- Home
- Blog
- SQL Server
- SQL Server Interview Questions

- SQL Server Cluster
- SQL Server Constraints with Example
- Error Handling in SQL Server
- SQL Server Joins
- R Data Tables Tutorial with Examples
- SQL Server 2019: New Features
- SQL Server DBA Interview Questions
- SQL Server Interview Questions for 2-5 Years Experienced
- Top 10 SQL Server Interview Questions for 5 years Experienced
- SQL Server Tutorial
- Creating a PowerPivot Data Model in Excel 2013
- How to Implement In-Memory OLTP SQL Server
- Creating a Power View Report in Excel
- What is PolyBase in SQL Server
- SQL Server In-Memory OLTP Architecture Overview
- In-Memory OLTP integration and application migration In SQL Server
- SQL Server In-Memory OLTP Investments
- Introducing Power BI for Office 365 – SQL Server
- Creating a Power Map Reporting Content from SQL Server
- Platform For Hybrid Cloud
- Database Testing Interview Questions
- Magento Interview Questions
- What is Magento - A Complete Tutorial Guide
- SQL Joins Interview Questions
- T-SQL Tutorial
- DBMS Interview Questions
- SQL Server Architecture - Detailed Explanation
- RDBMS Interview Questions
- BigQuery Interview Questions
- DB2 Interview Questions
- Testing Connection to SQL Server
- How to Install Microsoft SQL Server?
Data is getting bigger day by day and it plays a critical role in enterprise’s decision-making. For handling data, enterprises require a database management system. One of the most famous database management systems is SQL Server. Knowing SQL Server will open the doors to becoming an SQL Developer. To crack the SQL Interview, you need to be prepared to answer the SQL Interview Questions. This blog is prepared to help you go through the fresher and experienced SQL Server questions and answer them in the interviews.
We have categorized SQL Server Interview Questions - 2024 (Updated) into 3 levels they are:
Below mentioned are the Top Frequently asked SQL Server Interview Questions and Answers that will help you to prepare for the SQL Server interview. Let's have a look at them.
Top 10 Frequently Asked SQL Server Interview Questions
- What do you mean by RDBMS?
- Can you differentiate between SQL and MYSQL?
- What is a JOIN, and mention its Types?
- What are Triggers, and mention their types in the SQL server?
- What is SQL Server Profiler?
- What are the various SQL Database Functions?
- Can you mention the different types of Queries in SQL Servers?
- What are SQL Server Integration Services and their functions?
- Compare Local Variables and Global Variables.
- What is the difference between OLAP and OLTP?
SQL Server Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
1. What do you mean by database?
Ans: A database is a structured form of data storage where data can be retrieved and managed efficiently. It is the collection of tables where the data is stored in an organized way. Tables consist of rows and columns in which rows are also known as records or tuples, and columns are known as attributes. Bank Management Database and University Management Database are a few examples of databases.
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in SQL Server, then enroll in "SQL Server Online Training" - This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2. What is a Relational Database?
Ans: A relational database is the collection of data that have an established relationship with each other. It consists of rows and columns. Each row in a database is a record, and columns have the attributes of data. Each row in a table can be identified with a unique ID known as a primary key. And rows in a table can be related to other tables using foreign keys.
3. What do you mean by RDBMS?
Ans: RDBMS is nothing but a relational DataBase Management System. It is the software that allows storing, managing, querying, and retrieving data from a relational database. And RDBMS interacts with users and the database; it can also carry out administrative tasks such as – managing data storage, accessing data, and assessing database performance.
4. Can you differentiate between SQL and MYSQL?
Ans:
| SQL | MySQL |
| It is the licensed product of Microsoft | It is an open-source platform managed by Oracle Corporation |
| Known as Structured Query Language – It is a query programming language | It is the Relational Database Management System |
| It uses SQL queries to perform tasks in RDBMS | It has no separate querying language. Uses SQL to perform tasks in RDBMS |
| Data is protected safely by not allowing third parties to intrude on the SQL servers. | Unlike SQL, it is an open-source platform, so data security wouldn't be as expected. |
| SQL doesn’t support any connectors | MySQL supports connectors such as the workbench tool to build databases. |
5. What do you mean by Relationships between Tables and mention their Types?
Ans: Relationships between tables describe how a row in a table is related to a row or rows of another table in a database.
There are three types of relationships, as mentioned below:
1. One-to-one: When a row in a table has only one related row in another table.
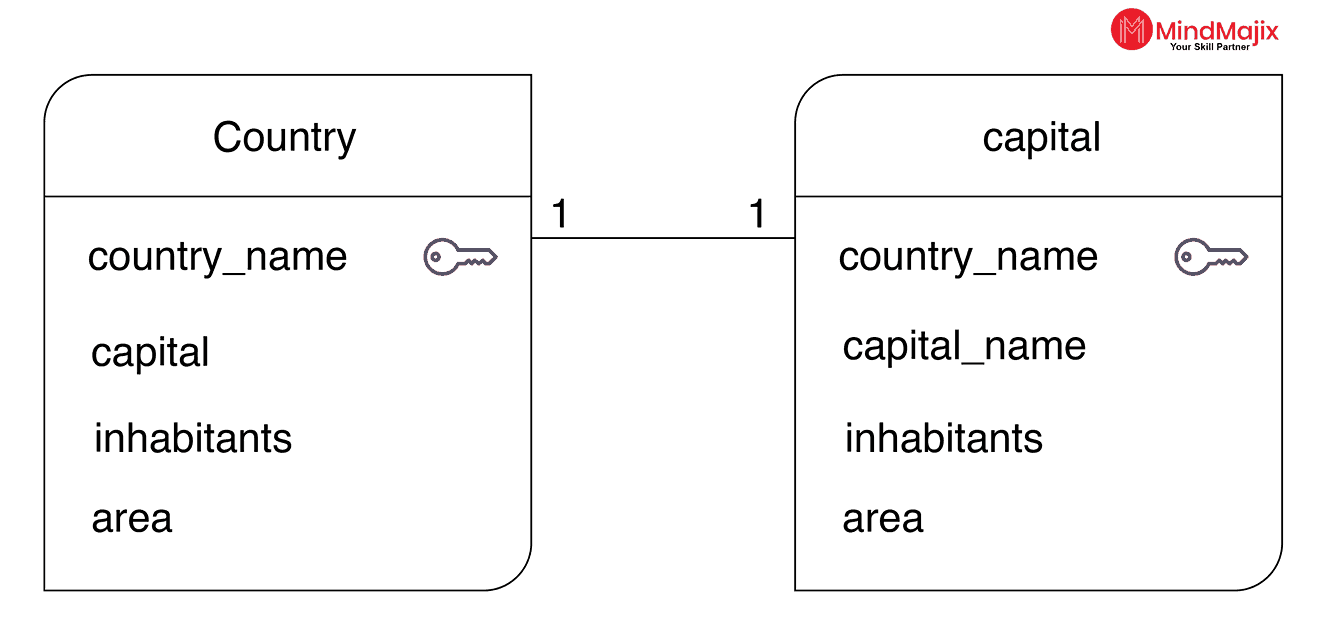
In the above, we can see a one-to-one relationship between “Country” and “Capital” tables. The key used for this relationship is “country_name.”
2. One to many: When a row in a table has multiple related rows in another table
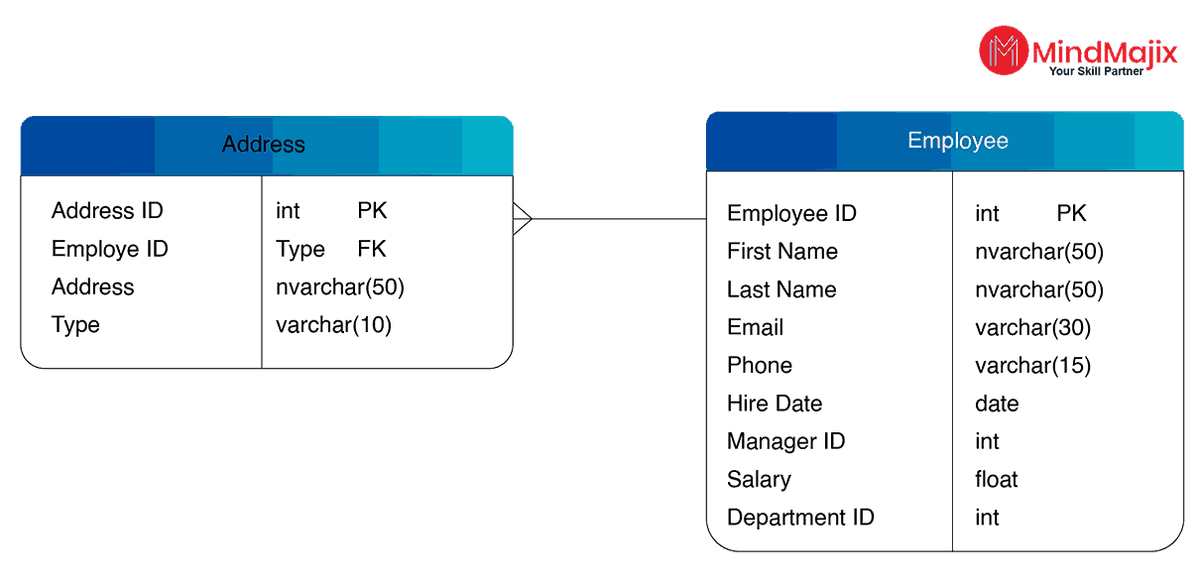
In the above diagram, we have two tables: “Employee” and “Address.” The primary key of the Employee Table “EmployeeID” is the foreign key in the Address Table and it links the Employee and Address Tables. This indicates that one record of the employee table can refer to multiple records in the Address Table. This is called a One-to-Many relationship.
3. Many to many: When a row has multiple related rows in another table and vice-versa.

In a university, a student can take multiple courses and a course will have multiple students. So, a Many-to-Many relationship is established between the “Student” and “Course” tables.
6. What is an Entity in a Database?
Ans: Entities are nothing but objects that are stored in the master data services models. They are real-world objects that can be distinguishable from other objects. Rows in an entity represent members of the master data, and columns represent attributes of the master data. Generally, entities group the same kind of data. For example, a list of employees of a company.
7. What do you mean by Attributes and mention their Types?
Ans: Attributes are the objects that are included in master data service entities. Also, attribute values are used to describe the members of the entity.
There are three types of attributes, as mentioned below:
- Free-form attributes
- Domain-based attributes
- File attributes
| Related Article: SQL Server Tutorial for Beginners |
8. What is SQL Server, and mention its core components?
Ans: SQL Server is an RDBMS developed by Microsoft. It has two core components – database engine and SQLOS. The database engine has a relation engine that supports processing queries, and managing database files, pages, indexes, etc. And SQLOS is nothing but a SQL Operating system. SQLOS provides operating systems such as memory and I/O management. It also performs the operations like exception handling and synchronization services.
| Related Article: SQL Server Architecture |
9. What is a transaction in SQL Server and mention its modes?
Ans: A transaction represents a single task. Once a transaction is over, modifications made to the data will be committed and stored in a database permanently. If an error occurs in the transaction, then the data changes will be canceled immediately.
The following are the modes of transactions:
- Autocommit transactions
- Explicit transactions
- Implicit transactions
- Batch-scoped transactions
10. What is a Transaction Log, and why is it important?
Ans: Transaction log records all transactions and related database modifications of every transaction. To be precise, it records the beginning of a transaction, the changes during the transaction, and the last COMMIT or ROLLBACK of the transaction. The transaction log is one of the vital components in database management since it is used to retrieve the database to a consistent state if there is a system failure.
11. What are ACID properties, and what do they mean?
Ans: The ACID properties are nothing but Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. Generally, all transactions must follow ACID properties.
- Atomicity: It ensures that a complete transaction must take place in a single execution. Suppose there is only a subset of operations during a transaction, then there could be a compromise in the aim of the transaction. But, atomicity eliminates this possibility.
- Consistency: It ensures that a transaction takes place with absolute data consistency before and after the transaction. Simply put, data consistency shouldn’t be compromised during transactions.
- Isolation: It ensures that each transaction takes place in complete isolation from other transactions. It means that each transaction must run as if it is the only transaction that is happening in the system.
- Durability: It makes sure that every transaction must be recoverable when required. Once a transaction is committed, it means that all the data updates have been made in the database then, and they can be retrieved at any time by users.
12. What is a Stored Procedure?
It is a function that consists of a group of statements, which can be stored and used repeatedly. Stored procedures can be called and executed as and when required. Stored procedures are stored as ‘Named objects’ in the SQL server database. The result set of the stored procedure depends on the values of the parameters.
Example:
CREATE PROCEDURE SelectAllEmployees
AS
SELECT * FROM Employees
13. What is the use of an Extended Stored Procedure?
Ans: Generally, stored procedures are the blocks of codes that can be accessed by simple application calls. At the same time, extended stored procedures help expand the functionality of SQL servers through external functions written in C or C++ languages. As a result, it allows returning result sets and parameters to the server from different data sources.
14. What is a Recursive Stored Procedure?
Ans: A stored procedure turns into a recursive stored procedure, including a CALL statement in the procedure body. Here, the CALL statements can be nested. In fact, there is no limit for recursions, but stored procedures nesting is limited by 15 times. Moreover, there are two forms of recursive stored procedures – mutual recursion and chain recursion.
15. What are Database Normalisation and Denormalisation?
Ans: Database normalization is the process of restructuring a relational database to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity. On the other hand, denormalization is a reverse engineering process that helps increase the read performance of a database. And it is achieved by either adding copies of data or grouping data. Hence, data can be read in a shorter time.
16. What is a JOIN, and mention its Types?
JOIN is a logical operation used to retrieve data from two or more two tables. It can only be accomplished when there is a logical relationship between two tables. Here, data from one table is used to select rows in another table.
There are five types of logical JOIN operations as mentioned below:
INNER JOIN: Inner Join is used for fetching the records that are common in both tables.
Example: Select employee.emp_id, employee.emp_name, employee.emp_address FROM Employee E INNER JOIN Department D ON Department.dept_id = Employee.emp_id where Department.dept_name = “EEE”
LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Left Join is used to fetch the records that are common in the both tables and available in the left side table.
Example: SELECT Customers, Customer_name, Orders.Order_ID from Customers LEFT JOIN Orders ON Customers.Customer_ID = Orders.Customer_ID ORDER BY Customers.Customer_name;
RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Right Join is used when we want to retrieve the records common in the both tables and available in the right side table.
Example: Select Order.Order_ID, Employee.Last_name, Employee.First_name From Order RIGHT JOIN Employee ON Order.Employee_ID = Employee.Employee_ID
FULL OUTER JOIN: Full Join is used to fetch all the records of both tables.
Example: SELECT Customer.Customer_name, Order.Order_id FROM Customer
FULL OUTER JOIN Order ON Customer.Customer_id= Order.Customer_id
ORDER BY Customer.Customer_name;
CROSS JOIN: Cross Join combines each row of the first table with the row of the second table.
Example: SELECT * FROM Employee CROSS JOIN Department
| Related Article: Different Types Of SQL Server Joins |
17. What is Subquery in SQL Server?
It is known as a subquery when a query is nested inside the statements such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE. Besides, a nested query inside a subquery is also known as a sub-query. Further, a subquery is also known as an inner query or an inner select. Similarly, the statement that has a subquery is known as an outer query or an outer select.
Example:
Select first_name from employees where age = (select max(age) from employee)
In the above query, the subquery will fetch the maximum age from the employee's table and the outer query will fetch the first of the employee who has the maximum age.
18. What are the Types of Subquery in SQL Server?
Ans: The following are the subquery types:
Subqueries with table aliases
Example: Select * from (SELECT EMP_ID, COUNT(*) AS count from Employee GROUP BY 1 ORDER BY 2) AS y LIMIT 1;Subqueries with IN and NOTIN
Example: Select from Employees where Emp_ID IN (Select Emp_ID FROM Manager Where Manager_ID = null)
Select from Employees where Emp_ID NOT IN (Select Emp_ID FROM Manager Where Manager_ID = null)Subqueries in UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT statements
DELETE FROM Employee
WHERE name NOT IN ( SELECT Emp_name
FROM Department
WHERE Date_of_joining >= CURRENT_DATE - interval ‘6 Months’
)Subqueries with comparison statements
Select * from employees where salary < (select AVG(salary) from employees)
Comparison operators modified by ANY, SOME, or ALL
SELECT Product_Name FROM Product WHERE Product_ID = ANY
(SELECT Product_ID FROM Orders WHERE Quantity = 10);
Subqueries with EXISTS and NOT EXISTS SELECT Supplier_Name FROM Supplier WHERE EXISTS (SELECT Product_Name FROM Product WHERE Product.Supplier_ID = Supplier.supplier_ID AND Price >20);19. How can you differentiate between a Primary Key and a Unique Key?
Ans: The primary key identifies each record in a table. It should have unique values but shouldn’t have NULL values. At the same time, the unique key ensures that all the values in a column are different. Simply put, the unique key avoids duplication of data in a column except for NULL Values. Moreover, a table will have only one primary key, but it may have many unique keys.
20. How can you relate a Foreign Key and a Primary Key?
Ans: A foreign key is a field (s) in a table that links the primary key with another table. A foreign key is mainly used to prevent the loss of a link between two tables. The table that has a primary key is known as the parent table, and a table that has a foreign key is known as the child table. A Foreign key can link with a unique key of another table as it links with a primary key.
21. What are the Defaults in the SQL Server?
Ans: Default is the value specified for a column in a database table. This value will be duplicated in all the new records of the column unless there is no other value specified. In this regard, SQL Server Management Studio is the tool used to specify a default value. Know that we can create defaults only for a current database, and the default value can be truncated when it exceeds the size of the column.
22. What are Cursors, and mention their types?
Ans: Cursors are known to be the extensions to result in sets that are the group of rows returned for a statement. They help retrieve one or more blocks of rows from the current position. Similarly, they can support data modifications for the rows in the current position in the result set.
There are four cursor types, as you can find below:
- Forward only
- Static
- Keyset
- Dynamic
23. What are Triggers, and mention their types in the SQL server?
Triggers are the special stored procedures. When there is an event in the SQL server, triggers will run automatically. There are three types of triggers: LOGON, DDL, and DML.
- LOGON Triggers: They are fired when a user establishes a LOGON event.
- DDL Triggers: They are fired when there is a Data Definition Language (DDL) event.
Example: Creating Employee Table:
CREATE TABLE Employee(
Emp_ID int IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
Emp_Salary xml NOT NULL,
Join_Date datetime NOT NULL,
ChangedName SYSNAME NOT NULL
)
Now we will create a trigger that will be fired every time an ALTER, DROP, or CREATE event happens.
CREATE TRIGGER Trigger1
ON DATABASE
FOR
CREATE_TABLE,
ALTER_TABLE,
DROP_TABLE
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
INSERT INTO Employee
(
Emp_Salary
DateChanged,
ChangedBy
)
VALUES (
EVENT DATA()
GETDATE(),
USER
);
END;DML Triggers: They are fired when there is a modification in data due to Data Manipulation Language (DML).
24. When can you use Triggers in the SQL Server?
Ans:
- When there is a need for an audit trail of activity in a database
- Deriving additional data that is not available within a database
- When enforcing referential integrity
- To implement a business rule
Related Article: JP Morgan Interview Questions
25. What is Referential Integrity?
Ans: Referential integrity aims at keeping SQL databases consistent. It is achieved using a group of rules that enforces relationships among data in tables. Generally, referential integrity is enforced with the support of foreign key constraints. Besides, it can be enforced with the help of check constraints with user-defined functions and triggers.
26. What do you mean by ER Diagram?
The ER diagram is known as the Entity-Relationship diagram. This diagram shows the visual representation of the structure of tables in databases and their logical relationships. ER Diagram displays table structures with column names and the associated data types, primary and foreign keys used, and relationships between the tables.

The above ER(Entity Relationship Diagram) shows relationships between Employee, Department, Country, and Folder tables.
| Related Article: Learn SQL Server Constraints with Examples |
27. What do you mean by CTE?
CTE is represented as a Common Table Expression. It specifies the temporary named result set. This result set is obtained by executing simple queries. CTE can be referred to in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and MERGE statements. Moreover, CTE can also be used in VIEW statements. There are two types of CTE – recursive and non-recursive.
Example:
CREATE TABLE Employee(
Emp_ID INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
Emp_Name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
Manager_ID INT NOT NULL
)
INSERT INTO Employee Values(101, ‘Amit’, 1)
INSERT INTO Employee Values(102, ‘Sameer’, 1)
INSERT INTO Employee Values(103, ‘Vamsi’,2)
INSERT INTO Employee Values(103, ‘Srikanth’, 3)
INSERT INTO Employee Values(105. ‘Mahesh’ 4)
After creating the ‘Employee‘ table, we can create ‘CTE‘ on that table through the “WITH” clause.
CTE:
WITH
example(Emp_ID, Emp_Name, Manager_ID)
AS
(
SELECT Emp_ID, Emp_Name, Manager_ID From Employee WHERE Manager_ID IS NULL
UNION ALL
SELECT e.Emp_ID, e.Emp_Name, e.Manager_ID From Employee e INNER JOIN cteExample c ON e.Manager_ID = C.Manager_ID
)28. What is a Sparse Column?
Ans: Sparse columns are nothing but ordinary table columns that provide optimized storage for NULL values. They reduce space requirements for NULL values by about 20 to 40 percent. Sparse columns can be used with filtered indexes and column sets. Sparse columns are defined by CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements.
29. What do you mean by Shared, Exclusive, and Updated locks?
Ans:
- Shared locks: It allows a page or rows only for reading. It restricts modifications of data by concurrent transactions.
- Exclusive locks: It allows exclusive transactions to modify a page or row using DML statements such as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
- Updated locks: It is used to avoid deadlocks. You can place a shared lock over a resource that already has an updated lock.
30. What is SQL Server Profiler?
Ans: It is a graphical user interface used for monitoring an instance of the database engine. It creates and manages traces and analyses the trace results when there is a demand. Generally, trace files record events, which can be replayed while diagnosing issues such as slow-running queries, finding the root cause of problems, etc.
31. What do you mean by Check Constraints?
Check constraints help to limit values to ensure their domain integrity. For instance, you can use logical operators that will only return either TRUE or FALSE. They can be used to create a check constraint to limit upper and lower values within a range. Also, you can apply multiple check constraints to a single column; similarly, you can apply a single constraint to multiple columns.
Syntax: Create Table Tablename(Column1 datatype check(expression), Column2, ColumnN)
Example: Create Table Employee(Emp_ID int check(Emp_ID>10), Emp_Name VARCHAR(25))
In the above example, we have applied a check constraint for the “Emp_ID” column.The Emp_ID value should be greater than 10. Now, if we give 8 as Emp_ID values, it will show an error:
INSERT INTO Employee(8, ‘Ram’)
When we execute the above code, it will show the following error:

32. What is an SQL Server Agent?
Ans: SQL server agent is a Microsoft Windows service that runs jobs on-demand, on schedule, or in response to an event. Generally, jobs are known as scheduled administrative tasks, and the SQL server agent executes the jobs in the SQL server. Jobs may contain one or more steps, and each step will have a task. For example, if there is a problem in a backup, the SQL server will record this event and notify the user.
33. What is COALESCE in SQL server and mention its few properties?
Ans: It is an expression that evaluates arguments in a list and returns only the first value that is not NULL.
For example, consider the following statement
SELECT COALESCE (NULL, 14, 15);
Now, the COALESCE expression returns the first value 14, which comes first after a NULL value.
Properties of COALESCE expression:
- The data type must be the same
- It can be a syntactic shortcut for the case expression
34. What is BULK COPY in SQL server?
Ans: BULK COPY allows a large amount of data transfer in and out of SQL tables or views. In addition, it allows data transfer between an SQL server and an Operating System data file such as ASCII.
BULK COPY in SQL server can be done in the following four modes:
- Native mode data file: Bulk copy from a table or view into a table or view in the same format.
- Character mode data file: Bulk copy from a table or view into another table in a different format
- Bulk copying from a data file into a table or view
- Loading data into program variables initially and then bulk copying into a table or view.
35. What do you mean by Collation?
Ans: Collation refers to the pre-defined rules to sort and compare data, and it also defines bit patterns that represent characters in a database. The rules help determine how the data should be stored, accessed, and compared. In addition, collation also provides case sensitivity and accent sensitivity for a dataset. SQL servers can store objects that have different collations in a single database.
36. What is the use of the UPDATE_STATISTICS command?
Ans: SQL Server updates query optimization statistics regularly in a database table or indexed view. In this regard, the SQL server's query optimizer performs this function by default. UPDATE_STATISTICS is the command that allows updating query statistics frequently in database tables. As a result, it improves query plans and query performance as well.
37. What is a Filtered Index?
Ans: A filtered index is nothing but a non-clustered index with an optimized disk-based restore. It uses a filter predicate to select a portion of rows in a table. A filtered index is created when a column has fewer relevant values for queries. Hence, it helps to improve query performance, reduce storage costs, and index maintenance.
38. How can you select data from an SQL table?
Ans: The SELECT statement helps to select data from databases.
The below example shows the retrieval of all the data from a table using the SELECT statement.
SELECT *
FROM DimEmployee
ORDER BY LastName;Suppose you need to select a portion of a table, then the WHERE clause must be used along with the SELECT statement to retrieve the required data. The below example shows the meaning of the WHERE clause in a SELECT statement.
SELECT FirstName, LastName, StartDate AS FirstDay
FROM DimEmployee
WHERE EndDate IS NOT NULL
AND MaritalStatus='M'
ORDER BY LastName;39. A table variable or a temporary table: which one is faster?
Ans: A table variable functions faster than a temporary table because table variables are stored in memory, whereas temporary tables are stored in a disk. Moreover, if a table variable’s size exceeds the size of memory, then its speed decreases.
40. What do you mean by Scheduled Tasks in SQL server?
Ans: To update the backups and statistics, databases must be maintained regularly. It can be achieved using scheduled jobs. In this way, the SQL server agent supports scheduling tasks in the SQL server to perform maintenance at regular intervals. In addition, the SQL server agent helps to view and modify the scheduled tasks.
| Related Article: How to Learn Error Handling in SQL Server |
41. What is the use of the SIGN function?
Ans: The SIGN function returns the sign of a number. The syntax for this function is shown as follows:
SIGN (numeric_expression)This function returns values based on the following conditions:
When numeric_expression > 0; returns positive (+1)
When numeric_expression = 0; returns zero (0)
When numeric_expression < 0; returns negative (-1)
42. What is a TABLESAMPLE?
Ans: This is the SQL statement that allows extracting random samples from a table using FROM statements. When users don’t require the entire dataset of a table, this statement can be applied to extract only the necessary samples. Note that the extracted rows won't be in any order, and sampling can be performed based on the percentage of rows.
43. What is SQL injection?
Ans: It is a malicious attack that would be sent targeting an SQL server instance. It is usually inserted through strings and will be passed into the SQL server for execution. TO OVERCOME THIS ATTACK, all SQL statements need to be verified for SQL injection vulnerabilities before their execution. Otherwise, the SQL server will execute the statements as usual, which will, in turn, cause harm to resources.
44. What is Database Mirroring, and mention its benefits?
Ans: Database mirroring allows keeping two copies of a single database in two different locations. The database is copied into different server instances of the SQL server database engine. It is applicable for the databases which adapt the full recovery model.
The benefits of database mirroring are as follows:
- It increases the availability of the database through high-safety mode with automatic failover
- It increases data protection irrespective of the mode –whether high-performance mode or operating mode
- It increases the availability of the production database during upgrades, which will reduce downtime significantly.
45. How do we create a primary key in a Table?
We can create a primary key in the following way:
CREATE TABLE Customer (
Customer_ID INT NOT NULL,
Customer_Name VARCHAR(25),
PRIMARY KEY(ID)
); 46. What is a Unique Key, and How can we create it?
A Unique Key is a constraint that assures all the values of a column are different. It helps you identify each row uniquely. We can create a Unique key in the following way:
CREATE TABLE Employee(
EMP_ID NOT NULL UNIQUE
EMP_FirstName VARCHAR(255)
EMP_LastName VARCHAR(255)
)47. What is the “ORDER BY” clause?
In an SQL Query, the “ORDER BY” clause is used for sorting the orders as per some fields in ascending or descending order.
Example:
SELECT * from students WHERE Graduation_Year = 2022 ORDER BY Student_ID ASCBy using the above query, we can retrieve the students who graduated in 2022 in the Ascending of their ID.
48. Explain in detail about Aggregate Functions.
Aggregate Functions are used for performing calculations on a group of values. Aggregate functions are used in “GROUP BY” and “HAVING” clauses. Following are the extensively used SQL Aggregate functions:
1) AVG(): It calculates the average value of the numeric values,
Example: Select AVG(Price) From Product WHERE Category_ID =1;2) MAX(): It calculates the maximum value of the chosen column
Example: Select MAX(Salary) FROM Employees3)MIN(): It calculates the minimum value of the chosen column
Example: Select MIN(Salary) FROM Employees4)SUM(): It calculates the sum of the collection of values
Example: SELECT SUM(Price) from Sales5) COUNT(): It Calculates the total number of records in a table
Example: SELECT COUNT(Emp_Name) FROM Employees49. What is a Constraint in SQL Server?
In SQL Server, Constraint acts as a rule that determines what type of data must be stored in the tables. SQL Server has six kinds of constraints:
1) Primary Key Constraint
2) Foreign Key Constraint
3) Unique Constraint
4) Check Constraint
5) Default Constraint
6) Not Null Constraint
Example: Create Table Constraint(
IF NOT NULL,
Salary int CHECK(Salary > 5000)
50. What is a Foreign Key?
A Foreign Key is a constraint used for defining the relationship between two tables that are connected by columns. In this Constraint, One table should point to the primary key in another table. A table can have multiple foreign keys, and each foreign key can have a different referenced table.
Example:
CREATE TABLE Customer(
Cust_ID PRIMARY KEY,
Cust_Name NOT NULL,
Age,
ContactNo,
GENDER,
Address)
CREATE TABLE VENDOR(
Vend_ID PRIMARY KEY,
Vend_Name NOT NULL,
Cust_ID FOREIGN KEY)In the above, “Cust_ID” is the foreign key of the Vendor Table.
51. What are the different types of commands in SQL Server?
In SQL Server, we have three different types of commands, they are:
1)DDL: Data Definition Language commands are used for handling the structure of the objects. With DDL commands, we can modify the object or entity structure. Following are the DDL Commands in SQL Server:
1)Create: It is used for creating data objects like Tables, Views, Functions, etc.
2)Alter: It is used for Altering the tables, views, functions, etc.
3) Drop: It is used for deleting the data objects permanently.
Example: Create Database DB1
Create Table Employee(
Emp_ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Emp_Name CHAR
)
DROP Database DB12)DML: Data Manipulation Language commands are used for manipulating data objects like views, tables, etc. These commands are helpful when we want to modify, insert, and delete the data. Following are the DML Commands of SQL Server:
1) Update: It is used for updating the data in the table.
2) Insert: It is used for inserting the data into the table.
3) Delete: It is used for deleting the data from the table
4) Insert Into It is used to Insert the bulk data into a table
Example:
INSERT INTO Table Values(101, ‘Amit’)
DELETE FROM Table where ID = 104
UPDATE Table SET Name = ‘Sumit’ WHERE ID = 1053)DCL: DCL commands are used for security purposes. These commands are used for providing permissions, access, and roles. DCL commands are as follows:
1) Revoke: This command is used when we want to take back access from the user.
2) Grant: It provides users access to the database or any object.
4)TCL: TCL commands are used for handling the Transactions in SQL Server. TCL commands are as follows:
1) Rollback: The rollback command is used for restoring the database to its last committed state.
2) Commit: It is used to save the transaction permanently.
3) Save Tran: It is used to save transactions so that we can roll back that transaction to the point whenever required.
SQL Server Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
52. What are the various SQL Database Functions?
Ans:
| Aggregate functions | They work on a group of values and return a single value. |
| Analytic functions | They work with a set of groups and can return multiple rows for each group. |
| Ranking functions | They return the ranking value for each row. |
| Rowset functions | They return a value that can be used as the table reference. |
| Scalar functions | They work on a single value and return a single value as well. |
53. What is the difference between Stored Procedures and Functions?
Ans: In stored procedures, codes are usually compiled, and these compiled codes are executed when the program calls them. But in functions, on the contrary, codes are compiled and executed every time they are called.
Also, there must be a return while executing functions, whereas it is optional while executing stored functions. Furthermore, functions can be called from stored procedures, but stored procedures cannot be called from functions.
54. Can you mention the different types of Queries in SQL Servers?
Ans:
- Select Query: This query creates the SQL SELECT statement. It retrieves data from tables or views.
- Insert results: This query creates the SQL INSERT INTO….SELECT statement. It allows copying rows from one table to another and copying rows within a table.
- Insert Values: This query creates the SQL INSERT INTO….VALUES statement. It creates new rows in tables and inserts values into them.
- Update Query: This query creates SQL UPDATE…SET statement. It allows updating values in multiple rows.
- Delete Query: This query creates the SQL delete statement. It helps to remove rows from a table.
- Make table query: This query creates the SQL SELECT…INTO statement. It creates a new table and rows in it.
55. What is the use of a Database Engine in the SQL Server?
Ans: The database engine can store, process, and secure data. It creates database objects such as stored procedures, views, and triggers; and executes the objects. It processes queries, provides controlled access, and optimizes transactions in a database. A SQL server can support up to 50 database engine instances in a single computer.
56. How can you differentiate between UNION and UNION ALL?
Ans: UNION is the operator that combines two queries into a single result set using select statements. Note that it functions based on specified conditions.
Syntax: query1 UNION query2
UNION ALL is the operator that combines two queries into a single result set, extracting all the rows from the tables without any conditions.
Syntax: query1 UNION ALL query2
57. Brief the different types of JOINS.
Ans:
- INNER JOIN: This command helps to return records that are common to both tables
- LEFT JOIN: This command helps to return values that are common to each other along with the complete records of the left table
- RIGHT JOIN: This command helps to return values that are common to each other along with the complete records of the right table
- FULL JOIN: This command helps return all the tables' records when there is a match between the two.
- CROSS JOIN: It is known as Cartesian Join. This command returns all combinations of each row from the tables. There is no specific condition for joining two tables.
58. What are the four types of physical JOIN operations?
Ans:
- Nested loop joins: They are applied when one join input is small, and the other join input is large because nested loop joins require minimum I/O and few comparisons.
- Merge joins: When two inputs are large and of the same size and sorted out based on the join column, then merge join will provide a fast join operation.
- Hash joins: They efficiently process large, non-indexed, and unsorted inputs. They are also helpful in getting intermediate results in complex queries.
- Adaptive joins: This join helps to decide when to switch to a Nested loop based on a threshold value
59. What is the difference between JOIN and UNION in an SQL server?
JOIN is the operator that combines data from many tables based on specific conditions, which creates new columns. In contrast, UNION combines data from many tables using SELECT statements, creating new rows.
The number of columns retrieved from the tables needn't be the same in JOIN statements, whereas the number of columns retrieved from the tables must be the same in UNION statements.
Consider two tables:
Employee
| ID | Name | Age |
| 1 | Mayank | 25 |
| 2 | Ram | 27 |
| 3 | Harry | 19 |
| 4 | Sathvik | 20 |
| 5 | Himanshu | 33 |
| 6 | Amit | 40 |
Customer
| ID | Name | City |
| 10 | Rahul | Dehradun |
| 5 | Khaled | Kolkata |
| 4 | Vamsi | Shimla |
| 11 | Seenu | Hyderabad |
| 15 | Prithvi | Patna |
| 6 | Vinay | Delhi |
Join
Select Employee.ID, Employee.Name, Customer. City FROM Employee INNER JOIN Customer ON Employee.ID = Customer. ID
Result
| ID | Name | City |
| 5 | Khaled | Kolkata |
| 4 | Sathvik | Shimla |
| 6 | Amit | Delhi |
Union
Select Name from Employee WHERE ID < 3 UNION Select Name from Customer WHERE ID < 6
| Name |
| Mayank |
| Ram |
| Khaled |
| Vamsi |
The above example will help you get in-depth knowledge of the difference between JOIN and UNION
60. What do you mean by Clustered Indexes?
Ans: The clustered index describes how data is stored in a table, and the table should have a key value. Know that there can be only one clustered index for a table. When there is a clustered index in a table, then it is known as the clustered table. When there is no clustered index in a table, then data is stored in tables unstructured.
61. How can you use the SCOPE_IDENTITY function in the SQL server?
Ans: This function returns the last identity value inserted into an identity column within the same scope. Here, the scope is nothing but a module, which will have a stored procedure, trigger, batch, and function. If two statements exist in the same stored procedure or batch or function, then it means that they are in the same scope.
The syntax for this function is provided as SCOPE_IDENTITY ( )
62. What is the use of WITH TIES?
Ans: WITH TIES allows adding one or more rows along with the rows limited by the TOP or similar statements. It works only when you use it alongside the ORDER BY expression.
The syntax is given as shown below:
[
TOP (expression) [PERCENT]
[WITH TIES]
]63. How can Deadlocks in the SQL server be resolved?
Ans: Deadlock occurs in an SQL server when two processes lock a single resource simultaneously and wait for the other process to unlock the resource. Generally, the SQL engine notices this type of incident and ends one of the processes voluntarily, which helps to release the lock. Thus, the SQL engine allows one process to complete successfully while stopping another process simultaneously.
| Related Article: What is PolyBase in SQL Server |
64. How can you compare the Local and Global Temporary tables?
Ans: Local temporary tables are visible only to the table creators when connected with an SQL instance. The tables will be deleted once the user disconnects the SQL instance.
On the other hand, global temporary tables are visible to any user. These tables are deleted only when any user referencing these tables gets disconnected from the SQL instance.
65. How can you distinguish between SUBSTR and CHARINDEX?
Ans: Given the starting position and length details, SUBSTR helps extract a substring from the specified string.
The syntax for this function is given by:
SUBSTRING (expression, starting_position, length)
On the contrary, the CHARINDEX function helps identify a substring's position from the specified string.
The syntax for this function is given by:
CHARINDEX (substring, input_string)
66. When to execute COMMIT and ROLLBACK commands?
COMMIT: A statement is executed to save the changes made on the current transaction; after that, the transaction becomes permanent.
Example:
| EMP_ID | EMP_NAME | EMP_AGE | EMP_ADDRESS | EMP_SALARY |
| 1 | Sai | 30 | Mumbai | 50,000 |
| 2 | Vijay | 25 | Chennai | 80,000 |
| 3 | Vikram | 28 | Pune | 40,000 |
| 4 | Sumith | 29 | Ahmedabad | 70,000 |
| 5 | Himesh | 33 | Chandigarh | 20,000 |
Delete from employee where age = 33;
COMMIT;
Now if we use the Select query we will get the below result:
Select * from Employee;
Result:
| EMP_ID | EMP_NAME | EMP_AGE | EMP_ADDRESS | EMP_SALARY |
| 1 | Sai | 30 | Mumbai | 50,000 |
| 2 | Vijay | 25 | Chennai | 80,000 |
| 3 | Vikram | 28 | Pune | 40,000 |
| 4 | Sumith | 29 | Ahmedabad | 70,000 |
In the above table, we can see that the changes made to the table are
ROLLBACK: A statement is executed to delete the changes made on the current transaction after the last COMMIT.
Example:
| EMP_ID | EMP_NAME | EMP_AGE | EMP_ADDRESS | EMP_SALARY |
| 101 | Karan | 28 | Delhi | 1,00,000 |
| 102 | Parth | 30 | Gwalior | 80,000 |
| 103 | Kiran | 28 | Jaipur | 35,000 |
| 104 | Karthik | 33 | Bangalore | 50,000 |
| 105 | Lokesh | 31 | Chennai | 75,000 |
DELETE From Employee WHERE EMP_AGE =28;
ROLLBACK;
After executing the “DELETE” command, we will get the below table
Example:
| EMP_ID | EMP_NAME | EMP_AGE | EMP_ADDRESS | EMP_SALARY |
| 102 | Parth | 30 | Gwalior | 80,000 |
| 103 | Karthik | 33 | Bangalore | 50,000 |
| 104 | Lokesh | 31 | Chennai | 75,000 |
And After that, ROLLBACK will undo the operations. So, after executing the ROLLBACK, we will get the following table:
| EMP_ID | EMP_NAME | EMP_AGE | EMP_ADDRESS | EMP_SALARY |
| 101 | Karan | 28 | Delhi | 1,00,000 |
| 102 | Parth | 30 | Gwalior | 80,000 |
| 103 | Kiran | 28 | Jaipur | 35,000 |
| 104 | Karthik | 33 | Bangalore | 50,000 |
| 105 | Lokesh | 31 | Chennai | 75,000 |
67. How can you distinguish between GETDATE and SYSDATETIME functions?
Ans: The GETDATE function returns the date and time of a location. In contrast, the SYSDATETIME function returns the date and time with a precision of 7 digits after the decimal point.
You can understand this from the following examples.
SELECT SYSDATETIME( ) AS CURRENT_DATE_TIME;
CURRENT_DATE_TIME
2015-1016 12:37:06 . 615177868. How to delete a table using SQL Server Management Studio?
- Select the table that you need to delete in Object Explorer
- Right-click on the table, then choose delete from the shortcut menu
In the above image, we can see the “Delete” option.
- Confirm deleting the table by clicking ‘Yes’ in the prompt box

In the above image, we can see the prompt box.
69. What is SSMA in an SQL server?
Ans: SSMA is known as Microsoft SQL Server Migration Assistant. It is an automation tool that helps migrate from Microsoft Access Database to SQL Server or Azure SQL Database or Azure SQL Database Managed Instance. It also supports DB2, MySQL, Oracle, and SAP ASE migration to SQL Server.
70. What do you mean by Data Quality Services (DQS)?
Ans: DQS is nothing but a knowledge-driven data quality platform that supports carrying out data quality tasks such as correction, enrichment, standardization, and de-duplication of data. In addition, DQS analyses the integrity of data using profiling that is integrated with data-quality tasks.DQS consists of two components: a Data Quality Server and a Data Quality Client.
71. What are SQL Server Integration Services and their functions?
Ans: It is the platform for enterprise-level data integration and data transformation services. It includes copying and downloading files, loading data warehouses, managing SQL Server objects, and cleansing and mining data to solve complex business problems quickly. Integration services consist of a group of built-in tasks, graphical tools, and an SSIS catalog database.
72. Compare the difference between the Clustered Index and the non-custered index.
Ans:
| Clustered Index | Non-clustered Index |
| It describes the order in which data is stored in tables physically. | It doesn’t sort tables physically inside a table but creates a logical order for stored data. |
| Each table will have only one clustered index. | There could be many non-clustered indexes for a table. |
| Less storage is required since they only sort tables. | A non-clustered index is stored in one location, and data is stored in another. So, large storage is required. |
| Supports faster operations than the non-clustered index. | Decreases the speed of performance due to extra lookup setup. |
73. Differentiate: Derived attribute, Derived persistent attribute, and Computed attribute?
Ans:
- Derived Attribute: It is the attribute that obtains values from other columns.
- Derived Persistent Attribute: It is the stored derived attribute.
- Computed Attributes: It is the attribute that is computed from internal system values
74. What are the different levels of normalization, and explain them shortly?
Ans:
- First Normal Form (1 NF): It avoids data duplication in a table. It creates a specific table for the related data and uses the primary key to identify the data.
- Second Normal Form (2 NF): It creates separate tables for the group of data that belongs to multiple records. The tables are linked with foreign keys.
- Third Normal Form (3 NF): It eliminates the fields that are not related to keys
- Boyce Codd normal form /Fourth Normal form (BCNF or 4NF): It should be in the form of the 3 NF. Also, there shouldn’t be any multi-valued dependencies.
75. What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE commands?
The DELETE command removes a row (s) from a table based on given conditions, whereas the TRUNCATE command removes the entire rows from a table. Also, changes have to be manually
COMMITTED after executing the DELETE command, whereas changes are COMMITTED automatically after the execution of the TRUNCATE command.
DELETE Command Example:
DELETE FROM Employees WHERE Employee_ID>100
TRUNCATE Command Example:
TRUNCATE TABLE Employees
76. Compare Local Variables and Global Variables.
Ans:
| Global Variables | Local Variables |
| Global variables can be declared outside of all functions, and any function of the program can access them. | Local variables are declared inside the function, and they can be called only by that function. |
| Global variables exist until the execution of the entire program. | Local variable exists until the execution of that specific function. |
| Global variables are stored in fixed memory and not cleaned up automatically. | Local variables are stored in stack memory and cleaned up automatically. |
77. What is the difference between OLAP and OLTP?
Ans: OLAP is known as Online Analytical Processing. It consists of the tools used for data analysis for making business decisions. It works on historical data and provides insights into multiple database systems. For example, NETFLIX and Spotify generate insights from past data.
On the other side, OLTP is the Online Transaction Processing and works on the operational data. It manages ACID properties during transactions. It performs faster than OLAP, so it is used to perform day-to-day activities such as online ticket booking, messaging, etc.
78. What is the FLOOR function in the SQL server?
Ans: This function allows returning the largest integer value, which is less than or equal to the specified value.
The syntax for this function is provided as:
FLOOR ( numeric_expression )For example, refer to the following statement about using the FLOOR function.
SELECT FLOOR (22.35) AS FloorValue
This statement will return a value less than 22.35 or the same.
79. What is the use of SQL server locks, and what resources can be locked by server locks?
Ans: If an exclusive lock locks a row in a table during a specific transaction, that row cannot be accessed by other transactions. So, others can view or modify that row only when the lock is released. Also, locks reduce concurrency in transactions, so locks must be minimized to improve transaction performance.
Note that the resources such as AllocUnit, application, database, extent, file, key, metadata, etc., can be locked using lock functions.
80. What is the use of the SET NOCOUNT function?
Ans: This function helps to stop the message that indicates how many rows are being affected while executing a T-SQL statement or stored procedure.
The syntax for the function is given as:
SET NOCOUNT { ON | OFF } If you set this function ON, then no count is returned in the result set; on the other hand, if you set this function OFF, then count is returned.
81. What do you mean by Magic Tables in SQL server?
Ans: Magic tables are virtual tables that exist in two types – INSERTED AND DELETED. They hold the information of the newly INSERTED and DELETED rows. The INSERTED table will have the newly inserted rows on top of it. The DELETED tables will have the recently deleted rows on top of it on similar tracks. Magic tables are stored in tempDB.
82. How can you prevent SQL injection vulnerabilities?
Ans: We can prevent SQL injection vulnerabilities in the following ways:
- Using Type-Safe SQL parameters
- Using parameterized input with stored procedures
- Filtering inputs
- Reviewing codes
- Wrapping parameters
83. What do you mean by the recovery model in SQL Server and its types?
Ans: The recovery model is the property that controls the transaction log maintenance in a database. It tracks the logging of transactions and decides about the necessary backup for the transactions and the availability of the restoration options. There are three types of recovery models Simple, Full, and Bulk-logged.
- Simple Recovery Model: There is no log backup, and it eliminates the need to manage the transaction log space.
- Full Recovery Model: This model requires log backups. It doesn’t allow any work to be lost for any reason.
- Bulk-logged Model: This model requires log backups. It allows high-performance bulk-copy operations.
84. What are the different types of backups used in SQL servers?
Ans:
- Copy-only backup: It is a special-use backup that is independent of the regular backups
- Data backup: It is a backup of data either entirely or partially
- Database backup: It is a backup of a complete database
- Differential backup: It is a record of only the changes made in a database after a database backup event
- Full backup: It is a backup of full data with the necessary transaction log for restoration
- Log backup: It is a backup of all transaction logs
- File backup: It is a backup of files in a database
- Partial backup: It is a backup of files from a specific filegroup such as primary, every read/write, and optionally specified read-only files.
85. How can you use HAVING and WHERE clauses in a single query?
Generally, the WHERE Clause acts on individual rows, whereas the HAVING clause acts on groups. A SQL query can be constructed using the HAVING clause and WHERE clause. In that situation, WHERE Clause acts first based on the given conditions and groups rows in a table. Then, the HAVING clause acts on the groups and creates a result set only including the groups based on the given conditions.
Example: Select category_id, AVG(price) FROM Products WHERE model_year = 2017 GROUP BY Category_id HAVING AVG(price) > 2000;
In the above query, we have used both “HAVING” and “WHERE” clauses for fetching the products that were introduced in 2017 and have an average price greater than 2000.
86. What are User-Defined Functions, and why do we have to use them?
Ans: User-defined functions (UDFs) are routines that accept parameters, perform complex functions, and return a value or the result set. There are three types of UDFs – user-defined scalar functions, table-valued functions, and system functions.
We can use UDFs for the following reasons:
- They can be created, stored, and called at any number of times.
- They allow faster execution because UDFs don’t need to be reparsed or reoptimized.
- They minimize network traffic as it reduces the number of rows sent to the client.
Department:
| Department_No | Department_Name |
| 101 | ECE |
| 102 | EEE |
| 103 | CSE |
| 104 | IT |
| 105 | MECH |
Employee Details:
| Employee_No | Emp_Name | Address | Age | Department_No | Salary |
| 1 | Kamal | Hyderabad | 23 | 101 | 25000 |
| 2 | Vijay | Bangalore | 22 | 102 | 24000 |
| 3 | Amar | Chennai | 21 | 103 | 23000 |
| 4 | Umar | Chennai | 24 | 104 | 22000 |
| 5 | Sunil | Hyderabad | 25 | 103 | 26000 |
87. Write a query to display employee details working in the EEE department.
Ans: SELECT employee.employee_name, employee. address, employee. salary, employee.age,
FROM Department D
INNER JOIN Employees E
ON department.D_no=employee.D_no WHERE department.D_name=’EEE’
88. Write a query to display employee details with their department names.
Ans: SELECT employee.employee_no, employee.employee_name, employee. address, employee. salary, employee.age, department.department_name
FROM department D
INNER JOIN employee E
ON department.D_no=employee.D_no
89. Write a query to display employee details along with department_name and their age between 21 to 25.
Ans: SELECT emp.e_no, emp.e_name, emp. address, emp. salary, emp. age, dept.d_name
FROM Department D
INNER JOIN employee E
ON dept.D_no=emp.D_no
WHERE E.age between 21 and 25
90. Write a query to display the employee details whose salary is above 23000 and age is above 22 and working in the CSE department.
Ans: SELECT emp.e_no, emp.e_name, emp. address, emp. salary, emp. age, dept.d_name
FROM Department D
INNER JOIN employee E
ON dept.D_no=emp.D_no
WHERE E.age>22 and E.salary>23000 and dept.D_name=’CSE’
91. Write an SQL Query to find all the employees whose salary is between 50000 and 100000?
Select * FROM Employee WHERE Salary BETWEEN ‘50000’ and ‘100000’92. Write a SQL Query to fetch the department-wise employees sorted by the department’s count in the ascending order?
Select Department, Count(Emp_ID) AS EmpDeptCount1 FROM Employees GROUP BY Department ORDER BY EmpDeptCount1 ASC93. Write an SQL Query to get only even rows from the tables?
SELECT * FROM Student where MOD(StID,2)=094. Write an SQL Query to fetch all the Employees who are also the managers from the Employee table?
Select DISTINCT E.Emp_Name FROM Employees E INNER JOIN Employee M ON E.Emp_ID = M.Emp_ID95. How do we get the current version of SQL Server?
By executing the following command, we will get the version of SQL Server:
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY(‘product version’)
96. What is the use of ISNULL()?
ISNULL() function is used for checking whether the given value is NULL or not NULL. It also includes an option to replace the value with a NULL.
97. What is a Function, and What are the different types of Functions in SQL Server?
The function is a sequence of statements that takes input and processes it to carry out a particular task and give output. Every function should have a name, and it should not start with special characters like @,$, #, etc. Types of Functions
1) Pre-Defined Functions
2) User-Defined Functions
In the user-defined function, we can write the logic as per our requirements. The main benefit of utilizing user-defined functions is that we are not just restricted to pre-defined functions; we can build our functions as per our requirements.
Example:
Create Function vs(@Id int)
returns table
as
return select * from Student where Student_ID = @Id98. How to rename the column of the table?
Using the “ALTER TABLE” command, we can rename the column in the table. Example:
ALTER TABLE Customer
RENAME COLUMN Customer_ID to CustomerID99. How to Delete a record from the table?
Using the “DELETE” command, we can delete a record from the table. Example:
DELETE FROM Employee WHERE Emp_Salary=50,000;100. How do you fetch the values in the text column of the “Employee” table that starts with “A”?
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE First_Name LIKE ‘A_’;101. How to find the 3rd highest salary in SQL Server?
Create Table Employee (
Emp_name VARCHAR(50),
Emp_salary DECIMAL
);
INSERT INTO Employee values (
(‘Vijay’, 50,000),
(‘Vikram’, 35,000),
(‘Yeshwanth’, 40,000),
(‘Rishab’, 55,000)
(‘Ram’, 65,000)The Employee table will be:
| Emp_name | Emp_salary |
| Vijay | 50,000 |
| Vikram | 35,000 |
| Yeshwanth | 40,000 |
| Rishab | 55,000 |
| Ram | 65,000 |
To find the 3rd highest salary from the above table, we have to write the following query:
Select * from(Select Emp_name, Emp_salary, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY Emp_salary DESC) AS r from Employee) AS x where r=3;
SQL Server Interview Questions and Answers for Advanced
102. How important is Database Design in SQL servers?
Ans: The performance of SQL servers depends on the factors such as proper data population in tables, a good relationship between tables, and elimination of data redundancy. Therefore, when building a new system or modifying an existing system, the design must be correctly designed to yield consistent performance.
103. Can you mention the advantages of Stored Procedures over Dynamic SQL?
Ans:
- A stored procedure is cached in server memory, so it is faster than dynamic SQL
- Stored procedures keep ‘business logic’ separate from ‘database logic’. So, if any error occurs in the business logic, you have to change the application codes only. Similarly, if there is an issue with the database logic, you have to change the stored procedures only.
- The stored procedure creates low network traffic, whereas dynamic SQL creates high network traffic.
- Stored procedures with static SQL can detect errors before they run, whereas stored procedures with dynamic SQL cannot detect errors before they run.
104. How can you hold the Stored Procedure scripts in the SQL server?
Ans: We can store the stored procedure scripts in a server table known as Sys.SQL_Modules. Also, Sys. procedures table is used to store the name of the stored procedures.
105. What are the advantages of using stored procedures in an SQL server?
Ans:
- Stored procedures provide faster performance since they are compiled and stored in executable form.
- A stored procedure is nothing but a piece of code that can be used many times, increasing productivity.
- It can be stored in a database server instead of on a client machine. As a result, it increases the speed of query execution.
- It can be used in many applications after the successful compilation
106. How can you hide an instance of the SQL Server database engine?
Ans: You can hide the SQL server database engine using the SQL Server configuration manager. The following two steps can accomplish it:
- Expand SQL server network configuration, right-click protocols, and then select properties.
- Open the Flags tab, select ‘YES’ in the HideInstance box, and click OK to close the dialogue box.
107. What are the different third-party tools used in SQL servers?
Ans: The following are the various third-party tools used in SQL servers:
- Red Gate SQL Compare
- SSW SQL Deploy
- SSW SQL Server Auditor
- Instant SQL formatter
- Apex SQL Doc
- LECCO SQL Expert
- Speed Ferret
- XPSMTP
108. What do you mean by SSRS in SQL Server?
Ans: SSRS is known as SQL Server Reporting Services, which provides a group of on-premises tools and services. SSRS allows creating, deploying, and managing mobile and paginated reports.
- Paginated Reports: They produce up-to-date reports with the support of updated tools and new features.
- Mobile Reports: This type has a format that adapts to different devices.
- Web Portal: Paginated reports, excel workbooks, KPIs, and mobile reports can be organized and viewed through the web portal. You can view the web portal using any modern browser.
109. How can you alter a table schema in an SQL server?
Ans: The following syntax is used to transfer ‘securable’ between schemas.
ALTER SCHEMA schema_name
TRANSFER [ <entity_type> : : ] securable_name
[ ; ]
<entity_type> : : =
{
object | Type | XML Schema Collection
}Schema_name: It is the name of the schema where the securable is to be moved.
Entity_type: It represents the class of the entity.
Securable _name: It is the one-part or two-part name of the securable.
110. How does Intelligent Query Processing improve the performance of SQL Server workloads?
Ans: The intelligent query processing (IQP) family has many features that improve the performance of workloads with minimum implementation effort. Here, the various IQP features are adaptive joins, batch mode on rowstore, approximate QP, etc. You can automatically apply IQP to all server workloads by enabling compatibility levels for databases.
111. What do you mean by in-memory OLTP database?
Ans: In-memory OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) is a database technology that supports optimizing the performance of various processes such as transaction processing, data ingestion, transient data scenarios, and data load. It provides low latency, higher throughput, and faster response time.
112. What is the use of isolation level in SQL transactions?
Ans: Isolation is the property of SQL transactions, which is used to isolate a SQL transaction from other transactions – as a result, it ensures data integrity in the transactions. The isolation feature helps lock a row during a transaction so that other transactions cannot access that row. There are five isolation levels in SQL transactions that support maintaining data concurrency in databases.
113. What are the benefits of Partially Contained Databases?
Ans:
- Partially contained databases can retain crucial information while making data transactions. So data can be accessed from databases even if there is missing data during transactions.
- It will be useful in ‘failover’ times when users use the 'Always On' availability groups.
- It helps developers detect ‘instance-level impacts’ and ‘instance-level concerns' on databases.
114. Compare Triggers with Event Notifications.
Ans:
| Triggers | Event Notifications |
| Triggers respond to both DML and DLL events | Event notifications respond to DDL events and a subset of SQL trace events |
| They run T-SQL or CLR codes | They don’t run any codes |
| They are processed synchronously within the scope of transactions | They are processed asynchronously, not within the scope of transactions |
| They must be processed on local servers | They can be processed on remote servers |
115. What is FILESTREAM, and when can you use it?
Ans: FILESTREAM allows SQL Server-based applications to store unstructured data such as images and documents. It helps maintain transactional consistency between unstructured data and the corresponding structured data. We can use FILESTREAM only when the following conditions are true:
- Objects have more than 1 MB file size
- Faster read access
- Applications have a middle tier for application logic
116. What is the Columnstore Index, and why should you use it?
Ans: A columnstore index is a method of storing, retrieving, and managing data using a columnar data format. Columnstore helps achieve query performance up to 10 times greater than the traditional row-oriented storage.
Columnstore index is used for the following reasons as follows:
- They provide high compression rates
- I/O Bottlenecks are minimized or removed
- Memory footprint is reduced
- Batch execution improves query performance
117. How to improve query performance in SQL server?
Ans: We can improve the query performance in the following ways:
- Defining the transaction requirements precisely
- Choosing the right query execution plan
- Reducing table sizes and simplifying joins
- Using ‘SELECT fields FROM’ instead of ‘SELECT*FROM’
- Using EXIST() instead of COUNT()
- Creating SQL query indexes
- Avoiding running queries in loops
118. How can we improve the performance of poor-performing SQL queries?
Ans: We can improve the performance of poor-performing SQL queries in the following ways:
- Using indexes properly
- Creating primary and foreign keys
- Not making table scans
- Avoiding using cursors
- Using partitioned views
119. What do you mean by Graph Database?
Ans: We can create a graph using node or edge tables for a database. Here, node tables are the collection of similar types of nodes. Similarly, edge tables are a collection of similar types of edges. Note that node tables can be created based on a logical graph and under any schema.
120. How to use Service Broker in SQL server?
Ans: SQL Server Service Broker is a message delivery framework that supports effective messaging and queuing in the SQL server database engine. Developers can use Service Broker to distribute workloads across various databases without programming efforts. Service Broker reduces workloads by managing communication paths and improves performance at the end.
121. What is the use of views in SQL server, and mention its types?
The view is the virtual database table created by selecting a few rows and columns from other tables. Rows and columns are selected through SQL query, which creates a view as a result. And it helps to organize data by simplifying complex queries, restricting access to data, and summarizing data from many tables.
There are two types of views. They are given as follows:
- System-defined views
- User-defined views
Example: Create View View1 AS Select Emp_Name where Emp_ID > 110;
This view will help you fetch the names of the employees whose ID is greater than 110.
123. What is a Logon Trigger, and when do they get triggered?
Ans: When there is a logon event, Logon triggers initiate stored procedures. It occurs when a user session is created with an instance of the SQL Server. Logon triggers fire only when the authentication stage of logging is over. If the authentication phase fails, logon triggers won't fire stored procedures.
124. Compare Extended Stored Procedures and CLR Integration.
Ans:
| Extended Stored Procedure | CLR Integration |
| They support the functionalities that cannot work with T-SQL stored procedures. | CLR provides managed code with services such as cross-language integration, object lifetime management, code access security, and debugging and profiling support. |
| Developers need to write server-side logic that is complex in a way | Provides an alternative method to writing codes simply. Logic is expressed in the form of table-valued functions |
| It compromises the integrity of the SQL server process | It doesn’t compromise the integrity of the SQL server process |
| It supports all the versions of the SQL server | It doesn’t support older versions of the SQL server |
| Codes can be written in C/C++ programming languages | Codes can be written in .NET programming languages |
125. What is SQL Latch Contention, and how can it be avoided?
Ans: Latch contention occurs when many threads try to acquire incompatible latches at the same time. It will happen when latches are in the same in-memory structure. SQL engine decides when to use latches automatically and hence ensures memory consistency. When there is a latch contention, the SQL server tends the incompatible latch requests to wait in the queue until outstanding latch requests are completed.
126. What is Spinlock Contention, and how to resolve it?
Ans: Spinlock can protect access to data structures. Familiar data structures are typically accessed by many threads concurrently, which in turn causes spinlock contention issues. Also, spinlock contention creates CPU overhead.
The spinlock contention can be diagnosed by tools such as performance meter, SQL server extended events, and memory dumps. To resolve the spinlock contention issues, the root cause must be identified first. A shorter code path will resolve contention issues significantly. In addition, the best practices such as Fully Qualified Names, Paremterised Queries, and LOCK_HASH contention.
127. What are the two execution modes in the Database Engine in the SQL server, and what is the difference between the two modes?
Ans: The database engine in the SQL server can execute T-SQL statements in the following two modes:
- Row-mode execution
- Batch-mode execution
Row-mode Execution: This mode of execution is applicable when data is stored in row format. In this mode, when a query is executed, rows are read one by one with respect to columns specified in the table schema. Then, the SQL server forms the result set from the data of columns using statements such as SELECT, JOIN, etc.
Batch-mode Execution: Multiple modes are executed together as a batch in this mode. It operates on compressed data. It offers better parallelism, faster performance, and increased memory throughput.
128. What are Data Cleansing and Data Matching in SQL Server?
Ans:
- Data Cleansing: This Data Quality Service (DQS) process identifies the incorrect or invalid data in the SQL database and then corrects it; cleansing is carried out in two steps such as computer-assisted and interactive. The computer-assisted method uses the knowledge of the DQS knowledge base to process the data and suggests corrections automatically. In the interactive method, the data steward approves, rejects, and modifies the changes required to correct the incorrect or incomplete data.
- Data Matching: This DQS process supports reducing data duplication and increases data accuracy. Data matching is carried out in two ways, such as creating a matching policy in the knowledge base and performing a deduplication process. The matching rules help to identify how the records are matching with each other and the degree of similarity.
129. How can you ensure DQS security in the SQL server?
Ans: DQS security infrastructure is designed based on SQL server security infrastructure. Here, the Data administrator provides access to DQS resources based on the defined DQS roles. There are four DQS roles to manage the security of DQS services. They are known as database administrators, DQS administrators, DQS KB Editors, and DQS KB operators. A set of permissions is assigned to each DQS role so that they can access the resources based on the given permissions.
130. What is the use of Windows PowerShell Snap-ins?
Ans: Windows PowerShell snap-in is a .NET framework assembly with Windows PowerShell providers and cmdlets. The PowerShell has a group of snap-ins as default; however, snap-ins can be added with them to increase the power of Windows PowerShell. Once the snap-ins are added to the PowerShell, they can be used by the current session itself. If the added snap-ins are required for future sessions, they must be saved in the Windows PowerShell profile.
131. Mention a few subquery restrictions in the SQL server.
Ans:
- The next, image, and text data types cannot be used in the select list of subqueries.
- If there is a column name in the WHERE clause of an outer query, then it should be join-compatible with the column in the subquery select list.
- The DISTINCT keyword cannot be used with subqueries that include GROUP BY
- A view created by using a subquery cannot be updated
- The COMPUTE and INTO clauses cannot be specified
132. What is Polybase, and why do you have to use it?
Ans: Polybase is the data virtualization feature of the SQL server. This feature supports connecting with external sources without installing client connection software. So, we can query data from SQL Server, Oracle, Teradata, MongoDB, Hadoop clusters, and Cosmos DB using T-SQL. Polybase allows data to stay in its original location and format. So, it reduces the need for ETL in data movement.
133. What is an SSIS designer in SQL Server, and why do we use it?
Ans: It is a graphical tool used to manage integration service packages in SQL servers. It allows for creating and maintaining the integration of service packages.
We can use SSIS Designer to accomplish the following tasks:
- Constructing the data and control flow in a package
- Adding event handlers to the packages
- Viewing package content and viewing expression progress
134. Compare Package-level Connection Managers and Project-level Connection Managers.
Ans: A connection manager is available for all the packages in the project when it is created at the project level. Similarly, a connection manager will be available only to the specific package when created at the package level.
135. Differentiate EXCEPT and INTERSECT commands?
Ans: These commands are used to return distinct rows by comparing the results of two separate queries.
EXCEPT: The operator allows returning distinct rows from the left input query only.
INTERCEPT: The operator allows returning distinct rows from both left and right input queries.
The syntax for these commands is given as follows:
{ <query_specification> | ( <query_expression> ) }
{ EXCEPT | INTERSECT }
{ <query_specification> | ( <query_expression> ) }
136. Explain the Pattern Matching in the SQL server.
Ans: SQL server uses the LIKE operator to identify whether a character string matches a specified pattern. A pattern may consist of regular characters as well as wildcard characters. So, pattern matching is performed using wildcard characters and string comparison characters. However, pattern matching using wildcard characters is more flexible than string comparison operators.
The syntax for the LIKE operator for pattern matching is given as below:
match_expression [ NOT ] LIKE pattern [ ESCAPE escape_character ]137. What are the various types of collation sensitivity, and brief them?
Ans:
- Case Sensitivity: It distinguishes uppercase and lowercase letters
- Accent Sensitivity: It distinguishes between accented and unaccented characters
- Kana Sensitivity: It distinguishes the two types of Japanese characters hiragana and katakana
- Width Sensitivity: It distinguishes the full-width and half-width characters
- Variation-selector Sensitivity: It distinguishes the variation selectors in Japanese collations.
138. What is the difference between ORDER BY expression and clustered index?
Ans: ORDER BY expression sorts the result set of a query as per the condition given in the statement. It can sort the result set either in ascending order or descending order. And, it can sort the result set based on attributes given in the statement such as country, company, etc. At the same time, the clustered index sorts data physically only in a specific way in the table. So, every table will have one clustered index only.
139. How can you improve the performance of stored procedures in the SQL server?
Ans:
- Using SET NOCOUNT ON messages, information messages can be prevented from the result set. It will reduce network traffic and increase operational performance.
- When the fully qualified procedure name is, the SQL server finds the compiled plan quickly, which in turn increases the performance
- Specifying stored procedures as sp_procedurename must be avoided because the SQL server will search the master database first if it finds ‘sp’ in the procedure name. It would decrease the performance and yield error results at times.
- Transactions need to be shorter so that deadlocks and blocking can be prevented.
140. What is the difference between INNER JOIN and OUTER JOIN?
In SQL Server, Joins are used for combining records from two or more tables as per the associated column between them. We have two types of Joins:1) Inner Join 2) Outer Join.
1) Inner Join
Inner Join fetches only the records where there is a match between joining columns in both tables. It can combine two or more tables as per a particular condition known as Join Predicate. The resulting table will only have matching records for both tables.
Syntax:
SELECT Columns from table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON join_condition;
2) Outer Join
The Outer Join will retrieve all the rows from one table and matched rows from another. It also includes the matched rows. Similar to Inner Join, it combines two or more tables as per a particular condition. The Outer Join includes the unmatched rows using null values. We have three kinds of Outer Join: 1) Left Outer Join, 2) Right Outer Join, 3) Full Outer Join
Syntax:
SELECT Columns from table1 LEFT OUTER JOIN table2 ON join_condition;
141. What are the commonly used techniques for Query Optimization?
The following are the most commonly used techniques for Query Optimization:
1)Analyzing Query Execution Plans: Determining the inefficiencies and obstacles in the query execution.
2)Streamline the Queries: Break the difficult queries into small parts, optimize the conditions, and remove the redundant joins
3)Indexing Strategies: Build and Modify the Indexes on the basis of sorting and filtering requirements.
4)Query Tuning: Optimizing Query Parameters, Adjusting Join Strategies, and Rewriting suboptimal queries.
5)Partitioning: Splitting the large tables into small tables to enhance the data parallelism and access.
142. Explain different types of Replication in SQL Server.
In SQL Server, we have three different kinds of Replications:
1) Snapshot Replication
In Snapshot Replication, we will take a snapshot of the replicated database and replicate it to the subscribers. Consequent modifications to the publisher database are not disseminated to subscribers. Rather, the latest snapshot must be created and applied to subscribers for synchronizing the data.
2) Transactional Replication
Transaction Replication will capture and replicate the separate data modifications like insert, update, and delete, as transactions happen on the publisher database.
3) Merge Replication
Merge Replication is the bidirectional replication methodology that enables modifications in both subscriber and publisher databases. It reconciles and traces the modifications done in every replica and resolves the struggles that happen when the same data is changed at multiple locations.
143. What are Indexes?
To get the required data efficiently in a massive amount of data, we use Indexes in SQL Server. An Index is defined as the database object created and maintained by the DBMS. Indexed columns are ordered and sorted to help you in data searching.
144. What are Scalar Functions?
Scalar Functions will work on each value and return a single value
1) LEN(): It returns the length of the string, like blank spaces.
2) UCASE(): It returns an upper case string.
3) LCASE: It returns a lowercase string.
4) MID(): It gives a substring of a string.
5) NOW: It returns the current date and time
145. What is the latest version of SQL Server?
SQL Server 2022 is the latest version of SQL Server and Microsoft released it in November 2022.
146. What are the new features and functionalities of SQL Server?
In comparison to SQL Server's previous version, the SQL Server 2022 version has more options for data types, programming languages, and replication to and from Azure. Following are some important features and functionalities introduced in SQL Server:
1) Azure Synapse Connectivity
Azure Synapse Connectivity is included in SQL Server 2022 to help you duplicate data from the SQL Server to Azure Synapse in real-time.
2) Azure SQL Managed Instance Link
SQL Server 2022 has a link for the Azure SQL Managed Instance that allows you to duplicate real-world data from the SQL Server to the Azure SQL Managed Instance.
3) Data Virtualization
SQL Server 2022 includes support to query the external data file through polybase with MongoDB API and Oracle TNS files for ODBC and Cosmos DB.
4) Performance Enhancements
In SQL Server 2022, Microsoft has included performance enhancement features like Improved in-memory OLTP Performance, Reduced I/O, and Optimized query performance to provide enhanced buffer pool management, rapid startup times, and better adaptive query optimization.
147. What are the job responsibilities of SQL Developers with 2-3 years of Experience?
- Importing or Exporting Data on SQL Server
- Strong understanding of database design principles, indexing, and normalization
- Hands-on Experience with database performance optimization and tuning techniques
- Able to handle internal business logic and implement solutions using T-SQL
- Analyze Existing SQL Queries for Query Improvement
148. What are the job responsibilities of a SQL Developer with 3-5 years of Experience?
- Architect the database for reporting efficiency and implementing best practices
- Create and Manage Data Marts and Database objects like Stored Procedures, Views, and Triggers as per the business requirements.
- Optimizing large and complicated SQL Statements
- Build Data Migration Methods and Scripts
- Implement SQL-based data transformations for producing sub-datasets
149. What secondary skills are needed to make a career in SQL Server?
Since SQL Server is used in different fields like Data Analysis, Data Engineering, and Data Science, you must have good knowledge of Data Visualization tools, Python Programming, Cloud Services, and Data Engineering tools to take your career to new heights in SQL Server.
Conclusion
We have covered most of the frequently asked SQL Server interview questions in this blog. We hope this blog might have been interesting to read and understand the core concepts of SQL servers. You know it – Hardwork Never Fails. Lastly, ALL THE BEST for your interview.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Server Training | Feb 21 to Mar 08 | View Details |
| SQL Server Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| SQL Server Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| SQL Server Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |

Arogyalokesh is a Technical Content Writer and manages content creation on various IT platforms at Mindmajix. He is dedicated to creating useful and engaging content on Salesforce, Blockchain, Docker, SQL Server, Tangle, Jira, and few other technologies. Get in touch with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.




