- Splunk API
- Splunk Careers
- IBM QRadar vs Splunk
- Splunk Architecture
- Splunk Admin Interview Questions
- Splunk Alerts
- Splunk Alternatives
- Splunk CIM
- Splunk Cloud
- Splunk Dashboard
- Splunk Dedup
- Splunk Education
- Splunk Enterprise
- Splunk Enterprise Security
- Splunk Eval Commands With Examples
- Splunk Interview Questions
- Splunk Logging
- Splunk Regex Cheatsheet
- Splunk Rest API Overview
- Introduction to Splunk Rex
- Splunk Search Commands
- Splunk Software
- Splunk Stats
- Splunk Streamstats Command
- Splunk Timechart
- Splunk Tool
- Splunk Tutorial For Beginners
- What are Splunk Universal Forwarder and its Benefits
- Splunk vs ELK
- Splunk Alert and Report
- Monitor Windows Event Log Data – Splunk
- What are the Splunkbase Apps and Add-ons
- Splunk Join - Subsearch Commands & Examples
- What are Splunk Apps and Add-ons and its benefits?
- Top 10 OSINT Tools - Open Source Intelligence
- Splunk Connect For Kubernetes
- Grafana vs Splunk
- Elasticsearch vs Splunk
- Splunk vs Dynatrace
Universal Forwarders, are dedicated, lightweight version of Splunk that contain only the essential components needed to send data. Let us look at how to install and set up forwarders on remote Linux and Windows hosts and send data to Splunk.
What are forwarders?
The most efficient way to gather data from any remote machine is to install Splunk universal forwarders on the remote hosts. A universal forwarder is a dedicated, lightweight version of Splunk that contains only the essential components needed to send data. It is similar to the Splunk server and it has many similar features, but it does not contain Splunk web and doesn’t come bundled with the Python executable and libraries.
Universal Forwarders provide reliable, secure data collection from remote sources and forward that data into Splunk (Enterprise, Light, Cloud or Hunk) for indexing and consolidation. They can scale to tens of thousands of remote systems, collecting terabytes of data with minimal impact on performance.
- Tagging of metadata (source, source type and host)
- Configurable throttling and buffering
- Data compression
- SSL security
- Transport over any available network ports
- Local scripted inputs
- Centralized management
| Learn how to use Splunk, from beginner basics to advanced techniques, with online video tutorials taught by industry experts. Enroll for Free Splunk Training Demo! |
Set up a receiver
To collect logs from remote machines, you need to configure both a receiver and a forwarder. The receiver is the Splunk instance that will receive the data and can be either a Splunk indexer or another forwarder configured to receive data from forwarders.
You can use the Splunk Web to set up a Splunk instance to serve as a receiver. Log in to Splunk Web using the administrative account and go to Settings > Forwarding and Receiving:
![]()
Click Add new under the Receive data section:
![]()
Specify the TCP port that you want the receiver to listen on. The port is usually 9997:
NOTE – Depending on the Splunk version, you might need to restart Splunk to apply the changes.
Install a Splunk forwarder on Windows
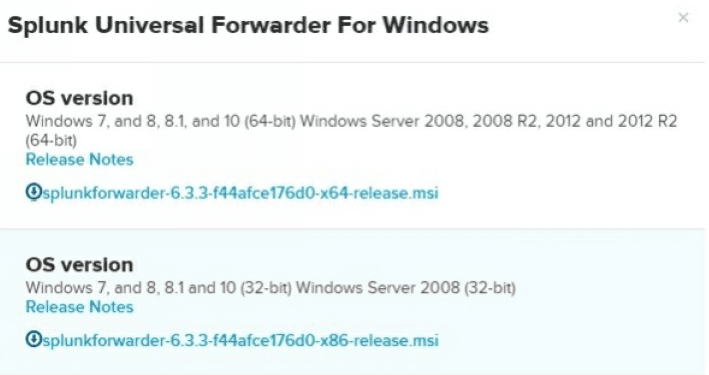
To install a Splunk forwarder, you need to download it first. Go to https://www.splunk.com/en_us/download/universal forwarder.html and choose the forwarder for your operating system:
Choose the right OS version:
In this example, we will install a Splunk forwarder on Windows Server 2012. Start the installation by double-clicking the installer file. You should be greeted with the Setup page. Here, you can accept the default options or customize the options. By default, the universal forwarder will be installed in C:Program FilesSplunkUniversalForwarder, use a local system account, and collect the Application, System, and Security Windows Event logs:
Next, you need to enter the hostname or IP address and management port of your deployment server (the default management port is 8089). The deployment server can be used to push configuration updates to the universal forwarder. Note that this is an optional step;if you skip it, you should enter a receiving indexer in the next step.
Enter the hostname or IP address and receiving port of your indexer (the default port is 9997):
Click Install to begin with the installation:
Once the installation is complete, the universal forwarder should automatically start.
| Preparing for Splunk Interview? Checkout Top Splunk Interview Questions & Answers and Crack you Interview |
Monitor logs using forwarders
To define which logs will be monitored and forwarded to the indexer, you need to edit the inputs.conf file in the $SPLUNK_HOMEetcsystemlocal directory. Here is how it can be done on Windows:
Open the inputs.conf file in a text editor:
Add the data inputs by specifying the stanzas. A stanza is a section of a configuration file that begins with a text string enclosed in brackets and contains one or more configuration parameters defined by key/value pairs. We will monitor the log file located at
C:logsremote_access.log, classify them as the source type of remote_access_logs, and store the data in the index called remotelogs:After you add the inputs, restart the forwarder in order to apply the changes. We can search the logs on the indexer to make sure, that the events have been received and indexed:

Monitor remote Windows event logs
If you’ve installed a forwarder on a Windows machine, you can edit the inputs.conf file to configure Windows event logs that you want to monitor. Here is the configuration to monitor Windows Security, Application, event logs and store them in the index called remotelogs:
Restart the forwarder in order for the changes to take effect. We can run a search on our Splunk indexer to verify that events have indeed been indexed:
| Related Blog: Splunk Logging |
Install a Splunk forwarder on Linux
You can install Splunk Enterprise on Linux using RPM or DEB packages or a tar file.
The universal forwarder is a separate executable, with its own set of installation procedures.
Tar file installation
The tar file is a manual form of installation. When you install Splunk Enterprise with a tar file:
- Some non-GNU versions of tar might not have the -C argument available. In this case, to install in /opt/splunk, either cd to /opt or place the tar file in /opt before you run the tar command. This method works for any accessible directory on your host file system.
- Splunk Enterprise does not create the splunk user. If you want Splunk Enterprise to run as a specific user, you must create the user manually before you install.
- Ensure that the disk partition has enough space to hold the uncompressed volume of the data, which you plan to keep indexed.
To install Splunk Enterprise on a Linux system, expand the tar file into an appropriate directory using the tar command:
tar xvzf splunk_package_name.tgz
The default installation directory is splunk in the current working directory. To install into /opt/splunk, use the following command:
tar xvzf splunk_package_name.tgz -C /opt?
RedHat RPM installation
RPM packages are available for Red Hat, CentOS, and similar versions of Linux.
Confirm that the RPM package you want is available locally on the target host. Verify that the Splunk Enterprise user can read and access the file.
1. If you need to, change permissions on the file:
chmod 744 splunk_package_name.rpm2. Invoke the following command to install the Splunk Enterprise RPM in the default directory /opt/splunk:
rpm -i splunk_package_name.rpmTo install Splunk in a different directory, use the --prefix flag:
rpm -i --prefix=/opt/new_directory splunk_package_name.rpmNote: The rpm executable offers no safety net at upgrade time. While you can use the --prefix flag to install it into a different directory, upgrade problems can occur. If the flag does not match the directory where you initially installed the software.
To Replace an existing Splunk Enterprise installation
rpm -i --replacepkgs --prefix=/splunkdirectory/ splunk_package_name.rpmIf you want to automate your RPM install with Kickstart, add the following to your kickstart file:
./splunk start --accept-license
./splunk enable boot-startNote: The second line is optional for the kick-start file.
| Explore Splunk Sample Resumes! Download & Edit, Get Noticed by Top Employers! |
Debian .DEB install
Prerequisites for installation
- You can install the Splunk Enterprise Debian package only into the default location, /opt/splunk.
- This location must be a regular directory, and cannot be a symbolic link.
- You must have access to the root user or have sudo permissions to install the package.
- The package does not create environment variables to access the Splunk Enterprise installation directory. You must set those variables on your own.
If you need to install Splunk Enterprise somewhere else, or if you use a symbolic link for /opt/splunk, then use a tar file to install the software.
To install the Splunk Enterprise Debian package:
dpkg -i splunk_package_name.debWhat gets installed
Splunk package status:
dpkg --status splunkList all packages:
dpkg --listConfigure a Splunk forwarder on Linux
Here are the steps to configure a Splunk forwarder installed on Linux to forward data to the Splunk indexer:
From the /opt/splunkforwarder/bin directory, run the sudo ./splunk enable boot-start command to enable Splunk auto-start:
Next, you need to configure the indexer that the forwarder will send its data to. This is done using the ./splunk add forward-server HOST:9997 -auth USERNAME:PASSWORD command, with admin and changeme as the default values for the username and password:
To add the data, you would like to consume and send to the indexer, run the sudo ./splunk add monitor LOG -sourcetype SOURCE_TYPE -index NAME. For example, to add the /var/log/syslog file with the sourcetype of linux_logs and store it to the index called remotelogs, we would use the following command:
Restart the forwarder to apply the changes (sudo./splunk restart). We can run a search to verify that events are indeed being sent:
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Splunk Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |
| Splunk Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Splunk Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| Splunk Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















