- Top 10 DevOps Tools for Continuous Integration
- Top 10 Devops Tools
- Repository Management Tools
- 10 Tools For Effective DevOps Collaboration
- Top 12 Open Source DevOps Build Tools
- Configuration Management Tools in DevOps
- Agile Vs DevOps
- Chef DevOps Interview Questions
- What is Continuous Integration in DevOps?
- Insights of DevOps Architect
- DevOps Automation: How is it Carried Out?
- Introduction To DevOps Docker
- DevOps For Dummies
- DevOps Interview Questions
- 13 DevOps Testing Tools For DevOps Professionals
- Best DevOps Tools and Frameworks to explore
- DevOps Tutorial For Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide To Learn DevOps
- Cacti Graphing And Monitoring
- RANCID Tool Keeps Config Files Clean
- How To Enable LLDP on Linux Servers for Link Discovery
- How to set up a modern web stack in Ubuntu
- Useful Iperf Commands for Network Troubleshooting
- Migration of MongoDB to DynamoDB
- MongoDB and Tree Structures
- Multihost SSH Wrapper
- DevOps Tools for Infrastructure Automation
- Introduction To Azure DevOps
- Introduction To DevOps Tools
- List of DevOps Monitoring Tools
- The Ultimate List of DevOps Deployment Tools
- Top 10 Open Source Containerization DevOps Tools
- Reasons for the Rise of DevOps
- Role Of a DevOps Engineer
- DevOps Security Tools
- Some Common Myths about DevOps
- Top 10 Devops tools in cloud
- Release Management Tools
- Top 10 SCM Tools
- Logging DevOps Tools
- DevOps And Its Significance
- DevSecOps Interview Questions
- Ansible vs Chef
- DevSecOps Tutorial
- What is Site Reliability Engineering - SRE Tools
- What is DataOps?
- DevOps Vs SysOps
- DevOps Engineer Job Description
- Azure DevOps Jira Integration
- What is Pipeline in DevOps?
- SonarQube Azure DevOps
- Azure DevOps CI/CD
More and more jobs are opening up as a result of progress in technology. The position of site reliability engineer is one that has been around for that long. However, there has been a rise in site reliability engineering (SRE), a term developed by Google to describe how they manage their production systems. A growing number of businesses are either actively seeking site reliability engineers or attempting to introduce SRE.
So, we have provided you with all the information you need to become a Site Reliability Engineer, including top SRE interview questions and answers.
We have categorized Site Reliability Engineer Interview Questions into 4 levels they are:
Top 10 Site Reliability Engineer Interview Questions
- What are the roles of SRE?
- What are physical data structures?
- How does DHCP work?
- What are the steps of APR?
- Give examples of Hardlink and Softlink.
- What are the types of Proc?
- How may OOPs be used when creating a server?
- Establish INodes.
- Where does server caching happen?
- What is a "/proc" file system?
SRE Interview Questions and Answers For Freshers
1. Describe SRE.
The term "SRE" stands for "Site Reliability Engineer." A software engineer with a focus on creating and maintaining dependable systems that can withstand unforeseen environmental changes is known as a site reliability engineer. Though they also operate with other kinds of software systems, they generally work on huge online projects.
| If you want to enrich your career and become an SRE, then enroll in "Site Reliability Engineer Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2. What are the roles of SRE?
They are in charge of ensuring that their system can accommodate any modifications that might arise in the real world. For instance, they must ensure that the system can function normally even if one of their servers fails. Additionally, they must guarantee that the website is safe from hackers and other intruders. A variety of technologies, including web applications, databases, and other systems, are used to create many websites. Each of these components must be understood by a site reliability engineer in order for them to ensure that everything functions properly as a whole.
3. Describe DevOps.
Software engineers and IT operations personnel work together as part of the DevOps process to create new software (Dev - Development, Ops - Operations). Overall productivity is increased as a result of this collaboration, which also offers improved quality assurance and a quicker time to market. DevOps is indeed a movement that strives to collaborate more closely between IT operations employees and developers by bringing the two together.
4. What's the distinction between SRE and DevOps?
A person who specializes in enhancing apps and services as they're being utilized is known by the names "DevOps" and "Site Reliability Engineer."
In contemporary IT firms, significant positions include DevOps and Site reliability engineering. But there is a significant distinction between them.
[ Learn Complete About What is Site Reliability Engineering? ]
5. Describe data structures.
A collection of guidelines called data structures is used by computers to organize and store data. Data structures are employed to manage memory, structure databases, and organize data. Data structures make it simple to organize data, make it simple to get data, and make good use of resources.
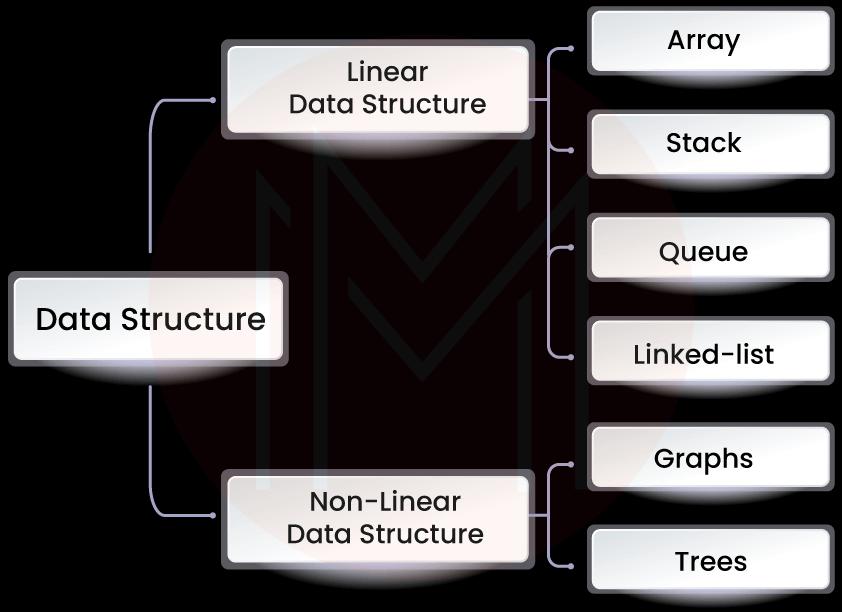
6. What are physical data structures?
Physical data objects can indeed be linked lists and arrays. Since the information residing in the real physiological memory is based on these two, we can refer to them as physical data structures. A group of adjacent data items from the same type is referred to as an array. The linked list, which still might not be consecutive in memory, is likewise a collection of data components.
7. What are logical data structures?
All data objects that are built utilizing the different physical data structures are referred to as logical data structures. Stack, queue, tree, graph, and other logical data structures are examples. These data structures only contain logic, which defines a property and stores the data in memory using matrices and linked lists.
8. What is cloud computing?
IT services including servers, storage, and software as a service (SaaS) are delivered over network-connected cloud infrastructure through cloud computing. The phrase can be used to describe both private clouds, controlled by a single company and shared by internal users, and cloud environments, owned by outside companies and provide computing capacity for rent, such as Amazon Web Services.
9. What is the use of cloud computing?
Additionally, cloud computing has the ability to completely transform IT operations by enabling businesses to provide IT services using a scalable, adaptable paradigm that lowers costs without sacrificing service quality. By automating common operations, it can help businesses decrease complexity and risk, combine older systems with more modern ones (like mobile applications), and manage remote assets more effectively. By making leasing or buying IT equipment less expensive than outright purchases, cloud computing can also help businesses save money.
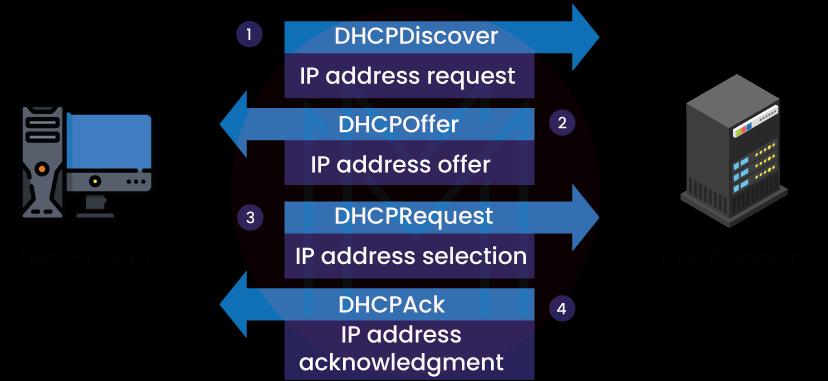
10. What is DHCP?
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is known as DHCP. It is a technique that enables networks to assign IP addresses to network hosts on a dynamic basis. Devices like PCs and routers are given IP addresses through the use of DHCP. An IP address may be required for a device to connect to The internet after installation. Therefore, when a new system is placed, DHCP will provide it an IP address so that it may access the network.
11. How does DHCP work?
In order to talk with some other hosts on a network, a device must first obtain an IP address when it joins a network. Additionally, since most networks only assign one IP address to each device, a system for dynamically allocating IP addresses must exist.
12. Briefly Explain DNS
The domain name system is known as DNS. It is a mechanism that converts hostnames to IP addresses so that, when you type a website address into your browser, you can quickly identify the right server. Each domain name has one or more "resolvers," or IP addresses, associated with them by the DNS system.
13. What is the importance of DNS?
When you enter a URL (such as www.google.com) into the browser, your computer requests the IP address connected with that web address from the DNS resolver. The IP address of a local machine or another server which has been set up to return that specific IP address is then returned to the browser by the DNS resolver.
14. Why is DNS necessary?
Since hosts on the Internet only have names that can be read by humans, like google.com, and not by computers, like 111.222.333.444, DNS is essential. Without DNS, finding a URL on the Internet would require you to understand how to interpret its human-readable name, which would be incredibly challenging without the aid of a centralized authority like Google.
15. Describe APR.
Address Resolution Protocol is referred to as ARP. ARP is a protocol that permits device communication on local networks. It makes it possible for devices connected to the same network to discover each other's MAC address, IP address, as well as other network details. In order for network devices to communicate with one another, it is used to dynamically assign An ip address to those devices.
16. What are the steps of APR?
There are three basic stages to this process:
- How to find an IP address (ARP packets are sent out).
- An IP address is resolved (the device looks up the IP address using its own IP address table).
- A MAC address is used (the device looks up the MAC address using its own MAC address table).
17. How does APR work?
ARP packets search for any devices with an IP address attached to them by putting out a request. The device that receives the packet will respond with a list of Email accounts and other data unique to that device. To be able to identify IP addresses when necessary, each device keeps a table of recognized addresses.
18. Give examples of Hardlink and Softlink.
The two forms of file system links that used to distribute files between directories are hardlinks and softlinks. Soft links generate a single reference to the position of a file in one location, whereas hard links provide a single reference to a file in two different locations. Each hardlink you make has the exact same length as the original.
19. What is Multithreading?
A programming method called multithreading enables the simultaneous execution of several tasks. Each task is given its own processor or processor in order to accomplish this. Multiple jobs can be processed at once by dividing the load across these processors. This can be useful when processing a lot of data or carrying out quick actions that need a lot of resources.
20. What are the benefits of Multithreading?
There are several advantages to multithreading. It enables faster computing performance and shorter computation execution times. Additionally, it can lower latency and increase the responsiveness of apps. In addition, short-lived, resource-intensive operations can be carried out using multithreading. Therefore, using multithreaded applications in IoT contexts.
21. What possible states could the process be in?
The computer programme that the CPU will run is called a process. And it does so at different moments throughout the process's cycle of execution. The process is in that state.
22. What is suspended ready?
The term "suspend ready state" refers to a process that is in the ready state but has been moved from main memory to secondary memory due to a lack of resources (primarily primary memory). The OS must move the lower-priority program to secondary memory in order to make room in the main memory if it is full and a higher-priority program arrives for execution. Processes that are prepared to suspend are held in secondary storage until the strongest memory is available.
23. Describe RAID.
A form of storage system with more than one hard disc to offer extra redundancy in the event that one disc fails is referred to as a "Redundant Array of Independent Disk." In networks and server farms, a redundant Array of Independent Disk is frequently used. Data centers frequently use multiple arrays of independent disc systems, which offer a second disc drive on a same physical system so that the user can access the second disc drive in the event that the first disc fails. Users won't have to think about data loss in the event of a drive failure thanks to this additional protection.
24. What is Vertical Scaling?
Vertical scaling is the process of expanding a system's size by adding more resources. This is frequently used to improve throughput, performance, and capacity. On an one physical server, it typically means adding additional hardware or servers. Another name for this procedure is scaling up. since doing so expands the system's size.
SRE Interview Questions For Experienced
25. What are the types of Proc?
Under /proc, there are three subdirectories:
- The /proc directory tree's initial subdirectory is designated as /proc/1. It includes details on the CPU's performance.
- The command line arguments given to the process that is presently running are stored in the subfolder /proc/1/cmdline.
- For running processes on Linux systems, virtual memory map information is stored in the subfolder /proc/1/maps. It has the ability to ascertain which processes are using which portions of the memory.
26. What is the kill command in Linux?
The Linux kills command makes it simple to end all active processes. You can kill any process with this command, including programmes, services, and processes that aren't even active on Linux systems. In other words, it will stop or end any process that is currently active on the system. You can terminate an unresponsive service or shut down an unresponsive programme on Linux by using the kill command. The kill command can be used to end problematic batch script jobs as well.
[ Related Article: List of Commands in Linux ]
27. How may OOPs be used when creating a server?
A programming paradigm known as OOPs promotes the construction of objects that represent the real entities and are subsequently utilized to carry out tasks. These can be helpful in the design of a server since they enable you to divide the jobs into manageable pieces, which will aid in maintaining control over your server. Additionally, OOPs enables you to write reusable code, which will save you money and time. It's crucial to adhere to several fundamental design principles when creating an OOPs-based server.
28. Describe CDN.
A network of servers known as a CDN (Content Delivery Network) stores and provides content to clients. These servers, which are often found in data centers, can be utilized to enhance performance by lowering latency, guaranteeing that the information is accessible when needed, and ensuring that it is provided promptly. Although HTML or JavaScript are examples of dynamic material, CDNs could also be used to store static information like photographs and movies.
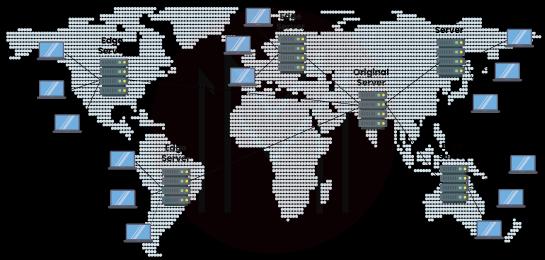
29. What is the use of CDN?
There are numerous applications for CDN, including
- By giving static content a central location.
- By giving dynamic content a central location.
- Giving content from several sources a central spot.
- Giving material from several data centers a central location.
- Giving essential infrastructure elements, such servers and routers, redundancy.
Due to their role in ensuring that the Internet functions properly for everyone, CDNs are a crucial component of the Internet infrastructure. They aid in ensuring that everyone has simultaneous access to the same information.
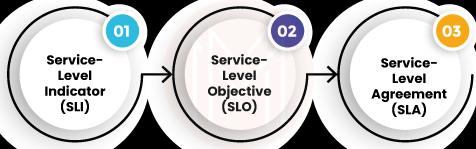
30. What do you mean by SLO?
A Service Level Objective (SLO), which is typically represented as a percentage, is a gauge of how excellent or terrible the service quality is. It demonstrates how well the service level's actual performance matches expectations. The client normally establishes an SLO, but management may also do so to track performance.
31. Can you briefly explain Service Level Indicators?
The main metrics that demonstrate whether a service is on track are called service level indicators. Without them, it is challenging to determine whether the company is accomplishing its goals. SLIs can be broadly classified into three categories: availability, response time, and quality of service.
32. Describe TCP.
Various TCP connection statuses are another. A TCP connection state connects a client and a server's TCP endpoints. The TCP three-way greeting mechanism defines these states. TCP is able to connect two endpoints thanks to the three-way handshake process, in which one side uses a SYN packet to start the connection setup and the other side replies with an ACK packet. An secured connection is made once the corresponding SYN and ACK packets have been sent and received by both parties. A client can start data transfer over a connection after it has been established by sending a FIN packet, which will trigger the server to reply with an ACK packet confirming that all pending data has been actually received.
33. Establish INodes.
The storage units of a Linux filesystem are called inodes. An inode, which is effectively a pointer to the file's location in the filesystem, is linked to every file, subdirectory, and block device. Other attributes of inodes include their size, owner, and group IDs. When a file or directory is destroyed, the corresponding inode is also erased, along with any associated data.
34. What is a service-level agreement?
A service-level agreement (SLA) is a guarantee of uptime that we give to a client. These are sometimes legally required, and there may be repercussions if the intended availability is not met. SLAs are often created with values that really are easier to meet than SLOs as a result.
35. What is a service level indicator?
Anything that can be accurately monitored and used to help you think through, define, and assess whether you are meeting SLOs and SLAs is referred to as a service-level indicator (SLI). They are frequently expressed as the proportion of exceptional occurrences to all events. The ratio of the total amount of HTTP inquiries to the number of HTTP requests that were successful is a straightforward example.
36. What is meant by virtualization?
The process of running numerous virtual machines on a single physical system is known as virtualization. Companies who want to pool their computing resources to keep them running round-the-clock without having to invest in extra hardware frequently employ it. Virtualization can also be utilized for testing, such as system performance testing or software development.
37. Explain the Sharding procedure.
A technique for breaking up a database into several parts is called sharding. Each component saves a portion of the data that can be utilized for various kinds of searches.
38. Where does server caching happen?
In order to use data that changes infrequently later, caching is the act of storing it in memory. It is frequently applied to boost performance and lessen network load.
In the field, a candidate for the position of SRE must possess a fundamental knowledge of programming, data structures, and algorithms. The candidate also needs to have a firm understanding of networking, operating system, and fundamental database concepts.
39. What is Horizontal Scaling?
By adding several logical resources, a system's size can be increased horizontally. To do this, either more virtual machines or containers can be added to each host. Additionally, it is possible by adding many hosts at once. This is also known as scaling out. as a result of the increase in systems.
40. Why is horizontal scaling preferred?
Due to the system's load and running time. This is expandable. Horizontal scaling (scaling-out) has the following benefits:
- It needs less money up front.
- It lowers administrative costs
- Facilitates simpler scalability as demand rises.
41. Describe LILO.
A bootloader known as LILO (Linux Loader) is used to load Linux into memory and launch the operating system. Due to its ability to support dual booting, it is also referred to as a boot manager. It can function as the primary boot programme or the secondary boot programme, and it can locate the kernel, load memory, identify other supporting programmes, and execute the kernel, among other things. Installing a special loader called LILO, which enables Linux OS to boot rapidly, is required if you want to use it.
42. How well do you understand Linux Shell?
The Linux OS wouldn't exist without the Linux Shell. Linus Torvalds created the free and open-source Linux operating system. The majority of servers and embedded systems run this OS. A command-line interface called a Linux shell enables user interaction with the system. The Linux command line interface (CLI) offers a text-based interface for carrying out system commands, managing files, and issuing other instructions.
43. What are the types of Linux shells?
Linux has two different types of shells:
- Interactive shell: When a user has logged into their computer, the interactive shell launches automatically.
- Non-Interactive shell: This shell can be manually launched to run any programme.
44. What is a "/proc" file system?
A special kind of file system with unique access rights is a "/proc" file system. When the kernel wants to run a process or access specific system resources, it is elevated in Linux systems. Information about the system's present condition, such as memory consumption and CPU speed, can be found in the /proc directory.
Site Reliability Engineer FAQs
45. What are the five pillars of SRE?
- Risk acceptance and mitigation plan.
- Service Level Objectives and Indicators (SLO and SLI).
- Automation, Automation, and Automation.
- Release and deployment.
- Proactive Monitoring.
46. What tools does SRE use?
Some SRE tools are:
- Automated Incident Response System.
- APM (Application Performance Management) and Monitoring Tools.
- Configuration Management tools.
- Real-Time Communication tools.
47. Is SRE part of DevOps?
SRE might be considered an implementation of DevOps. Like DevOps, SRE is about team culture and relationships. Connecting the dots between the dev and ops teams is a goal shared by SRE and DevOps.
48. Does SRE write code?
SREs will spend a great deal of time writing code and developing tools to facilitate engineers' communication with infrastructure.
49. What is uptime in SRE?
A server with 99.9 percent uptime would be down for more than 10 minutes per week, or 1 minute and 26.4 seconds per day. That's adequate for a generic business server.
50. What is SRE in Scrum?
Site reliability engineering (SRE) teams do both operational works that is interrupted and planned work, which could include some software development. Scrum is for software development teams that are working on one or a few products.
51. What is SRE role of SRE in DevOps?
Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) is in charge of putting the product that the Core Development team made into action. The main goal of SREs is to implement and automate DevOps practices to reduce the number of problems and make the system more reliable and able to grow.
52. Is SRE role in demand?
High expectations from users role are that companies need SREs to help them meet higher reliability expectations. Even just five years ago, people were more understanding when websites or apps didn't work. But that's not true anymore.
53. Is SRE a cloud engineer?
SREs do not pay special attention to the cloud. An SRE, on the other hand, is a general-purpose role whose goal is to manage reliability in any kind of environment. Almost all businesses use the cloud today, so it's a big part of an SRE's job to make sure the cloud is reliable.
SRE Interview Preparation Tips
Tip #1. Be on Time
This usually means being 10–15 minutes early. Most of the time, interviewers are ready before the meeting.
Tip #2. Pay Close Attention To The Interviewer
Make sure you understand the question. If you don't, ask for clarification or restate it in your own words. Give a full and clear answer. Keep talking about the topic at hand.
Tip #3. Prepare Some of Your Own Questions Ahead of Time
There's nothing wrong with having a short list of questions and thoughts. It shows that you've done your research and want to learn more about the company and the job.
Tip #4. Focus
Don't apologize for not having enough experience. Instead, talk about your strengths in terms of what you can do for the organization.
Conclusion
The SRE interview process can be a good way to show the employer your skills and qualifications when you're trying to get a job as a site reliability engineer. Reviewing site reliability engineer interview questions before the interview can help you feel more confident about your answers.
If you have any doubts, reach out to us in our MindMajix Community
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Site Reliability Engineer Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Site Reliability Engineer Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Site Reliability Engineer Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| Site Reliability Engineer Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















