- Abstraction in Java
- Clojure Tutorial
- Control Statements in Java
- Core Java Interview Questions
- Data Types in java
- Top 9 Java EE Frameworks
- Java EE vs Spring Framework
- Java Frameworks List - Top 14 Java Frameworks
- Java Tutorial
- Java Web Dynpro Interview Questions
- JavaFX Interview Questions
- Method Overloading in Java
- Multithreading in Java
- List of Popular Open Source Java Build tools
- Operators in Java
- Program Logics in Java
- String Handling in Java
- Why You Should Learn Java Programming
- Data Structures Interview Questions
- Exception Handling in Java
- Multithreading Interview Questions
- Design Patterns Interview Questions and Answers
- C++ Interview Questions and Answers
- JSP Interview Questions
- EJB Interview Questions
- SOAP in Web Services
- JPA Interview Questions
- DXC Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Architect Interview Questions
- Java Concurrency Interview Questions
- What is Java Concurrency?
- What is JPA - Complete Tutorial Guide
- What is EJB?
- Java Collections Interview Questions
- Java Swing Tutorial
- Java Stream Tutorial
- Linked List Interview Questions
- Compiler Design Interview Questions
- Java Collection Tutorial
- Java Stream Interview Questions
- Thymeleaf vs JSP
- Thymeleaf Tutorial - What is Thymeleaf
- Socket Programming in Java - What is TCP
- Apache Tomcat Interview Questions
- Capgemini Interview Questions
- Zoho Interview Questions
- PwC Interview Questions
- Hexaware Interview Questions
- Intuit Interview Questions
- Tech Mahindra Interview Questions
- Qualcomm Interview Questions
- Arcesium Interview Questions
- PayTM Interview Questions
- DXC Technology Interview Questions
- Java Developer Job Description
- MAQ Software Interview Questions
- Amdocs Interview Questions
- TCS NQT Interview Questions
- Virtusa Interview Questions
- Siemens Interview Questions
- Tricky Java Interview Questions
Java has been a popular general-purpose programming language for more than 20 years. It has been a favourite programming language for developers and enterprises because it supports the development of a variety of robust software applications.
According to Oracle, Java runs on more than 60 billion JVMs worldwide. That’s why the demand for Java developers is soaring all the time. Keeping that in mind, I have compiled the top Java interview questions and answers to help Java aspirants crack their Java interviews easily. The interview questions cover crucial Java topics like classes, loops, objects, operators, OOP concepts, control statements, and constructors.
Additionally, I have given many example programs for many questions. It will help you to enhance your hands-on skills and make you job-ready.
Let’s jump in!
| Table of Content - Java Interview Questions |
Skills and Responsibilities of Java Developers
I have curated the various skills required for Java developers in this section. I have also added the job responsibilities of Java developers from entry-level to senior level.
Let’s go through them!
Primary Skills For Java Developers:
Here are the primary skills required for Java developers.
- Proficiency in core Java concepts such as OOP concepts, abstract classes, JSP/servlets, design patterns, and serialisation.
- Exposure to Java EE components such as Java server pages, Java beans, and servlets.
- Familiar with web technologies like JavaScript, HTML, CSS, and JQuery.
- Exposure to web frameworks such as Spring MVC and struts
- Good knowledge of Oracle, MySQL, SQL, DB2, etc.
- Knowledge of web services, web APIs, and RESTful services.
- Strong understanding of Microservices and ORM framework.
- Sound time management and communication skills.
Secondary Skills For Java Developers:
You can find the secondary skills required for Java developers in the following.
- Knowledge of object-oriented design
- Agile project development methodologies
- Familiar with SOLID principles to improve code quality and simplify maintenance
- Exposure to version control systems like Git
- Familiar with markup languages like JSON and XML
- Exposure to cloud computing technologies
- Familiar with testing tools like Selenium and TestNG
- Good problem-solving and analytical skills.
Job Responsibilities of Java Developers with 1-2 years of Experience
Below is the list of the job responsibilities of beginner-level Java developers.
- Design, develop, and maintain Java applications
- Perform testing, debugging, and analyzing errors
- Develop RESTful APIs to integrate with external systems
- Design and build microservices-based architectures
- Write efficient, well-designed, and testable code
- Stay current with the latest technologies and incorporate them to enhance applications.
Job Responsibilities of Java Developers with 3-5 years of Experience
The following are the job responsibilities of Java developers with middle-level experience.
- Understand and analyze user requirements and define project objectives
- Design and develop user interfaces for intranet and Internet applications
- Design server scripting and database architecture
- Design and perform software testing
- Troubleshoot and resolve development and production environment issues across multiple operating systems
- Ensure applications meet the user requirements
- Involve in detailed design and product documentation.
Job Responsibilities of Java Developers with More Than Five Years of Experience
Below are the job responsibilities of senior-level Java developers.
- Design and develop high-quality mission-critical Java applications with analytics features
- Design and develop high-performance multimedia applications
- Perform peer code reviewing against standard code practices
- Examine and resolve issues while deploying applications in the production environment
- Support continuous improvement, examining alternatives and technologies, etc.
Okay! We have gone through the skills and responsibilities of Java developers. Next, we will dive into the Java interview questions straight.
Top 10 Frequently Asked Java Interview Questions
- What is Java?
- What is the latest version of Java?
- What are the key features of Java?
- What is a class in Java?
- Define Object in Java
- Define JVM
- What is JDK
- What are the data types in Java
- What are the bitwise operators in Java
- What is a static variable?
Java Interview Questions For Freshers
In this section, I have developed the Java interview questions for beginners based on basic Java concepts. You will find questions from the Java version and features, classes, objects, variables, etc. It will undeniably help you get a strong foundation in Java concepts.
Let’s start now!
1. What is Java?
Java is an open-source, general-purpose, platform-independent language. It is an OOP-based language that we can use to develop web, IoT, gaming, big data, AI, mobile, and enterprise applications. Java was released by the company Sun Microsystems in 1995. Since then, it has been a reliable, secure platform for developers and enterprises.
Furthermore, Java is a fast, multi-platform, and versatile programming language. It is called WORA (Write Once and Run Anywhere) language since we can seamlessly write Java programs on any platform. That’s why Java is the right choice for developing cloud-based applications. Above all, Java offers a robust ecosystem with a rich set of libraries and in-built functions, allowing the development of various applications.
| If you would like to become a Core Java Certified professional, then visit Mindmajix - A Global online training platform: "Core Java Training".This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2. Explain in brief the history of Java.
A small group of Sun Microsystems engineers, the ' Green Team' led by James Gosling, invented the Java language. They introduced Java to the world in 1995. Java continues to be one of the top-ranked programming languages. Developers and Enterprises use Java to build a range of applications.
Initially, the language was designed to develop embedded systems for use in electronic appliances. The initial names of Java are ‘Greentalk’ and ‘Oak’. Then, it got the name Java, which refers to an island in Indonesia where coffee was first invented.
3. What is the latest version of Java?
The latest version of Java is Java 22 or JDK22. This version was released on March 19, 2024. JDK 21 is the latest Long-Term Support (LTS) release of the Java SE platform on September 19, 2023. JDK 21 replaced JDK 17, the earlier LTS of the Java SE platform.
4. What are the features of the latest Java version, JDK 22?
The latest Java version, JDK 22, has many new features and capabilities. Below are some of the key features of the JDK 22.
- Statements before Super (…) – JDK 22 provides more flexibility to developers to express constructor behaviour.
- String Templates – They include runtime-computed values that simplify expressing strings. Also, it improves readability and security while composing strings.
- Unnamed variables and patterns – This feature increases code reusability and reduces code errors and maintenance.
- Implicitly Declared Classes – It provides organised declarations for single-class Java programs.
- Structured Concurrency – It offers an API for structured Concurrency, which allows us to streamline error handling and more.
5. What are the key differences between the JDK 22 and JDK 21?
JDK 22 is the long-term support release, whereas JDK 21 is the short-term support release.
6. What was the need to invent Java language?
Java is the first programming language to write virtual machine code. That's why Java is called JVM (Java Virtual Machine). It also provides a new feature called code reusability.
7. Compare the Java and C++ languages.
| Java |
C++ |
| Java is platform-independent | C++ is platform-dependent |
| It supports the Go-to statement | It supports the go-to statement |
| It doesn’t support structures and unions | It does support unions and structures |
| It has built-in support for threading | It does not support threading |
| We use Java for building applications | We use this language for system programming |
| Java uses both an interpreter and a compiler | C++ uses compiler only |
8. What are the key features of Java?
The following are the key features of Java:
- Dynamic: Java is more dynamic when compared to C++ and C. Java can quickly adapt to any evolving environment.
- Object-oriented: Java is an OOP-based language.
- Simple: Java is straightforward to learn and code.
- Secure: Java is a safe platform for developing applications.
- Platform Independent: While compiling codes in Java, codes change into platform-independent bytecode – not platform-specific machine code.
- Portable: Java is a highly portable language.
- High-Performance: Java provides improved performance with its built-in Just-in-Time compiler.
- Multithreaded: We can perform multiple tasks simultaneously in Java.
- Bug-free: Java eliminates errors even during the runtime check and compile-time check.
9. What is a class in Java?
A class in Java is a blueprint that supports the creation of individual objects. We can use classes to define object data types and methods. We can consider classes as categories and objects as items of the categories. The important thing is that all the class objects must have the class properties.
Main.java
- public class Main {
int x = 5;
-public static void main(String[] args) {
Main myObj = new Main();
System.out.println(myObj.x);
}
}An example of a Java class is shown below.
10. Define Object in Java.
In Java, we refer to an instance of a class as an object. Every object in Java has both state and behavior. To understand objects better, consider a real-time object – a bicycle. A bicycle has states like current gear, speed, pedal cadence, etc. Similarly, a bicycle can have behaviors like applying brakes, changing gears, etc.

An object stores its state in fields and expresses its behavior through methods. Know that Methods operate on an object’s internal state. It acts as the critical mechanism for object-to-object communication.
11. Write a basic Hello World program in Java.
Code:
Main.java
class elearning
- {
public static void main(String args[])
- {
System.out.println("MindMajix");
}
}
Output:
java -cp /tmp/YG7EbOTmWS/elearning
MindMajix
=== Code Execution Successful ===12. Define JVM.
JVM stands for the Java Virtual Machine. JVM is a part of JRE (Java Runtime Environment. It is a virtual machine that provides a runtime environment to write Java codes. We use JVM to execute Java bytecodes.
The JVM acts as an interpreter between Java and the underlying hardware. It allows Java applications to run on different operating systems and platforms. The main thing is that JVM plays a crucial role in memory management through automatic memory allocation and garbage collection.
13. Name the memory areas allocated by JVM.
The memory in the JVM is divided into five areas. They are:
- Class or Method Area
- Stack area
- Heap area
- Native Method Stack
- Program counter Register
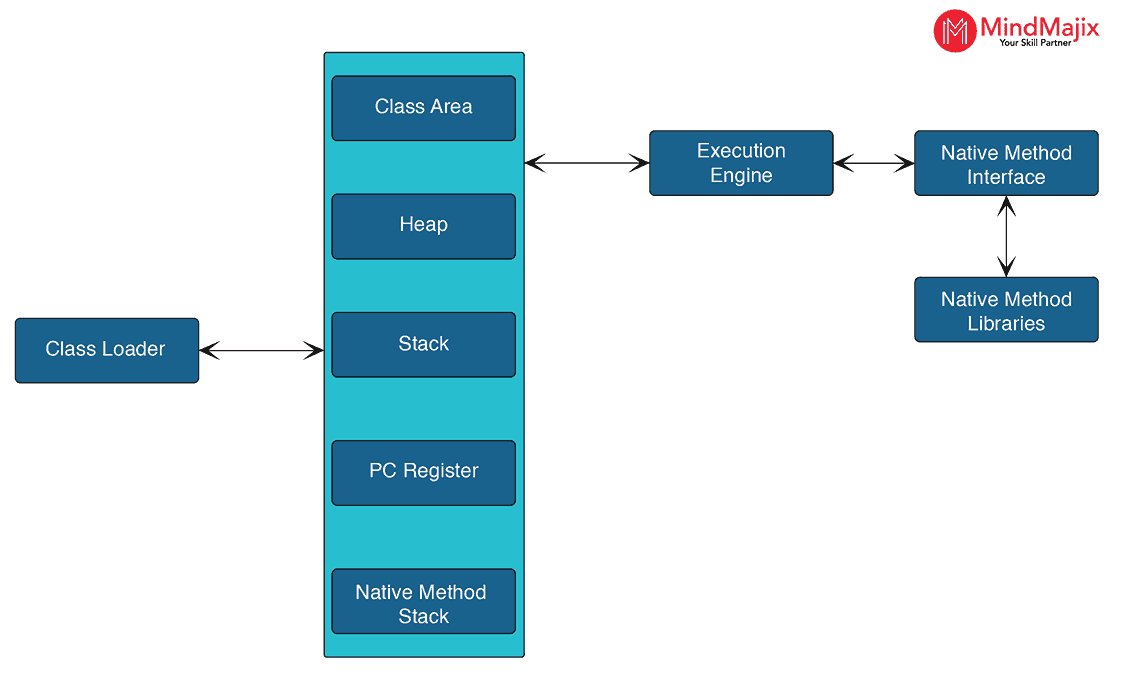
14. What is the class loader in JVM?
A class loader dynamically loads Java classes into the JVM during the execution. Data will be loaded from the Classloader first whenever we run Java programs. A class loader is one of the components of the JRE. The JVM doesn’t need underlying files to run Java programs.
There are three class loaders in JVM in total. They are:
- Application or System Classloader
- Bootstrap or primordial Classloader
- Extensions Classloader
15. What is JDK?
Java Development Kit, or JDK, is one of the three technology packages used in Java programming. We use JDK to implement Java platform specifications such as class libraries and compilers. With JDK, we can develop software applications and applets.
JDK is a platform-specific component that contains the Java interpreter, Java compiler, Java classes, and development tools. JDK is the core package of Java, also known as the superset of the JRE.
16. What is JRE?
Java Runtime Environment, or JRE, is one of the three Java platform components besides JVM and JDK. JRE is a collection of software tools that support developing high-performance Java applications. Though JRE is a part of JDK, we can download it separately.
JRE enables communication between Java programs and the operating system. It acts as a facilitator, offering all the required resources to developers. So, developers can run applications on any operating system without any customisation.
17. What is the JIT compiler?
Just-In-Time Compiler or JIT is one of the critical components of JRE. JIT compiles the bytecodes of a particular method into the native machine code at runtime. In a way, the JIT compiler helps to improve the performance of Java applications.
When a method is compiled, the compiled code is directly called by the JVM without interpretation. The important thing is that the compilation doesn’t require a processor and memory, which speeds up program compilation.
18. What are variables in Java programming?
Variables in Java are the basic storage units that hold data values. We can access and modify these values. Variables are the memory locations where we can store values. We need to declare all variables before using them. Also, we can assign a variable with a data type such as a number, string, character, etc.
The syntax for a variable is given as below:
type variableName = value;
type – It can be an integer or string
variableName – The name of the variable
Value – The value assigned to the variable
An example of a variable is given below.
int mynumber = 10;19. What are the various types of variables in Java?
There are three main variables available in Java. They are:
- Static Variables or class variables
- Instance Variables or non-static fields
- Local Variables
Static Variables: A variable declared with the static keyword is called a static variable. A static variable cannot be a local variable. We can allocate memory only once for these variables.
Instance Variables: an instance variable declared inside the class but outside the body of a method. An instance variable is instance-specific. So, we cannot share instance variables.
Local Variables: A variable declared inside a method's body within a class is called a local variable.
Example:
class A
-{
int num-30;//instance variable
static char name=MindMajix;//static variable
void method()
- {
int n=90;//local variable
}
}//end of class20. What is Type Casting in Java?
We use type casting in Java to convert one data type into another. The casting operator can perform typecasting while designing a Java program.
There are two types of typecasting, as listed below.
- Widening Typecasting or automatic – It is about converting a smaller data type into a larger data type size.
- Narrowing Typecasting or manual – It is about converting a larger data type into a smaller data type
The below flow diagram shows the conversions.

21. What are the data types in Java?
Datatypes in Java specify the values and sizes we can store in variables. The data type informs the compiler how to handle a variable or method.
There are two types of data types in Java. They are:
- Primitive Data Types – integers, characters, floating point numbers, and Booleans
- Non-primitive Data Types – arrays, strings, classes, enum, and interfaces.
22. What are the default values and sizes of primitive data types?
| Primitive Data Type | Default Size | Default Value |
| Integer | 4 bytes | 0 |
| Character | 2 bytes | ‘u0000’ |
| Byte | 1 byte | 0 |
| Short | 2 bytes | 0 |
| Long | 8 bytes | 0L |
| Floating point numbers | 4 bytes | 0.0f |
| Double | 8 bytes | 0.0d |
| Boolean | 1 bit | False |
23. Write the syntax for object creation in Java.
We need to use the new keyword to create an object in Java. The syntax for the object creation is given below.
ClassName objectName = new ClassName();ClassName – The name of the class where the object is created
objectName – The name of the object created.
An example of object creation is given below.
// creating an object for MindMajix
MindMajix m1 = new MindMajix();24. What is the Unicode system?
Unicode is a Universal International Standard Character Encoding system. All the written programming languages comply with this unicode system worldwide. The hexadecimal number is used to represent characters in the Unicode system. For example, the value 0x0041 in the Unicode system represents the Latin character A.
Java supports the Unicode system and represents characters with a 16-bit data type. The characters in hexadecimal numbers range from 0x0000 to 0xFFFF. At the same time, characters that are larger than 16 bits are called supplementary characters. They range from 0x10000 to 0x10FFFF.
25. What makes Java a ‘Run Anywhere’ language?
Java compiler converts source codes into bytecodes. Generally, bytecodes are platform-independent, so we can compile and execute them on any platform.
26. Are null, main, delete, and next the keywords of Java?
No, they are not Java keywords.
27. What happens if you write ‘public static void’ instead of ‘static public void’?
Nothing changes. The compilation and execution of programs will occur properly since the order of specifiers doesn’t matter in Java.
28. Is there any default value for a local variable in Java?
No, there is no default value for a local variable in Java. So, we must assign values for local variables before compilation. Otherwise, the compiler will throw an error.
29. How many types of operators are available in Java?
Java supports eight types of operators. They are:
1. Arithmetic operators
2. Logical operators
3. Assignment operators
4. Relational operators
5. Unary operators
6. Bitwise operators
7. The ternary or conditional operator
8. Instanceof operator
30. What is operator precedence in Java?
Java provides a set of rules and regulations to specify how to execute operators. If an expression has many operators, then the execution of the expression is done based on the operator precedence.
This operator precedence evaluates the operators based on the priority. For example, multiplication has the highest priority over addition and subtraction.
31. What are the J2EE design patterns?
The J2EE design patterns are a set of practices that help to solve recurring design problems. Design patterns are ready-made solutions to solve different issues. Java offers various design patterns, such as MVC, data transfer objects, session facades, and business delegates.
The MVC pattern is automatically chosen when we choose a web application template in the workspace. The session façade design pattern reduces complex interactions between lower-level EJBs. The data transfer object provides enhanced reusability and maintainability. The business delegate design pattern separates clients and business services to hide implementation details of business services.
32. What are the different logical operators used in Java?
| Operator | Description |
| Logical NOT |
|
| Logical OR |
|
| Logical AND |
|
33. What is the role of the unary operator in Java?
The unary operator in Java has only one operand. It performs various operations, including negating an expression, incrementing or decrementing a value by one, etc.
An example of the unary operator is given below:
Code:
Main.java
class UnaryExample
- {
public static void main(String args[])
- {
int x=10;
System.out.println(x++);
System.out.println(++x);
System.out.println(x--);
System.out.println(--x);
}
}Output:
java -cp /tmp/nRpgsmRLTQ/UnaryExample
=== Code Execution Successful ===34. What is Method Overriding in Java?
If the subclass in a Java program has the same method as declared in the superclass, it is known as method overriding. It allows the subclass to customise the method's behaviour without impacting the parent class.
When you want to override a method, you need to use the @override annotation. It tells the compiler that we want to override a method in the superclass. Method overriding provides better reusability of codes and extensibility of functionalities. It makes codes modular and maintainable.
Below is an example showing the use of method overriding.
Main.java
▾ class Animal {
▾ public void displayInfo() {
System.out.println("I am an animal.");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
▾public void displayInfo() {
System.out.println("I am a dog.");
}
}
▾class Main {
▾public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d1 = new Dog();
d1.displayInfo();
}
}35. What is the super keyword in Java?
We use the super keyword to invoke the overridden method if the method overrides one of the superclass’s methods. We also call the super keyword a reference variable that helps to refer to the immediate superclass of a class. We can apply the super keyword to access the elements of the superclass from within the subclass.
Consider the superclass and subclass below and see how the super keyword invokes the overridden method.
public class Superclass {
public void printMethod() {}
System.out.println("Printed in Superclass.");
}
}
public class Subclass extends Superclass {
// overrides printMethod in Superclass
public void printMethod() {
super.printMethod();
System.out.println("Printed in Subclass");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subclass s = new Subclass();
s.printMethod();
}
}
36. What is the method overloading in Java?
If a Java class has multiple methods with the same name and different parameters, we call it method overloading. The main advantage of method overloading is that it increases the readability of a Java program.
Method overloading also supports reducing code duplication. So developers can write a single method for multiple purposes. For example, you can apply the add method to add integers, floating point numbers, and so on. Besides, it improves flexibility by allowing different arguments in a single method.
The example below shows the use of method overloading in Java.
Code:
class MethodOverloading {
private static void display(int ,a){
System.out.println("Arguments:+ a);
}
private static void display(int a, int b){
System.out.println("Arguments: " + a + " and " + b);
}
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
display(2);
display(3, 6);
}
}Output:
java -cp /tmp/aZdRq9gbSx/MethodOverloading
Arguments: 2
Arguments: 3 and 6
=== Code Execution Successful ===37. What are Java packages?
In Java, the package is typically a collection of classes and interfaces bundled together and related to each other. Packages in a program help developers group the code to increase reusability. We can use packages by importing them into different classes.
We use packages to eliminate name conflicts. We can also organise codes into logical units using packages. There are two types of Java packages: built-in and user-defined. We can use the package keyword to create packages in Java.
Here is an example of using the package keyword.
package mypack;38. What is a singleton class in Java?
We can define a singleton class as a class that consists of only one instance. In this class, all methods and variables belong to only one instance. We use a singleton class to limit objects for a class.
A singleton class, a private static instance variable along with a private constructor. We can use the single instance of a singleton class throughout the lifecycle of a software program.
39. Define the ‘this’ keyword in Java.
The primary use of the ‘this’ keyword is to refer to the current object in a Java program.
40. What is a Spring Boot?
Spring Boot is a Java-based tool that we use to develop Microservices and web applications. It is also an extension built on the Spring framework. We use Spring Boot to create high-quality web applications, reducing development time significantly.
Major companies like Uber, Netflix, and Airbnb use Spring Boot to develop their applications because Spring Boot helps to create standalone applications and improve productivity.
41. What is the usage of the ‘this’ keyword in Java?
The following are the uses of this keyword in Java. They are:
- We use this keyword to refer to the current class instance variable.
- We use this keyword to invoke the current class method
- We use this keyword to invoke the current class constructor.
- We can pass this keyword as an argument in the constructor and method calls.
42. Which class is the superclass for all the classes in Java?
An object class is the superclass for all the classes in Java.
Sure! This section might have strengthened your basics of Java concepts. It will help you learn advanced Java concepts effortlessly.
Java Interview Questions for Experienced
In this section, I have prepared the Java interview questions and answers for learners who wish to explore further Java concepts. You will gain a comprehensive knowledge of Java by reading through this part of the article.
Let’s go ahead!
43. What are the differences between C and Java languages?
The following are the key differences between C and Java languages.
| C language | Java |
| C is a Procedural-Oriented language | Java is an Object-Oriented programming language. |
| Functions play a crucial role in C. | Objects play a vital role in Java. |
| It is an intermediate-level coding language. | It is a high-level coding language. |
| It does not support OOP Concepts. | Java supports OOP concepts |
| We can use the malloc() keyword for memory allocation. | We can use the new keyword for memory allocation. |
| It doesn’t support the threading concept. | Java supports threading |
| It is not a portable language | It is a portable language |
| Default members of C are public | Default members of Java are private |
| C supports storage classes. | Java doesn’t support storage classes. |
44. What is the difference between ++a and a++ increment operators?
++a is a prefix increment operator, whereas a++ is a postfix increment operator. The prefix increment operator returns the value ‘a’ after incrementing it. The postfix increment operator returns the ‘a’ value before incrementing it.
The below example shows the use of the operators.
Code:
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String args[ ])
int a, b;
// Pre-increment
a = 1;
b = ++a;
System.out.println( b );// prints 2
// Post-increment
a = 1;
b = a++;
System.out.println( b );// prints 1
}
}Result:
java -cp /tmp/dbMsHKUKUr/HelloWorld
=== Code Execution Successful ===45. What are the differences between JVM, JDK, and JRE?
| JVM | JDK | JRE |
| It stands for Java Virtual Machine | It stands for Java Development Kit | It stands for Java Runtime Environment |
| It is the heart of Java programming. | It is a development platform and the superset of the JRE. | We use JRE for code execution |
| It executes programs line by line | It has the JVM | It has the JVM |
| It converts bytecodes into machine codes. | It provides executables, tools, and binaries | It contains Java classes, binaries, and JVM. |
46. Define left shift and right shift operators in Java.
Left Shift: The left shift is a bitwise operator in Java. In this shift, bits are moved towards the left-hand side, and zeros are placed at the rightmost places.
The example below shows the left shift.
Code:
public class LeftShiftOperator {
public static void main(String[] args)
int a=2;//
int i;
i=a<<1;//4
System.out.println("the value of a before left
shift is: " +a);
System.out.println("the value of a after applying
left shift is: " +i);
}
}Output:
java -cp /tmp/GIYi18A02D/LeftShiftOperator
the value of a before left shift is: 2
the value of a after applying left shift is: 4
=== Code Execution Successful ===|Right Shift: The right shift is also the bitwise operator in Java. In this shift, bits are moved towards the right-hand side, and zeros are placed at the leftmost place.
The example below shows the right shift.
Code:
public class RightShiftOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=2;
int I;
i=a>>1;
System.out.println("the value of a before right shift is:
" +a);
System.out.println("the value of a after applying rightOutput:
java -cp /tmp/xy76CaCCuR/RightShiftOperator
the value of a before right shift is: 2
the value of a after applying right shift is: 1
=== Code Execution Successful ===47. What are the bitwise operators in Java?
We use bitwise operators in Java to perform bit operations.
The following are the bitwise operators in Java. They are:
- Bitwise OR (A&B)
- Bitwise XOR (A^B)
- Bitwise AND (A|B)
- Bitwise complement (~A)
- Left shift ( A<<2)
- Right shift (A>>2)
- Unsigned right shift (>>>)
- Unsigned left shift ( <<<)
48. What is a ternary operator?
We use the ternary operator in Java to replace the if-else statement. It is also known as the conditional operator that uses three operands.
The syntax for the ternary operator is given as:
variable = (expression)? expression true:expression falseThe example below shows the use of the ternary operator.
int age = 21;
String result = (age 18) ? "adult" : "minor";49. What does the ‘u0000’ notation represent in the Unicode system of Java?
In Java, every character is represented by 2 bytes. The notation ‘u0000’ is the lowest range of the Unicode system. The notation ‘uFFFF’ is the highest range of the Unicode system. Also, it is the default value of the character data type.
50. Is the empty .java file a valid source file name?
Yes, an empty Java file is a valid source file name. But we cannot run an empty file since it has no codes. Java allows saving Java files by using the .java extension. We must compile the files using the javac .java command and run them using their class name.
51. What are Java keywords?
Java keywords, called "Reserved keywords, " act as a code key. Keywords in Java are predefined. We cannot use a Java keyword as an object name, variable, or identifier in Java programs.
Java offers nearly 50 keywords, including abstract, default, break, new, extend, static, import, etc. Though true, false, and null seem like keywords, they are literal.
52. What are various access specifiers in Java?
Java has four access specifiers. They are:
1. Private: We can access the methods or classes declared private within the same class.
2. Public: We can access the methods or classes declared public anywhere in a program. In other words, we can access them within and outside the class.
3. Default: By default, all the variables, classes, and methods are of default scope. The default is accessible only within the package.
4. Protected: We can access the methods, variables, and classes defined as private within the same class of the same package or by the subclass of the same class.
53. What are the uses of packages in Java?
By using packages in Java, we can:
- arrange the group of classes into a single API unit
- ensure access protection
- control the naming conflicts
- locate related classes easily
- reuse the existing classes
54. What is the output of the following program?
The program is given as follows:
Code:
class Java
{
public static void main (String args[ ])
{
System.out.println(10 * 20 + "MindMajix");Output:
java -cp /tmp/tKdYXDrlIn/Java
200MindMajix
MindMajix200
=== Code Execution Successful ===55. What are control statements in Java?
Control statements are divided into three types in Java. They are:
- Decision-making Statements
- Jump Statements
- Iterative/looping Statements
56. What are the selection statements in Java?
Selection statements are also called conditional or branching statements. We can use the selection statement to control the execution flow of a Java program. It allows Java programs to make decisions based on conditions. Once the condition is satisfied, they direct the program to follow a certain path. If not, they direct the program to follow another path.
Selection/Conditional statements in Java include:
- If statement
- Switch statements
- If-else statement
57. What are the different types of iterative statements?
The iterative statements in Java are also called looping statements. They are a set of statements that we can run repeatedly until the condition for the termination is not met.
Looping/iterative statements in Java include:
- For loop
- Do-while loop
- While loop
58. What are the jump statements of Java?
We use Jump statements in Java to transfer control to another part of a program based on a condition. Also, we use these statements to jump directly to other statements.
The jump statements used in Java are break, continue, and return.
59. Explain the ‘For-Each’ loop in Java.
The ‘For-Each’ loop is an array traversing technique used in Java, such as for and while loops. We use this loop to iterate over a collection or array-like ArrayList.
An example of a ‘For-Each’ loop is given as follows:
Code:
class ForEachPro{
public static void main(String args[ ]){
//declaring an array
int arr[ ]={21, 22, 23, 24};
//traversing the array with for-each loopOutput:
java -cp /tmp/FD2FPUTNPJ/F8rEachpro60. What is the difference between a while loop and a do-while loop?
When it comes to the while loop, we test the condition first. If the condition is true, then the loop continues. If not, execution is stopped.
When it comes to the do-while loop, we execute the condition first. We test the condition at the end of the loop.
The syntax for the while loop is given as follows:
while(condition){
//code to be executed
}The syntax for the do-while loop is given as follows:
do {
//code to be executed /
//update statement
}while (condition);61. What are the comments in Java?
Java comments are statements that are not executed by the compiler and interpreter. We use comments to provide information about the class, methods, variables, and statements. Moreover, we use them to hide program code for a specific time.
There are three types of comments in Java. They are:
- Documentation comments
- Single-line comments
- Multi-line comments
62. Describe OOP concepts in brief.
OOP is the short form for Object-Oriented Programming Language.
Simula is the first object-oriented programming language. The most popular OOP languages are Java, PHP, C++, Python, and many more.
The following are the OOP concepts used in Java:
- Abstraction
- Inheritance
- Encapsulation
- Polymorphism
63. What is Abstraction?
Abstraction is an OOP concept that hides unnecessary data and only shows necessary data to users. In other words, abstraction hides internal processes and indicates only the functionalities of an application.
64. Define Encapsulation.
Encapsulation is an OOP property that binds data and code into a single unit.
65. What is Inheritance in Java?
According to the inheritance property, a child class object can acquire the properties of its parent class. We apply inheritance to acquire runtime polymorphism and also provide code reusability.
66. What is Polymorphism in Java?
Polymorphism in Java provides a way to perform one task in different possible ways. We use method overriding and method overloading to achieve polymorphism in Java.
67. What are the advantages of OOP concepts?
The following are the advantages of OOP concepts. They are:
- OOP provides data-hiding
- They can stimulate real-world entities effectively.
- They make development and maintenance more effortless than a procedural programming language.
68. What is the significant difference between object-oriented language and object-based language?
Object-oriented programming language supports all the features of OOP concepts. Examples of object-oriented programming languages are Python and Java.
An object-based programming language supports the features of OOP concepts except inheritance. JavaScript and VBScript are some examples of Object-based programming languages.
69. What will be an initial value for an object reference defined as an instance variable?
All the object references in Java are initialised to null.
70. What is the Object-oriented paradigm?
The object-oriented paradigm depends on objects that have defined methods in the class. We use this paradigm to incorporate code reusability and modularity. Objects are defined as instances of classes that interact with one another to design programs and applications.
The features of the object-oriented paradigm are given as follows:
- Focusing on data containing methods to operate on an object’s data
- Following the bottom-up approach in the program design
- Building enhanced real-time approaches such as abstraction, inheritance, etc.
71. What are Java naming conventions?
Java naming convention is a rule that we follow to name identifiers such as packages, methods, variables, and constants. Many Java communities, such as Sun Microsystems and Netscape, support these conventions. All the fields of Java programming are given Java naming conventions.
72. What are the rules that you must follow to declare a class?
The rules that we must follow to declare a class are given as follows:
- The class name must be nouns such as Thread, Java, Class, etc.
- It should start with an uppercase letter.
An example of the class is given below.
public class Thread
{
//code
}73. Define Constructor in Java.
A constructor is a special type of method with a block of code to initialize the state of an object. A constructor is called when the instance of the object is created. Similarly, a constructor is called when a Java object is created using the new keyword.
74. What rules that you must follow while creating a constructor in Java?
We need to follow the rules below:
- The constructor should have the same name as its class name.
- A constructor shouldn’t be synchronized, final, abstract, or static.
- There shouldn’t be any explicit return type for a constructor.
75. What are the different types of constructors available in Java?
Java has two types of constructors. They are:
- Parameterized constructor
- Default constructor
Parameterized constructor: A parameterized constructor is another constructor used to initialize instance variables with the given values. A parameterized constructor is a constructor that accepts arguments.
Default constructor: We call a default constructor as a no-argument constructor. We use this constructor to initialize an instance variable with a default value. Moreover, we use this constructor to perform some useful tasks in object creation. The compiler implicitly invokes the default constructor if no constructor exists for a particular class.
76. Give examples for both a default constructor and a parameterized constructor.
An example of a default constructor is as follows:
Code:
// Java Program to create and call a default constructor
class MindMajix1{
//creating a default constructor
MindMajix1()
{
System.out.println("Welcome to MindMajix");
}
//main method
public static void main(String args[]){
//calling a default constructor
MindMajix1 m=new MindMajix1();
}
}Output:
java -cp /tmp/UHJIOYInbH/MindMajix1
Welcome to MindMajix
=== Code Execution Successful ===An example of a parameterized constructor is as follows:
Code:
class Student{
int id;
String name;
//creating a parameterized constructor
Student (int i, String n){
id = i;
name = n;
}
//method to display the values
void display() { System.out.println(id+" "+name); }
public static void main(String args[]){
//creating objects and passing values
Student s1 = new Student (111,"Mind");
Student s2 = new Student (222, "Majix");
//calling method to display the values of object
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}output:
java -cp /tmp/lyrufeqn7m/Student
111 Mind
222 Majix
=== Code Execution Successful ===|77. Does a constructor in Java return any value?
A Java constructor will return the class's current or present instance.
78. Can a constructor in Java be inherited?
No, a constructor in Java cannot be inherited.
79. Can a constructor be overloaded?
Yes, it is possible to overload a constructor by changing the number of arguments for each constructor in a particular program. It is also possible to overload a constructor by changing the parameter data types.
80. Can you declare a constructor as final?
No, we cannot declare a constructor as final. If we declare a constructor as final, the compiler will throw a "modified final not allowed" error.
81. Is any Constructor class available in Java, and what is its purpose?
Yes, the constructor class is available in Java. The purpose of the constructor class is to get the constructor's internal information. The information is available in the Java.lang.reflect package.
82. What is the use of the copy constructor in Java?
There is no copy constructor in Java.
Java allows the copying of values of one object to another in the following ways:
- By using Clone() of object class
- By assigning the value of one object to another
- By using a constructor.
83. Define a method in Java.
In Java, we can define a method as a set of codes represented by a name. Using a method's name, we can invoke the method at any point in a program. Every method in a program has its own name, which is not the same as that of a class name.
Good! This section might have enhanced your expertise in Java to the next level. You have gained solid knowledge of constructors, OOP concepts, Java methods, and more from this section.
Java Interview Questions for Advanced Learners
In this section, I have created Java interview questions and answers from advanced Java concepts, elevating your expertise in Java to greater heights.
Let’s move on!
84. Explain Object-Oriented Design.
Object-Oriented Design (ODD) is a process of using Object-Oriented methodology to develop software applications. In other words, it is a part of the object-oriented programming process. ODD supports the design of the system architecture after the object-oriented analysis (OAA) is made.
The output of OOA, such as the conceptual systems model, user interface, system rational model, etc., are given as input to the OOD process. These inputs help to identify relationships and design systems classes and objects, interfaces, etc.
85. What are JAS RS and JAS WS?
Both JAS RS and JAS WS are Java APIs that we use to develop web services. JAS WS or Jakarta XML web services is an API with which we can create SOAP web services that interact with XML. Besides, it allows developers to build RPC-oriented and message-oriented web services.
JAS RS or Jakarta RESTful web services is an API with which we can create Java web services using the REST architectural style. This API provides declarative annotations to identify components of applications, extract data, route requests, and provide metadata.
86. What is the common convention for Spring converter-type classes?
The common convention for Spring converter-type classes is to use suffixes before a converter. For example, StringConverter is a converter that converts a string into an integer. Note that a converter class must implement the converter interface.
Java Spring also provides built-in converters to convert the basic types such as string, Boolean, integer, etc. Additionally, Java provides a solid type conversion SPI for creating custom converters.
An example of a Spring converter class is given below.
public class StringConverter implements Converter<String, Integer> {
}
@Override
public Integer convert(String source) {
return Integer.parseInt(source);
}
@Override
public boolean canConvert (Class<?> targetType) {
return targetType == Integer.class;
}
}We can use this converter type to convert a string into an integer. We need to call the convert() method for this conversion.
87. What are the key differences between checked and unchecked exceptions?
| Checked Exceptions | Unchecked Exceptions |
| These exceptions occur at the compile time. | These exceptions arise at the run time. |
| They are the subclass of the exception class | They are not part of the exception class |
| Compilers check these exceptions | Compilers don’t check these exceptions |
| We catch these exceptions during the compile time. | We cannot catch these exceptions during the compile time. |
| The JVM needs these exceptions to catch and hold. | The JVM doesn’t need these exceptions to catch and hold. |
88. How many ways can you achieve abstraction in Java?
We can achieve abstraction in two ways in Java.
- By using interfaces
Interfaces achieve complete abstraction. They can contain only abstract methods and constant declarations.
- By using abstract classes
Abstract classes achieve partial abstraction. We cannot instantiate abstract classes. We can use them as base classes for other classes.
89. What are the differences between ArrayList and Vector in Java?
| ArrayList | Vector |
| It is not synchronized, so it is fast. | It is synchronized, so it is slow. |
| Multiple threads can access ArrayList at a time | Only one vector can access a vector at a time. |
| It increments by 50 % of the array size when the number of elements increases its capacity. | It increments by 100% of the array size when the number of elements increases. |
| It uses the iterator interface to traverse elements | It uses both an iterator and enumeration interface to traverse elements |
| It is not a legacy class | It is a legacy class. |
90. What are the equals () and hashCode () methods in Java?
We use the equals () method to compare the equality of two objects. We can compare equality in two ways: shallow comparison and deep comparison.
The syntax for the equals () method is given as follows.
public boolean equals (objects obj)We use the hashCode () method to return the hashcode value. The value is returned as an integer. We use the hashcode value in hashing-based collections such as HashMap, HashTable, HashSet, etc.
The syntax for the hashCode () method is given below.
public int hashCode()91. What is the difference between a constructor and a method?
The differences between the constructor and method are given as follows:
| Constructor | Method |
| A constructor should have the same name as the class name | A method name is not the same as that of a class name |
| A constructor has no return type | A method must have a return type |
| It can be invoked implicitly | It can be invoked explicitly |
| We can use a constructor to initialize the state of the object | We can use a method to expose the behavior of an object. |
| Java compiler provides the Default constructor | Java compiler doesn’t provide the default method. |
92. What is a method signature in Java?
In Java, a method signature is a specified format followed by a method with its type, name, and order of parameters. Exceptions are not considered a part of a method signature.
An example of a method signature is given below.
return-type method name (parameter list)
{
//code
}93. What is the role of static keywords in Java?
We use static keywords to manage memory. We can declare block, method, variable, and nested classes as static.
94. What is a static variable?
In Java, we can declare a variable as static. When we do so, we must ensure that the following rules are satisfied. They are:
- We must use a static variable to refer to all the common properties of objects.
- We must assign memory for the static variable only once in the class during class loading.
An example of a static variable is given as follows:
Code:
class Student{
}
int rollno;//instance variable
String name;
static String training ="MindMajix";//static variable
Student (int r, String n){
rollno = r;
name = n;
}
void display (){System.out.println(rollno+" "+name+"
+training);}
public class TestStaticVariable1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Student s1 = new Student (111, "Ram");
Student s2 = new Student (222, "Kareem");
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
Output:
java -cp /tmp/UMrGH30Zbe/TestStaticVariable1
111 Ram MindMajix
222 Kareem MindMajix
=== Code Execution Successful ===95. What happens if you declare a method as static?
If we declare a method as static, the following operations take place. They are:
- We must invoke a static method without creating an instance of the class.
- In most cases, the static method belongs to the class rather than the object of the class.
- Only a static method can access static data members and can change the value of a particular data member.
96. What are the restrictions you encounter when declaring a method static in Java?
The restrictions that we encounter are:
- A static method cannot access non-static members. Not only that but it can also not be called a non-static method directly.
- Since they are non-static, we cannot use this and super keywords when declaring static methods.
97. Why is the main() method in Java known as Static?
The main reason is that we don't need an object to call for a static method. If we declare the main() method non-static, we must create an object first. Only then can we call the main () method. That’s why we declare the main() method static to save memory.
98. Can we override the static method in Java?
No, we cannot override the static method in Java.
99. What is a static block in Java?
We use a Static block in Java to initialise the static data members. It is executed before the main method is executed during class loading.
An example of a static block is given as follows:
Code:
Class Mindmajix{
static { System.out.println("static block"
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}Output:
static block
Hello World100. Can you execute a program in Java without the main () method?
Using a static block, we can execute a Java program without the main() method. However, it is possible only for the JDK 1.6 version. Executing a Java program without the main() method from the JDK 1.7 version is not supported.
101. What happens if you remove the static modifier from the signature of the main () method?
The program will be compiled. But it throws a NoSuchMethodError error at runtime.
102. Can you declare a constructor using static?
The static context is suitable for only variable, class, and method - not for the object. Constructors are usually invoked when an object is created. So, we can't declare a constructor as static in Java.
103. Can you make abstract methods static in Java?
No. If we declare abstract methods static, they become part of the class. Therefore, declaring an abstract method static is not allowed.
104. Can you declare static methods and variables in the abstract class?
Yes, we can. There is no need for an object to access the static block. Therefore, we can access static methods and variables declared inside the abstract class by using the name.
Consider the following example.
Code:
abstract class Check
{
static int i = 100;
static void CheckMethod()
{
System.out.println("MindMajix");
}
}
public class CheckClass extends Check
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
Check. CheckMethod();
System.out.println("i = "+Check.i);
}
}
Output:
java -cp /tmp/2XCeCLt7vL/CheckClass
MindMajix
i = 100
=== Code Execution Successful ===105. Can the ‘this’ keyword refer to the current class instance variable?
Yes, this keyword refers to the current class instance variable. We use this keyword to initiate or invoke the current class constructor.
106. Write the syntax for inheritance in Java.
The syntax for inheritance in Java is as follows:
class Superclass extends subclass
{
//code
}107. How can you generate random numbers in Java?
Using the Math. random() method, we can generate random numbers in Java ranging from 0.1 to less than 1.0. Moreover, we can generate the random numbers using the Random class in Java.util package.
108. Can the main() method in Java return any data?
Java's main() method doesn't return any data because we declare it with a void return type.
109. Why are multiple inheritances not supported in Java?
Java doesn’t support multiple inheritances to reduce the complexity.
If we apply multiple inheritance in a Java program, the result will be as follows:
Code:
class X{
void msg()
{
System.out.println("Hello");}
}
class Y{
void msg()
{
System.out.println("Welcome"); }
}
class Z extends X,Y{//suppose if it were
public static void main(String args[]){
Z obj=new Z();
}
}
obj.msg(); //Now which msg() method would be invoked?Output:
ERROR!
/tmp/xdn0K4y85E/X.java:11: error: '{' expected
class Z extends X,Y{//suppose if it were
1 error
=== Code Exited With Errors ===110. Can you declare the main () method in Java as private?
Java's main() method must be public static to run any program. If we declare the main () method as private, there will be no complications. But the method will throw a runtime error.
111. Can a class in Java have multiple constructors?
Yes, Java classes can have multiple constructors with different parameters.
112. What are the different ways to overload a method?
There are two different ways to overload a method. They are:
- By changing the data type
- By changing the number of arguments
113. Write a program to demonstrate the method overloading by changing the data types.
Below is an example of a Java program that uses the method overloading by changing the data types.
Code:
class MethodOverloading {
private static void display(int a){
}
System.out.println("Got Integer data.");
private static void display(String a){
}
System.out.println("Got String object.");
public static void main(String[] args) {
display(1);
display("Hello");
}
}Output:
java -cp /tmp/QHf3014Szm/MethodOverloading
Got Integer data.
Got String object.
=== Code Execution Successful ===114. Write a program to demonstrate the method overloading by changing the number of arguments.
Below is an example of a Java program that uses the method overloading by changing the data types.
Code:
class MethodOverloading {
private static void display(int a){
}
System.out.println("Arguments: " + a);
private static void display(int a, int b){
}
System.out.println("Arguments:+ a +and+ b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
display(1);
display(1, 4);
}
}Output:
java -cp /tmp/EGHKFTF4P3/MethodOverloading
Arguments: 1
Arguments: 1 and 4
=== Code Execution Successful ===115. Why is method overloading in Java not possible by changing the method's return type?
Ambiguity is the reason why method overloading is not supported in Java by changing the method's return type.
116. Is it possible to overload the main() method in Java?
It is possible to overload the main() method using method overloading. However, JVM only calls the main() method, which receives string arrays as arguments.
117. What is the use of method overriding in Java?
We use method overriding to achieve runtime polymorphism. We also use method overriding to provide a specific implementation for a method given by its subclass.
118. What are the rules you need to follow during method overriding?
We need to follow the rules below during method overriding:
- The method must have the same parameters as they exist in the parent class.
- The method should have the same name as the class name.
- There must be an IS-A relationship, known as inheritance.
119. Write a program to demonstrate method overriding.
Code:
class Shape{
void run()
{
System.out.println("Shape is ready");
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
{
}
void run()
System.out.println("Rectangle is drawn");
public static void main(String args[]){
Rectangle obj = new Rectangle();//creating object
obj.run(); //calling method
}
}Output:
java -cp /tmp/Joi65Hfvhs/Shape
Rectangle is drawn120. Can you override a static method?
No, we cannot override a static method. A class bounds a static method, whereas an object bounds an instance method. Moreover, a static method belongs to the class area, whereas an instance method belongs to the heap area.
121. Can you override a main ( ) method in Java?
No, we cannot override a main () method in Java since the main () method is static.
122. What is the difference between aggregation and composition?
Aggregation in Java is built to represent a weak relationship. But, the composition is built to represent a strong relationship.
123. Why does Java not support pointers?
A pointer is a variable that refers to the memory address. Java doesn’t support pointers because they are complex and insecure.
124. What are the uses of super keywords in Java?
The uses of the super keyword in Java are given as follows:
- We use the super keyword to indicate the immediate superclass instance variable.
- It supports invoking an immediate parent class constructor.
125. Can you have virtual functions in Java?
Yes, all the functions in Java are virtual by default.
Cheers! You have completed learning Java interview questions and answers. Now, you are ready for Java interviews. Undoubtedly, you will crack your interviews and land your dream job.
Java Interview FAQs
1. Is learning Java easy?
Yes, learning Java is easy. Learning the fundamentals of Java is easy and fun. You only need strong determination, hard work, and effort to learn Java. Java has many advantages, such as vast community support and open-source language so that you can get support from many sides. MindMajix offers Java training with industry-experienced trainers and a comprehensive course curriculum. No doubt learning Java is a piece of cake in MindMajix.
2. Is learning Java worth it? 210
Developers and enterprises leverage Java to build mobile, web, and desktop GUI applications. That’s why it has been one of the high-demand programming languages for more than two decades. AmbitionBox says Java developers get an average annual salary of 6 Lakhs in India. According to Glassdoor, the average annual package for Java developers in the USA is 124k USD. From these key figures, you can understand that learning Java is promising and rewarding.
3. Which companies hire Java developers?
According to Glassdoor, top companies such as TCS, Accenture, CTS, Capgemini, Wipro, Virtusa, and Tech Mahindra hire Java developers in large numbers with fantastic salary packages.
4. Is Java good for AI?
Java is suitable for AI since it is a robust, versatile coding language with a large user community. Also, it offers better security, reliability, and scalability. Also, Java is platform-independent. So you can run Java applications on any platform. Java has many libraries for NLP, machine learning, etc. Some AI applications built based on Java are Netflix, Google Search, and IBM Watson.
5. How long will it take to learn Java?
For beginners, it may take 2-4 months to learn Java. For experienced learners, it may take 1-2 months. Mindmajix offers 25 hours of core Java training in live online and self-paced video modes. You will learn core Java in 25 hours if you choose live online mode. If you prefer self-paced videos and watch two videos per day, you will learn core Java in 13 days.
Conclusion
All right! You have gone through the key Java interview questions and answers in this blog. This article must have enhanced your knowledge of Java concepts. The example Java programs in this blog must have elevated your hands-on skills to new heights. However, if you go through professional Java training, it will boost your Java knowledge and skills dramatically.
MindMajix is the leading eLearning provider that offers top-class Java training with an industry-designed course curriculum. Once you complete the training, you will be job-ready and stand out. You will become a highly competent Java developer with the skills employers seek from candidates today.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Core Java Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Pranaya is working as a Content Writer at Mindmajix. She is a technology enthusiast and loves to write about various technologies which include, Java, MongoDB, Automation Anywhere, SQL, Artificial Intelligence, and Big Data. You can connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter.
















