- Abstraction in Java
- Clojure Tutorial
- Control Statements in Java
- Core Java Interview Questions
- Data Types in java
- Top 9 Java EE Frameworks
- Java EE vs Spring Framework
- Java Frameworks List - Top 14 Java Frameworks
- Java Interview Questions
- Java Tutorial
- Java Web Dynpro Interview Questions
- JavaFX Interview Questions
- Method Overloading in Java
- Multithreading in Java
- List of Popular Open Source Java Build tools
- Operators in Java
- Program Logics in Java
- String Handling in Java
- Why You Should Learn Java Programming
- Exception Handling in Java
- Multithreading Interview Questions
- Design Patterns Interview Questions and Answers
- C++ Interview Questions and Answers
- JSP Interview Questions
- EJB Interview Questions
- SOAP in Web Services
- JPA Interview Questions
- DXC Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Architect Interview Questions
- Java Concurrency Interview Questions
- What is Java Concurrency?
- What is JPA - Complete Tutorial Guide
- What is EJB?
- Java Collections Interview Questions
- Java Swing Tutorial
- Java Stream Tutorial
- Linked List Interview Questions
- Compiler Design Interview Questions
- Java Collection Tutorial
- Java Stream Interview Questions
- Thymeleaf vs JSP
- Thymeleaf Tutorial - What is Thymeleaf
- Socket Programming in Java - What is TCP
- Apache Tomcat Interview Questions
- Capgemini Interview Questions
- Zoho Interview Questions
- PwC Interview Questions
- Hexaware Interview Questions
- Intuit Interview Questions
- Tech Mahindra Interview Questions
- Qualcomm Interview Questions
- Arcesium Interview Questions
- PayTM Interview Questions
- DXC Technology Interview Questions
- Java Developer Job Description
- MAQ Software Interview Questions
- Amdocs Interview Questions
- TCS NQT Interview Questions
- Virtusa Interview Questions
- Siemens Interview Questions
- Tricky Java Interview Questions
Data Structures are the base of software engineering. Almost all coding interviews you face today are mainly comprised of Data structure and Algorithm based questions. And big organizations like Google, Amazon, Facebook, etc., are also hiring programmers who are exceptionally good at optimizing data structures.
If you're aspiring to take your career to the next level in Data Structures but are confused about what kind of programming questions you'll face in your interview? Well, you've reached the right place!
This article shares the latest 2024 Data Structure Interview questions and answers collected from different interviews for programmers at varying levels of experience. We hope the topic areas covered in this blog help both beginners and experienced crack their next interview!
According to research Data structures has a market share of about 9.4%. So, You still have the opportunity to move ahead in your career in Data structures. Mindmajix offers Advanced Data structures Interview Questions 2021 that help you in cracking your interview & acquire a dream career as a Data structures Developer.
Data structures Interview Questions and Answers
| Types of Data Structure Interview Questions |
Below mentioned are the Top Frequently asked Data structures Interview Questions and Answers that will help you to prepare for the Data structures interview. Let's have a look into them.
Frequently Asked Data structures Interview Questions
- Explain what is data structure?
- Explain what is a linked list?
- Explain about Linked List Data Structure.
- What are the basic operations performed on various data structures?
- What are infix, prefix, and postfix in data structure?
- Define what is an array?
- How would you implement a queue using a stack?
- Name some applications of data structures?
Top Data structures Interview Questions and Answers
1. Explain what is data structure?
The data structure is nothing but an entity where the data is perfectly aligned and can be manipulated as per the requirement. When we deal with data structure it is not just about one table of data but it is about different data sets and how well they are aligned with each other. Overall, it helps the data to be organized.
| If you would like to Enrich your career with a Java-certified professional, then Enrol Our “Core Java Training” Course. This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2. What are the basic operations performed on various data structures?
The basic operations performed on data structures are as follows:
- Insertion - Adds a new data element in the data structure.
- Deletion - Removes a data element in a data structure.
- Searching - Involves searching for a specified data element in a data structure.
- Traversal - Processing all data elements present in it.
- Merging - Combines two similar data structures to form a new data structure of the same type.
- Sorting - Arranging data elements of a data structure in a specified order.
3. Explain what is a linked list?
A linked list is nothing but a sequence of nodes. With this sequence, each node is connected to the following node. It forms a chain of data storage.
4. Explain the process of how do you reference all the elements in the one-dimension array in detail?
To reference all the elements in the one-dimension array, we have to use an indexed loop. With the help of this, it executes from “0” to array size minus one. By following this process the loop counter will be able to refer to all the elements.
Related Article: Amazon Interview Questions
5. List out the areas where the data structure is applied?
The data structure is a vital aspect while handling data. The following are specific areas where the data structure is applied:
- Numerical analysis
- Operating systems
- A.I.
- Database management
- Statistical analysis
The above are few areas where the data structure is applied and not limited to.
6. What is infix, prefix, and postfix in data structure?
The way to write arithmetic expressions is known as notation. There are three types of notations used in an arithmetic expression, i.e., without changing the essence or output of expression. These notations are:
- Prefix (Polish) Notation - In this, the operator is prefixed to operands, i.e. ahead of operands.
- Infix Notation - In this, operators are used in between operands.
- Postfix (Reverse-Polish) Notation - In this, the operator is postfixed to the operands, i.e., after the operands.
The following table briefly tries to show the difference in all three notations −
| Infix Notation | Prefix Notation | Postfix Notation |
| x + y | + x y | x y + |
| (x + y) ∗ z | ∗ + x y z | x y + z ∗ |
| x ∗ (y + z) | ∗ x + y z | x y z + ∗ |
| x / y + z / w | + / x y / z w | x y / z w / + |
| (x + y) ∗ (z + w) | ∗ + x y + z w | x y + z w + ∗ |
| ((x + y) ∗ z) - w | - ∗ + x y z w | x y + z ∗ w - |
Data Structures Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
7. Explain the terminology LIFO?
LIFO stands for Last In First Out.
This process describes how the data is accessed, stored, and then retrieved. So the latest data that is stored in the database can be extracted first.
8. Explain what is a binary tree?
It is one type of data structure that has two nodes, has left node and a right node. In a programming language, binary trees are considered to be an extension to the linked list.
9. Define what is a stack?
The stack is considered as a data structure where the top layer element can be accessed. The data is stored in the stack and every time when data is stored, it pushes the data downwards which enables the users to access the latest data from the top layers.
10. Explain what is multidimensional arrays?
Multidimensional arrays use multiple indexes in order to store data in the database. In a few scenarios, data cannot be stored using a single dimension index, in these scenarios multidimensional arrays are useful.
Related Article: LinkedIn Interview Questions
11. Explain whether a linked list is considered as a linear or non-linear data structure?
This is purely determined on the requirement basis, a linked list can be considered as a linear data structure or a non-linear data structure. For example: If the linked list is used on storage, then the linked list is considered as a nonlinear data structure.
If linked lists are used against access strategies then they are considered as a linear data structure.
12. Explain how does dynamic memory allocation will help you in managing data?
A dynamic memory allocation will help you effectively manage your data by allocating structured blocks to have composite structures that can be flexible, i.e. it can expand and can contract based on the need.
Also, they are capable of storing simple structured data types.
13. What is FIFO?
FIFO in data terminology stands as “First in, First Out”.
This process defines or depicts how the data is stored inserted and accessed in a queue. Within this process, the data that is inserted at the beginning of the queue will only be extracted or accessed first.
14. Explain what is merge sort and how it is useful?
A merge sort is nothing but a process where the data is divided and sorted to reach the end goal. Within this process, the adjacent elements are merged and sorted to create bigger elements. These sorted elements are gathered again and made the even bigger list. This process is continuous and repetitive until and unless they have nailed it down to a single sorted list.
15. List out all the advantages of a linked list?
The important aspect or advantage of a linked list is that it is the perfect data structure where the data can be modified very easily. Also, it doesn’t matter how many elements are available on the linked list.
16. Explain the main difference between PUSH and a POP?
The two main activities, i.e. Pushing and Popping applies the way how data is stored and retrieved in an entity. So if you check in detail, a Push is nothing but a process where data is added to the stack. On the contrary, a Pop is an activity where data is retrieved from the stack. When we discuss data retrieval it only considers the topmost available data.
17. Can you explain with an example how does a variable declaration activity will consume or affect the memory allocation?
The amount of space or memory is occupied or allocated depends upon the data type of the variables that are declared. So let’s explain the same by considering an example: Let’s say the variable is declared as an integer type then 32 bits of memory storage is allocated for that particular variable.
So based on the data type of the variable, the memory space will be allocated.
| Explore Core Java Programming Tutorial For More Information. |
18. Define the advantages and disadvantages of the heap compared to a stack?
The advantages of the heap compared to a stack are listed below:
- Heap is more flexible when compared to a stack
- Memory space of the heap can actually be allocated and de-allocated as per the need.
On the contrary, the disadvantages of the heap compared to a stack is listed below:
- The memory of the heap is slower when compared to the memory of the stack
19. Explain how new data can be inserted into the tree?
The following are the steps that you need to follow to insert the data into the tree:
- First of all, check whether the data is unique or not ( i.e. check whether the data that you are going to insert doesn’t already exist in the tree).
- Then check if the tree is empty. If the tree is empty then all you need to do is just insert a new item into the root. If the key is smaller than that of a root’s key then insert that data into the root’s left subtree or otherwise, insert the data into the right side of the root’s subtree.
20. Can you tell me the minimum number of nodes that a binary tree can have?
A binary tree is allowed or can have a minimum of zero nodes. Further, a binary tree can also have 1 or 2 nodes.
21. Explain a little bit about the dynamic data structure?
The nature of the dynamic data structure is different compared to the standard data structures, the word dynamic data structures means that the data structure is flexible in nature. As per the need, the data structure can be expanded and contracted. Thus it helps the users to manipulate the data without worrying too much about the data structure flexibility.
22. Define what is an array?
While referring to array the data is stored and utilized based on the index and this number actually co-relates to the element number in the data sequence. So thus making it flexible to access data in any order. Within programming language, an array is considered as a variable having a certain number of indexed elements.
23. Can you tell me the minimum number of queues that are needed to implement a priority queue?
The minimum number of queues that are needed is two. Out of which, one queue is intended for sorting priorities and the other queue is meant for the actual storage of data.
24. List out all different sorting algorithms that are available and state which sorting algorithm is considered as the fastest?
The list of all sorting algorithms are below:
- Quicksort
- Bubble sort
- Balloon sort
- Radix sort
- Merge sort
Out of the above sorting options, none of the sorting algorithms can be tagged as the fastest algorithm, because each of these sorting algorithms is defined for a specific purpose. So based on the data structure and data sets available the sorting algorithms are used.
25. Explain what is a dequeue?
A de queue is nothing but a double-ended queue. Within this structure, the elements can be inserted or deleted from both sides.
26. Explain the process of how a selection sort works?
A selection sort is a process where it picks up the smallest number from the entire data setlist and places it at the beginning. The same process is continued where the second position is already filled in. The same process is continued all the way until the list is completed. The selection sort is defined as a simple sort algorithm when compared to others.
Data Structures Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
27. Explain what is a graph?
A graph is nothing but a type of data structure that has a set of ordered pairs. In turn, these pairs are again acknowledged as edges or arcs. These are used to connect different nodes where the data can be accessed and stored based on the needs.
28. Is it possible to implement a stack using a queue?
Yes, you can implement a stack using two queues. Any data structure to act like a stack should have a push() method to add data on top and a pop() method to remove the top data.
29. How would you implement a queue using a stack?
Using two stacks, you can implement a queue. The purpose is to complete the queue's en queue operation so that the initially entered element always ends up at the top of the stack.
- First, to enqueue an item into the queue, migrate all the elements from the beginning stack to the second stack, push the item into the stack, and send all elements back to the first stack.
- To dequeue an item from the queue, return the top item from the first stack.
30. Where is the LRU cache used in data structure?
In data structures, you use LRU (Least Recently Used) cache to organize items in order of use, enabling you to quickly find out which item hasn't been used for a long time.
31. Which Data Structure is used to implement LRU cache?
To implement the LRU cache, you should use two data structures: a hashmap and a doubly linked list.
A hashmap helps with the lookup of cached keys, and a doubly-linked list helps maintain the eviction order.
32. What is the difference between an array and a linked list?
Array and Linked list are two ways of organizing the data in memory. The below table lists the various differences between the array and linked lists:
| Array | Linked List |
| An array is a sequence of elements of a similar data type. | A Linked list is a set of objects known as a node, where it internally consists of two parts, i.e., data and address. |
| It can be accessed irregularly using the array index. | Linked lists support random access. Only supports sequential access. |
| Array elements store in contiguous locations in memory. | New elements can be stored anywhere, and a reference is created for the new element using pointers. |
| In arrays, memory allocation is done during compile time. | In linked lists, memory allocation is done during runtime. |
| Array size must be defined at the time of declaration/initialization. | Linked list size grows when new elements are inserted or deleted. |
33. What are the advantages of Linked Lists over Array?
The following are the advantages of Linked Lists over Arrays:
- Dynamic Data Structure - A Linked list is a dynamic data structure so that it can grow at runtime by deallocating and allocating memory. There is no need to present the linked list initial size.
- Insertion and Deletion Operations - Insertion and Deletion operations are easier in linked lists. You need to have to update the address present in the next pointer of a node.
- Implementation - Data structures like queue, tree, and stack are easily implemented using the Linked list.
- No memory wastage - Efficient memory utilization can be achieved in the linked lists.
34. What are the applications of a stack in a data structure?
Following are some of the essential applications in a data structure:
- Expression evaluation
- Backtracking
- Function calling and return
- Memory management
- Checking parenthesis matching in an expression
35. What are the different types of Linked List?
The following are the different types of Linked Lists.
- Singly Linked List - This is the most common type, and each node has data and a pointer to the next node.

- Doubly Linked List - In this type, the pointer is added to the previous node, either in a forward or backward direction.
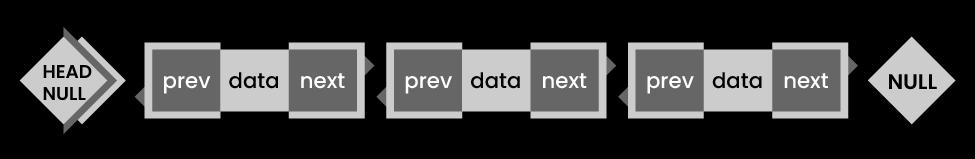
- Circular Linked List - In this type, the last element is linked to the first element.

36. What is the difference between storage structure and file structure?
The main difference between storage structure and file structure depends on the memory area that is accessed.
- Storage structure: It's a data structure representation in computer memory.
- File structure: It's a storage structure representation in the auxiliary memory.
37. What operations can be performed on a stack?
Mainly the following operations are performed on a stack:
- Push operation: To add an item to the stack. If the stack is complete, then it is in an overflow condition.
- Pop operation: It is used to remove an item from the stack. If it's an empty stack, then it is in underflow condition.
- isEmpty operation: If the stack is empty returns true, else false.
- Peek or Top operation: This returns the top element of the stack.
38. Name some applications of data structures?
- Operating system
- Artificial Intelligence
- Statistical analysis
- Database management
- Compiler design
- Graphics
- Simulation
- Numerical analysis
39. Explain about Linked List Data Structure.
A linked list is a series of data structures connected via links. In simple words, it's a sequence of links that contain items. After the array, the linked list is the second most used data structure. The essential terms to understand the linked list are:
Link - In a linked list, each link stores data called an element.
Next - In a linked list, each link is connected to the following link called next.
LinkedList - It contains the connection link to the first link called first.
The below diagram depicts how nodes are connected in the Linked List:

Basic operations supported by a linked list:
- Insertion - Inserts an element at the list beginning.
- Deletion - Deletes an element at the list beginning.
- Display - Displays the complete list.
- Search - Searches an element using the given key.
- Delete - Deletes an element using the given key.
40. Are linked lists considered non-linear or linear data structures?
It depends on where you plan to use Linked lists. You can consider a linked list for both non-linear and linear data structures. When used for data storage, it is regarded as a non-linear data structure. When used for access strategies, it is considered a linear data structure.
41. What is a doubly-linked list used for?
A doubly linked list is o
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Core Java Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Ravindra Savaram is a Technical Lead at Mindmajix.com. His passion lies in writing articles on the most popular IT platforms including Machine learning, DevOps, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, RPA, Deep Learning, and so on. You can stay up to date on all these technologies by following him on LinkedIn and Twitter.
















