- Abstraction in Java
- Clojure Tutorial
- Control Statements in Java
- Core Java Interview Questions
- Data Types in java
- Top 9 Java EE Frameworks
- Java EE vs Spring Framework
- Java Frameworks List - Top 14 Java Frameworks
- Java Interview Questions
- Java Tutorial
- Java Web Dynpro Interview Questions
- JavaFX Interview Questions
- Method Overloading in Java
- Multithreading in Java
- List of Popular Open Source Java Build tools
- Operators in Java
- Program Logics in Java
- String Handling in Java
- Why You Should Learn Java Programming
- Data Structures Interview Questions
- Exception Handling in Java
- Multithreading Interview Questions
- Design Patterns Interview Questions and Answers
- JSP Interview Questions
- EJB Interview Questions
- SOAP in Web Services
- JPA Interview Questions
- DXC Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Architect Interview Questions
- Java Concurrency Interview Questions
- What is Java Concurrency?
- What is JPA - Complete Tutorial Guide
- What is EJB?
- Java Collections Interview Questions
- Java Swing Tutorial
- Java Stream Tutorial
- Linked List Interview Questions
- Compiler Design Interview Questions
- Java Collection Tutorial
- Java Stream Interview Questions
- Thymeleaf vs JSP
- Thymeleaf Tutorial - What is Thymeleaf
- Socket Programming in Java - What is TCP
- Apache Tomcat Interview Questions
- Capgemini Interview Questions
- Zoho Interview Questions
- PwC Interview Questions
- Hexaware Interview Questions
- Intuit Interview Questions
- Tech Mahindra Interview Questions
- Qualcomm Interview Questions
- Arcesium Interview Questions
- PayTM Interview Questions
- DXC Technology Interview Questions
- Java Developer Job Description
- MAQ Software Interview Questions
- Amdocs Interview Questions
- TCS NQT Interview Questions
- Virtusa Interview Questions
- Siemens Interview Questions
- Tricky Java Interview Questions
C++ has been popular since the mid-1980s. It is the fourth most used programming language in the world, accounting for approximately 7.5 percent of the index. As a result, for a number of professions, a strong understanding of C++ is necessary. If you want to work in software development, you must be familiar with C++. It is in high demand due to its dependability, performance, and efficiency. So, now that you understand the significance of C++, this blog will address the most often-asked interview questions in C++ to help you ace the interview and land a well-paying job.
We have categorized CPP Interview Questions into 3 levels they are:
- C++ Interview Questions for Freshers
- C++ Interview Questions for Advanced
- C++ Interview Questions for Experienced
C++ Interview Questions and Answers For Freshers
If you're applying for a Fresher role, you need to become familiar with these basic CPP Interview Questions first.
1. What is C++?
C++, an object-oriented programming language was designed by Bjarne Stroustrup, in 1985, it was released. C++ is a superset of C, with the exception of classes, which are present in C. Stroustrup dubbed the new language "C with Classes" at first. After a while, though, the name was changed to C++. C++ was inspired by the C increment operator ++.
2. What is a class?
The class is a data type that has been defined by the user. The term class is used to declare the class. The data members and member functions are contained in the class, and their access is controlled by the three modifiers: private, public, and protected. The type definition of the category of objects is defined by the class. It defines a datatype, but not the data itself; rather, it determines the data's structure.
If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in Core Java, then enroll in "Core Java Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain.
3. What are the advantages of C++?
C++ not only maintains all features of the C language but also improves virtual memory and introduces a myriad of benefits, such as:
- C++ is a highly versatile programming language, which indicates that software written in it can run on almost any platform.
- Classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction are all elements of C++, which is an object-oriented programming language.
- Inheritance is a principle in C++. With inheritance, redundant code can be eliminated and preexisting classes can be retained.
- Data hiding aids the programmer in implementing security applications that are not susceptible to hackers.
- Message passing is a connectivity methodology that enables objects to interact with one another.
- C++ has a vast library of functions.
4. Define tokens in C++
A token is the smallest element of a programme that the compiler can understand. Tokens are categorised as follows:
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- Constants
- Strings
- Special Symbols
- Operators
5. What are the different data types present in C++?
There are 4 Data types present in C++, they are
- Primitive Datatype(basic datatype). Example- char, short, int, float, long, double, bool, etc.
- Derived datatype. Example- array, pointer, etc.
- Enumeration. Example- enum
- User-defined data types. Example- structure, class, etc
| Check out the Related Article Data Types in Java |
6. What is Data binding and Abstraction?
Data Binding: Data binding is the method of constructing a link between both the application's user interface and the information it shows. If the binding has the correct parameters and the information provides the appropriate notification, whenever the data has changed its value, the components that are connected to it instantly adapt to the change.
Data Abstraction: Data abstraction is a process of reducing an enormous amount of information to a simple representation of the whole. Abstraction is the process of diminishing something to a set of basic characteristics by eliminating or subtracting characteristics.
7. What is the difference between C and C++?
| C | C++ |
| C is a procedure-oriented programming language. | C++ is an object-oriented programming language. |
| C does not support Data hiding. | Encapsulation hides data to guarantee that data structures and operators are used correctly. |
| C is a subset of C++. | C++ is a superset of C. |
| Overloading of functions and operators is not possible in C. | Overloading of functions and operators is possible in C++. |
| In C, there are no namespace characteristics. | C++ makes use of a namespace to avoid name clashes. |
8. What is the object in C++?
A class's instance is an object. Because a class is a user-defined data type, it's possible to refer to an object as a variable of that data type.
9. How can you specify a class in C++?
In C++, you can specify a class by using the term class followed by an identifier (class name). The body of the class is defined inside curly brackets. It comes to an end with a semi-colon.
For example,
class name{
// some data
// some functions
};
10. What are the different types of Operators in C++?
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Other Operators
11. Explain what are the characteristics of Class Members in C++?
- In C++, data and functions are members.
- Data members and methods must always be defined within the class declaration.
- A member cannot be re-declared within a class.
- No other members can be added outside of the class specification.
12. Discuss the difference between prefix and postfix.
In computing, there are two notations: prefix and postfix. The distinction between prefix and postfix notation is that the prefix writes the operator before the operands, whereas the postfix writes the operator after the operands.
[Related Article: Qualcomm Interview Questions]
13. What is the difference between equal to (==) and assignment operator(=)?
Equal to (==)
The '==' operator determines whether or not the two operands are equal. If this is the case, it returns true. Otherwise, false is returned.
For example,
5==5
This will return true.
Assignment operator(=)
The assignment operator "=" assign the right-hand value to the left-hand variable.
For example,
a = 10;
b = 20;
ch = 'y';
14. What is the difference between struct and class?
| Structure | Class |
| By default, the structure's members are open to the public. | By default, members of the class are private. |
| When creating a struct from a class/struct, the underlying class/default struct's access specifiers are public. | Default access specifiers are private when deriving a class. |
|
Declaration of a structure: struct structure_name |
Declaration of class: class class_name |
15. What is polymorphism in C++?
Polymorphism is defined as the presence of several forms. Its function depends greatly upon the circumstances. While we have several classes which are connected to each other through inheritance, this happens. Consider a base class named car, which has a method called car brand (). Mercedes, BMW, and Audi are examples of derived automobile classes, and each has its own implementation of a car.
Polymorphism has two types,
- Compile Time Polymorphism.
- Runtime Polymorphism.
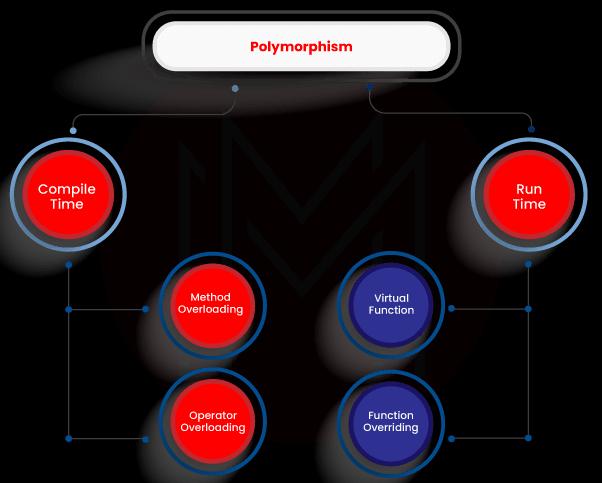
16. What is operator overloading?
Operator overloading is a necessary component for performing operations on user-defined data types. We can change the default meaning of operators like +, -, *, /, =, and so on by overloading them.
For example, Using operator overloading, the following code adds two complex numbers:
class complex{
private:
float r, i;
public:
complex(float r, float i){
this->r=r;
this->i=i;
}
complex(){}
void displaydata(){
cout<<”real part = “<<r<<endl;
cout<<”imaginary part = “<<i<<endl;
}
complex operator+(complex c){
return complex(r+c.r, i+c.i);
}
};
int main(){
complex a(2,3);
complex b(3,4);
complex c=a+b;
c.displaydata();
return 0;
}
17. What is the difference between a reference and a pointer?
| Reference | Pointer |
| Reference is a temporary variable that acts as an alias for an existing variable. | A pointer is a variable that stores a variable's address. |
| To retrieve the value of a reference variable, no indirection operator is required. The value of a reference variable can be accessed directly. | To get to the value of a pointer variable, you'll need to use an indirection operator. |
| The reference variable cannot be reassigned with various address values once it has been assigned. | Because the pointer variable is an independent variable, it can be renamed to point to various objects. |
| The reference variable cannot have a null value applied to it. | The reference variable can be given a null value. |
| At the moment of declaration, the variable must be initialized. | The variable does not need to be initialized at the moment of declaration. |
18. What are access modifiers?
C++ has three access modifiers: public, private, and protected. Data hiding is one of the most important characteristics of object-oriented programming languages like C++. Data hiding refers to limiting access to a class's data members.
| Check out Core Java Interview Questions and Answers that help you grab high-paying jobs. |
19. Define the basic type of the variable used for a different condition in C++
In C++, a variable is used for a variety of circumstances.
- Bool: Stores boolean values in a variable (true or false)
- char: Character kinds are stored
- int: variable with integral values
- float and double: Variables with large and floating-point values.
20. Explain what is the use of void main () in C++ language?
The void main() specifies that the function will not return any value, whereas the int main() specifies that the function can return data of the integer type. We can utilise the void main when our programme is basic and will not terminate before reaching the last line of code, or when the code is error-free ().
Advanced C++ Interview Questions and Answers
Now it's time to ramp up the difficulty, we've covered the CPP Interview Questions for advanced candidates in the below questions.
21. Explain constructor in C++
When an object is formed, the function Object() { [native code] } is a member function that is called automatically. Constructors have the same name as the class they belong to, so the compiler recognises the member function as a function Object() { [native code] }. Constructors also don't have a return type.
Example:
class A{
private:
int val;
public:
A(int x){ //one argument constructor
val=x;
}
A(){ //zero argument constructor
}
}
int main(){
A a(3);
return 0;
}
22. What are destructors in C++?
When an object is created for the first time, the function Object() { [native code] } is automatically invoked. Similarly, when an object is destroyed, a destructor function is automatically invoked. A destructor is preceded by a tilde and has the same name as the function Object() { [native code] } (which is the same as the class name).
Example:
class A{
private:
int val;
public:
A(int x){
val=x;
}
A(){
}
~A(){ //destructor
}
}
int main(){
A a(3);
return 0;
}
23. What are the various OOPs concepts in C++?
The various OOPs Concepts in C++,
- Object
- Class
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Encapsulation
- Abstraction
24. Define virtual function
- To replace the implementations provided by the base class, a virtual function is utilised. Even if the object in question is accessed via a base pointer rather than a derived pointer, the substitution has always been called when the object in question is of the derived class.
- A virtual function is a member function that is defined by the derived class but is present in the base class.
- When the same function name is used in both the base and derived classes, the base class function is declared with the keyword virtual.
- Whenever a function is declared virtual, C++ determines which function to call at runtime based on the type of object referenced by the base class pointer. By altering the base class pointer to point to distinct objects, we can execute many copies of the virtual functions.
25. What is the purpose of the "delete" operator?
An object's delete operation removes a specified property. If the deletion is successful, it will return true; otherwise, it will return false.
26. What is the difference between delete and delete[]?
Delete [] releases an array of allocated memory that was allocated with new[], whereas delete releases a single chunk of memory that was allocated with new.
27. What is a class template?
A class template specifies how classes are generated based on parameters. Containers are typically implemented using class templates. A class template is created by providing it with a set of types as template parameters.
28. What is call-by value and call-by reference in C++?
Call by value: We transmit a copy of the parameter to the functions when using the call-by-value approach. A new memory is assigned to these duplicated values, and changes to these values do not affect the variable in the main function.
Call by reference: We supply the address of the variable to the call by reference technique, and the address is utilized to retrieve the actual argument used in the function call. As a result, changes to the parameter affect the passing argument.
29. What is an inline function?
If a function is inline, the compiler stores a copy of the function's code at each point where it is called during compile time. One of the most significant advantages of using an inline function is that it avoids the overhead of calling a regular function.
30. Explain how functions are classified in C++?
In C++ functions are classified as
- Return type
- Function Name
- Parameters
- Function body
31. What is a scope resolution operator?
The:: (scope resolution) operator qualifies concealed names so they can be utilized. If an explicit declaration of the same name in a block or class obscures a namespace scope or global scope name, you can use the unary scope operator.
32. What is function overloading?
Multiple functions with the same name can be defined in the same scope in C++. Overloaded functions are what they're termed when they're overloaded. You can provide alternative meanings for a function depending on the kinds and quantity of arguments with overloaded functions.
33. Difference between operator overloading and function overloading?
Operator overloading: Operator overloading is defined as the ability to redefine a standard operator such that it takes on a new meaning when applied to instances of a class.
Function overloading: Function overloading is when a function can have multiple versions. A function's signature varies, indicating that it has a different set of parameters in each iteration.
34. Define 'std'.
STL is derived as Standard Template Library. In C++, the default namespace standard is Std.
35. Compare compile-time polymorphism and Run-time polymorphism
| Compile-time polymorphism | Run-time polymorphism |
| In this function, we'll find out which method will be called at build time. The compiler then resolves the call. | In this function, we learn which method will be invoked during runtime. The compiler does not resolve the call. |
| Because it is known at compile-time, it allows for quick execution. | Because it is known at run time, it delivers slower execution than compile-time polymorphism. |
| Function overloading and operator overloading are used to achieve this. | Virtual functions and pointers can help with this. |
36. What do you know about friend class and friend function?
- A friend class has access to the secret, protected, and public members of other classes it has marked as friends.
- Friend functions, like friend class, can access members who are secret, protected, or public. Friend functions, on the other hand, are not members.
37. What are the characteristics of a friend function?
- The function isn't part of the class to something that is been added as a buddy.
- Because it isn't in the scope of that class, it can't be called using the object.
- It can be used without the object, just like any other function.
- It can't get at the member names simply, so it has to utilize an object name and the dot membership, operator.
- It might be stated in either the private or public sections.
38. Which operations are permitted on pointers?
The operations that can be performed on pointers are as follows:
Incrementing or decrementing a pointer: Increasing the size of a pointer means increasing the size of the data type to which it points.
There are two types of increment pointers:
- Pre-increment pointer: The pre-increment operator increases the operand's value by one, and the expression's value becomes the increased value. If ptr is a pointer, then ++ptr represents a pre-increment pointer.
Let's understand this through an example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
int *ptr;
ptr=&a[0];
cout<<"Value of *ptr is : "<<*ptr<<"\n";
cout<<"Value of *++ptr : "<<*++ptr;
return 0;
}
Output:
Value of *ptr is : 1
Value of *++ptr : 2
- Post-increment pointer: The post-increment operator increases the operand by one, but the value of the expression will be the operand's value before it was increased by one. If ptr is a pointer, then ptr++ represents a post-increment pointer.
Let's understand this through an example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
int *ptr;
ptr=&a[0];
cout<<"Value of *ptr is : "<<*ptr<<"\n";
cout<<"Value of *ptr++ : "<<*ptr++;
return 0;
}
Output:
Value of *ptr is : 1
Value of *ptr++ : 1
Subtracting a pointer from another pointer: The number of elements existing between two members of an array is returned when two pointers pointing to the members of the array are subtracted.
39. What is the difference between an array and a list?
- A list is made up of heterogeneous elements, whereas an array is made up of homogenous components.
- Memory allocation in an array is static and continuous, whereas memory allocation in a list is dynamic and unpredictable.
- Users of Array do not need to keep track of the next memory allocation, whereas users of List must keep track of the next memory allocation location.
40. Discuss the difference between new and malloc
| new | malloc |
| new is an operator | malloc() is a function |
| It calls the constructor | The malloc function doesn’t call the constructor |
| When using new, there is no need to specify memory size () | You have to specify the memory size |
| new operator can be overloaded | malloc() can never be overloaded |
C++ Interview Questions and Answers For Experienced
This section contains questions to help experienced candidates demonstrate their breadth of expertise to the CPP Interviewer.
41. What is an abstract class and when do you use it?
An abstract class is one that has no objects that can be created. As a parent for the derived classes, such a class exists. By including a pure virtual function in a class, we can make it abstract.
42. What is an overflow error?
Whenever a program is provided a number, value, or variable that it cannot manage, an overflow error occurs. This is a common programming mistake, collaborating with integer or even other numerals.
43. Explain inheritance
The act of creating new classes, known as derived classes, from existing classes is referred to as inheritance. Base classes refer to the pre-existing classes. Derived classes inherit all of the capabilities of the base class, but they can add their own features and enhancements.
Example:
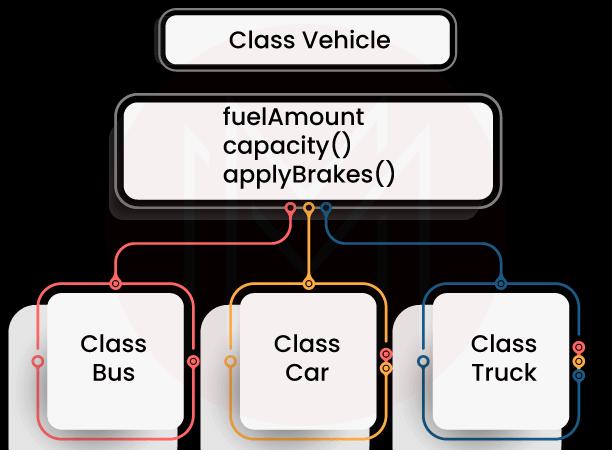
The properties of Class Vehicle are passed down to Class Bus, Class Car, and Class Truck. The most significant aspect of inheritance is that it allows for code reuse.
44. What is overloading?
When a single object behaves in multiple ways, it is called overloading. Even if two objects have the same name, they execute different functions.
C++ allows you to define multiple definitions for the same function name or operator within the same scope. Overloading is a term that refers to the same thing as function overloading.
Overloading is of two types:
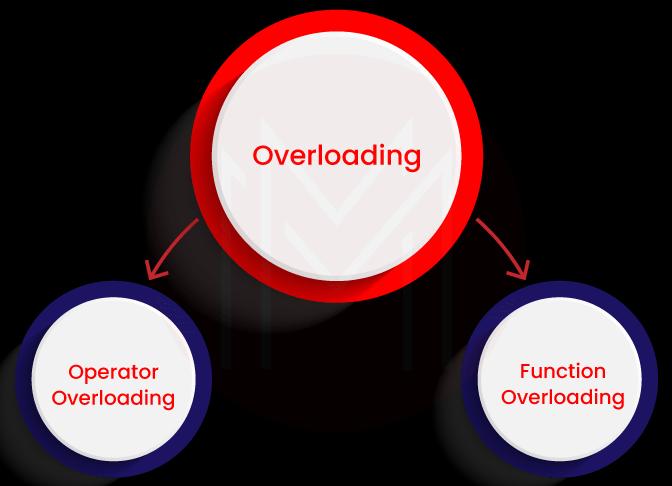
45. What is STL?
The Standard Template Library (STL) is a set of C++ template classes that would provide commonly used programming data structures and operations, such as lists, stacks, and arrays. It's an algorithm, iterator, and container class library.
46. What are the methods of exporting a function from a DLL?
There are two approaches:
- By Using the type library in the DLL.
- By Using the DLL instance to get a reference to the function.
47. Explain what is C++ exceptional handling?
The practice of handling runtime faults in C++ is known as exception handling. We handle exceptions so that the application's usual flow can be preserved even when runtime issues occur. An exception in C++ is a run-time event or object. The std::exception class is where all exceptions are derived.
48. Mention what are the types of Member Functions?
The types of member functions are
- Simple functions
- Static functions
- Const functions
- Inline functions
- Friend functions
49. What is a copy constructor?
A copy constructor is a member function that uses another object from the same class to initialize an object. The general function prototype of a copy constructor is as follows:
ClassName (const ClassName &old_obj);
50. Mention what are the decision-making statements in C++? Explain if statement with an example?
The decision-making statements in C++ are
- if statement
- switch statement
- conditional operator
For example, we want to use C++ to implement an if condition.
#include
int main ( )
{
int, x, y;
X= 10;
Y= 5;
if (x > y)
{
Cout << "x is greater than y";
}
}
51. Explain what is multi-threading in C++?
- Multitasking is the capability that allows your computer to execute two or more programs at the same time. Multithreading is a sophisticated form of multitasking.
- A multithreaded program is made up of two or more components that can run at the same time. A thread is a component of such a program, and each thread defines a distinct execution path.
52. What is the difference between virtual functions and pure virtual functions?
A virtual function is a base class member function which may modify in a derived class. The keyword virtual is used to declare it.
Example:
class base{
public:
virtual void fun(){
}
};
A pure virtual function is one that has no implementation and is declared by setting the value to 0. It doesn't have a body.
Example:
class base{
public:
virtual void fun()=0;
};
The value 0 is not allocated to anything, and the = sign has no bearing on the assignment. Its sole purpose is to inform the compiler that a function will be pure and will not contain anyone.
53. What are void pointers?
A void pointer is a pointer that doesn't have a datatype attached to it. It may store any form of address.
Example:
void *ptr;
char *str;
p=str; // no error
str=p; // error because of type mismatchWe can assign any type of pointer to a void pointer, but we can't do the opposite unless we typecast it as void.
str=(char*) ptr;54. How do you allocate and deallocate memory in C++?
In C++, the new operator is used to allocate memory, whereas the deletes operator is used to deallocate memory.
Example:
int value=new int; //allocates memory for storing 1 integer
delete value; // deallocates memory taken by value
int *arr=new int[10]; //allocates memory for storing 10 int
delete []arr; // deallocates memory occupied by arr55. What is a virtual destructor?
In C++, a virtual destructor is used in the base class to allow the derived class object to be destroyed as well. The tilde operator and the virtual keyword are used before the constructor to declare a virtual destructor.
56. What should be the output of the below code?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=5;
int b=6;
int c;
c=(a>b) ? a : b;
cout<<c;
return 0;
}Output: 6
Explanation: Ternary operator is used, and the value of a is less than b which violates the condition that is why 6 is the answer
57. Define the Local and Global scope of a variable.
Global variables are useful for data that are relatively constant or that must be accessed by multiple functions in the script, such as a session id. A local variable, on the other hand, has a limited scope: it only exists within the block in which it was defined. The variable is destroyed and its values are lost once that block ends.
58. Example program for Overloading Using Different Types of Parameter.
// Program to compute absolute value
// Works for both int and float
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function with float type parameter
float absolute(float var){
if (var < 0.0)
var = -var;
return var;
}
// function with int type parameter
int absolute(int var) {
if (var < 0)
var = -var;
return var;
}
int main() {
// call function with int type parameter
cout << "Absolute value of -5 = " << absolute(-5) << endl;
// call function with float type parameter
cout << "Absolute value of 5.5 = " << absolute(5.5f) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Absolute value of -5 = 5
Absolute value of 5.5 = 5.5
59. Can we call a virtual function from a constructor?
We can use a constructor to call a virtual function. However, in this scenario, the behavior differs slightly. The virtual call is resolved at runtime when a virtual function is invoked. The current class's member function is always invoked. That is, the constructor does not support virtual machines.
Example:
class base{
private:
int value;
public:
base(int x){
value=x;
}
virtual void fun(){
}
}
class derived{
private:
int a;
public:
derived(int x, int y):base(x){
base *b;
b=this;
b->fun(); //calls derived::fun()
}
void fun(){
cout<<”fun inside derived class”<<endl;
}
}
60. Explain what is upcasting in C++?
Upcasting is the process of transforming a derived-class pointer or reference to a base class. To look at it another way, one can consider a derived type as though it were its base type by upcasting it. Public inheritance is always allowed when no explicit typecast is used.
Conclusion
You should have gained an understanding of numerous important CPP topics after reading this blog. We hope you got a sense of output-based questions, programming questions, and conceptual questions.
If u have any queries feel free to ask in the comment box below.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Core Java Training | Feb 21 to Mar 08 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















