- SAP Interview Questions
- SAP MDG Interview Questions
- SAP PS Interview Questions
- SAP C4C Interview Questions
- SAP ISU Interview Questions
- SAP Analytics Cloud Interview Questions
- SAP CO Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Interview Questions
- SAP VIM Interview Questions
- SAP SCM Interview Questions
- SAP IBP Interview Questions
- SAP RAR Interview Questions
- SAP TM Interview Questions
- What is SAP Transportation Management ?
- What is SAP SCM?
- What is SAP PO - SAP Process Orchestration Architecture
- SAP PO Interview Questions
- What is SAP EDI?
- What is SAP Vistex?
- What is SAP Cloud Platform?
- What is SAP MRP - SAP MRP Tutorial
- What is SAP BTP?
- What is SAP Fieldglass?
- What is SAP C4C?
- What is SAP ISU
- What is SAP Solution Manager?
- SAP Analytics Cloud Tutorial
- SAP HCM Interview Questions
- What is SAP APO?
- SAP CPI Tutorial - A Beginner’s Guide
- What is SAP CAR?
- What is SAP PS - SAP PS Tutorial
- What is SAP IBP?
- What is SAP CPQ
- What Is Sap Netweaver
- What Is SAP BRIM
- What is SAP Master Data Governance (MDG)?
- What is SAP VIM?
- SAP MDG Architecture
- What is SAP MDG
- SAP HCM Tutorial
- SAP MDG Tutorial
- SAP TRM Interview Questions
Complex businesses have varying needs, and these are often met with third-party products and services. To enable data exchange between your SAP ERP and external systems, you need middleware. Middleware allows SAP to access data collected from your third-party products, and vice-versa. Without this communication, your information will be stored in silos. This defeats the purpose of investing in any service, as you will not be able to leverage its features. SAP has obviously thought of this, which is why it offers middleware options to its customers. SAP CPI is one of these options. Let us see what is SAP CPI in detail.
SAP HANA Cloud Integration allows you to connect your cloud applications quickly and seamlessly to other SAP and non-SAP enterprise software – without extensive coding. This integration as a service solution from SAP can help you harmonize business processes and data in a secure and reliable environment. The architecture includes an integration, connectivity, and process layer, each with components and functionalities. SAP CPI also offers features for security and compliance, scalability and flexibility, and integration with other SAP products.
You can perform Bi-directional integration to connect your cloud and enterprise applications, gain a unified view of all business data and eliminate data entry, perform centralized monitoring and management of integrations, speed implementation using pre-packaged integration content, and get lower TCO with an affordable, pay-as-you-go subscription model and minimal up-front investment. Architectural Overview of SAP Platform Cloud Integration (f.k.a HCI-PI) is another capability offered by SAP HANA Cloud Integration.
| SAP CPI Architecture - Table of contents |
What is SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI)
SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) is a cloud-based integration platform that integrates various business systems and data sources. It offers a variety of features and capabilities for designing, executing, and monitoring integrations between different applications and services. The structure of SAP CPI is based on the concept of integration flows, a set of tasks or steps that define the integration logic. Integration flows consist of three main components- sender adapter, message mapping, and receiver adapter.
In addition to these main components, SAP CPI also offers a variety of other features and capabilities, such as pre-built integration content and templates for popular systems and applications, such as SAP ERP, Salesforce, and ServiceNow, a web-based designer tool for creating and modifying integration flows. It also monitors and error handles capabilities for managing integration flows and diagnosing issues. There are many security and compliance features to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of integrated data. Overall, the structure of SAP CPI is designed to be flexible, scalable, and customizable, allowing users to create and manage integrations that meet their specific business needs.
SAP Platform Cloud Integration is a cloud-based solution. The tenants are provisioned for you on request. For all matters of operation, it functions as a black box. However, seeing SAP Platform Cloud Integration is powered under the hood would be interesting. Developers can build integrations in virtualized environments, focus on enterprise integration patterns implementation challenges, and leave out the maintenance efforts on the platform. The platform has many advantages that might be unfamiliar to integration developers on SAP Process Orchestration.
| If you want to enrich your career and become an SAP CPI professional, enroll in "SAP CPI Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
What is SAP CPI Architecture?
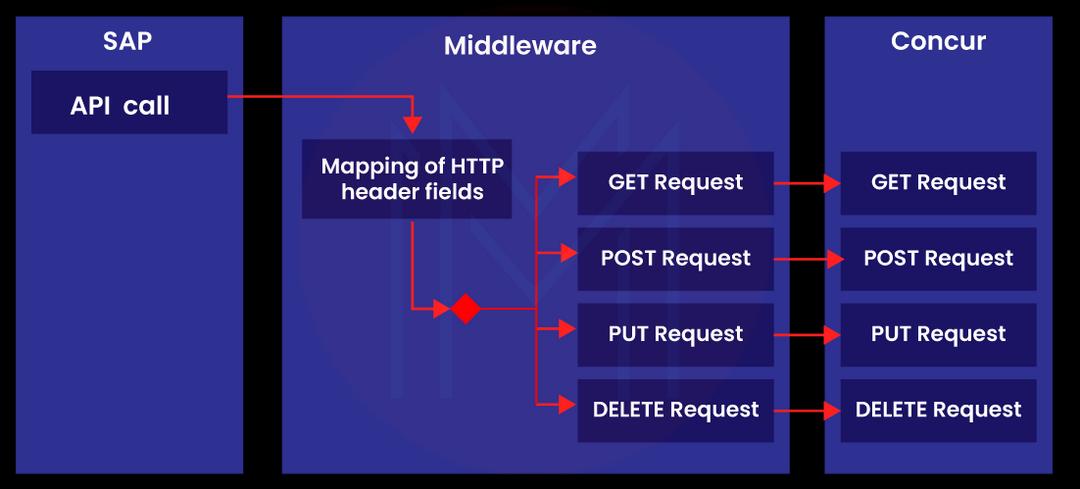
Understanding the SAP CPI architecture is essential for organizations that want to integrate their business systems and data sources effectively. Organizations can design, develop, and deploy integration flows that meet their business needs and requirements by understanding the CPI architecture. One of the key benefits of understanding the SAP CPI architecture is that it enables organizations to create integrations that are scalable and flexible.
With a clear understanding of the various components of the architecture, organizations can design integration flows that can handle large volumes of data and adapt to changes in business requirements over time. In addition, understanding the SAP CPI architecture allows organizations to optimize their use of the platform and its features. Knowing how the various components of the architecture work together, organizations can identify opportunities to streamline their integration processes, improve performance, and minimize errors and downtime.
Understanding the SAP CPI architecture is critical for organizations that want to achieve seamless and efficient integration of their business systems and data sources. By investing in learning about the architecture and its capabilities, organizations can leverage the full potential of SAP CPI to drive business growth and success.
[Related Article: SAP CPI Interview Questions]
Architecture Layers in SAP CPI
Overall, the three layers of the SAP CPI architecture work together to provide a comprehensive and powerful platform for integrating business systems and data sources. By leveraging the capabilities of each layer, organizations can create flexible, scalable, and secure integration solutions that meet their specific business needs and requirements. The SAP CPI architecture can also be described in terms of three layers that are closely related to the integration, connectivity, and process components of the platform –
1. Integration Layer:
This layer is focused on the integration components of SAP CPI, including the integration flows, mappings, and other artifacts that define the data transformation and routing rules between the various systems and data sources.
- Components of the integration layer:
The integration layer of SAP CPI architecture consists of several vital components that work together to enable seamless integration between business systems and data sources.
-
- Integration Flows - These are the core components of the integration layer, which define the logic for data transformation and routing between systems. Integration flows comprise sender and receiver adapters, message mappings, and other integration components defining data transformation and routing rules.
- Message Mappings - These transform the data between different formats and structures, from XML to JSON or vice versa. Message mappings are defined using the graphical mapping editor in SAP CPI.
- Sender and Receiver Adapters - These connect to different systems and data sources and provide the communication channels for the integration flows. SAP CPI offers various adapters for various systems, including SAP systems, cloud applications, databases, and web services.
- Content Modifier - This component is used to modify the content of the messages processed by the integration flow. It can add, remove, or modify fields in the message payload.
- Router - This component is used to route messages to different integration flows based on specific criteria, such as the content of the message or the sender system.
- Splitter and Aggregator - These components are used to split large messages into smaller ones for processing and to aggregate multiple messages into one.
[Related Article: JSON Interview Questions]
2. Connectivity Layer:
This layer is focused on the connectivity components of SAP CPI architecture, including the adapters, connectors, and other runtime services that provide communication between the various systems and data sources. This layer also includes the security and authentication components ensuring secure data exchange. Overall, the components of the connectivity layer in SAP CPI architecture provide a powerful and flexible platform for connecting different systems and data sources, ensuring seamless communication and integration across the enterprise.
- Components of the connectivity layer:
The connectivity layer of SAP SPI architecture consists of several vital components that work together to enable communication and integration between different systems and data sources –
-
- Adapters - SAP CPI provides various adapters that support various communication protocols and data formats. These adapters enable SAP CPI to connect to different systems and applications, such as SAP systems, non-SAP systems, cloud applications, databases, and web services.
- Connectors - Connectors connect to various cloud services and data sources, such as Salesforce, Workday, SuccessFactors, etc. SAP CPI provides pre-built connectors for many popular cloud services.
- Security - The connectivity layer provides various security features that ensure the secure exchange of data between systems. These include user authentication, encryption, and data masking.
- Protocol Conversion - The connectivity layer supports protocol conversion between different systems and data sources, enabling SAP CPI to transform data formats and structures to ensure seamless integration.
- Monitoring - The connectivity layer includes monitoring features that enable users to track the performance and health of integration flows and identify any errors or issues.
- Content-Based Routing - This feature enables SAP CPI to route messages based on the content of the message, allowing users to define specific routing rules for different messages.
3. Process Layer:
This layer is focused on the process components of SAP CPI, including the workflow and process management capabilities that enable users to design and automate business processes. This layer also includes the monitoring and analytics components that provide visibility into the performance and health of the integration processes.
- Components of the process layer:
The process layer of SAP CPI architecture consists of several vital components that work together to enable the automation of business processes –
-
- Process Designer - This is the core component of the process layer, which enables users to design, configure, and deploy business processes using a drag-and-drop interface. The process designer includes a library of pre-built process templates and integration flows that can be customized and extended.
- Decision Tables - These define decision-making rules within the business processes. Decision tables enable users to define complex rules that automate decision-making based on various conditions.
- Process Templates - These templates can quickly build and deploy standard business processes, such as purchase order approval, invoice processing, etc.
- Message Monitoring - The process layer includes monitoring features that enable users to track the status and progress of business processes and integration flows in real time. Users can view detailed logs and error messages to identify issues or bottlenecks.
- Notification - The process layer includes notification features that enable users to receive alerts and notifications when specific events occur within the business processes, such as when an error occurs or when a cycle is completed.
- Data Mapping - This component maps data between different systems and applications within the business processes. Users can define mapping rules to transform and format data to ensure seamless integration.
System Landscape for SAP CPI
1. Cloud Integration Runtime Environment (CIRE)
The Cloud Integration Runtime Environment (CIRE) is a critical component of the SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) system landscape. It is a cloud-based runtime environment that provides the infrastructure and resources needed to execute integration flows and business processes within the CPI platform. It provides a scalable and reliable platform for executing integration flows and business processes within the SAP CPI system landscape. The CIRE enables users to deploy, manage, and monitor complex integration scenarios, and to ensure seamless communication and integration between different systems and data sources.
- Components of CIRE:
The CIRE consists of several components that work together to provide a scalable and reliable runtime environment for integration flows, including –
-
- Cloud Integration Servers - These servers execute integration flows within the CPI platform. The CIRE provides a pool of integration servers that can be dynamically allocated and de-allocated based on workload and demand.
- Message Queues - The CIRE includes message queues that enable the decoupling of message production and consumption, ensuring reliable message delivery and processing.
- Data Storage - The CIRE includes a storage layer that provides persistent storage for integration artefacts, such as message definitions, mapping rules, and process configurations.
- Load Balancer - The CIRE includes a load balancer that distributes incoming traffic across multiple integration servers, ensuring optimal performance and scalability.
- Monitoring and Management - The CIRE includes monitoring and management features that enable users to track the status and performance of integration flows and servers in real-time.
2. Cloud Integration Tenant (CIT)
The Cloud Integration Tenant (CIT) is another critical component of the SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) system landscape. It is a logical entity within the CPI platform that represents a specific customer or organization and provides a dedicated environment for developing, testing, and deploying integration scenarios. Cloud Integration Tenant (CIT) is a vital component of the system landscape for SAP CPI provides a dedicated environment for creating, testing, and deploying integration scenarios. It enables users to integrate different easily systems and data sources and to ensure seamless communication and collaboration across the enterprise.
- Components of CIT
The Cloud Integration Tenant (CIT) includes several key components that enable users to create, manage, and deploy integration scenarios, including
-
- Integration Directory - The Integration Directory is a central repository for managing integration artefacts, such as message definitions, mapping rules, and process configurations. It enables users to define and manage integration scenarios and configure communication channels between systems and data sources.
- Eclipse-based Design Time Environment - The CIT provides an Eclipse-based Design Time Environment (DTE) that enables users to design, develop, and test integration scenarios using a visual drag-and-drop interface. The DTE includes various pre-built integration adapters and connectors and supports different integration standards and protocols.
- Runtime Environment - The CIT includes a runtime environment that provides the infrastructure and resources needed to execute integration scenarios and business processes. It consists of a Cloud Integration Runtime Environment (CIRE) that provides a scalable and reliable platform for managing integration flows and message queues, load balancers, and other components.
- Monitoring and Analytics - The CIT includes various monitoring and analytics features that enable users to track the status and performance of integration scenarios and components in real time. It includes dashboards, reports, and alerts that provide visibility into system health and performance and enables users to identify and troubleshoot issues quickly.
Components OF SAP CIP Architecture
1. Integration Flows:
Integration flows are the core building blocks of SAP CPI architecture. They represent the end-to-end integration scenarios between different systems and data sources and define the message routing, transformation, and processing logic needed to ensure seamless communication and collaboration. Integration flows are created using the Eclipse-based Design Time Environment and are executed on the Cloud Integration Runtime Environment.
Integration Flows are a core component of the SAP CPI architecture, and they play a crucial role in enabling data transfer between systems and applications. Integration flows are pre-built templates that define data flow between different systems and applications, including mapping, transforming, and routing data.
In SAP CPI, integration flows are created using the Web-based Integration Designer, which provides a drag-and-drop interface for configuring the different components of the flow. The Integration Flow editor allows users to define the flow of data between the other components of the architecture, including the endpoints, data mapping, transformation, and routing. The role of integration flows in the SAP CPI architecture to enable the creation of complex integrations between different systems and applications without the need for custom coding or development.
Integration flows allow developers to build integrations quickly and efficiently, using pre-built templates and a simple, drag-and-drop interface. This helps to reduce the time and cost of building integrations while also improving the reliability and scalability of the integration architecture. Overall, integration flows are a critical component of the SAP CPI architecture, providing the foundation for building robust, scalable, and flexible integrations between systems and applications
2. Cloud Connectors:
Cloud connectors enable connectivity between SAP CPI and on-premise systems. They provide a secure and reliable way to access data and services behind the firewall and support a variety of protocols and standards, such as HTTP, HTTPS, SOAP, REST, and OData. Cloud connectors can be deployed on-premise or in the cloud and are managed through the Integration Directory.
Cloud Connectors are a vital component of the SAP CPI architecture, providing a secure and reliable way to connect cloud-based applications with on-premise systems. Cloud Connectors are software agents installed on a local server or network and provide a secure communication channel between SAP CPI and on-premise systems. The Cloud connector acts as a gateway between the SAP CPI cloud platform and an on-premise system, providing a secure communication channel that enables data to be transferred between the two environments.
The Cloud Connector establishes a connection with the SAP CPI platform and uses safe, encrypted communication protocols to transmit data to and from the on-premise system. They can be configured to support a wide range of on-premise systems, including databases, file systems, and other applications. They can also be configured to support a variety of authentication and encryption mechanisms, ensuring that data is transmitted securely and only authorized users are able to access the on-premise system.
- Adapters - Adapters are pre-built connectors that provide out-of-the-box connectivity to a wide range of systems and data sources, such as SAP ERP, Salesforce, Amazon S3, and FTP servers. SAP CPI includes a rich set of adapters that support different protocols and integration scenarios, such as file-based integration, web services integration, and message queuing. Adapters can be configured and managed through the Integration Directory. SAP CPI provides various adapters that enable seamless integration between multiple applications and systems. Each adapter has specific capabilities and supports different protocols. For example, the HTTP adapter can support both REST and SOAP web services, while the SFTP adapter only supports the SSH File Transfer Protocol. The adapters make integrating SAP CPI with various systems and applications more accessible, ensuring that data can be exchanged securely and efficiently. Here is a list of some of the most used adapters –
-
- HTTP - The HTTP adapter enables REST and SOAP web services to communicate.
- SFTP - The SFTP adapter transfers files securely over the SSH File Transfer Protocol.
- JDBC - The JDBC adapter allows connectivity to relational databases such as Oracle, SQL Server, and MySQL.
- FTP(S) - The FTP(S) adapter transfers files over the FTP or FTPS protocols.
- Mail - The Mail adapter enables communication with mail servers to send and receive emails.
- SuccessFactors - The SuccessFactors adapter integrates with SAP SuccessFactors, a cloud-based human resources management system.
- Salesforce - The Salesforce adapter integrates with Salesforce, a cloud-based customer relationship management system.
- Workday - The Workday adapter enables integration with Workday, a cloud-based human capital management system.
- OData - The OData adapter is used for integration with OData services.
- JMS - The JMS adapter allows communication with Java Messaging Service providers.
3. Messaging Infrastructure:
The messaging infrastructure in SAP CPI is used to ensure reliable and secure message exchange between different systems and data sources. It includes message queues, topics, and subscribers and supports different messaging patterns, such as point-to-point and publish-subscribe. Messages can be persisted to ensure data consistency and integrity and monitored and managed through the Integration Directory.
SAP CPI uses a messaging infrastructure to handle data flow between systems and applications. The messaging infrastructure consists of topics, queues, and message persistence. Topics and queues route messages to the appropriate destination in an integration flow. Topics are used for one-to-many message distribution, where a single message is sent to multiple subscribers who are interested in receiving the message. Conversely, Queues are used for one-to-one message distribution, where a message is sent to a single subscriber.
Message persistence is another crucial aspect of the messaging infrastructure. Messages are stored in a persistent store to ensure they are not lost in case of system failures or network interruptions. SAP CPI provides different levels of message persistence, including guaranteed and best-effort persistence. Guaranteed persistence ensures that messages are not lost, while best-effort persistence tries to deliver messages but does not guarantee delivery.
SAP CPI also supports different message formats, including XML, JSON, and plain text. This flexibility allows for seamless integration with various systems and applications. Overall, the messaging infrastructure in SAP CPI plays a crucial role in ensuring that messages are delivered securely, reliably, and efficiently. It allows for the seamless flow of data between different systems and applications, facilitating efficient business processes.
4. Data Mapping and Transformation:
Data mapping and transformation is an essential capability in SAP CPI that enables users to convert data between different formats and structures and to transform data based on specific business rules and requirements. SAP CPI includes a graphical data mapping tool that allows users to define data transformations using a drag-and-drop interface and supports a wide range of data formats, such as XML, JSON, CSV, and EDI.
Data mapping and transformation capabilities are essential for any integration platform, and SAP CPI offers a robust set of tools to accomplish these tasks. In SAP CPI, data mapping and transformation are achieved using a graphical mapping editor, which allows users to define the mapping rules between different data formats and structures. The editor provides a drag-and-drop interface to map the source fields to the target fields, and it supports various mapping functions such as concatenation, arithmetic operations, and data type conversions. Users can also define custom functions and use them in their mapping rules.
SAP CPI supports a wide range of data formats, including XML, JSON, flat files, and EDI. This allows users to integrate different systems and applications regardless of their data formats. Data mapping and transformation are used extensively in integration flows to transform data between different systems and applications. For example, in an order-to-cash process, data may need to be transformed from an XML format used by an e-commerce application to a flat-file design used by an accounting system. The mapping editor in SAP CPI can be used to define the transformation rules, and the integration flow can be configured to execute the transformation as part of the overall process. It is a flexible and powerful toolset to transform data between different formats and structures, enabling seamless integration between other systems and applications.
5. Security:
Security is a critical aspect of SAP CPI architecture and includes several features and capabilities to ensure data privacy, confidentiality, and integrity. It provides transport layer security (TLS) to encrypt data in transit, access control to restrict access to sensitive data and services, and message encryption to ensure data privacy and confidentiality. Security can be configured and managed through the Integration Directory and customized based on specific business requirements and compliance standards.
Security features in SAP CPI ensure that data is protected throughout its journey between systems, and only authorized users have access to it. SAP CPI provides various security features to ensure safe and secure data exchange between systems. Some of the critical security features are –
- Transport Layer Security - SAP CPI supports HTTPS protocol, ensuring secure data transfer by encrypting the data in transit. This ensures that data transmitted between systems is protected against interception and eavesdropping.
- Access Control - SAP CPI allows administrators to control access to the system by defining roles and permissions. Only authorized users can access the system and perform actions based on their assigned roles.
- Message Encryption - SAP CPI supports message encryption using various encryption algorithms such as AES, RSA, and SHA. This ensures that messages transmitted between systems are protected against unauthorized access and interception.
- Identity and Access Management - SAP CPI integrates with various identity and access management systems, such as LDAP, SAML, and OAuth, to provide secure user authentication and authorization.
- Audit Logging - SAP CPI provides audit logging capabilities that allow administrators to track and monitor system activities. This ensures that any unauthorized access or suspicious activities can be identified and addressed.
Key features of SAP CPI architecture
Here is a more detailed explanation of each key feature of SAP CPI architecture.
- Pre-packaged content and integration flow: SAP CPI offers pre-built integration flows and pre-packaged content that can help organizations quickly integrate various systems and applications without having to start from scratch. This saves time and effort in building integrations and ensures best practices are followed.
- Adapters and connectors: SAP CPI support various adapters and connectors that enable communication between systems and applications. These adapters support protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SFTP, SOAP, and OData. Some examples of adapters supported in SAP CPI include JDBC, SFTP, SAP Cloud Platform Identity Authentication, SuccessFactors, and Salesforce.
- Security and Compliance: SAP CPI offers robust security features to ensure data privacy, confidentiality, and compliance. The platform supports various security protocols such as SSL/TLS, OAuth 2.0, and SAML. It also includes role-based access control, message encryption, and auditing capabilities to monitor data access and usage.
- Scalability and flexibility: SAP CPI architecture is designed to be highly scalable and flexible, enabling organizations to handle a large volume of integrations and adapt to changing business needs. The platform can handle large volumes of data and supports horizontal scaling to add more resources as needed. Additionally, it offers various deployment options such as cloud-based, on-premise, and hybrid, providing flexibility to organizations based on their requirements.
- Integration with other SAP products: SAP CPI is fully integrated with other SAP products such as SAP S/4HANA, SAP SuccessFactors, and SAP Ariba, among others. This enables seamless integration between different SAP applications and provides a unified data view across the organization. Additionally, the platform supports integration with third-party systems, allowing the organizations to integrate with external partners and suppliers.
SAP CPI Architecture FAQs
1. What is SAP CPI architecture?
SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) architecture is an integration platform that facilitates the integration of cloud applications with other on-premise or cloud-based applications. The architecture of SAP CPI is designed to simplify the integration process, providing pre-packaged content and integration flows, as well as adapters and connectors to connect with various systems easily.
2. How does SAP CPI work?
SAP CPI is a cloud-based integration platform allowing businesses to connect different systems, applications, and data sources on-premise and in the cloud. SAP CPI provides a central hub for creating, managing, and monitoring system integration flows. These integration flows are created using a visual drag-and-drop interface, allowing users to define the integration's data mapping and transformation, routing, and processing logic.
SAP CPI also includes pre-packaged integration content, such as integration flows, adapters, and connectors, which can be easily configured and customized to meet the specific integration needs of a business. Additionally, SAP CPI provides a range of security features, including transport layer security, access control, and message encryption, to ensure the secure transfer of data between systems.
Once the integration flows are defined, SAP CPI executes them in the cloud using a messaging infrastructure that supports synchronous and asynchronous communication. SAP CPI also provides real-time monitoring and analytics capabilities, allowing users to monitor the performance and status of their integration flows and troubleshoot any issues.
3. Is SAP CPI an ETL?
Yes, SAP Cloud Platform Integration is an ETL (extract, transform, load) tool for data services. It allows you to move data efficiently and securely between on-premise systems and the cloud.
4. What is the SAP CPI module?
SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) is a module of the SAP Cloud Platform that enables businesses to integrate their cloud-based applications with other cloud or on-premise applications. The SAP CPI module provides a range of integration features, including pre-packaged integration content, adapters and connectors for various systems, and tools for data mapping and transformation. It also includes a messaging infrastructure for reliable message delivery, a web-based design interface for easy creation, and integration flow management.
5. Is SAP CPI tough to learn?
No. With proper training and understanding, you can make and excel in your career in SAP CPI.
6. Is SAP CPI difficult?
No. It is not really difficult to learn SAP CPI and make a career out of it.
7. Is SAP CPI a middleware?
Yes. SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) is a middleware. It facilitates the connection between users’ SAP ERP systems and third-party products or services. These can be cloud-based, on-premises, SAP, or non-SAP products. The service allows real-time data exchange between these systems.
8. What is SAP CPI called now?
SAP CPI is now called SAP Event Mesh.
9. Is SAP CPI a SAAS or PaaS?
SAP Integration Suite (SAP CPI) is an integration platform-as-a-service.
10. Why CPI is used in SAP?
Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) used in SAP is a cloud middleware. It facilitates a connection between users’ SAP ERP systems and third-party products or services. These can be cloud-based, on-premises, SAP, or non-SAP products.
Conclusion
SAP’s focus on the Cloud increases by the year. When we glance at the SAP roadmap, it is clear and evident that cloud solutions will prevail. And what is not to like about the Cloud? Less need for infrastructure, minimal maintenance worries, lower costs, and increased accessibility. Overall, the components in SAP CPI architecture provide a powerful and flexible platform for automating business processes and streamlining operations. Move your business processes to the Cloud with SAP CPI; start migrating to a fully cloud-based system for a more sustainable IT landscape.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SAP CPI Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| SAP CPI Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| SAP CPI Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| SAP CPI Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















