- SAP MDG Interview Questions
- SAP PS Interview Questions
- SAP C4C Interview Questions
- SAP ISU Interview Questions
- SAP Analytics Cloud Interview Questions
- SAP CO Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Interview Questions
- SAP VIM Interview Questions
- SAP SCM Interview Questions
- SAP IBP Interview Questions
- SAP RAR Interview Questions
- SAP TM Interview Questions
- SAP CPI Architecture
- What is SAP Transportation Management ?
- What is SAP SCM?
- What is SAP PO - SAP Process Orchestration Architecture
- SAP PO Interview Questions
- What is SAP EDI?
- What is SAP Vistex?
- What is SAP Cloud Platform?
- What is SAP MRP - SAP MRP Tutorial
- What is SAP BTP?
- What is SAP Fieldglass?
- What is SAP C4C?
- What is SAP ISU
- What is SAP Solution Manager?
- SAP Analytics Cloud Tutorial
- SAP HCM Interview Questions
- What is SAP APO?
- SAP CPI Tutorial - A Beginner’s Guide
- What is SAP CAR?
- What is SAP PS - SAP PS Tutorial
- What is SAP IBP?
- What is SAP CPQ
- What Is Sap Netweaver
- What Is SAP BRIM
- What is SAP Master Data Governance (MDG)?
- What is SAP VIM?
- SAP MDG Architecture
- What is SAP MDG
- SAP HCM Tutorial
- SAP MDG Tutorial
- SAP TRM Interview Questions
Developed in 1972 in Germany, SAP(Systems, Applications, & Products in Data Processing) is a robust and famous enterprise resource planning(ERP) tool utilized by corporations worldwide. It has plenty of completely integrated modules covering all business management aspects. These days users are more interested in interaction with a single unified system. SAP handles data in such a way that it can achieve efficiency through extensive modules developed.
The SAP implementation indicates that data handling is complex and implementation nature is also tricky, so there is a requirement for in-depth SAP knowledge and experience. That’s why there is a massive demand for certification in SAP technologies. SAP has now become a highly-paid specialization; thus, we can tell that it is an ambitious area of IT. As the SAP field has become saturated with talent, it is the right time to make a promising career. Thus, we have curated these SAP Interview questions with inline answers. If you are attending the SAP interview anytime soon, reviewing these frequently asked SAP interview questions and answers would be helpful.
Top 10 Frequently Asked SAP Interview Questions
- What are the different modules of SAP?
- Why is SAP used?
- What are the disadvantages of using SAP?
- What are the three phases of Data Mining?
- What is Data Dictionary?
- Differentiate SAP ABAP and SAP BASIS?
- What are the standard phases of SAP Payment Run?
- Explain the Information Model.
- Explain the SAP launchpad.
- What products does SAP provide?
SAP Interview Questions For Freshers
1. Explain Briefly about SAP?
Established in 1972, SAP refers to Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing. SAP is headed by Plattner, Hector, Tschira, Hopp, and Wellenreuther. SAP refers to the name of the organization and product. It is the world's most famous enterprise resource planner with more than 1,40,000 installations and has more than 75,000 active customers spread throughout 120 different countries.
2. Explain ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning is the software or integrated computer-based system that is efficiently utilized by the business to plan and handle daily activities like supply chain, services, financials, manufacturing, and other processes. It assures fluent information flow and handles the workflows of different departments in an enterprise or a company. SAP is one of the first companies to offer world-class ERP solutions and build standard software for business solutions.
3. What are the different kinds of ERP?
Following are the different kinds of ERP:
- Baan
- JD Edwards(bought by Oracle)
- SAP
- Siebel
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Peoplesoft(bought by Oracle)
4. Describe NetWeaver?
NetWeaver is the integrated technology platform that provides an instance called “SAP Web Application Server(SAP WEBAs)” to all the products of mySAP.
5. What are the different modules of SAP?
Following are the different modules of SAP:
- CO(Controlling)
- FI(Financial Accounting)
- TR(treasury)
- EC(Enterprise Controlling)
- HR(Human Resource)
- IM(Investment Management)
- MM(Materials Management)
- PM(Plant Maintenance)
- SD(Sales and Distribution)
- PP(Product Planning)
- PM(Plant Maintenance)
- BW(Business Warehousing)
- QM(Quality Management)
6. Is SAP a Database?
No, SAP is not a database, but it is the application that uses the databases provided by other vendors like SQL Server, Oracle, etc.
7. Explain Master Data, Meta Data, and Transaction Data?
Master Data is critical information that includes employee info, customer data, materials, available, etc. Meta Data is the collection of data about data stored, and it eases the setup using the meta-objects and gives the overview of data structure. Transaction Data is the data that traces everyday transactions.
8. Explain SAP R/3?
SAP R/3, the 3rd generation group of highly integrated software modules, is a flagship product of SAP. The 'R' signifies real-time, while the '3' represents the three-tier application architecture. This enterprise-wide information system is meticulously designed to efficiently coordinate all the information, resources, and activities necessary for seamless business processes such as billing, human resource management, production planning, and order fulfillment. SAP R/3's robust structure encompasses three primary layers:
- Application Layer: It includes single or multiple application servers and a message server. The message server sends the request from one application server to another. Moreover, it stores the application server groups' relevant information and current load balancing.
- Presentation Layer: It includes software elements comprising SAP GUI(Graphical User Interface). This layer is responsible for sending the user's input to the application server and receiving data for displaying.
- Database Layer: It includes the central database system that contains all the data in the R/3 system. SAP has built its own HANA database, which is harmonious with several databases, such as Oracle.
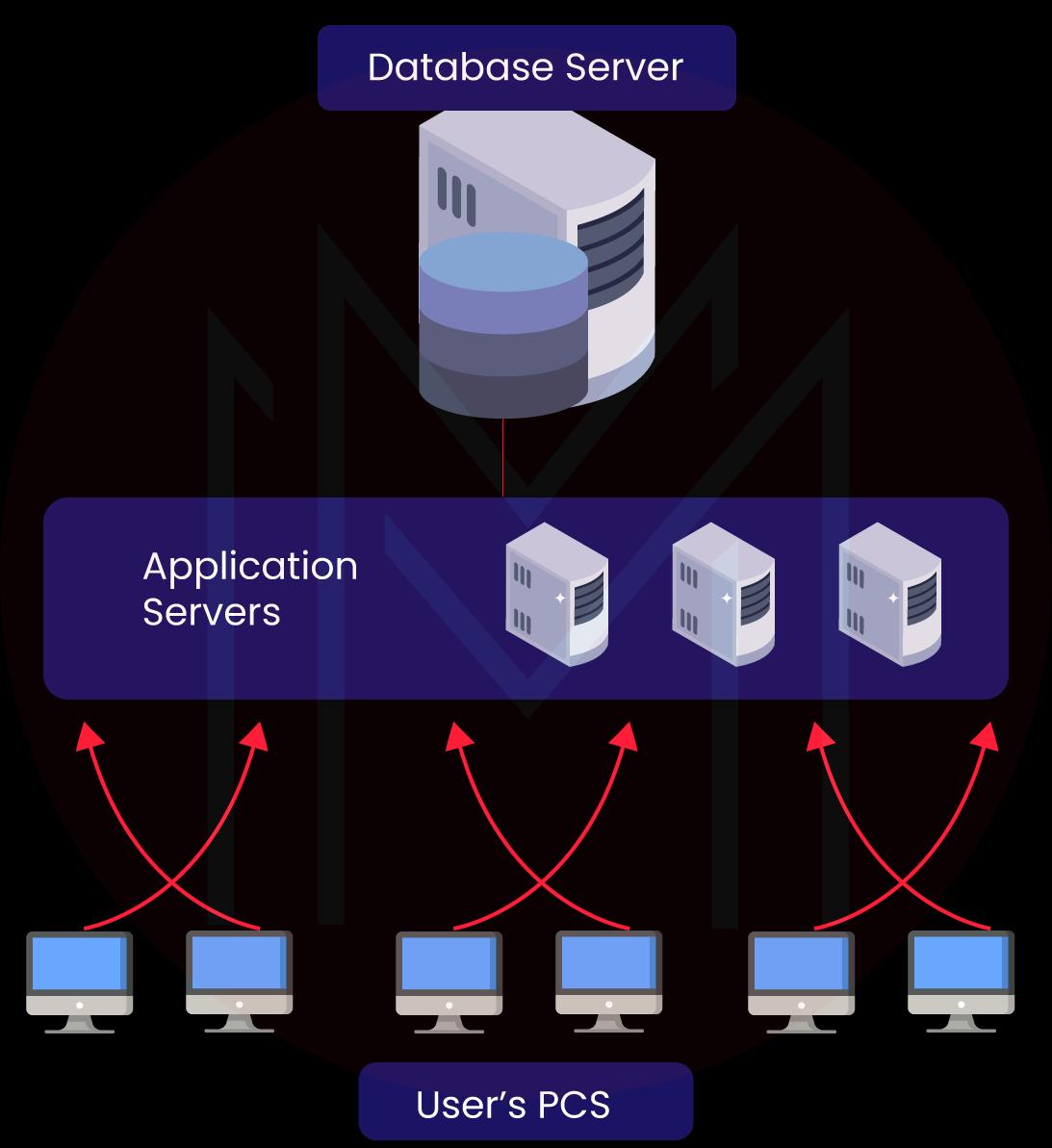
9. Why is SAP used?
- SAP allows companies and organizations of all sizes to run their businesses profitably.
- SAP will also develop solutions that can be useful for mid-sized companies, large corporations, and smaller businesses.
- Moreover, SAP solutions help predict how revenue will be generated in the next half-year when the machine requires repair.
10. How many SAP sessions can run Parallels?
For a specific client, we can run up to 6 sessions simultaneously.
11. What does Transaction mean in SAP Terminology?
The transaction is a series of logically linked dialog steps in the SAP terms, and individuals can learn all the transactions while learning SAP.
12. What is Dataset?
A dataset is a subsequential file processed on the application server and is essential to handle the files in the SAP.
13. What is a Variable?
Variables are a group of parameters that acts as a particular query. They abide by the parameters in the query definition. They will only include value once the corresponding queries are entered into workbooks.
14. What are the disadvantages of using SAP?
Following are some of the disadvantages of using SAP:
- Needed Experienced Employees for handling it
- Expensive Solution
- It takes time to be implemented
- Does not have the ability to discover the location of the master data
- Difficult Interfaces are not simple to understand
15. What are the different kinds of Variables?
The following are the different kinds of Variables:
- Formulas
- Characteristics Variables
- Hierarchies
- Processing Types
- Hierarchy nodes
- Text
- Replacement Path
- Default type/User Entry
16. What is the process for creating the table in the data directory?
To create the table in the data directory, follow the below steps:
- Create domain(field length, data type, range)
- Create tables(SE 11)
- Create data elements(Types and Properties for the data field)
17. What are the three phases of Data Mining?
Three Phases of Data Mining are:
- Initial Exploration
- Model building
- Deployment
18. Explain AWB?
AWB refers to Administrator Workbench. It is a tool used to control, maintain, and monitor all processes linked to data processing and staging in business data warehousing.
19. What is the significance of ODS in BIW?
The ODS object stores the debugged and consolidated transaction data on the document level. It specifies the consolidated dataset from multiple sources. This dataset can be assessed with the Bex query or the Infoset query. The data of the ODS object will be updated with the delta update into the InfoCubes or the other ODS objects.
20. Define ABAP?
The term ABAP refers to Advanced Business Application Programming. It is a high-level programming language developed by the software company SAP SE. Currently, it is ranked together with Java as the programming language for the SAP NetWeaver Application Server, which is part of the SAP NetWeaver platform to build business applications. It is one of the various application-specific languages of the fourth generation and was designed in the 1980s.
22. Can we work with an enterprise warehouse without utilizing SAP R/3?
Even without R/3 installation, an enterprise warehouse can function well. We can link our raw data and other information sources by shifting the structures linked to the industrial warehouse data sources to incoming data files; alternatively, you can use the tools that a third party offers.
23. What are the different tiers in SAP R/3 System?
The following are the three different tiers of SAP R/3 System:
- Database Stack
- Implementation Stack
- Presentation Stack
24. How do we create a table in the data directory?
To create a table in the data directory, you need to follow the below steps:
- Making new domains available
- Building Datasets
- Creating Table Layouts
25. What is Bex?
Bex refers to "Business Explorer." The client can search reports, study the data, run the queries, and read the reports because of various tool features. The queries available in the workbook can be stored in the Bex browser in categories that are suitable for them. It includes the following elements:
- The Bex analyser
- The Bex site
- The Bex Map
26. What are ALE, EDI, RFC, and EDI?
ALE refers to Application Linking Enabling
IDOC stands for Intermediary Documents
RFC refers to Remote Function Call
EDI stands for Electronic Data Interchange
27. What does SAP S/4 HANA contain?
The SAP S/4 HANA ERP software package was developed on SAP HANA, and it gives businesses the capability to make ERP trades and carry out real-world analysis of their enterprise data. S/4 Hana is more user and administrator-friendly than its forebears, making it suitable for difficult problem solutions and parallelly handling massive amounts of data.
Since it can be deployed on-site, in the cloud, or the hybrid environment, SAP insists that its clients move to the cloud deployment model. Enterprises are using SAP S/4 HANA for real-time integration and business operations management like accounting, selling, human resource management, and sourcing.
28. Explain SAP Portal
The SAP EP(Enterprise Portal) gives you web-based accessibility customized to your responsibilities and secure access to all the resources, operations, and products hosted in the SAP infrastructures. To work with it, you require a desktop computer and a web application, and you can work with it as soon as you have authenticated yourself through the portal.
The capability to use several Java Server Pages parallelly is the best benefit of utilizing this platform. Every view can be a website link or JSP section that communicates with the J2EE server, enabling you to handle multiple products on the same page. Moreover, it can also be used with the non-platform-specific softwares. It can also be utilized to handle a broad variety of products, like Microsoft Outlook, etc.
29. How do we make the CMC's online analytical processing(OLAP)?
We can link the BEX query through the BICS Connection, sometimes called the OLAP connection, starting with SAP B.O. 4.0. The OLAP Connection can be created and saved with the help of the information design tool or the central management console. If the connectivity is used only for the Search, Single Cube, or Multi-Provider, it will be conveyed in the base of either the cube or the search term. If it does not happen, a relationship can be established on B.I. A platform that can be utilized for establishing the link to any BEx query.
30. Describe Posting Key
When we put a transaction into the line item, the posting key(two-digit numeric numeric code) is used to identify the type of transactions made. It determines the kinds of accounts, the structure of input screens, and different types of posting. While publishing particular transactions to the general ledger, particular posting keys can assist.
31. Describe MultiProvider and InfoSet
MultiProvider is the logical view that integrates the data from various InfoProviders in the SAP BW. It enables us to analyse the data since it was stored in a single InfoProvider.
InfoSet is the virtual table that integrates data from different InfoProviders in the SAP BW. It enables us to carry out analysis on a data set that the Standard InfoProvider does not provide.
32. Explain the difference between SAP HANA and SAP ECC.
SAP ECC is the conventional ERP system, whereas SAP HANA is the in-memory platform. The SAP HANA platform can carry out quicker data analytics and processing than SAP ECC. The SAP ECC needs optimization for enhancing performance, whereas SAP HANA can manage massive data sets.
SAP Interview Questions For Experienced
33. What is the main difference between transparent tables and pool tables?
The main difference between transparent tables and pool tables is that the transparent table will have a one-to-one relationship with the database tables; on the other hand, pool tables will have a many-to-one relationship with the database tables.
34. What is Data Dictionary?
The ABAP Data Dictionary is used for creating and managing the metadata(data definitions). The APAP Dictionary enables a critical description of all the data utilized in the system without repetitions. Updated or New information is automatically provided for every system component. This assures data consistency, data integrity, and data security.
ABAP Dictionary endorses the definition of the user-defined data elements. table types, and structures. We can create the related objects(views or tables) in the relational database through these data definitions. ABAP Dircetory explains the logical structure of objects which is utilized in application development. These objects display the linkage with the inherent relational database in views or tables. The following diagram gives a graphical representation of the ABAP Dictionary.
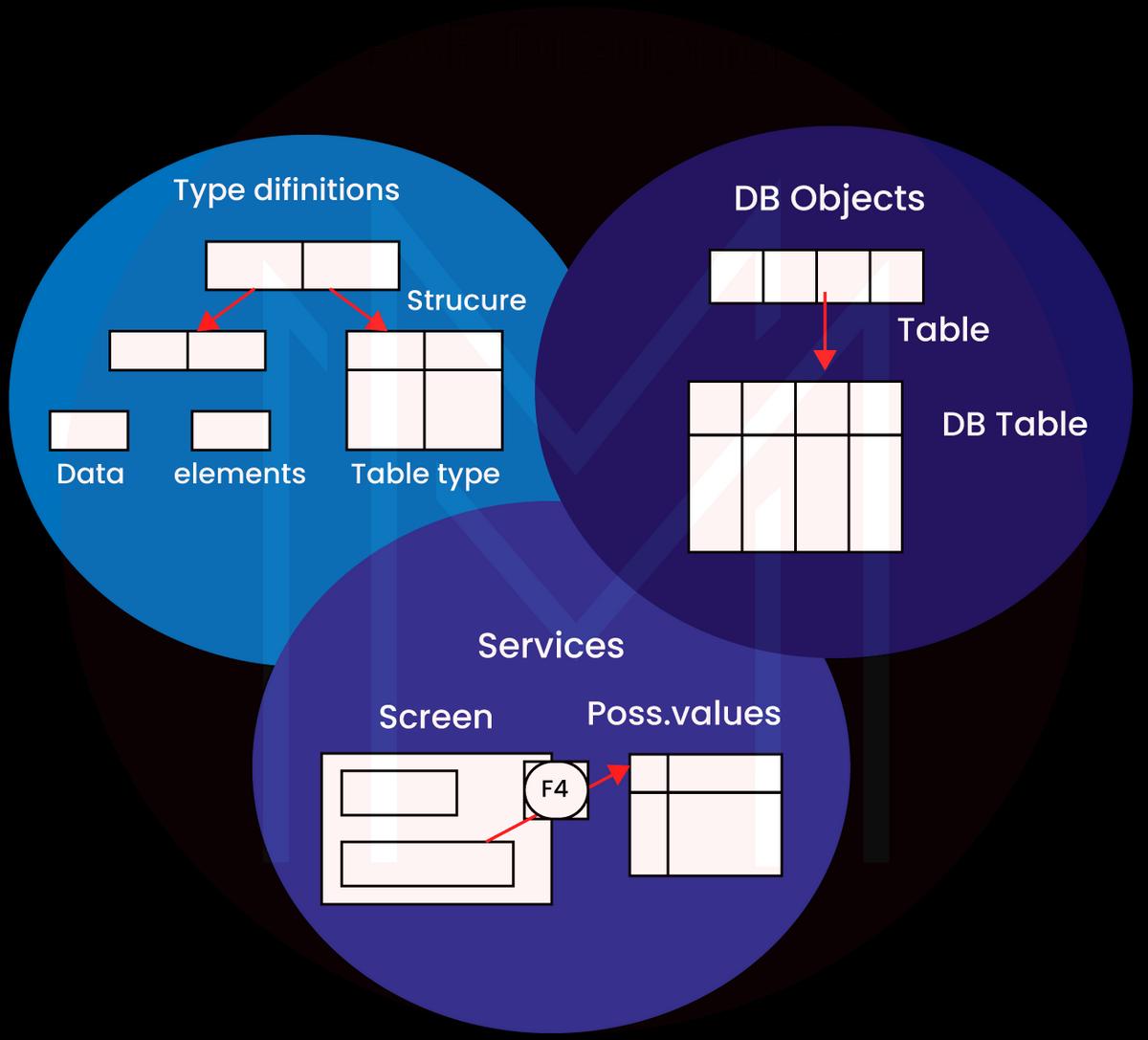
ABAP Dictionary also supports standard functions to edit the fields on the screen, like assigning input help to the screen field.
35. Explain SAP PI/PO?
SAP PI/PO is a tool that allows you to integrate the solutions from the SAP systems into the other SAP systems or Non-SAP systems. SAP PI/PO allows data between several systems to be easily synchronized.
36. What is the difference between Data Mining and OLAP?
| OLAP(Online Analytical Processing) | Data Mining |
| OLAP is the reporting tool utilised to understand the database dimensions, schema, and composition facts. | Data Mining is a helpful analytic process or data analysis for discovering consistent patterns. |
| It is utilized for analyzing the past data. | It is utilized for Future Prediction. |
| It handles detailed transaction-level data. | It handles data summaries. |
| A top-down data analysis approach is utilized, where the insights are retrieved by analyzing the big picture. | A bottom-up analysis approach is utilized to retrieve the insights by analyzing the data. |
37. Differentiate Data Element and Domain?
- Domain: It specifies the attributes like possible value range, type, and length.
- Data Element: It is the intermediary object between table type and domain.
38. What are the important objects of the ABAP Dictionary?
Some of the crucial objects of the ABAP Directory are as follows:
- Tables: Tables are specified independently in the ABAP Dictionary of Database.
- Types: The type structure can be declared globally in ABAP programs. Modifications to the type are activated automatically in every program through the type.
- Views: Views are the rational views of multiple tables. The view structure is specified in ABAP Dictionary. The overlook of the database can be built from this structure.
- Domains: A domain can be integrated with fields having similar technical types. A domain specifies the value range of all the structure modules and table fields that refer to the domain.
- Lock objects: Lock objects are utilized for synchronizing different users' access to the same data.
39. Explain GET parameters and SET parameters.
For using the parameter IDs, we have to “set” values in the global memory area and next “get” values from the parameter ID memory area. In the online program, we have to “Set” the values from the screen fields, and we will “get” these values for the screen fields.
40. Define LUW?
LUW is the time span during which the database records are updated, either rollback or commit.
41. Describe IDOC, ALE, RFC, and EDI?
- IDOC: Intermediary Documents
- ALE: Application Linking Enabling
- RFC: Remote Function Call
- EDI: Electronic Data Interchange
42. Differentiate SAP ABAP and SAP BASIS?
SAP BASIS is the administration module of SAP utilized for controlling code modifications, database admin, upgrades, network setup, etc. In contrast, SAP ABAP is the programming language utilized in SAP for generating forms, customizing, creating reports, etc.
| Related Article: SAP Basis Interview Questions |
43. Describe the Extractor.
In the SAP source system, extracts are the data retrieval mechanism. It can occupy the structure of the data source with the data from the SAP source system datasets.
44. What is the approach for writing the BDC program?
The approach to writing the BDC program is as follows:
Step 1: Create the recording
Step 2: Transform the inherent system data to the flat file into an internal table called “conversion.”
Step 3: Transfer the Flat files into the SAP system known as “SAP Data Transfer.”
Step 4: As per the BDC, type “CREATE SESSIONS” or “CALL TRANSACTION.”
45. What are the two kinds of services that are used for handling communication?
To handle communication, we have two kinds of services:
- Gateway Service: This service enables interaction between external applications and R/3 through CPI-C protocol.
- Message Service: For exchanging short internal messages and this service is utilized by application servers.
46. Explain Pooled and Cluster Tables.
Cluster and Pooled tables are the special kinds of tables in the ABAP Dictionary. We can save the data from many different tables into the table cluster or table pool. Tables allocated to a table cluster or a table pool are implied as cluster tables or pooled tables.
We must use the table pool to store the implicit control information. The control information can be program parameters, screen sequences, continuous texts, and temporary data like documentation. Commercial significance data is saved in the transparent tables.
47. What are the reasons codes are utilized in Account Receivable?
The “Reason Codes” act as the tags that we can allocate to explain over/under payments in allocating incoming customer payments. They must not be mixed up in “void reason codes” utilized when outgoing cheques are generated.
48. What are the main advantages of reporting with BW over R/3?
The business warehouse utilizes a data warehouse and OLAP concepts to analyze and store the data, while R/3 was designed for transaction processing. We can get a similar analysis out of R/3, yet it would be more straightforward from a BW.
49. What are the standard phases of SAP Payment Run?
While implementing SAP Payment Run, the standard phases of SAP contain:
- Entering the Parameters: This includes entering vendor accounts, company codes, payment methods, etc.
- Scheduling the Proposals: The system proposes the list of invoices to be paid.
- Payment Booking: Booking of actual payments into the ledger.
- Printing of the Payment forms: Printing the Payment forms.
50. Explain check tables, value tables, transparent tables, and internal tables.
Internal tables are the standard data type object; they exist only during the program's runtime. Check tables are used for field-level checking. Value tables are used for domain-level checking. A transparent table is available with a similar structure both in the dictionary and the database, with similar data and fields.
51. What are the different kinds of source systems in SAP?
Following are the different kinds of source systems:
- SAP BW
- SAP R/3 source system
- External Systems
- Flat files
52. Describe the Extended Star Schema?
The star schema contains dimension tables and fact tables. The master data-related tables are stored in separate tables, referring to characteristics in the dimension tables. These separate tables for the master data are called Extended Star Schema.
53. What is BAPI in SAP?
In SAP, BAPI refers to Business Application Programming Interface. It is the standardised interface that integrates SAP applications with third-party applications. It enables the developers to use the SAP system's business data and functionalities, making it simple to build custom applications.
54. What is SAP HANA?
SAP HANA is an in-memory and high-performance database that can process vast amounts of data in the real world. It allows organisations to carry out real-time processing and analytics, making it simple to gain insights into the business operations.
55. What is the difference between the ALV List and the ALV Grid?
ALV List displays the data in a list, whereas ALV Grid displays the data in a grid format. ALV Grid is a modern version of ALV List, and it includes advanced features like grouping, sorting, and filtering.
56. What key factors must be examined while planning the SAP Data Migration?
While planning the SAP Data Migration, we must consider the following factors:
- Data Cleansing and Quality: Identifying and Resolving the Data Quality issues, like incomplete or duplicate records.
- Data Mapping and Conversion: Ensuring the accurate conversion and Mapping of the legacy system data to SAP structure/
- Data Performance and Volume: Evaluating the data volume to be migrated and maximizing the migration process for effective performance.
- Data Reconciliation and Validation: Checking the Migrated data against the source system for completeness and accuracy.
- Data Security: Applying proper security measures for protecting critical data during the migration.
57. Explain the steps to migrate the SAP HR data to the new systems.
- Step1: Analyzing the legacy HR Data structure and mapping it to the intent SAP HR structure
- Step2: Retrieving the related H.R. data from the inherited systems, assuring its integrity.
- Step3: Converting and Transforming the retrieved data into the format compatible with the intent SAP HR System.
- Step4: Loading transformed data into SAP HR system through the proper migration methods or tools.
- Step5: Enriching and Cleansing data, resolving the data quality gaps or issues
- Step6: Checking the Completeness and Accuracy of the migrated data using the validation reconciliations and checks
- Step7: Performing extensive testing and validation to ensure appropriate functionality and attachment to the business rules.
58. How do we minimize the impact of the data migration on end-users?
To minimize the impact of data migration on end users, we have to follow the following steps:
- Carry out user training and give clear interaction about the migration process, like its benefits and any modifications they can experience.
- Engage the end-users and key stakeholders in the decision-making and migration planning processes to handle their concerns and ensure their buy-in.
- Set up a strong user support system, like training materials, dedicated helpdesk, and user guides, to help users during and after the migration.
- Extensive testing and validation of the migrated data will be performed to reduce disruptions and ensure that the SAP environment coordinates with the end user's expectations.
59. How do we ensure security authorization is adequately implemented in the SAP solutions?
To ensure that the security authorization is properly implemented in the SAP solutions, we should follow the below approaches:
- Performing risk evaluations and applying proper security controls as per the latest industry requirements.
- Collaborating with the security teams for understanding the compliance standards and security requirements.
- Conducting the regular security assessments and audits for identifying the vulnerabilities and implementing the required remediation measures.
- Defining the user permissions, roles, and segregation of duties rules aligned with the enterprises' security policies.
60. What are Metadata, Master Data, and Transaction Data?
Master Data: Masterdata includes whatever the organization does and how it is differently specified over business competitors or units. It allows us to establish a 360-degree business view.
Metadata: Metadata depicts data about Data. It offers information about the data structure and database table objects. For instance, the ABAP Dictionary will provide information about the data available in the RDBMS.
Transaction Data: Transaction data contains data associated with the regular transactions. For instance, the production details associated with the materials, daily transactions, etc.
61. Describe Matchcode W.
Matchcode W is the SAP HR feature that allows us to search for employee records through different criteria. The criteria contain several employee-specific and general options, like the employee's address, name, personnel area, personnel number, and organizational unit. It is a robust tool that helps you rapidly utilize the employee records required to complete their jobs.
SAP Interview Questions For Advanced Level
62. What is the difference between “Partial Payment” and “Residual Payment?”
- Partial Payment
For example, if invoice A341 is issued for $300, and the buyer pays $250. After subtracting the partial amount from the invoice, a balance of $50 is left.
- Residual Payment
While the customer receives the residual payments, invoice number A341 is paid completely, clearing the method for creating a new financial statement that makes up the outstanding amount of $50.
63. Describe one-time vendors?
We can only create new records for some vendor trading partners in some industries. One-time vendor allows the dummy vendor code to be utilized on the invoice entry, and the data generally stored in the vendor master is stapled on the invoice itself.
64. What are the most common transit mistakes?
The most common transit mistakes are as follows:
- Return code 8: Errors in import processes like glossary activation, program syntax, program creation, etc.
- Return code 4: Columns or Rows are missing from the data while it is imported, and warnings are transmitted.
- Return code 18: Because of the expired system or user downtime and limited roles or authorization, it indicates the import has been stopped.
- Return code 12: It implies that the import was interrupted because of the absence of the item, the static object, or anything the same.
65. Define transactional RFC?
Transactional RFC, also called Transactional Remote Function Call, allows fetching the formerly made request if it was mistakenly entered into the system. This happens when the transaction process, called TID, has been allocated a unique identifier. Accessing the remote system is optional at the moment in the transactional RFC.
66. What are the advantages of SQL Script?
SQL Scripts are the most suitable approach to work as they can be loaded and stored anytime it is required to do so.
- No directions are typed manually, so there is no space for human errors in the process. This helps to reduce the overall error rate.
- We can execute the SQL script at a time that is more suitable for us or when there is no one around to do it.
- A local variable can be defined in the SQL Script for saving intermediate results.
- Table types that can be utilized as the arguments in the SQL statement may be defined globally or locally.
67. Explain the Information Model?
The information model contains Attribute, Calculation, and Analytic views, and it is primarily utilized to hide the data selection technicalities such that it is easy for business users to model the data who have only functional knowledge of the database and don’t have technical knowledge.
68. Explain Code pushdown?
Code pushdown is transferring the data-intense applications to the database layer. Every calculation cannot be pushed into the database, only the needed calculations can be pushed. For instance, if we want to calculate the number of positions of invoices, it is not necessary to choose all the positions of those invoices and calculate the sum through a loop.
69. Explain the SAP launchpad?
The SAP launchpad simplifies accessing the corporate solution that offers the launchpad site that is personalized and based on the user's activity. This service allows organizations to develop the centralized location for third-party services, SAP, custom-made apps, and other services in the cloud and on-premises. Some of the capabilities of the SAP launchpad are as follows:
- A User Experience that is Interesting and Easy to Use
Besides providing a role-based and customized launchpad, it also offers a data structure that adheres to and is adaptable to SAP Fiori 3 design criteria.
- Adaptability
It is considered the scalable foundation for the modifications that can be achieved using personalized branding and shell extensions.
- Integration of the Applications
It provides a centralized entry point for the tasks and apps, with infinite integration to different user interface methods and third-party software programs.
- Integration Services
Integration with the essential services of SAP BTP, like cloud identity and email services, is a feature of the product.
70. How can stock transfer between two plants be distinguished that relates to the same company code and that of a different company code?
Stock transfer between the plants of different company codes is similar to the purchase order in Stock Transfer Order. The first case is intra-company stock transfer, and the second is inter-company stock transfer. The inventory movement without pricing is included in the stock transfer between the same company code plants. Inventory accounts transfer is included in this.
71. What is Legacy System Migration Workbench? In SAP SD, how can it be performed?
Using EDI LSMW is utilized. The SAP System is linked to the Non SAP systems through the EDI programmers. During this, Data migration is required. The destination code differs from the source code while the data migrates from source to destination. Thus LSMW allows us to transform the data into batch files; next, the batch files are transformed into the batch files of source code, and later data is migrated. During this process, standard interfaces like Idoc or BAPI are utilized.
72. What fields are available in purchasing view?
The following fields are available in purchasing view:
- Requisition for the purchase
- Quotation/RFQ
- Outline agreements
- Order for purchase
- Master data(Source list, Info record, Vendors, Conditions, etc.)
73. In SAP MM, How the Price determination process works?
Price determination process: A schema will be created. A condition type is inserted if required, and the Access sequence is allocated to the condition type. A condition table is made, and the fields needed are defined. A cond. Rec is created. The price schema has the condition type for a specific mat. The price determination process is invoked by pricing. To the condition type, the access sequence is allocated, which searches the condition type for determining the price and finding a specific cond. rec.
| Related Article: SAP MM Tutorial |
74. How do we configure manual bank statements?
An electronic bank statement configuration is needed, but not a manual bank statement. Type the data and save it in the manual bank statement.
75. How exclusion and listing are used in real-time?
In the pharma and chemical industries, exclusion and listing are utilized; for example, a particular customer is ordering medicines or chemicals despite not having a valid license. Exclusion and Listing are helpful in this situation.
76. What products does SAP provide?
SAP provides the following products:
- SuccessFactors
It is a cloud-based human resources management system that eases handling different HR tasks. The SaaS paradigm offers a foundation for the SuccessFactors platform.
- Ariba
It is a unique approach hosted in the cloud, allowing sellers and customers to interact with one another for conducting business on the unified platform. It streamlined the business operations, which resulted in enhancement in the organization’s complete system to handle the vendors. These enhancements will lead to cost savings for the firm.
- Fiori
It is a new user interface that has been implemented throughout all the SAP software packages. It includes the collection of the programs that are used in general company operations. These applications include process authorization programs, financial applications, computation systems, information processing software, and self-service implementations.
- Concur
Using Concur, we can refer to all your spending on expenditures, transport, and the seller bank statements in the unified system. This can be achieved by providing a technique for collecting more excellent transaction permeability, handling spending from inception to delivery, simplifying processes, and promoting compliance for everyone.
- Fieldglass
It is hosted in the cloud and comes along with the open VMS, both of which help businesses in finding, manage, engage, and pay vendors. Through the SAP Cloud Platform Interface, web applications, or SAP Process Management, SAP Fieldglass can integrate into the free capacity and on-site SAP applications.
77. Describe “Business Content” in SAP?
In SAP, Business Content is a pre-defined or pre-configured model of the information included in the SAP warehouse, which can be utilized directly or with the required modification in the different industries.
78. Describe .sca files?
.sca refers to the SAP component archive. It is used for deploying the patches, java components, and other java deployments in the form of .sda, .sca, .jar, and .war.
79. What is the update type referencing the match code ID?
If the data is the base table of the match code ID modifications, the match code data has to be upgraded. The updated type requires when the match code has to be updated and how it has to be performed. The update type specifies which method will be utilized for the building match codes.
80. What are the differences between Native SQL and Open SQL?
| Native SQL | Open SQL |
| It contains database-specific SQL statements. | It includes Cross-database SQL statements. |
| It can be utilized on the database tables that are administrated by the ABAP dictionary. | It can work only on the tables that were built into the ABAP dictionary. |
| It does not endorse the buffering of the tables in the SAP Application Server. | It supports buffering of the tables in the SAP Application server. |
| It does not endorse the conjunction with the ABAP constructions that ease or accelerate the access | It will support conjunction with the ABAP constructions that ease or quicken the access. |
81. What are the differences between SAP and Salesforce?
| SAP | Salesforce |
| SAP CRM is the most famous ERP software that provides tools that can be utilized by enterprises in an extensive range of industries and enables users to choose the needed functions. | Salesforce provides an extensive Customer Relationship Management(CRM) tool with all the features covered in one plan and offers software solutions and products to users and developers. |
| SAP utilizes the cloud-oriented deployment model and supports on-site deployment. | Salesforce utilizes the Cloud-Oriented deployment model and does not support on-site deployment. |
| Any further changes are optional for SAP; we have to pay for the intuitive licenses annually for maintenance and support. | To use the Salesforce CRM features, an extra amount has to be paid. |
| In SAP, users should buy the online training module and certification |
Salesforce offers a “Get Started” guide to customers, which includes a subscription price. The user has to buy customized training or different directions. |
82. Explain SAP HRIS(Human Resource Information System)
SAP HRIS is an extensive and integrated human resources management system developed to simplify and streamline data handling. It is a flexible and strong tool that allows enterprises to automate several H.R. processes like payroll, performance appraisal, etc. With the SAP HRIS, enterprises can handle employee records like demographics, skills, and employment history more effectively.
83. How are you updated with the latest SAP trends and technologies?
To get updated with the latest SAP trends and technologies, we must follow the below approaches:
- Connecting with SAP community forums, social media groups, and blogs to stay connected with industry peers and experts.
- Engaging in the SAP certification programs for validating your knowledge and skills in particular SAP technologies and modules.
- Attending the SAP conferences, training sessions, and webinars for learning about the latest technologies, best practices, and product updates.
- Participating in the SAP certification programs for validating your knowledge and skills, particularly SAP technologies and modules.
84. What is BDC?(Batch Data Communication)?
Batch Data Communication(BDC) is utilized for data transfer from Non-SAP to SAP R/3 system. Massive amounts of data can be added to the database of SAP tables rather than the manual entry of data. We utilize SHDB transactions for the cursor movement and recording.
85. Describe SAP Services.
Following are some of the SAP Services:
- SAP Application Management Services: It contains application development, integration, implementation, help desk services, maintenance and support, and backup and recovery.
- SAP S/4 Implementation Services: It enables enterprises to fulfil the digital economy-relevant objects.
- SAP Platform Modernization: The advanced approach will transform SAP into a dynamic and agile company that is suitable for regularly modifying the market requirements and conditions of customers.
- SAP Technology Platform & Infrastructure Services: These services will assure you that your ERP platforms are solid and secure, whether the available SAP platform or part of the S/4 HANA or cloud implementation/migration.
- SAP S/4 HANA Migration and Transition Services: Incorporated business strategies and planning of the digital transition for the S/4 HANA migrations will be offered. We intend to migrate useful features while deploying the technology that supports the present and future requirements of the enterprise.
86. Explain AWB
AWB is the tool used to maintain, control, and monitor every process connected with data staging and processing in SAP business information warehousing. Moreover, it can also be used for creating, customizing, and modifying all kinds of metadata objects in the enterprise warehouse. The following are the critical functions of AWB:
- Monitoring
- Modeling
- Transport Connection
- Reporting Agent
- Document
- Translation
- Metadata Repository
- Business Content
SAP FAQs
1. What are the basic interview questions in SAP?
Following are some basic interview questions in SAP:
- What is SAP?
- Define NetWeaver.
- What are the different modules in SAP?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of SAP
- What are the different products offered by SAP?
- What are the different layers in the R/3 system?
2. How to prepare for SAP Interview?
The market for talent is getting more competitive, considering that SAP-based employment perspectives offer attractive perks and more excellent compensation to those with the needed technical expertise. Following are some things that you must consider while preparing for the SAP interview:
- Research the Job and organization.
- Try to get a projected format for the interview
- Prepare the most frequently asked and behavioral interview questions
- Before going to the interview, please go through your resume.
- Complete the interview on a solid note.
3. What is SAP's basic knowledge?
A person is said to have basic SAP knowledge if he or she has an understanding of working with any of the SAP modules like SAP Basis, SAP HANA, SAP ABAP, SAP FI, SAP HANA, etc.
4. Why choose SAP interview questions?
Everyone who is going to take an SAP interview must go through SAP interview questions to know what kind of questions they can face in the interview and assess their understanding of SAP modules.
5. What is the full form of SAP?
The full form of SAP is Systems, Applications, & Products in Data Processing.
6. What is the main purpose of SAP?
The main purpose of SAP is to allow organizations and companies of all sizes to adapt continuously, run their businesses profitably, and develop sustainably.
7. What is SAP in simple words?
SAP is one of the dominant software producers for handling business processes and building solutions that give efficient data processing and data flow throughout enterprises.
8. How many types of SAP are there?
There are no types of SAP. SAP is an application software that is based on Enterprise Resource Planning(ERP); in simple words, it is the software where we can maintain any business.
9. What are the SAP skills?
SAP skills are the capability to utilize the SAP software suite to solve business problems. A suite is a group of integrated applications that enable organizations to handle their business processes. Some of the SAP skills are:
- Handling hybrid and public multi-clouds
- Management and Integration of SAP SaaS solutions
- Basis Automation
- Orchestration Automation
- AIOps
- Containerization and Kubernetes
10. What are the two main modules of SAP?
Following are the two main modules of SAP
- SAP Financial Accounting
- SAP Sales and Distribution
SAP Interview Preparation Tips
Tip #1: Research
This is the first tip for SAP interview preparation. You must focus your research on three points. First is the job. Understand the job description, project specification, required qualifications, future prospects, and work environment. This will help you understand whether it is the proper job for you and the areas you must concentrate your preparation on.
Tip #2: Revise Your Resume
It is better to build a new resume, especially for the job you are applying for. Make sure that your resume focuses on experiences and skills that are relevant to the job.
Tip #3: Prepare for the Expected Questions
You can easily find various SAP interview QUestions online. Create a list of those questions. The questions must be of personal, technical, and behavioral types:
- Personal Questions: The objective of the personal questions is to test your dedication, willingness, and interest to take the job.
- Technical Questions: The objective of technical questions is to test your technical skill and knowledge.
- Behavioral Questions: Behavioral Questions are about your past work experience.
Tip #4: Prepare Notes
Prepare notes about the essential points that you would like to memorize. These notes will help you refresh your mind before attending the interview and assist you in future interview preparation.
Tip #5: Attire
Dress adeptly and think corporate. If you need more clarification about attire, discover how the people in the organization generally dress and take tips from them.
Conclusion
To crack any technical interview, theory, practical, project, and applied concepts are necessary for those applying for the job. This SAP interview questions blog covered all the frequently asked SAP interview questions and answers that suit the interview requirements. A candidate who wants to achieve the job in SAP must look through these SAP interview questions and answers before going to the SAP interview to give his best.
Explore SAP Sample Resumes! Download & Edit, Get Noticed by Top Employers!
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| SIEBEL CRM Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| SIEBEL CRM Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |
| SIEBEL CRM Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| SIEBEL CRM Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .






