- SAP Interview Questions
- SAP MDG Interview Questions
- SAP PS Interview Questions
- SAP C4C Interview Questions
- SAP ISU Interview Questions
- SAP Analytics Cloud Interview Questions
- SAP CO Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Interview Questions
- SAP VIM Interview Questions
- SAP SCM Interview Questions
- SAP IBP Interview Questions
- SAP RAR Interview Questions
- SAP TM Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Architecture
- What is SAP Transportation Management ?
- What is SAP SCM?
- What is SAP PO - SAP Process Orchestration Architecture
- SAP PO Interview Questions
- What is SAP EDI?
- What is SAP Vistex?
- What is SAP Cloud Platform?
- What is SAP MRP - SAP MRP Tutorial
- What is SAP BTP?
- What is SAP Fieldglass?
- What is SAP C4C?
- What is SAP ISU
- What is SAP Solution Manager?
- SAP Analytics Cloud Tutorial
- SAP HCM Interview Questions
- What is SAP APO?
- SAP CPI Tutorial - A Beginner’s Guide
- What is SAP CAR?
- What is SAP PS - SAP PS Tutorial
- What is SAP IBP?
- What is SAP CPQ
- What Is Sap Netweaver
- What Is SAP BRIM
- What is SAP Master Data Governance (MDG)?
- What is SAP VIM?
- SAP MDG Architecture
- What is SAP MDG
- SAP HCM Tutorial
- SAP TRM Interview Questions
Access to reliable and accurate data can enhance the business but lack of the same can become the cause of a downturn. Therefore, strategic decision-making requires a good data management system. This is the place from where the top key stakeholders can analyze past and current reports to improve the business process of the future.
In this case, the Master Data helps them to achieve this goal. It plays a crucial role in the business operations within the organization. Let us walk through this tutorial to learn about managing this Master Data with SAP MDG.
Table of Contents
- Overview of SAP MDG?
- Why is SAP MDG needed?
- Modules in SAP MDG
- Features of SAP MDG
- SAP MDG: Key Functions
- SAP MDG Architecture
- SAP MDG Data Entities
- SAP MDG Vs SAP MDM
- Frequently Asked Questions
Overview of SAP MDG
SAP MDG is a tool that allows us to centrally create, update, and distribute the master data. Its main purpose is to provide a common reference to the data for multiple business processes like finance, customer management, sales, supply chain, decision-making, etc. We can say that it is an integrated solution to optimize business operations in terms of cost, time, and resources.
| Learn more about SAP MDG modules and features in our SAP MDG Training thoroughly addressed by our Expert trainers. |
Generally, it is a part of the SAP System but we can also integrate and customize it with the Non-SAP Systems to centrally manage our data. It enables the users to reuse the already existing business logic which promotes reusability. Along with this, it also assures that our central data fulfills compliance and regulatory standards. There are a lot more topics in this SAP MDG Tutorial but let us see why we need to learn it.
Why is SAP MDG needed?
While managing the business operations, you may face multiple challenges related to the central data management. Following are the master data challenges that are possible in our business process.
- Key decision-makers are unable to see an integrated view of Customer Data to improve customer transactions and sales channels.
- There is a lack of transparency related to suppliers and products due to which we cannot select suppliers properly. This increases the cost.
- We are unable to take advantage of new market opportunities due to less real-time information.
- Data across various channels is inconsistent which leads to poor decision-making in the business operations.
- The various key stakeholders like the CIO, CFO, Sales, Supply Chain Managers, etc. face domain-specific challenges in data management.
Therefore, SAP MDG plays an important role in overcoming the above challenges within our organization. We are now ready to take a look at SAP MDG Modules.
Modules in SAP MDG
- Data Modeling:
The Data Modelling Module in MDG allows us to create and define the data structures for the master data entities. This defined structure or schema is called the Master Data Model which helps business owners fulfill specific data management needs. The main functionalities of this module are Entity Definition, Attribute Configuration, Hierarchy Design, and Relationship Management.
- Data Quality:
Defining the data entities is not enough for successful master data management. It is also important to maintain the quality of master data. Thus, this module maintains the accuracy and consistency of the data by providing the data quality standards and correcting the data quality issues. Its main features are Data Profiling, Data Cleansing, Duplicate Detection, and Quality Monitoring.
- Data Governance:
This module deals with the policies related to access controls and data ownership. Also, it supports the Audit Trails to maintain detailed records of changes or transactions occurring in master data. Hence, using this module, we can easily define roles, maintain data policies, and resolve data governance issues.
- Data Replication:
For managing the master data, you need to distribute it consistently across various systems so that its recovery becomes easy at the time of failure. This module provides the Replication Models and Queue Management feature to replicate and transfer the data. You can also perform real-time replication and resolve replication conflicts using this module.
- UI Modelling:
It is equally important to make sure that the users can easily utilize the various modules of SAP MDG. Hence, UI Modelling allows us to manage a user-friendly interface for master data management. We can perform UI Component Configuration and Customization to create an easy interface for users. It uses the Web Dynpro technology of SAP to create the interface.
Features of SAP MDG
- It provides detailed data coverage for Material, Supplier, and Customer Data:
MDG supports detailed information coverage for various data entities such as Plant data, Distribution Channel data, Valuation data, Tax Classification, Withholding Tax Types, Sales Area Data, Tax Indicators, etc.
- It has numerous integration supports:
MDG has inbound processing of the material master data using the enterprise services. Along with this, it allows integration with the Information Steward and other third-party services.
- It provides SLC for supplier maintenance:
You can manage all the supplier information through Supplier Lifecycle Maintenance(SLC) to improve the visibility of supplier information and their involvement in the business process.
- It offers multiple replication options:
We can configure the automatic or manual replication of master data in the SAP as well as the Non-SAP System. This makes the data accessibility flexible and independent.
- It has Cloud Ready and Federated mode:
SAP MDG supports seamless deployment over the S/4 HANA. Also, it can be managed in a decentralized manner in the SAP S/4 HANA. Thus, the MDG system on the SAP HANA acts as the core data owner, and SAP HANA Systems acts as the application data owner.
SAP MDG: Key Functions
Central Data Governance
Before anyone accesses the master data, it should be compliant with the appropriate regulatory requirements. Due to this, SAP MDG provides the Central Data Governance through which the data is created, governed, and distributed across the whole enterprise system. This helps the organization to smoothly execute the business processes. It supports a broad domain coverage along with the single and mass processing of the data.
Additionally, it also has an automation feature in the creation or change processes which is done through two methods- data provider integration or rule-based derivation. The data provider integration allows integration with the external data providers. In rule-based derivation, users use predefined rules to calculate values for specific data fields during creating or changing the records. The process flow of the Central Data Governance is shown in the below diagram.
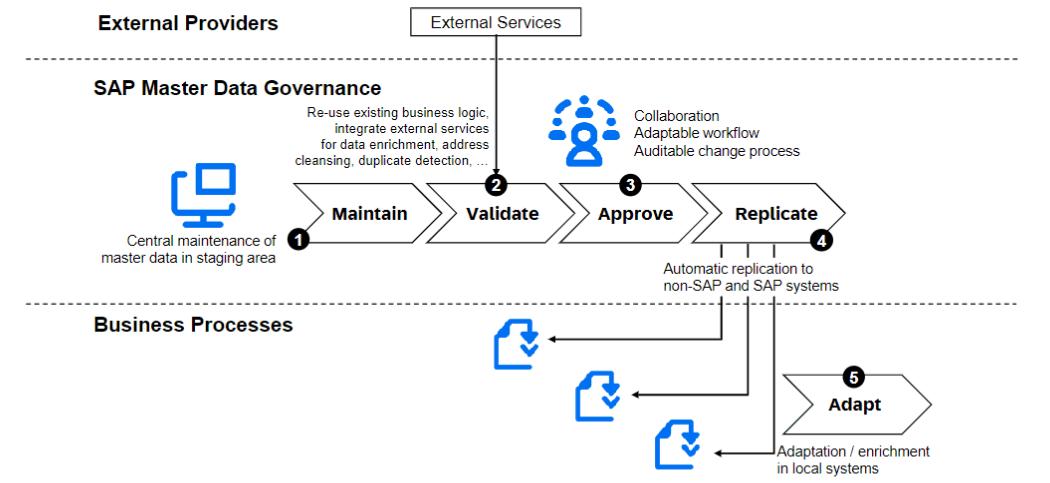
Process Flow of the Central Data Governance
Data Quality Management
This functionality is responsible for controlling the master data quality by defining the business rules, and monitoring and controlling master data compliance. It directly addresses the errors to maintain the master data quality. This high-quality data can be consistently accessed across all points of the SAP Ecosystem to ensure transparency in the business processes.
This feature provides a pre-configured solution to manage the quality of both business data and customer data. It also enables us to involve the key stakeholders while defining the data quality rules through a collaborative approach. One more function is to schedule the evaluations and analyze the results to correct the errors in the data quality.
The diagram below showcases the process flow of Data Quality Management.
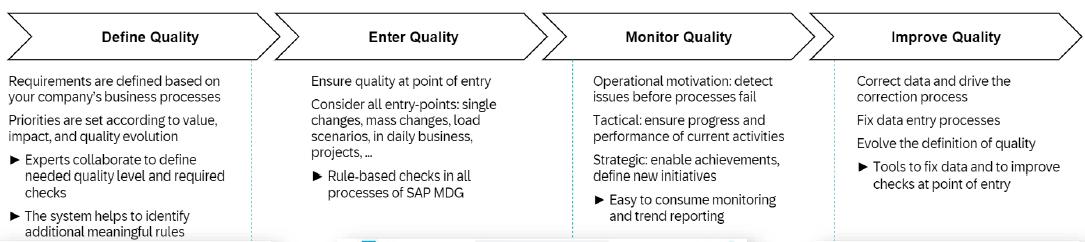
Data Quality Management Flow in SAP MDG
Master Data Consolidation
This feature ensures that the Master Data is decentralized across multiple Systems is not redundant and is of high quality. The main purpose of this functionality is to provide an integrated view of the customers, suppliers, and product data. This view helps the specialist to easily process the data through an easy-to-use UI. You can get the consolidated view in the form of drill-down, show changes, match view, or best record view.
It also provides the matching capability to identify the redundant data in the records loaded in the system. Thus, we can achieve transparency while loading and managing the master data in our SAP MDG System. Refer to the following diagram to understand the process flow of Master Data Consolidation.
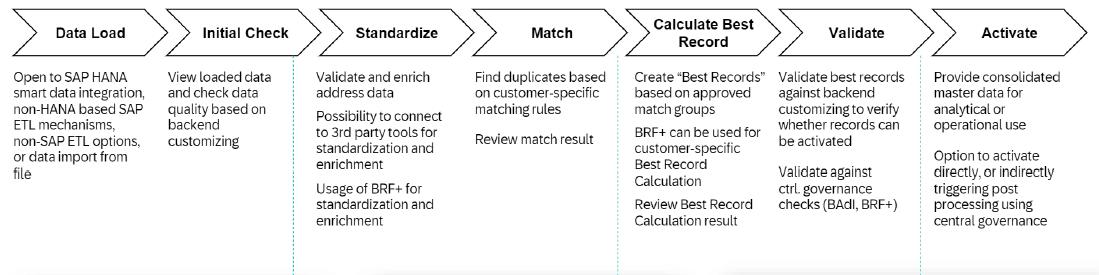
The flow of activities in SAP MDG Master Data Consolidation
SAP MDG Architecture
After we have seen the key modules and functionality of SAP MDG, we are able to know the high-level architecture of the entire Master Data Governance module in the SAP System. It has a Central System that manages the Master Data and multiple client systems that can access the master data. The following diagram shows the high-level architecture of SAP MDG.
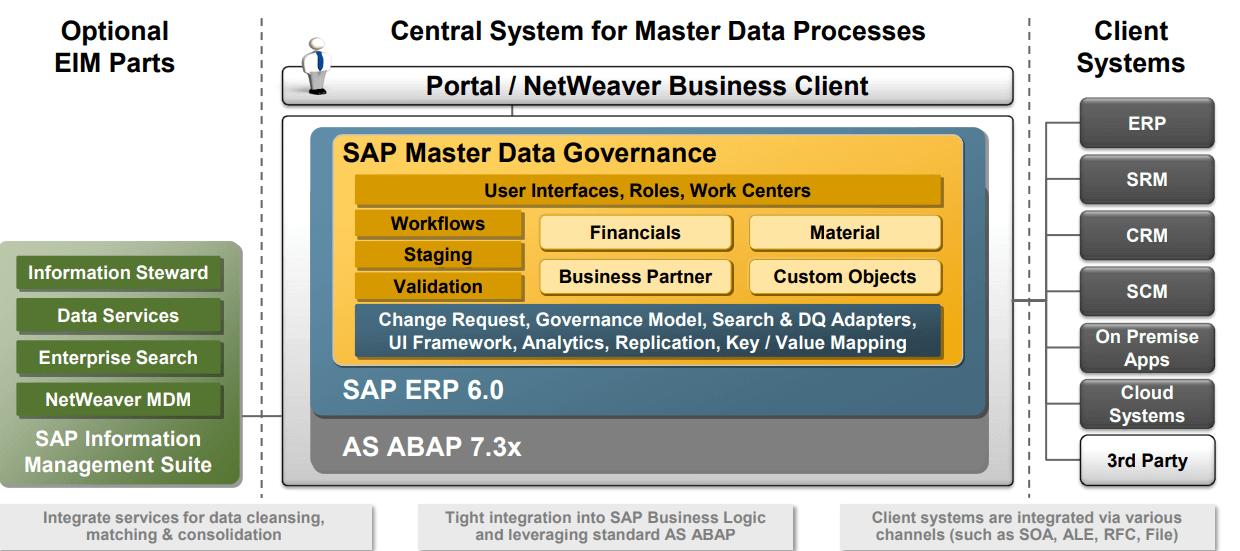
SAP MDG Architecture
Let us now discuss each component in the above architecture in detail.
Central System for Master Data Processes
In this part, the various sub-components are provided for various functionalities. It has the following main parts:
- User Interfaces (UI), Roles, and Work Centers: The MDG interfaces use the SAP Fiori UI framework to enhance user engagement and efficiency in master data management. Roles in SAP MDG define the access and permissions assigned to users based on their responsibilities. In addition to this, work centers allow us to manage the functionalities and tasks within the user interface. Each work center is dedicated to particular business activities for managing the workflow.
- Workflows: These are the sequence of steps and approvals required for master data modifications. The workflows include a structured and controlled process of creating, modifying, and approving master data changes. It is also ensured that the activities adhere to the policies and standards.
- Staging: It’s always better to perform a rough operation on data before the final update. Thus, Staging enables the users to temporarily store and process data before committing it to master data records. It provides validation of data before we make the permanent changes during mass data uploads.
- Validation: Various data compliance standards, predefined business rules, and quality criteria are available in this module. Users can implement rule-based validations and error-handling mechanisms to enhance data accuracy and adherence to governance policies.
- Data System: It includes data entities such as custom objects, finance, material, and business partners. We can use these entities to store the data. It is an important fact that Data Entities slightly differ from the data model as the Data model describes the structure or schema of the data object and the data entities are an instance of that model.
- Change Request: It helps us to modify the master data so that we can perform approval and validation of changes in data.
Other than the above components, there is a government model to manage various policies, roles, and responsibilities for managing master data. Search & DQ Adapters allow us to search and retrieve master data records. Also, the DQ adapters can integrate external tools to enhance overall data quality management. The central part also has Analytics to gain insights into master data, usage, and compliance.
Moreover, SAP Experts need to distribute the master data across connected systems. This ensures the consistency and synchronization of master data across the organization. Key-value mapping involves the translation and alignment of data keys and values between different systems. Thus, System Experts define these mapping rules to ensure consistency, easy data integration, and minimize errors in data translation.
Client System
- ERP(Enterprise Resource Planning): It works as an Integrated software solution so that we can manage the various business processes. It provides a way to access the central data for the management of enterprise operations.
- SRM and SCM: Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) maintains the supplier information to maintain reliable supplier relationships. In addition to this, the SCM manages the master data related to the supply chain, including products, materials, and logistical information used by this system. This can help you to optimize the supply chain processes.
- CRM: This helps us to gain the customer view of the data. It uses the master data of the customers to provide an accurate view of the customer information.
- On-Premise and Cloud: It is a deployment model using which all the resources are maintained within the organization's premise. It offers full control over the master data. while the cloud is just like On-Premise, it is a deployment option to host the software over external servers.
- Third Party: Moreover, you can use third-party services to enhance the master data management services through third-party providers.
Optional Enterprise Information Management (EIM) System
- Information Steward: It helps us in data governance and quality management such as Data Profiling, Data Cleansing, and Metadata Management.
- Data Services: It allows you to connect, transform, and improve the quality of data across various sources.
- Enterprise Search: This feature helps the users to locate master data records and relevant information. Thus, it has advanced search capabilities to search the data on the basis of various criteria.
- NetWeaver MDM: NetWeaver Master Data Management (MDM) is another tool that we can use the manage our master data. It is based on the NetWeaver technology of SAP for centralized data management.
SAP MDG Data Entities
The data entity is created using the data model which outlines the structure, attributes, relationship, and rules associated with the data. After this, every unit of master data is stored in the data entity. Then, these data entities are customized according to the business processes. However, let us see the standard data entities that are defined in the Master Data Module of SAP.
Financial Data
The organizations use the Financial Master Data to manage the data related to the financial structure, including accounts, cost centers, general ledger, hierarchies, organizational units, and profit centers. It plays a crucial role in the reporting, analysis, and standards of the various business processes. It has built-in validation for the SAP business logic so that we can deliver consistent data across the corporate groups and local systems.
Material Data
We can utilize Material Data to create workflow-driven processes for materials in our business. It lists the material specifications, categories, and other logistic details. Here, the change request process manages the maintenance and approval process of new or changed data. It also has the document changes for audits and work lists to manage the pending changes. In short, we can create, search, and display the single material master data as well as manage the mass processing.
Supplier Data
This data entity is used to maintain the supplier information including the data quality validation, duplicate check, address validation, supplier on-boarding, etc. It not only manages the supplier information but also focuses on the relationship among the different supplier entities, procurement systems, and supply chains.
If any of the above data entities do not fit into your business process, you can create custom data models for your business. Master Data Governance provides the framework for data modeling, UI configuration, validation, and distribution of custom-defined master data objects. Therefore, MDG makes the central data management flexible for multiple business scenarios.
Customer Data
It is important for the stakeholders to get an accurate view of the end-user's data so that they make the key decisions for their business processes. Thus, SAP MDG has a Customer Data Entity that includes contact information, transaction history, and customer classifications. We can also fetch a personalized view of data for an individual customer to analyze customer satisfaction.
Custom Objects
If any of the above data entities do not fit into your business process, you can create custom data models for your business. Master Data Governance provides the framework for data modeling, UI configuration, validation, and distribution of custom-defined master data objects. Therefore, MDG makes the central data management flexible for multiple business scenarios.
SAP MDG Vs SAP MDM
MDM in SAP stands for Master Data Management. It is a process of creating a single master data record which is called ‘Single Source of Truth.’ It covers the entire information about the people, processes, and products in the business. It simply deals with creating and maintaining the master records for improved business processes.
In terms of definition, they both are similar but they are different. The key difference lies in the distribution of the data. In MDM, the master data is created and directly distributed to the ERP systems. On the other hand, MDG first takes up data from ERP and consolidates it. This may cause changes or updates in the data. After this, the data is distributed to the ERP using Process Integration. The following tables highlight the key differences between the MDG and MDM.
|
Feature |
SAP MDG |
SAP MDM |
|---|---|---|
|
Key Focus |
Its main focus is on master data governance and integrity. |
It focuses on data consolidation and harmonization. |
|
Scope |
It is good for organizations that focus on data governance. |
It is suitable for enterprises with diverse requirements for data consolidation. |
|
UI |
MDG uses the modern Fiori-based user interface. |
It is based on the traditional Web Dynpro-based interfaces. |
|
Application |
Its main application is to maintain data consistency among multiple systems |
It is used when we need to synchronize the data across the organization. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Does SAP provide training and certification support for SAP MDG?
SAP provides wide support for learning, training, and certification. Its official learning portal has many resources and courses for the SAP Master Data Management. We recommend visiting the official website https://help.sap.com/learning-journeys/500364457a2610149194f4d6d354c9a6 to find more detailed information.
What is ‘Out-of-the-box Delivery’ in SAP MDG?
The ‘Out-of-the-box Delivery’ is a feature of MDG through which it focuses on delivering process-centric solutions using pre-configured Data Quality Services. It mainly refers to ensuring the high quality of the master data so that the business process becomes transparent.
What is the pricing of SAP MDG?
Pricing of the MDG in SAP starts from $ 87 per 5,000 Objects / Month. You can also request a quote from the contact support of SAP. It also has a 90-day free trial which is available on the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP).
How many deployment options are available for Master Data Governance?
SAP provides On-premise deployment through which MDG is configured in the company’s physical infrastructure. It also allows the Private Cloud as well as the Public SAP HANA Cloud for MDG. And now, you can also use the hybrid deployment options on the S/4 HANA Cloud for the SAP MDG.
Explore SAP MDG Sample Resumes! Download & Edit, Get Noticed by Top Employers!
Conclusion
The SAP Master Data Governance Module is a trusted tool for managing all your enterprise data in a centralized manner. This will help the key stakeholders to easily access the data, analyze it, and make strategic business decisions. It has various data models for defining the structure of the data entities such as Customer Supplier, Financial, and Material Data. Along with this, it also has advanced features such as integration with the EIM systems and third-party services.
We hope that this guide provided you with sufficient information to get started with the SAP MDG. Go ahead and experience master data management with SAP.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP MDG Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| SAP MDG Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| SAP MDG Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| SAP MDG Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |

Anji Velagana is working as a Digital Marketing Analyst and Content Contributor for Mindmajix. He writes about various platforms like Servicenow, Business analysis, Performance testing, Mulesoft, Oracle Exadata, Azure, and few other courses. Contact him via anjivelagana@gmail.com and LinkedIn.









