- SAP Interview Questions
- SAP MDG Interview Questions
- SAP PS Interview Questions
- SAP C4C Interview Questions
- SAP ISU Interview Questions
- SAP Analytics Cloud Interview Questions
- SAP CO Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Interview Questions
- SAP VIM Interview Questions
- SAP SCM Interview Questions
- SAP IBP Interview Questions
- SAP RAR Interview Questions
- SAP TM Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Architecture
- What is SAP Transportation Management ?
- What is SAP SCM?
- What is SAP PO - SAP Process Orchestration Architecture
- SAP PO Interview Questions
- What is SAP EDI?
- What is SAP Vistex?
- What is SAP Cloud Platform?
- What is SAP MRP - SAP MRP Tutorial
- What is SAP BTP?
- What is SAP Fieldglass?
- What is SAP C4C?
- What is SAP ISU
- SAP Analytics Cloud Tutorial
- SAP HCM Interview Questions
- What is SAP APO?
- SAP CPI Tutorial - A Beginner’s Guide
- What is SAP CAR?
- What is SAP PS - SAP PS Tutorial
- What is SAP IBP?
- What is SAP CPQ
- What Is Sap Netweaver
- What Is SAP BRIM
- What is SAP Master Data Governance (MDG)?
- What is SAP VIM?
- SAP MDG Architecture
- What is SAP MDG
- SAP HCM Tutorial
- SAP MDG Tutorial
- SAP TRM Interview Questions
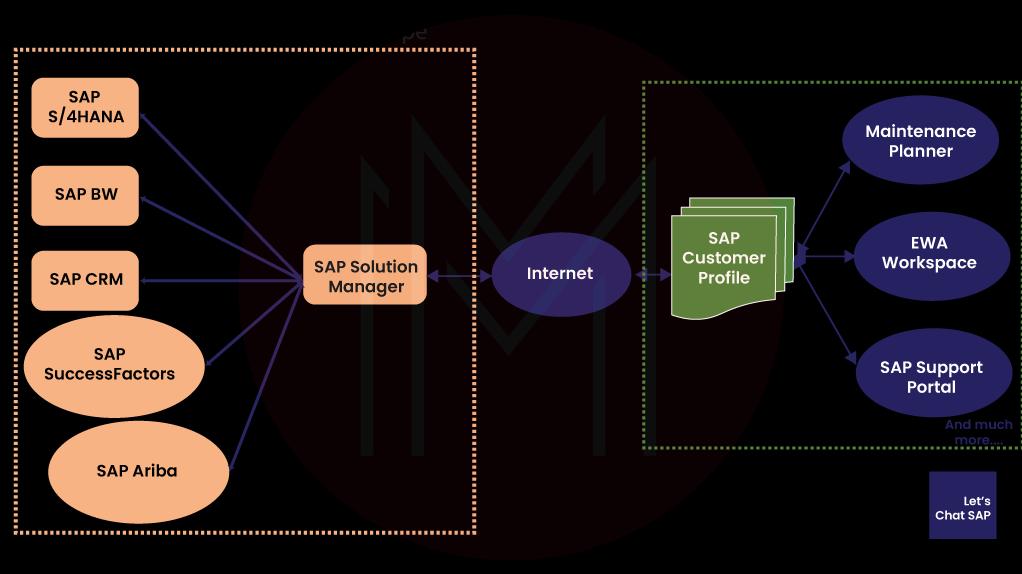
If you have been part of the SAP ecosystem, you may have already heard of SAP Solution Manager, which is one of their most well-known tools. Solution Manager is primarily used to manage SAP applications but can also control non-SAP applications up to a certain point. It has requirements that can be used to monitor and enhance technological and commercial procedures.
SAP Solution Manager is a software created by SAP SE, a German multinational software firm. Its purpose is to assist organizations in successfully managing and monitoring their SAP systems and applications.
The SAP system Manager (SM) module offers integrated information, processes, tools, and other resources to aid in developing, operating, monitoring, and supporting an enterprise's SAP system. The SAP Solution Manager oversees non-SAP and SAP solutions in an organization's IT environment, ensuring business procedures and IT systems run without hiccups. For people responsible for administering SAP Basis, it is a useful tool.
| What is SAP Solution Manager - Table of Contents |
What is SAP Solution Manager?
SAP Solution Manager (SM) is a comprehensive management solution that integrates various tools, content, and direct SAP access. Its primary purpose is to efficiently manage organizational processes throughout the entire lifecycle, from solution deployment to monitoring. This powerful solution plays a crucial role in optimizing essential business processes and providing technical support for a wide range of distributed systems and IT infrastructure. By utilizing SAP Solution Manager, organizations can streamline their operations, enhance efficiency, and ensure the smooth functioning of their SAP landscape.
The key functionalities of SAP Solman are:
- It provides methods, tools, and process management content for a business blueprint's preparation, configuration, and implementation.
- With the help of SAP Solman, you can ensure that the SAP solution environment operates at its fullest potential while keeping costs to a minimum.
- SAP Solman offers integration tools to SAP BASIS Administrators for managing the underlying infrastructure, applications, and business processes. Additionally, it reduces the effort required to manage centralized SAP and non-SAP systems.
- In a distributed environment, SAP Solution Manager efficiently handles the system and SAP applications, such as ECC, BI, and the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) module, as well as non-SAP systems throughout the solution life cycle.
| If you want to enrich your career and become an SAP Solution Manager professional, enroll in "SAP Solution Manager Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
SAP Solution Manager Overview
SAP Solution Manager is vital in improving collaboration between IT and business teams by bringing together different parts of an organization's infrastructure. It acts as a unified solution that seamlessly integrates SAP and non-SAP applications, ensuring compatibility with future SAP updates. This compatibility ensures that businesses can leverage their existing IT investments and avoid disruptions caused by system upgrades.
Furthermore, by utilizing SAP Solution Manager, businesses can optimize their IT budgets and derive maximum value from their technology investments. The platform offers a range of functionalities and tools that enable efficient management of IT resources, resulting in operational efficiency and cost savings.
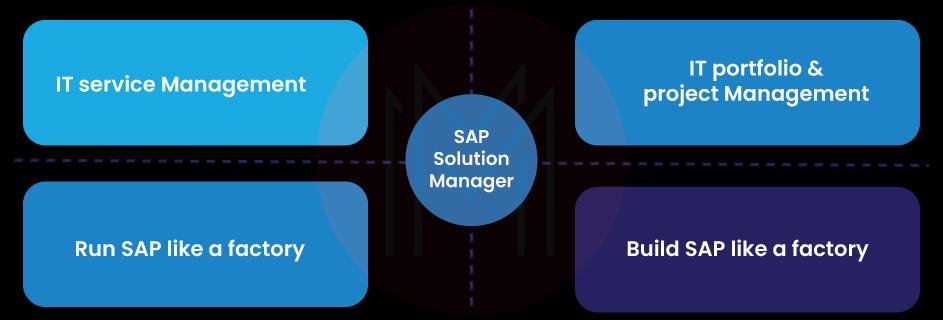
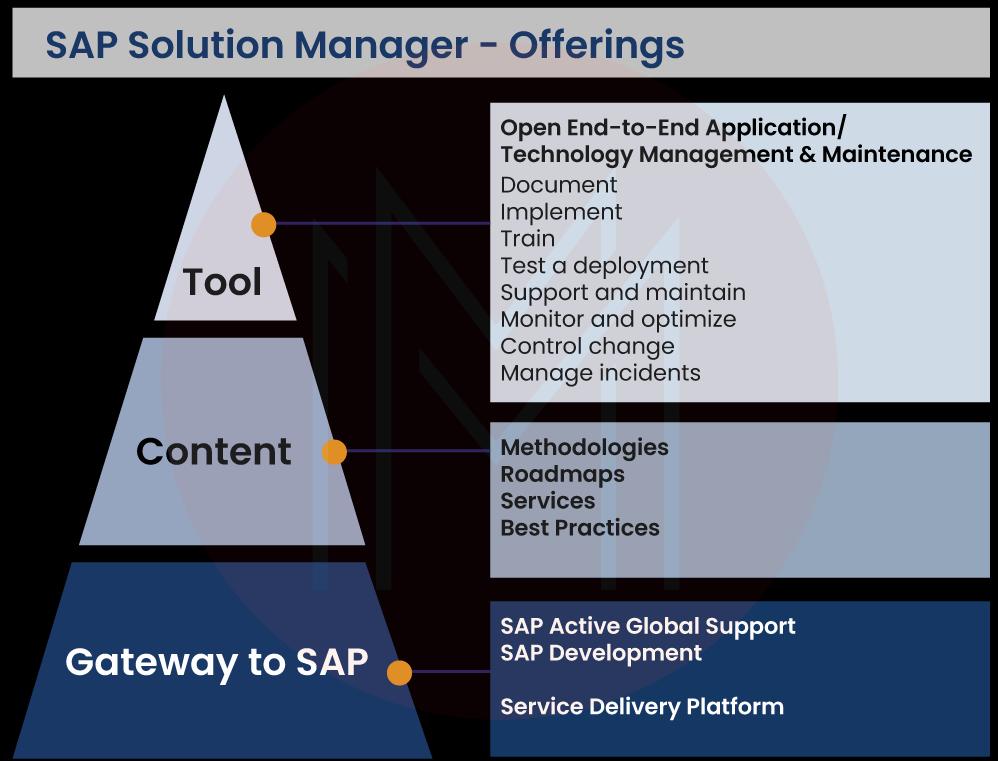
Now, let's dive into an explanation of each point you mentioned regarding SAP Solution Manager.
- Gateway to SAP
- Tools
- Content
Let's get into detail!
1. Gateway to SAP:
SAP Solution Manager is a central hub or gateway to SAP systems and applications. It provides a unified and integrated platform for managing various SAP solutions within an organization. It lets you connect and access different SAP systems, components, and applications from a single entry point.
2. Tools:
SAP Solution Manager offers a wide range of tools and functionalities to support different aspects of application lifecycle management. These tools assist in various activities, including project planning, system implementation, operations, monitoring, and continuous improvement.
Some of the key tools available in SAP Solution Manager are
- IT Service Management (ITSM)
- Business Process Operations (BPO)
- Test Suite
- Change Control Management
- Solution Documentation
- Incident Management
These are examples of the tools available in SAP Solution Manager. The platform offers a rich set of additional tools and functionalities to support different aspects of SAP system management.
3. Content:
SAP Solution Manager offers pre-configured content, templates, and best practices that can be utilized during various phases of the application lifecycle. The content provided by SAP Solution Manager is based on industry standards and SAP's experience in implementing and managing SAP systems. This content includes ready-to-use processes, documentation templates, project plans, and methodologies, which help organizations accelerate the implementation and operation of SAP solutions.
| “If you are preparing for an SAP SM Interview, then refer to these SAP Solution Manager Interview Questions to ace the interview well.” |
Process Flow of SAP Solution Manager
The process flow of SAP Solution Manager involves several stages that cover the entire lifecycle of an SAP solution.
Here is a detailed process flow explanation:
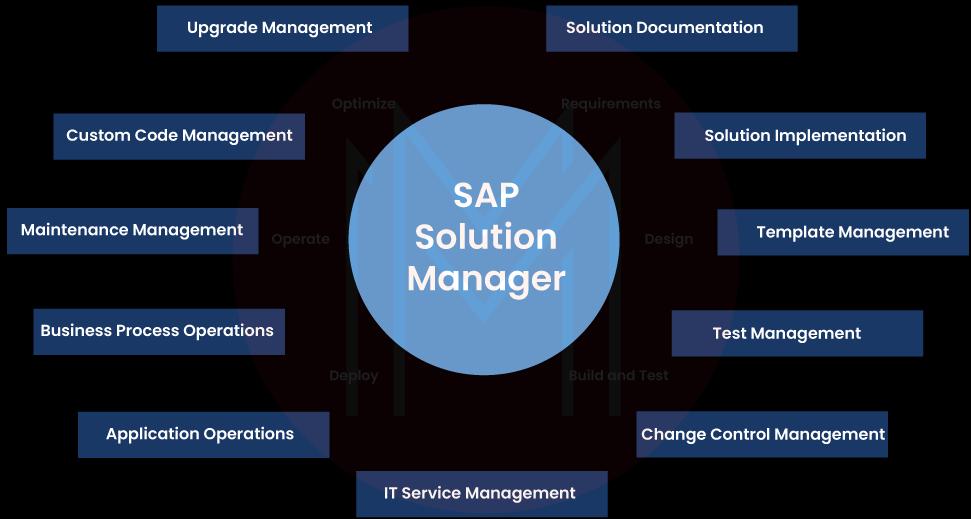
1. Solution Implementation: The first step in the process is implementation, during which the SAP solution is configured and set up. It involves establishing the system landscape, setting up business processes, and modifying the solution to meet the needs of the organization. SAP Solution Manager offers tools and processes to support the project planning, blueprinting, and realization phases of the implementation.
2. Solution Documentation: The next stage after implementing the solution is to generate and keep up-to-date thorough documentation of the solution. Business processes, system architectures, technical configurations, and other pertinent data should all be documented. To make the process of creating and managing solution documentation easier, SAP Solution Manager offers tools like the Solution Documentation Assistant (SDA). The creation and upkeep of thorough documentation for the SAP solution fall under this category. It consists of methods and tools for recording technical setups, system landscapes, business processes, and other pertinent data.
3. Template Management: It is a functionality within SAP Solution Manager that allows you to create, manage, and deploy templates for various SAP implementation projects. Templates serve as reusable frameworks that contain predefined configurations, settings, and best practices for specific business processes or industry requirements.
4. Test Management: Test management involves planning, executing, and managing testing activities for the SAP solution. SAP Solution Manager provides tools and functionalities to support test planning, test case creation, test execution, and test result analysis. It helps ensure the reliability and quality of the SAP solution before it is deployed into production.
5. Change Control Management: Change control management involves managing and controlling changes to the SAP solution. SAP Solution Manager provides tools to track and document changes, including change requests, approvals, and transport management. It helps ensure that changes are properly planned, tested, and implemented while minimizing risks and maintaining system integrity.
6. IT Service Management (ITSM): ITSM covers IT services and incidents management. SAP Solution Manager provides incident, problem, change, and service-level management functionalities.
7. Application Operations: ALM comprises a set of tools and functionalities that support the entire lifecycle of SAP applications, including project management, requirements management, testing, and deployment.
8. Technical Operations: Technical operations encompass the ongoing monitoring, administration, and maintenance of the SAP solution. SAP Solution Manager provides functionalities to monitor system performance, manage technical configurations, perform system administration tasks, and schedule background jobs. It helps ensure the smooth operation of the SAP solution and proactively identifies and resolves technical issues.
9. Business Process Operations: Business process operations focus on monitoring and managing end-to-end business processes supported by the SAP solution. SAP Solution Manager provides tools for monitoring key business processes, setting up alerts and notifications, and analyzing process performance. It helps identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and ensure business operations run smoothly.
10. Maintenance Management: With maintenance planning capabilities, users can schedule and coordinate maintenance activities, such as software updates and upgrades, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations. The change management features allow for efficient tracking and management of system changes, from documentation to testing and implementation. Incident management capabilities enable the timely resolution of system issues and ensure the smooth functioning of SAP systems.
11. Custom Code Management: Custom Code Management manages custom developments within the SAP solution. It includes functionalities for analyzing, documenting, and monitoring custom code objects.
12. Upgrade and Release Management: This category covers managing the upgrade and release processes of the SAP solution. It includes functionalities for planning, executing, and tracking upgrades and managing software patches and updates.
13. Incident Management: Incident management handles and resolves incidents reported in the SAP solution. SAP Solution Manager offers tools for creating, tracking, and managing incidents, including categorization, prioritization, assignment, and resolution. It helps streamline incident handling processes and ensures the timely resolution of issues to minimize business disruptions.
14. Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement involves analyzing system performance, user feedback, and business requirements to identify areas for enhancement and optimization. SAP Solution Manager provides functionalities for conducting root cause analysis, implementing corrective actions, and driving continuous improvement initiatives. It helps organizations derive maximum value from their SAP solution by continuously refining and enhancing its performance and capabilities.
The process flow of SAP Solution Manager is designed to cover the entire lifecycle of an SAP solution, from implementation to continuous improvement. It provides a structured approach and a comprehensive set of tools and functionalities to ensure the successful management and optimization of SAP solutions within an organization.
Key Features of SAP Solution Manager
Certainly! Here are some key features of SAP Solution Manager:
- Roadmaps: Using Roadmaps, you can generate predefined project plans encompassing the essential duties and phases of project implementation as part of solution implementation.
- Application Operations: Application Operations dashboards can show the uptime and performance of your managed infrastructure.
- Test Management: With Test management, you can handle tests from the planning phase to the evaluation phase from one place.
- Landscape Management Database: This single location can gather information on the system landscape.
- Centralized Administration Work Center: SAP Solman allows you to control access to all administrative features from a single location.
- Template Management: You can roll out templates all over the world with the help of template management.
- IT Service Management: This is managed centrally and includes IT infrastructure. You can establish an external Service Desk and connect to the SAP service-support center. IT management processes can be aligned with the Information Technology Infrastructure Library ITIL.
- Change Control Management: You can use a centralized method for change management that works with Transport Management. The Transport Management Infrastructure can be used to move both ABAP and non-ABAP projects.
- Issue Management: Using the issue management tool, you may keep track of problems and their causes.
- Maintenance Management: You can use Maintenance Planner to make plans for maintenance and stack XML files so that Software Update Manager (SUM) can run them. You can also use the system's suggestions to find and show the right SAP Notes. The maintenance process in the production system can be started with the help of a maintenance planner. This gives you clear directions on downloading and installing system maintenance files.
| Related Article: SAP Interview Questions |
Advantages of SAP Solution Manager
SAP Solution Manager offers several advantages for organizations using SAP systems.
Here are some key advantages:
- Centralized Management: A centralized platform for managing and monitoring SAP solutions is provided by SAP Solution Manager, allowing for effective administration and control.
- Application Lifecycle Management (ALM): It supports the full SAP application lifecycle, from implementation to ongoing improvement, ensuring efficient and effective operations.
- Integrated Tools and Functionalities: Project planning, system monitoring, incident management, and change control are just a few of the operations that are streamlined by the extensive selection of integrated tools, features, and content that SAP Solution Manager provides
- Improved Collaboration: By offering a unified platform and shared view into business processes, system landscapes, and technical settings, it improves collaboration between IT and business teams.
- Enhanced System Stability and Performance: Through the provision of system monitoring, diagnostics, and optimization tools, SAP Solution Manager contributes to the stability and performance of the system.
- Documentation and Knowledge Management: It ensures knowledge retention and transfer by making it easier to create and maintain complete documentation, including business process documentation, system landscapes, and technical configurations.
- Support for SAP and Non-SAP Solutions: Both SAP and non-SAP systems are supported by the SAP Solution Manager, allowing for the integrated management and monitoring of the whole IT infrastructure.
- Cost Optimization: It helped optimize IT costs by providing tools for efficient resource management, change control, and incident management, resulting in improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
- Compliance and Governance: SAP Solution Manager assists organizations in achieving compliance with regulatory standards and internal governance policies through its tools and functionalities for change control management, documentation, and audit trail.
- Continuous Improvement: It enables continuous improvement through tools for analyzing system performance, identifying areas for optimization, and implementing corrective actions, leading to enhanced business processes and user satisfaction.
Challenges of using Solution Manager
While SAP Solution Manager offers numerous advantages, there are also some challenges that organizations may face when using it.
Here are some challenges associated with SAP Solution Manager:
- Implementation effort
- Maintaining a Solution Manager
- significant training
- send incorrect information
Let's explore this in detail
a) Implementation Effort:
Implementing SAP Solution Manager can be a complex and time-consuming process. It requires proper planning, configuration, and integration with existing systems. The implementation effort may vary depending on the organization's size, the complexity of the SAP landscape, and the desired functionalities to be implemented.
b) Maintaining a Solution Manager:
Once SAP Solution Manager is implemented, it requires ongoing maintenance and administration. This includes tasks such as system updates, applying patches, and ensuring compatibility with other SAP applications. It may also involve regular performance monitoring, database maintenance, and user management.
c) Significant Training:
SAP Solution Manager is a comprehensive tool with a wide range of functionalities. Using it effectively requires training and expertise. Administrators and users must be trained on various features and best practices for managing and utilizing the solution. This training can be time-consuming and may require additional resources and investment.
d) Sending Incorrect Information:
There is a risk of sending incorrect information through the SAP Solution Manager if the system is not configured correctly or users make errors in data entry or communication. This can lead to miscommunication, inaccurate reporting, and potential business impact. Ensuring proper data validation and review processes minimizes the chances of sending incorrect information.
While these challenges exist, they can be mitigated through proper planning, training, and regular maintenance. SAP Solution Manager offers extensive documentation and support resources to help organizations address these challenges effectively.
Functional Categories of SAP Solution Manager
SAP Solution Manager encompasses various functional categories that cater to different aspects of managing and optimizing SAP solutions.
Here are the functional categories of SAP Solution Manager:
- SAP Solution Manager Operations: This category focuses on managing and monitoring the technical aspects of SAP systems, such as system availability, performance, and technical administration.
- Business Process Operations: This category involves monitoring and managing end-to-end business processes within SAP systems. It helps ensure that critical business processes are running smoothly and efficiently.
- Data Volume Management (DVM): DVM helps manage data volume growth within SAP systems. It includes functionalities for data archiving, data aging, and data deletion to optimize system performance and reduce storage costs.
- Custom Code Management: This category deals with managing custom-developed code in SAP systems. It includes functionalities for analyzing, monitoring, and optimizing custom code to improve system performance and stability.
- IT Service Management: IT Service Management in SAP Solution Manager focuses on managing IT service processes, such as incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management. It helps align IT services with business requirements and delivers efficient IT service.
- Process Management: Process Management enables business process documentation, modeling, and optimization. It provides tools for process modeling, process documentation, and process improvement initiatives.
- Project Management: Project Management functionalities in SAP Solution Manager support the planning, execution, and monitoring of SAP implementation projects. It includes project planning, resource management, progress tracking, and collaboration features.
- Test Management: Test Management encompasses functionalities for planning, executing, and evaluating testing activities in SAP projects. It supports various types of testing, such as unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing.
- Diagnostics & Monitoring: This category focuses on monitoring and analyzing the performance and availability of SAP systems. It includes tools for real-time monitoring, root cause analysis, and performance optimization.
These functional categories provide a comprehensive framework for managing and optimizing SAP solutions throughout their lifecycle, covering various aspects of application management, business processes, IT service management, documentation, testing, change control, technical operations, and more.
Benefits of SAP Solution Manager
SAP Solution Manager offers several benefits that contribute to the efficient management and optimization of SAP solutions.
Here are some key benefits of using SAP Solution Manager:
- Faster ROI
- Reduces Administration Effort
- Lowering Cost
- Easy Integration
- Automated Alerts
- Centralized Management
- Automated configuration tracking
- Improved patch and upgrade management
Know more about each advantage:
- Faster ROI: It speeds up installation while also facilitating ongoing improvement. Learning is sped up, and projects are moved along more quickly when implementation roadmaps, best practice guidelines, and SAP solution management services are readily available.
- Reduces Administration Effort: It monitors systems, interfaces, and business processes in real-time, hence minimizing the amount of effort required for management.
- Lowering Costs: You can maximize the value of SAP's support services with the aid of SAP Solution Manager, which can significantly reduce your total cost of ownership.
- Easy Integration: Integrates with many IT landscapes, including SAP and applications from other vendors.
- Automated Alerts: The team is not required to manually look for system errors because they will automatically be notified of any problems or mistakes.
- Centralized Management: It serves as the principal point of control for the complete solution field and the primary point of management for projects with several components.
- Automated configuration tracking: Users can monitor any configuration changes with the assistance of a knowledge library that always features the most recent information.
- Upgrade management and Improved patch: A single hub will handle the entire system's patching and synchronization.
SAP Solution Manager FAQs
1. What does an SAP Solution Manager do?
SAP Solution Manager assists businesses in managing and monitoring their SAP systems and applications, assisting with implementation, operations, and continuing maintenance.
2. How do I access SAP Solution Manager?
With the proper user credentials and permissions, SAP Solution Manager can be accessed via a web-based user interface, often via a web browser.
3. What are the benefits of SAP Solution Manager?
The benefit of SAP Solution Manager to centralize and streamline SAP system management leads to increased efficiency, proactive issue identification, and optimized system performance.
4. What is the future of SAP Solution Manager?
SAP Solution Manager's future is projected to include changes and updates to meet SAP clients' increasing needs, such as increased cloud integration, enhanced analytics, and expanded features.
5. What is the branch of SAP Solution Manager?
In SAP Solution Manager, a branch represents a logical separation of SAP systems or landscapes, allowing for separate management and control of system changes, testing, and documentation.
6. How much is the SAP Solution Manager license?
The cost of SAP Solution Manager licenses can vary based on factors such as the organization's size, specific requirements, and licensing agreements. It is recommended to consult with SAP or an authorized SAP partner for accurate pricing information.
7. What is the latest version of SAP Solution Manager?
The latest version of SAP Solution Manager is 7.2 since August 2016.
8. What are the benefits of a solution manager?
Some benefits of an SAP Solution Manager include centralized management of SAP systems, improved operational efficiency, proactive issue detection, streamlined implementation and upgrades, comprehensive documentation, and enhanced collaboration and knowledge sharing.
9. What is the role of solution management?
The role of solution management is to oversee a solution's development, maintenance, and optimization throughout its lifecycle. It involves tasks such as defining product strategies, gathering customer requirements, managing product releases, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
SAP Solution Manager is excellent software. It includes everything a company could possibly need to manage SAP and non-SAP IT applications. However, it can become complicated when attempting to implement, maintain, and operate its functionalities. Therefore, your organization's optimal Solution Manager implementation is to commence small. Implement something simple to implement and maintain, such as Technical Monitoring. Then, gradually investigate other functionalities based on your organization's needs.
Join Mindmajix’s SAP Solution Manager Training course to deep dive into technical concepts and make your career in the SAP field.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP Solution Manager Certification Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| SAP Solution Manager Certification Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |
| SAP Solution Manager Certification Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| SAP Solution Manager Certification Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .














