- SAP Interview Questions
- SAP MDG Interview Questions
- SAP PS Interview Questions
- SAP C4C Interview Questions
- SAP ISU Interview Questions
- SAP Analytics Cloud Interview Questions
- SAP CO Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Interview Questions
- SAP VIM Interview Questions
- SAP SCM Interview Questions
- SAP IBP Interview Questions
- SAP RAR Interview Questions
- SAP TM Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Architecture
- What is SAP Transportation Management ?
- What is SAP SCM?
- What is SAP PO - SAP Process Orchestration Architecture
- SAP PO Interview Questions
- What is SAP EDI?
- What is SAP Vistex?
- What is SAP Cloud Platform?
- What is SAP BTP?
- What is SAP Fieldglass?
- What is SAP C4C?
- What is SAP ISU
- What is SAP Solution Manager?
- SAP Analytics Cloud Tutorial
- SAP HCM Interview Questions
- What is SAP APO?
- SAP CPI Tutorial - A Beginner’s Guide
- What is SAP CAR?
- What is SAP PS - SAP PS Tutorial
- What is SAP IBP?
- What is SAP CPQ
- What Is Sap Netweaver
- What Is SAP BRIM
- What is SAP Master Data Governance (MDG)?
- What is SAP VIM?
- SAP MDG Architecture
- What is SAP MDG
- SAP HCM Tutorial
- SAP MDG Tutorial
- SAP TRM Interview Questions
MRP is the function or software that determines the material acquisition plans necessary to meet production plans and consumer demand. It ensures the availability of the material for which MRP is performed and the availability of the components (at all levels of the BOM). MRP is a planning mechanism for manufacturing production. It identifies necessary materials, estimates quantities, determines when materials will be required to meet the production schedule, and manages delivery schedules to satisfy customer demands and boost overall productivity.
SAP MRP (Material Requirements Planning) is a module of the SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system that assists businesses in planning and managing their material requirements. MRP is predominantly utilized in manufacturing and production industries to ensure that materials are available in the appropriate quantity, at the appropriate time, and in the appropriate location to meet production demands.
| What is SAP MRP? - Tables of Contents |
What is SAP MRP?
When it comes to material management, SAP MRP (Material Requirements Planning) is an indispensable subsystem of SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). SAP MRP plays a critical role in optimizing inventory levels, minimizing stockouts, and maintaining smooth production operations in manufacturing and production industries, where the timely availability of resources is crucial. SAP MRP helps with dependable production plans that satisfy customer requests while efficiently utilizing resources by analyzing demand, calculating replenishment quantities, and generating procurement recommendations. SAP MRP allows businesses to improve procurement and manufacturing efficiency by considering stock levels, purchase orders, sales orders, and lead times, among other aspects.
SAP MRP makes use of a series of algorithms and calculations in order to conduct an analysis of a variety of elements, including, but not limited to, production schedules, inventory levels, and lead times. MRP develops a complete plan that defines when and how much of each material should be acquired or produced to fulfill future demand. This plan is generated by taking into consideration the aforementioned criteria.
| If you want to enrich your career and become an SAP MRP professional, enroll in " SAP MRP Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
How does SAP MRP Work?
SAP MRP functions by analyzing demand, considering multiple factors, and generating procurement proposals to ensure the availability of production materials.
Here is an explanation of how SAP MRP operates and the processes involved:
- MRP Process flow
- Master Production Schedule (MPS)
- MRP Planning Parameters
- How to run MRP for all Products
- How to run MRP for single material
- How to run Master Production Schedule (MPS)
- How to do MRP evaluation – Stock/Requirement List
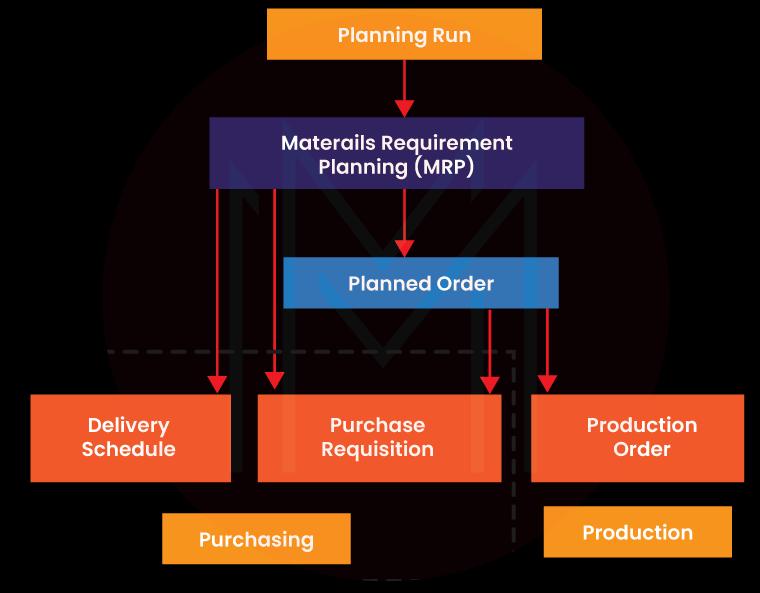
1) MRP Process flow
- By scheduling receipts in accordance with demand, MRP enables inventory to be optimized and excess inventory to be avoided.
- Specific consumer requirements are provided to the market through sales and distribution.
- Sales are anticipated and scheduled in advance when using demand management. The requirement for the final product, or Planned Independent Requirement (PIR), is entered into demand management alongside the sales estimate.
- The net need calculation is carried out using MRP, and the quantities and dates for the material's production or procurement are plotted.
- The MRP system SAP breaks down the BOM if the material is produced internally and determines the dependent needs or the number of components needed to make the finished product.
- In the event of a material shortage, purchase requests are issued for raw materials that must be obtained from outside sources, and planned orders are generated at each BOM level to meet needs. For items that must be obtained from outside sources, you can also establish planned orders that can be changed into purchase requests.
- Based on lead time scheduling and routing times, MRP determines the scheduled order dates. In essence, it determines how long planned orders will take to complete based on the need date, less any delays in GR processing, in-house production, and float time before production.
- Production orders and purchase orders are generated as a result of the conversion of planned orders and purchase requisitions.
- Materials MRP requires MRP type "PD" in the material master MRP 1 view. If MRP is not desired for the material, MRP type "ND" might be kept in the material master.
2) Master Production Schedule (MPS)
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) is the first step in the MRP process. The MPS depicts the finished goods production plan based on consumer demand, sales predictions, and corporate objectives.
It is mostly used for important materials, usually high-value items, where you don't want to change your production plan within the planning time fence in the next MPS run. Unlike an MRP run, the production plan is set as soon as it gets to the planning time fence.
3) MRP Planning Parameters
Several planning criteria must be defined before executing MRP. These characteristics include lead times, safety stock levels, reorder points, lot-sizing methodologies, and other material planning factors. These parameters influence how the MRP computations are carried out.
Processing Key
- Net change (NETCH): The system assesses materials in the planning run from the previous MRP run that have changed receipts, problems, or stock levels.
- Net Change in Planning Horizon (NETPL): In this run, the system looks at the materials that have changed in terms of receipts, issues, or stock amounts since the previous MRP run. Unlike the NETCH key, which looks at all future needs, it only looks at needs within a planning window that has already been set.
- Regenerative Planning (NEUPL): It plans all of the items for the MRP Run, no matter how they change. This approach doesn't get used very often. It takes a lot of time to get where you want to go.
Planning Mode
- Adapt planning data: Only the modified data are processed.
- Re explodes BOM and Routing: Repeatedly read BOM and routing data for existing orders.
- Delete and recreate planning data: It entirely deletes and recreates all planning data (receipts).
Scheduling
- Fundamental Scheduling: MRP calculates only fundamental dates for orders and uses the material master's in-house production time.
- Time Lead Scheduling: The production schedule is determined by the advance time scheduling for orders in the pipeline. To schedule and calculate the capacity requirements for work centers, the routings are read.
4) How to run MRP for all Products
To run MRP for all products, the MRP process is initiated in SAP. The system will calculate based on planned production quantities, extant stock levels, open purchase orders, and open sales orders. MRP analyzes the demand and supply situation and generates procurement proposals, such as planned orders, purchase requisitions, and production orders, to meet material needs.
Step 1: We will run MRP at the Plant level from the SAP easy access screen by opening transaction MD01.
- Enter the manufacturing plant for which you wish to perform an MRP.
- Enter "NETCH" (Net change in the total horizon) as the Processing key
- Enter "1" in Create Purchase requisition. In other words, MRP will generate purchase requisitions instead of planned orders for externally sourced materials.
- Enter "3" for schedule lines to generate schedule lines for primary materials with a scheduling agreement.
- Enter "1" in the MRP List field, and the system will generate an MRP list comparable to the stock/requirements list for future analysis of previous MRP operations.
- Enter Planning mode "3" as all planning data for all materials will be deleted and recreated.
- Enter Scheduling indicator "2" to have MRP calculate planned order dates using lead time scheduling and routing times.
After filling in all the fields, click "Next" to move to the next screen.
Step 2: The System will need some time to determine the required material.
Upon completion of the calculation, a report will appear. Here, it is feasible to view how many materials were planned for the run and what parameters were used.
5) How to Run MRP for single material
You may need to perform MRP for a specific material rather than all items at times. In this situation, you can run the MRP run especially for that material, taking into account its unique planning parameters and requirements. This allows you to concentrate on the planning and purchase of a specific material without interfering with the remainder of the MRP calculations.
Step 1: We will run MRP for a single material in Transaction MD02.
- Enter the material code for which MRP will be executed.
- Enter the plant code for which you wish to perform an MRP run.
- Enter "NETCH" (Net change in the total horizon) as the Processing key
- Enter "1" in Create Purchase req to have MRP generate purchase requisitions instead of planned orders for externally procured materials.
- Enter "3" for schedule lines to generate schedule lines for primary materials with a scheduling agreement.
- Enter "1" in the MRP List field, and the system will generate an MRP list comparable to the stock/requirements list for future analysis of previous MRP operations.
- Enter Planning mode "3" as all planning data for all materials will be deleted and recreated.
- Enter Scheduling indicator "2" to have MRP calculate planned order dates using lead time scheduling and routing times.
After filling in all the fields, click "Next" to move to the next screen.
Step 2: It will take some time for the system to calculate the material demand.
Upon completion of the calculation, a report will appear. Here you can view the planned quantity of materials.
Note: There are only 22 materials that can be used in the plant, thus only those were considered.
6) How to run Master Production Schedule (MPS)
Executing the MPS planning run is a part of running the Master Production Schedule (MPS). The MPS run looks at the planned production quantities, open sales orders, and other factors to figure out the exact production needs and schedules for the finished goods.
Step 1: In Transaction MD43, MPS for a specific material will be executed.
- Type in the information you want to run MPS on. Here, we've used the number "13967476" as the ID.
- Enter the "INA2" production plant that you want to run the MPS for.
- Enter "NETCH" (Net change in total range) as the Processing Key.
- Put "1" in the "Create Purchase req." box. So, when materials are bought from outside the company, MPS will make buy requisitions instead of planned orders.
- If you put "3" for schedule lines, MPS will make schedule lines for raw products that have scheduling agreements.
- Enter "1" in the MRP List field, and the system will make an MRP list similar to the stock/requirements list so that earlier MPS runs can be analyzed later.
- Enter "3" as the planning mode because we are going to remove and re-create all planning data for all materials.
- Enter the number "2" for the Scheduling indicator. This tells MRP to do lead time scheduling and take route times into account when figuring out planned order dates.
After completing all fields, the system will display a confirmation message; select again if everything is correct.
Step 2: In this step, we will make the planning data live so that you can see the planning results at the same time.
- When you press the "Planning" button, planned orders for the shortage amount will be made.
- Check the orders that were made.
7) How to do MRP evaluation – Stock/Requirement List
A key result of the MRP evaluation method is the stock/requirement list. It gives an outline of the current stock levels, how materials are moving in and out, and how much of each material is needed. This list helps track what's in stock, determine what's missing or too much, and make better decisions about what to buy and how much to make. On this list, you can see what is needed, what is already in stock, and what is going to be ordered.
By following these steps and utilizing the SAP MRP module's functionalities, organizations can effectively plan and manage their material requirements, optimize their inventory levels, and ensure seamless production operations.
Benefits of SAP MRP
Implementing SAP MRP (Material Requirements Planning) offers several significant benefits for businesses.
Here are some key advantages:
- Improved Inventory Management: SAP MRP calculates material quantities based on demand projections, sales orders, and manufacturing schedules to optimize inventory levels. This decreases surplus stock, stockouts, and carrying expenses.
- Enhanced Customer Service: With SAP MRP, companies can better and more reliably meet customer needs. By making sure materials and products are available, organizations can increase the number of orders they can fill, cut down on wait times, and improve customer happiness.
- Streamlined Production Planning: SAP MRP helps production planning go smoothly by making planned orders and scheduling output based on how much material is needed. It takes into account things like lead times, capacity limits, and production priorities. This helps businesses improve their production methods and meet customer needs on time.
- Cost Reduction: SAP MRP helps lower running costs by optimizing inventory levels, reducing stock-outs, and making production more efficient. It cuts down on the need for rush orders, gets rid of the costs of keeping too many goods on hand, and cuts down on the costs of production delays or interruptions.
- Real-time Visibility and Reporting: SAP MRP offers visibility into material requirements, inventory levels, and production schedules in real-time. This allows businesses to monitor and analyze key performance indicators, identify obstacles or inefficiencies, and optimize supply chain operations based on data-driven decisions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Whether a business is expanding its operations or diversifying its product offerings, SAP MRP can accommodate its expanding requirements. It allows for scalability and adaptability to altering market conditions, demand patterns, and production needs.
[Related Article: SAP Interview Questions]
SAP MRP Configuration
SAP MRP Configuration involves setting up various parameters and settings to tailor the Material Requirements Planning (MRP) process according to the organization's specific requirements.
Here's an overview of three key configuration MRP elements in SAP:
1. Planning Horizon:
Within the planning horizon, MRP considers material requirements. It specifies how many days or weeks into the future MRP calculations will be performed. By configuring the planning horizon, organizations can manage the material requirements' visibility and planning scope. If the planning horizon is set to four weeks, for instance, MRP calculations will consider the demand and supply for materials over the next four weeks.
2. Lot Size:
The configuration of lot sizes determines the quantities of materials procured or manufactured. SAP MRP supports various lot sizing methods, including fixed lot size, lot-for-lot (L4L), economic order quantity (EOQ), and intermittent lot sizing. Organizations can balance production costs, inventory carrying costs, and order frequency by selecting an appropriate quantity size method. For example, a configuration with a fixed lot size may ensure consistent production quantities, whereas EOQ may strive to minimize total production and procurement costs.
3. Safety Stock:
Safety stock configuration entails determining the buffer stock level to mitigate demand and supply uncertainties. Safety stock serves as a buffer against fluctuations, variability, and unanticipated occurrences such as increased demand or delayed deliveries. Organizations are able to configure safety stock levels in accordance with variables such as intended service levels, demand patterns, lead times, and supply chain variability. By establishing adequate levels of safeguard stock, businesses can improve customer service, reduce stockouts, and maintain production reliability.
SAP MRP FAQs
1. Is SAP an MRP or ERP?
SAP is an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system that includes modules for various business functions, including MRP (Material Requirements Planning).
2. What is MRP Planning in SAP?
MRP Planning in SAP involves calculating material requirements and generating procurement proposals based on demand, inventory levels, and other factors to ensure efficient production and inventory management.
3. What are MRP and its types in SAP?
MRP (Material Requirements Planning) in SAP is a process that determines material requirements and generates procurement proposals. SAP MRP types include MRP at plant, storage location, and MRP area levels, defining the scope and granularity of the calculations.
4. What is SAP ERP called?
SAP ERP is commonly referred to as SAP ECC (SAP ERP Central Component) or SAP S/4HANA (the successor to SAP ECC).
[Related Article: SAP ERP Interview Questions]
5. What is MRP type P3 in SAP?
MRP type P3 in SAP is a planning type used for externally procured materials. It considers gross requirements but does not create planned orders for the material.
6. What is the V1 MRP type in SAP?
V1 MRP type in SAP is a planning type used for consumption-based planning with historical demand data. It is suitable for spare parts or low-value items without the need for forecasting or dependent demand calculations.
Conclusion
In summary, SAP MRP is a sophisticated planning tool that allows businesses to effectively manage their materials and resources effectively, ensuring smooth production processes, improved customer service, and increased profitability. By leveraging the power of SAP MRP, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, agility, and control over their supply chain operations.
If you want to enrich your career and become an SAP professional, then enroll in the "SAP MRP Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP MRP Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| SAP MRP Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| SAP MRP Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| SAP MRP Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















