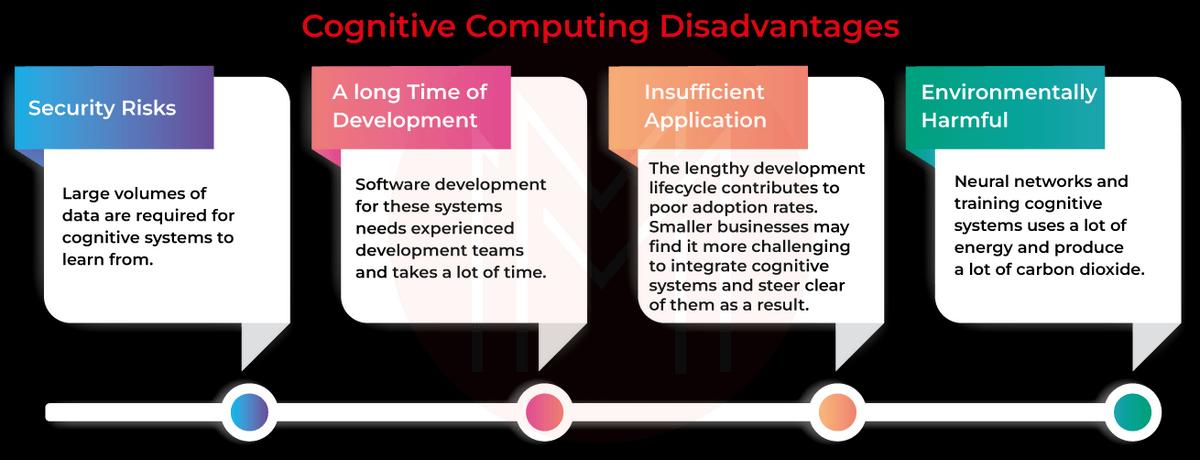
- Security Challenges: Large volumes of data are required for cognitive systems to learn from. Organizations employing the systems must preserve the data properly, especially if it pertains to customers' health or other types of personal information.
- Long Development Cycle Length: Software development for these systems needs experienced development teams and takes a lot of time. For the systems to comprehend certain jobs and procedures, they require substantial and in-depth training using massive data sets.
- Slow Adoption: The lengthy development lifecycle contributes to poor adoption rates. Smaller businesses may find it more challenging to integrate cognitive systems and steer clear of them as a result.
- Negative Environmental Impact: Neural networks and training cognitive systems uses a lot of energy and produce a lot of carbon dioxide.
Cognitive Computing vs AI
We could also say that Cognitive Computing "tries" to solve problems in the same way that a human would, in contrast to Artificial Intelligence, which always seeks to find new solutions to problems that may be superior to those that a human would have chosen, and does so without imitating human reasoning but rather by using the best algorithm.
Although the terms cognitive computing and artificial intelligence are sometimes used interchangeably, there are several key differences between the two.
| Artificial Intelligence | Cognitive Computing |
| Without using any human input, AI algorithms produce the most accurate results. | Based on using thinking, logic, and opinion from humans as input to produce output |
| AI is independent. | It depends on cognitive |
| The machine is a self-aware agent. It performs the functions of the human brain. | A machine acts as an agent for a human's aim or business operation. It is merely a tool for information. |
| It depicts reality. | It mimics how people act. |
| The algorithm used to deliver results and judgments is created by AI itself. | It just produces the information, leaving human interpretation of the final product to humans. |
| Makes use of trained algorithms | Uses analysis and prediction as fundamental techniques. |
| A few industries that use AI are manufacturing security, retail, and finance. | Improves procedures in a variety of fields, including industries, client relations, and health care |
| AI's role is to facilitate our work. | Cognitive comes into play if we make complicated human-like decisions. |
| Speech recognition, NLP, video analytics, image processing, and chatbots are technologies AI is used. | Facial recognition, sentiment analysis, risk assessment, fraud detection, and other cognitive tasks used. |
The ability of machines to respond, adapt, and reason based on experience it has learned underlies the similarities between the two. They have different techniques to deal with people but comparable intentions. Both of these technologies are in a stage of development where they will advance quickly. Cognitive computing and artificial intelligence (AI) are both supported by machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks.
Future of Cognitive Computing
The potential uses of cognitive computing are limitless. Both internal and external software troubleshooting can be facilitated with the use of the technology. As more companies invest in its development and as more individuals utilize it in their daily lives, we will see greater technological improvements. Therefore, it is clear that cognitive computing is here to stay.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, cognitive computing will fundamentally change the world in the coming years. Organizations are adopting cognitive computing and budgeting for certified professionals in the field. As this field expands, it will impact daily life and have considerable implications for many other industries.
To become a pro in the field, check out our interactive, live-online MindMajix’s AI Certification Courses, which come with 24*7 support to help you throughout the learning period.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence Course | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| Artificial Intelligence Course | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |
| Artificial Intelligence Course | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Artificial Intelligence Course | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .




