- Abstraction in Java
- Clojure Tutorial
- Control Statements in Java
- Core Java Interview Questions
- Data Types in java
- Top 9 Java EE Frameworks
- Java EE vs Spring Framework
- Java Frameworks List - Top 14 Java Frameworks
- Java Interview Questions
- Java Tutorial
- Java Web Dynpro Interview Questions
- JavaFX Interview Questions
- Method Overloading in Java
- Multithreading in Java
- List of Popular Open Source Java Build tools
- Operators in Java
- Program Logics in Java
- String Handling in Java
- Why You Should Learn Java Programming
- Data Structures Interview Questions
- Exception Handling in Java
- Multithreading Interview Questions
- Design Patterns Interview Questions and Answers
- C++ Interview Questions and Answers
- JSP Interview Questions
- EJB Interview Questions
- SOAP in Web Services
- JPA Interview Questions
- Java Architect Interview Questions
- Java Concurrency Interview Questions
- What is Java Concurrency?
- What is JPA - Complete Tutorial Guide
- What is EJB?
- Java Collections Interview Questions
- Java Swing Tutorial
- Java Stream Tutorial
- Linked List Interview Questions
- Compiler Design Interview Questions
- Java Collection Tutorial
- Java Stream Interview Questions
- Thymeleaf vs JSP
- Thymeleaf Tutorial - What is Thymeleaf
- Socket Programming in Java - What is TCP
- Apache Tomcat Interview Questions
- Capgemini Interview Questions
- Zoho Interview Questions
- PwC Interview Questions
- Hexaware Interview Questions
- Intuit Interview Questions
- Tech Mahindra Interview Questions
- Qualcomm Interview Questions
- Arcesium Interview Questions
- PayTM Interview Questions
- DXC Technology Interview Questions
- Java Developer Job Description
- MAQ Software Interview Questions
- Amdocs Interview Questions
- TCS NQT Interview Questions
- Virtusa Interview Questions
- Siemens Interview Questions
- Tricky Java Interview Questions
DXC is the leading IT services company that offers solutions in design and engineering, data analytics, software applications, cloud services, banking and insurance, mainframe, networks, security, and so on. DXC is mainly providing IT services for B2B companies.
According to the report of Statista (2023), the annual revenue of DXC has hit $17.73 billion US in the 2021 financial year. It's no wonder DXC is ranked as the most prominent IT services company in terms of revenue.
This blog post will show the most useful DXC Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers, Experienced and Advanced learners. These QA covers a range of areas, such as programming concepts in C++ and Java, Computer Networks, Cloud Platforms, Data Structures, Operating Systems, Computer Architecture, and many more. Let’s begin now!
We have categorized DXC Interview Questions into three levels:
Top 10 DXC Interview Questions and Answers
1. What are the DXC CLEAR values?
2. What are the Different Unary Operations that you know?
3. Mention the various data types used in the C language?
4. What are the four pillars of OOP?
5. What is RTOS, and mention its types?
6. What is VPN, and mention its different types?
7. Mention the different layers of the TCP/IP model?
8. What are the many layers of the OSI model?
9. What is Network Reliability?
10. What are the various types of cloud platforms?
DXC Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
1. What are the DXC CLEAR values?
Ans: DXC’s CLEAR values are defined as follows:
C – Client-focused
L – Leadership
E – Execution
A – Aspiration
R – Results
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in Core Java, then enroll in "Core Java Certification Training" - This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
2. What do you mean by the BPaaS solution?
Ans: BPaaS is nothing but Business Process as a Service. In other words, it is the automated delivery of business processes from the cloud. BPaas can be connected with other SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS services. With a PaaS solution, companies can access people, processes, and technology as a pay-per-use service. Thus, businesses can only access resources based on demand, reducing costs dramatically.
3. What are the Different Unary Operations that you know?
Ans: Basically, unary operators act on a single operand and produce a new value. Know that unary operations have equal precedence and follow right-to-left associativity.
Unary operations are listed as follows:
- Unary Minus (-)
- Unary plus (+)
- Prefix Increment (++)
- Prefix Decrement (--)
- Logical Negation - NOT (!)
- Bitwise negation (~)
- Address of Operator (&)
- Indirection (*)
- Size of Operator - the size of(expression )
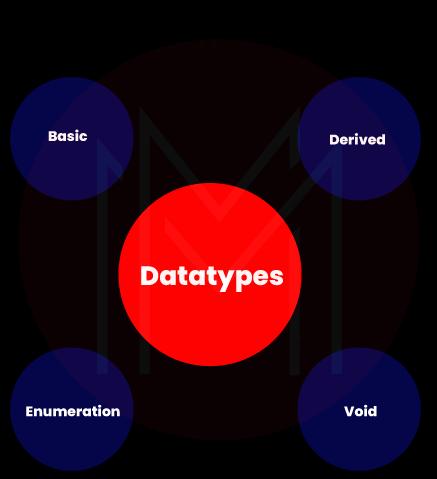
4. Mention the various data types used in the C language?
Ans: C language uses four data types. They are listed as follows:
- Basic data type: It includes data types such as int, float, char, and double.
- Derived data type: It includes data types such as an array, pointer, structure, and union
- Enumeration data type
- Void data type
5. What do you understand by an Abstract Class in Java?
Ans: In Java, it is known as an abstract class when a class is declared with an abstract keyword. An abstract class will have both abstract and non-abstract methods. Note that an abstract class cannot be used to create objects. Also, abstract classes can be accessed only when inherited from another class. They hide crucial information from users and show only the necessary information.
6. What do you understand by OOP and SOP?
Ans: OOP stands for Object-Oriented Programming, in which developers use a set of objects while developing programs. In OOP, data is represented as attributes, and code is represented as methods. Here, objects communicate within themselves by passing messages. Besides, you can easily modify programs in Object-Oriented Programming.
On the other hand, SOP stands for Structured-Oriented Programming, in which developers use a set of functions or modules while developing programs. In SOP, each function or module acts as a sub-program. Whenever functions are required, they are called by the main program. Unlike OOP, it is challenging to modify programs in the SOP.
| Related Article: A Complete Guide for Java Tutorial |
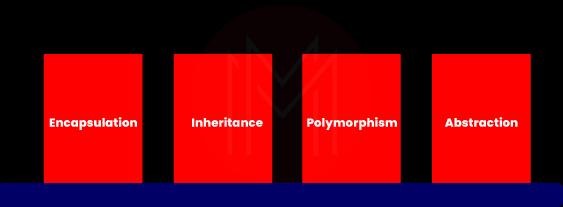
7. What are the four pillars of OOP?
Ans: The four pillars of OOP are encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. Given below is a brief of them:
Encapsulation: It combines data and methods or procedures into a single unit. Encapsulation is accomplished in the form of classes.
Inheritance: A class is said to have inheritance when it inherits the data and methods of another class. Here, the class from which data and methods are inherited is known as a parent, and the class inherited is known as a child.
Polymorphism: It describes a property in which you can use different classes with the same interface. Here, data can be processed in more than one form. So, it allows sending any message to the objects of different classes. Method Overriding and Operator Overloading are the two ways used in polymorphism.
Abstraction: It is about hiding the internal details of the objects from the data source and allowing users to see only the necessary information.
8. What are the types of Operating Systems?
Ans: Given below are the various Operating Systems used in computer applications:
- Batch Operating System
- Time-sharing or multitasking Operating System
- Distributed Operating System
- Network Operating Systems
- Real-time Operating Systems
- Mobile Operating Systems
9. What is Demand Paging in OS?
Ans: In-demand paging, the pages of the secondary memory are loaded into the main memory based on demands. In other terms, it is the process of loading pages into the main memory on-demand. With demand paging, we can have a large virtual memory. Also, we can run programs that are larger than physical memory. On the whole, we can say it simplifies page transfer.
10. What do you understand by a Process Scheduler in Operating Systems, and mention the different Scheduling Algorithms?
Ans: A Process scheduler assigns various processes to the CPU based on scheduling algorithms.
Following are the six scheduling algorithms of Operating Systems.
- First Come First Serve Scheduling (FCFS)
- Shortest Job Next Scheduling (SJN)
- Priority Scheduling
- Shortest remaining time
- Round Robin Scheduling (RR)
- Multiple level queues scheduling
11. What is RTOS, and mention its types?
Ans: RTOS is known as a Real-Time Operating System. It supports accepting and processing real-time events within a short time. RTOS is specially used in environments where processing time must be short. That is why RTOS is mainly employed in air traffic control systems, industrial control, telephone switching equipment, etc.
Know that the following are the three types of RTOS.
- Hard Real-Time Operating System
- Soft Real-Time Operating System
- Firm Real-Time Operating System
12. What is VPN, and mention its different types?
Ans: VPN is the Virtual Private Network used to establish a protected network while using public networks. VPN uses the encryption method to protect your data and network. All you have to notice here is that encryption takes place in real-time. Mainly, VPN helps to hide IP addresses by hiding your location. As a result, you can restrict unauthorized people from entering your network and accessing data.
The following types of VPN;
PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunnelling Protocol
L2TP: Layer-2 Tunnel Protocol
Open VPN: Open source VPN
SSTP: Secure Socket Tunnelling Protocol
IKE2: Internet Key Exchange version 2
13. Mention the different layers of the TCP/IP model?
Ans: The following are the four layers of the TCP/IP model:
- Application/Process layer
- Host to Host/ Transport layer
- Internet layer
- Network Access/Link layer
14. What are the many layers of the OSI model?
Ans: The following are the layers of the OSI model:
- Physical layer
- Data Link layer
- Network layer
- Transport layer
- Session layer
- Presentation layer
- Application layer
| Related Article: Advanced Level Core Java Interview Questions and Answers |
15. What is Network Reliability?
Ans: The reliability of a network depends on the frequency of failures on a network and the time taken to recover from the failures. This way, network monitoring systems, and devices play significant roles in tracking and ensuring network reliability. Generally, network reliability is measured by the following three factors.
- Downtime
- Catastrophe
- Failure frequency
16. What do you mean by DNS?
Ans: DNS is known as the Domain Name System. It maps the directory of names with numbers where numbers denote IP addresses. Or, we can say, DNS translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses. Actually, DNS is the TCP/IP application layer protocol used to transfer messages between clients and servers. To understand easily, let us compare DNS with a phonebook. Each name will have its corresponding phone number in a phonebook, like IP addresses in DNS.
17. What do you mean by Routers in a Computer Network?
Ans: A router is a device that links two or more networks or subnetworks. Here, networks are packet-switched. Routers carry out two vital functions: one is forwarding data packets to target IP addresses. Another one is, allowing many devices to use a single internet connection.
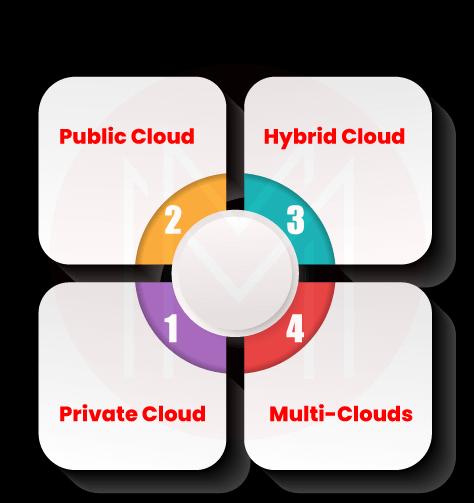
18. What are the various types of cloud platforms?
Ans: There are four types of cloud platforms: Private Clouds, Hybrid Clouds, Public Clouds, and Multi-clouds. Let’s look over them one by one.
Private Clouds: They can be used by a single user or group dedicatedly. With a private cloud, end-users can own and manage cloud resources according to their needs. Know that private clouds are further divided into managed private clouds and dedicated ones.
Public Clouds: They are not owned by end-users or groups, but they can use the cloud environment. For example, Alibaba Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and IBM Cloud are a few examples of public clouds.
Hybrid Clouds: They are formed by private clouds and public clouds, but there must be at least one private cloud. They are connected through LAN, WAN, VPN, and API connections.
MultiClouds: They are cloud platforms created by more than one public cloud and different cloud services or vendors.
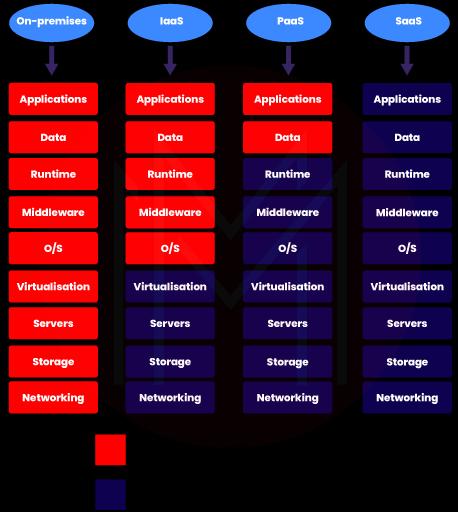
19. What do you mean by SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS?
Ans: SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS are cloud services that can be used by users or groups based on their needs.
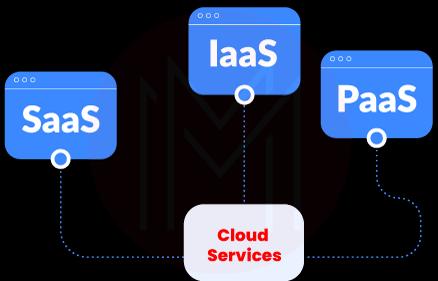
SaaS: It is Software as a Service With a SaaS service, you can access the required software from the cloud over the internet. Here, the entire infrastructure is managed by a third-party vendor. You can only access and use the software in this service, not more than that.
PaaS: Platform as a Service With a PaaS service, both hardware and software can be accessed over the internet. And you can only manage data and applications.
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service With an IaaS service, you can manage applications, data, middleware, and OS. The other resources, such as servers, storage, etc., are only managed by the cloud vendors.
20. What do you mean by Git?
Ans: Git is an open-source and version control system, and a distributed code management tool. Whether content management or configuration management, you can use Git for better results. With this tool, you can avoid code conflicts while many developers work on different project modules parallel. Version control system eases the traceability of written codes. So, developers can access them easily whenever they need them.
DXC Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced
21. What do you mean by Tree Traversals?
Ans: Tree traversal is the data structure in which the arrangement of nodes forms a tree shape. And traversal represents visiting the nodes of the tree. There are three ways of traversing through nodes of a tree. Let’s find the listicles below:
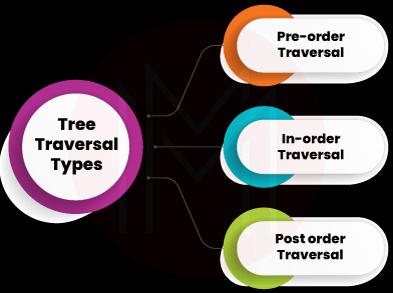
- Pre-order traversal: It follows the 'root-left-right' path in which the root node in a tree is visited first, then left nodes are visited, and finally, right nodes are visited.
- In order traversal: It follows the ‘left-root-right’ path in which left nodes in a tree are visited first, then the root node is visited, and finally, right nodes are visited.
- Post-order traversal: It follows the ‘left-right-root’ path in which left nodes of a tree are visited first, then right nodes are visited, and lastly, the root is visited.
22. Differentiate between BFS and DFS?
Ans:
| BFS | DFS |
| BFS is the short form of Breadth-First-Search | DFS is the short form of Depth-First-Search |
| It uses queue data structure to find the shortest path | It uses the stack data structure to find the shortest path |
| It searches all the neighbour nodes at first, so it is best suitable for searching vertices closer to the source | It goes beyond neighbour nodes during searching, so it is suitable for games and puzzle applications. |
| It requires large size memory | Less memory is required |
23. What are the Advantages of C++ Language?
Ans:
Portability: A same C++ program can be run on Windows, Linux, and macOS platforms.
Reliability: With its featured concepts such as classes, polymorphism, inheritance, and encapsulation, C++ supports reusability and increases the reliability of programs.
Multi-paradigm: C++ allows different styles of programming – Generic, Object-oriented, and Imperatives. These three styles are known as the three paradigms of C++.
Low-level Manipulation: As C++ is closely related to C programming, it makes low-level data manipulation after a certain level.
Memory Management: C++ allows developers to have complete control over memory. It can be achieved by Direct Memory Allocation (DMA) with pointers.
Scalability: C++ can run small codes as well as large-scale codes. When there is a need to expand programs, C++ adapts to it and offers feasibility.
| Related Article: Multithreading in Core Java |
24. Can you tell the limitations of inheritance in Java?
Ans: The dependence between parent and child classes is the minus point of inheritance in Java. Consider that parent and child classes are tightly-coupled, so changing the codes of a parent class will affect all the child classes that inherit from the parent class. This dependency will decrease the efficiency of programs finally.
25. Can you list out the PROS and CONS of OOP languages?
Ans: Java, Python, C++, and Objective-C are a few examples of OOP languages. They have both PROS and CONS. Let’s find the listicles below:
PROS of OOP Languages:
Reusability: OOP allows using written codes as many times as possible. It can be done using classes.
Redundancy: OOP allows using the same functionalities in multiple classes. It means applying inheritance in programming.
Easy Maintenance: Developers can easily modify codes to create new ones.
Security: The features such as abstraction and data hiding help provide only the necessary data, thereby ensuring data security.
CONS of OOP Languages:
Size: OOP programs are usually larger than other programs
Speed: As program sizes are large, program execution speed tends to be slow.
Complexity: Before working in OOP, developers must have developed their programming skills significantly. Otherwise, they could create complexity in programs.
Limited use: OOP is not a universal method, so it cannot be used everywhere. So, you cannot solve all problems using OOP.
26. What are the requirements for a pure OOP language?
Ans: For a language to be classified as a pure OOP language, it must have the following seven qualities:
- Encapsulation/Data Hiding
- Inheritance
- Abstraction
- Polymorphism
- Every predefined type is an object
- Every operation performed on an object has to be a method exposed to the objects
- Every user-defined type is an object
27. What do you mean by Coupling in OOP?
Ans: Coupling refers to the knowledge that an element has in relation to another element. There are two types of coupling in OOP based on one element's degree of knowledge over another. They are known as – Tight Coupling and Loose Coupling.
Tight Coupling: In this type, the changes you make in one class affect another class.
Loose Coupling: In this type, classes are independent, so changes in one class won't affect another class.
28. What do you mean by the inline function in C++?
Ans: Inline function is the enhancement feature used in C++, which supports increasing the speed of execution of programs. To effectively use inline functions, you need to keep inline functions as short as possible. Suppose you convert a large function into an inline function; it may lead to a 'code bloat' and decrease the program's quality.
The syntax for the inline function is given as:
inline return_type function_name (data_type arg1, data_type arg2)
{
//definition
}29. Can you brief me about Servlet Collaboration?
Ans: It is the process of exchanging data between servlets of a Java application. To effectively carry out servlet collaboration, every servlet must know about other servlets.
Servlet collaboration is performed by two interfaces as given below:
- Javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher
- Javax.servlet.http:HttpServletResponse
30. Write a Java program to print a half Pyramid using numbers?
Ans:
Program:
Public class Main{
Public static void main (string[ ] args) {
int rows=5;
for (int i=1 ; i<=rows ; ++i) {
for (int j=1 ; j<=i ; ++i) {
system.outprint (j + " " );
}
system.out.println();
}
}
}Output:
1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
31. What do you mean by public static main void (string args []) in Java?
Ans:
![public static main void (string args []) in Java](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn.mindmajix.com%2Fblog%2Fimages%2Fpublic-static-main-void-110822.png&w=1080&q=75)
Public: It is the access modifier. It defines who to access the method and where to access the method.
Static: It is a keyword. It allows JVM to load the class into memory.
Void: It is also a keyword. Void is used to mention that a method won’t return any values.
Main: It is an identifier. Main represents the ‘Java main method’ and the starting point of the java program.
String [] args: It is an array type. It belongs to the class of ‘Java.lang.String’ and stores command-line arguments of Java.
32. Can you differentiate between C++ and Java?
Ans:
| C++ | Java |
| Supports both Object-Oriented Programming and Procedural Programming | Supports only Object-Oriented Programming |
| C++ is platform-dependent and works based on the concept of – Write Once and Compile Anywhere | It is platform-independent and works based on the concept of – Write Once and Run Anywhere. |
| C++ can be compiled but cannot be interpreted | Java allows both compiling and interpreting |
| It is provided with limited libraries and low-level functionalities | It is provided with plenty of libraries. |
| It supports operator overloading, pointers, unions, and Goto statements. | Java doesn’t support all these features. |
33. How would you differentiate String Builder and String Buffer in Java?
Ans:
| String Builder | String Buffer |
| It was introduced with version - Java 1.5 | It was introduced with version - Java 1.0 |
| Operations are not thread-safe because string Builder is not synchronized | Have thread-safe operations because of synchronization |
| It can be used in a single-threaded environment | It can be used while multiple threads are working on the same string |
| It is efficient when compared with StringBuffer | Not efficient when compared with StringBuilder |
34. What do you understand by Wrapper Classes in Java?
Ans: Generally, generic classes in Java don’t support primitives, but they support objects. Therefore, while working using primitives, we have to convert primitive values into corresponding wrapper objects. Note that primitive values can be converted into the corresponding wrapper classes manually. You can achieve this using constructor or factory methods.
35. Differentiate: Compile-time Polymorphism and Runtime Polymorphism?
Ans:
| Compile-time Polymorphism | Runtime Polymorphism |
| Also known as early or static binding | Known as late or dynamic binding |
| It is achieved through the process - Method Overloading | It is achieved through the process – Method Overriding |
| Java Virtual Machine (JVM) calls the proper method during compile time | JVM calls the proper method only at runtime |
| Execution is faster | Execution is slower |
| Less flexible | More flexible |
36. Can you create an instance for an abstract class in Java?
Ans: No, we can’t create an instance for an abstract class. As abstract classes in Java are incomplete, they cannot be instantiated. However, we can expand abstract classes.
37. Compare Copy Constructor and Assignment Operator?
Ans:
| Copy Constructor | Assignment Operator |
| It is an overloaded constructor | It is a bitwise operator |
| It allows copying existing objects without affecting source objects | It allows assigning new values to variables |
| It creates a separate memory block while copying | It doesn’t create any memory space |
38. How would you differentiate Abstract Class and Interface in Java?
Ans: An abstract class has both abstract and non-abstract methods. Interface, on the other hand, has only abstract methods. The abstract class supports multiple inheritances, whereas an interface cannot support multiple inheritances. Moreover, 'extends' is the keyword used to extend abstract classes; the interface uses 'implements' as the keyword for implementation.
39. What do you mean by volatile keyword?
Ans: A volatile keyword changes the value of a variable with the support of threads. The volatile keyword usually doesn’t store the values of variables in caches but reads them from the main memory. In a way, volatile memory reduces the memory consistency error. Note that volatile memory cannot be used with classes or methods.
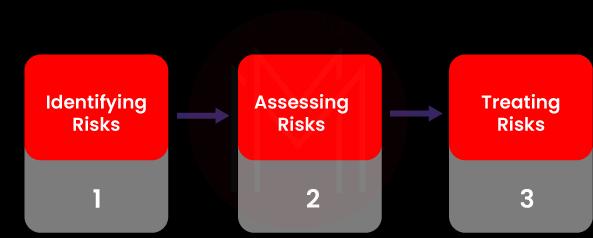
40. What do you mean by Security Risk Management in Computer Networks?
Ans: Security risk management ensures the security of networks through three stages. The three stages include identifying risks, assessing the severity of risks, and treating or controlling risks.
The identification stage includes identifying the affected assets, identifying vulnerabilities, and identifying threats.
The assessment stage includes defining risks and their severity.
The third stage, the treating or controlling stage, includes risk remediation, risk mitigation, risk transfer, acceptance, and avoidance.
41. What are the various Git Repository Functions?
Ans: The following are the various Git repository functions.
- Gitlab
- Gitbucket
- Sourceforge
- GitHub
42. Compare: Git and GitHub?
Ans:
| Git | GitHub |
| It is an open-source software | It is a web-based hosting service |
| It can be installed on local computers. Without servers, developers can manage their source codes on local machines. | It is a cloud service with a built-in user management system and a user-friendly GUI. |
| Helps to manage the history of all source codes | Git Repositories can be loaded on GitHub |
| Git performs operations such as push and pulls, reset, commit, fetch and merge. | It acts as the host to store codes in a centralized place. |
| It supports editing versions of codes and then moving to Git repositories | Repository copies are uploaded on GitHub |
43. Can you brief the differences between Operating Systems and Kernel?
Ans: Operating System is the system software, which interfaces computers and users. On the other hand, Kernel is part of the Operating system and is the core component of the Operating System. Know that Operating System provides security and protection to computers. At the same time, the Kernel performs memory management, task management, disk management, and process management.
44. What do you mean by Bootstrapping in Operating Systems?
Ans: Bootstrap is the initial set of codes used to load the operating system on a computer. It is the first code that runs once the computer is switched on. Bootstrapping is the process that involves self-tests, loading BIOS, configuration settings, etc.
DXC Interview Questions and Answers for Advanced
45. What do you mean by Class and Class declaration in Java?
Ans: A class in Java is a template used to create objects. It also includes object data types and methods. We can define ‘classes’ as categories in which objects are identified as items. The vital point to note is that objects in a class will have common methods and properties.
Know that class declaration in Java includes the following parameters:
- Modifiers
- Class keyword
- Class name
- Superclass
- Interfaces
- Body
46. What do you mean by FCFS Scheduling Algorithms?
Ans: FCFS stands for First Come - First Serve. It is an operating system algorithm that allocates CPU for the jobs that arrive first. The following jobs have to wait until the preceding jobs get completed. Although this algorithm is simple and easy to implement, it yields poor performance as the wait time is longer at times. Know that it supports both pre-emptive and non-preemptive scheduling.
47. Compare the malloc ( ) and calloc ( ) functions in C programming?
Ans:
| malloc( ) | Calloc( ) |
| malloc is the abbreviation of memory allocation | calloc stands for contiguous allocation |
| This function creates a single block of memory | This function creates multiple blocks of memory for variables |
| Malloc doesn't initialize memory | It is initialized with zero value |
| It is faster than calloc | Slower than malloc |
| It doesn't perform memory initialization | Performs memory initialization |
| This function has only one argument | There are two arguments in the calloc function |
48. Differentiate between Preemptive scheduling and Non-preemptive scheduling?
Ans: Preemptive scheduling can be applied when a process switches to a ready state from a running state or waiting for a state. At the same time, non-preemptive scheduling can be applied when a process is terminated or changes from a running state into a waiting state.
In preemptive scheduling, suppose a high-priority job arrives in the ready queue; it stops the execution of the running job in the processor even before completing its burst time and places the running job in the ready queue.
Until the priority job gets completed, the running job will be waiting in the ready queue, and it is allowed for execution once the priority job got over. Whereas in non-preemptive scheduling, interruption is not allowed. The running job will be allowed for execution until completing its burst time.
49. Which type of polymorphism in Java is more important?
Ans: Runtime or overriding polymorphism is considered more important since it has many features such as contracting, plugging, and interfacing. So, it easily allows the development of libraries and frameworks.
50. How would you differentiate hybrid cloud from multi-cloud?
Ans: A hybrid cloud includes a private cloud, whereas a multi-cloud includes more than one public cloud. A hybrid cloud is a combination of both private cloud and public cloud. Note that a multi-cloud can have a private cloud; in that case, it can be both a multi-cloud and hybrid cloud.
A hybrid cloud is used to solve an IT solution, whereas a multi-cloud solves many problems. Also, hybrid may use the on-premises resources, but multi-cloud uses only the cloud resources.
51. How does OOP support Dependency Injection?
Ans: When a software program or module needs external resources to complete its objectives, it uses the dependency injection method. In this method, a piece of code is used to locate the reference resources and how to communicate with them. Moreover, the injected resources can be customized using XML files outside the source code, reducing the burden of compiling the entire codebase.
Conclusion
We are confident that now you will be able to answer questions on programming concepts in C languages and Java in your forthcoming DXC interviews. In addition, you must have been through with data structures, operating systems, etc. Read this blog more than once to become familiar with the DXC QAs. We wish you to bag your dream job as soon as possible.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Core Java Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| Core Java Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















