- Introduction to Amazon Elastic File System
- Amazon On-Demand Instance Pricing
- AWS Kinesis
- Amazon Redshift Tutorial
- Amazon SageMaker - AIs Next Game Changer
- AWS Console - Amazon Web Services
- AWS Architect Interview Questions
- AWS Architecture
- Amazon Athena
- Top 11 AWS Certifications List and Exam Learning Path
- How to Create Alarms in Amazon CloudWatch
- AWS CloudWatch Tutorial
- Introduction To AWS CLI
- AWS Configuration
- AWS Data Pipeline Documentation
- AWS EC2 Instance Types
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk Available in AWS GovCloud (US)
- AWS Free Tier Limits and Faq
- Choosing The Right EC2 Instance Type For Your Application
- AWS Interview Questions And Answers
- AWS Key Management Service
- AWS Lambda Interview Questions
- AWS Lambda Tutorial
- What Is AWS Management Console?
- Complete AWS Marketplace User Guide
- AWS Outage
- AWS Reserved Instances
- AWS SDK
- What is AWS SNS?
- AWS Simple Queue Service
- AWS SysOps Interview Questions
- AWS vs Azure
- AWS Vs Azure Vs Google Cloud Free Tier
- Introduction to AWS Pricing
- Brief Introduction to Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Clean Up Process in AWS
- Creating a Custom AMI in AWS
- Creating an Elastic Load Balancer in AWS
- How to Deploy Your Web Application into AWS
- How to Launch Amazon EC2 Instance Using AMI?
- How to Launch Amazon EC2 Instances Using Auto Scaling
- How to Sign Up for the AWS Service?
- How to Update Your Amazon EC2 Security Group
- Process of Installing the Command Line Tools in AWS
- Big Data in AWS
- Earning Big Money With AWS Certification
- AWS Certification Without IT Experience. Is It Possible?
- How to deploy a Java enterprise application to AWS cloud
- What is AWS Lambda?
- Top 10 Reasons To Learn AWS
- Run a Controlled Deploy With AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Apache Spark Clusters on Amazon EC2
- Top 30 AWS Services List in 2024
- What is Amazon S3? A Complete AWS S3 Tutorial
- What is AMI in AWS
- What is AWS? Amazon Web Services Introduction
- What is AWS Elasticsearch?
- What is AWS ELB? – A Complete AWS Load Balancer Tutorial
- What is AWS Glue?
- AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management)
- AWS IoT Core Tutorial - What is AWS IoT?
- What is Cloud Computing - Introduction to Cloud Computing
- Why AWS Has Gained Popularity?
- Top 10 Cloud Computing Tools
- AWS Glue Tutorial
- AWS Glue Interview Questions
- AWS S3 Interview Questions
- AWS Projects and Use Cases
- AWS VPC Interview Questions and Answers
- AWS EC2 Tutorial
- AWS VPC Tutorial
- AWS EC2 Interview Questions
- AWS DynamoDB Interview Questions
- AWS API Gateway Interview Questions
- How to Become a Big Data Engineer
- What is AWS Fargate?
- What is AWS CloudFront
- AWS CloudWatch Interview Questions
- What is AWS CloudFormation?
- What is AWS Cloudformation
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- What is AWS Batch
- What is AWS Amplify? - AWS Amplify Alternatives
- Types of Cloud Computing - Cloud Services
- AWS DevOps Tutorial - A Complete Guide
- What is AWS SageMaker - AWS SageMaker Tutorial
- Amazon Interview Questions
- AWS DevOps Interview Questions
- Cognizant Interview Questions
- Cognizant Genc Interview Questions
- Nutanix Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Projects and Use Cases
- test info
Are you looking to grow and scale your online business to the next level using cloud-powered services? The AWS network can help you get there. Amazon Web Services (or AWS) is the global leader in providing Infrastructure-as-a-Service (or IaaS) to web users looking for remote and cost-effective web services. In short, it allows you to run your own websites on cloud-powered web or application servers.
AWS EC2 Instance Pricing Introduction
Among the key blocks of AWS technology, EC2 – or Elastic Compute Cloud – is a network of virtual machines running on the AWS cloud. It enables you to run multiple applications on virtual machines that can be scaled up according to your computing requirements.
Thanks to its flexibility, AWS EC2 allows you to choose from different types of EC2 instances each having its own CPU, memory, and storage configurations. Depending on your workload, you can choose the EC2 instance with the operating system and deploy your applications on its servers.
How do you pay for AWS EC2 instances? Based on the fundamental principle of pay-as-you-go, you are charged only for the computing resources that you utilize. Through this guide, we shall discuss the various types and pricing models of AWS EC2 instances, so that you can decide which one is most suitable for your business.
| If you would like to become an AWS Certified professional, then visit Mindmajix - A Global online training platform: "AWS Online Training Course".This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
What are the types of AWS EC2 Instances?
AWS EC2 instances are broadly classified into the following 5 categories:
General Purpose
The most common and popular type of EC2 instance is used for most web applications with a consistent workload.
Compute Optimized
This instance type is designed for highly computer-intensive applications - that require high-performance web servers – such as real-time applications and scientific modeling.
Memory-Optimized
As the name suggests, this is used for memory-intensive applications, for example, those running big data analytics or Hadoop applications.
Accelerated Computing
This instance type is designed for applications that require additional GPUs and parallel processing, for example, tasks such as machine learning and graphics processing.
Storage Optimized
Finally, this instance type is utilized for applications with high storage capabilities such as those with sequential read-write processes.
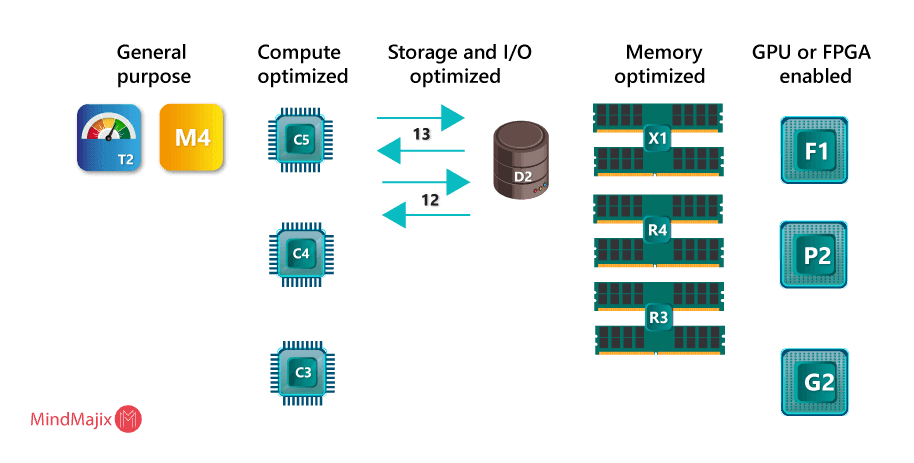
Depending on the EC2 instance category, you can select any of the following instance types:
| Category | Type | Description |
| General Purpose | A1 | Based on AWS Graviton processor and 64-bit ARM Core |
| M5 | Intel-based processes | |
| T3/ T3a | For both Intel and AMD processes, and cost-efficient for dynamic workloads | |
| Compute Optimized | C5 | Suited for high processing applications |
| Memory-Optimized | R5/ R5a | Designed for applications with real-time analytics and large memory caches; utilizes the AWS Nitro System. |
| X1/ X1e | Optimized for applications with high memory requirements such as SAP HANA. | |
| High Memory | Allocates memory as high as 6-12TB in a single instance | |
| Accelerated Computing | P3 | Good for applications that require high parallel processing. |
| G3 | Used for graphics-intensive tasks including rendering and encoding. | |
| F1 | Offers FGPA instances for accelerated processing. | |
| Storage Optimized | H1 | Used for HDD-based storage for large datasets; maximum storage of 16TB |
| D2 | Another HDD-based storage; maximum storage of 48TB | |
| I3 | Used for SSD-based storage with lower latency than H1 & D2; offers AWS Nitro system; maximum storage: 16GB |
Next, let’s understand the 4 different pricing models for AWS EC2 instances and when each of them is recommended.
Which are the 4 Pricing Models for AWS?
Free tier model
With over 60 products, the AWS free tier is offered in the following types:
12-Months Free: Available only for new AWS customers for a period of 12 months following sign-up.
Always Free: These free trials do not expire at the end of 12 months and are available indefinitely for both new and existing AWS customers.
Trials: These are short-term free trials that start from the day of first-time use.
[ Related Article:- 75 AWS Interview Questions ]
1. On-Demand instances
In simple language, you only pay what you consume with on-demand instances. With no upfront payment, you are charged based on the consumed computing capacity – by the day or hour – for the EC2 instance.
2. Reserved instances
Provides a discounted price – up to 75% of on-demand instance costs – in return for a one-time upfront payment. In the long run, reserved instances can be very cost-effective as compared to the on-demand pricing model.
3. Spot instances
This pricing model allows you to bid for spare or unused EC2 computing power for up to 90% of on-demand pricing. Spot instance pricing can depend majorly on the supply & demand for unused AWS EC2 cloud capacity.
4. Dedicated hosts
In this model, an AWS EC2 server is dedicated for your use. You are not billed on the basis of the number of instances that you have used. You can purchase a dedicated host either through an hourly on-demand price or through a reservation price that is 70% cheaper than on-demand pricing.
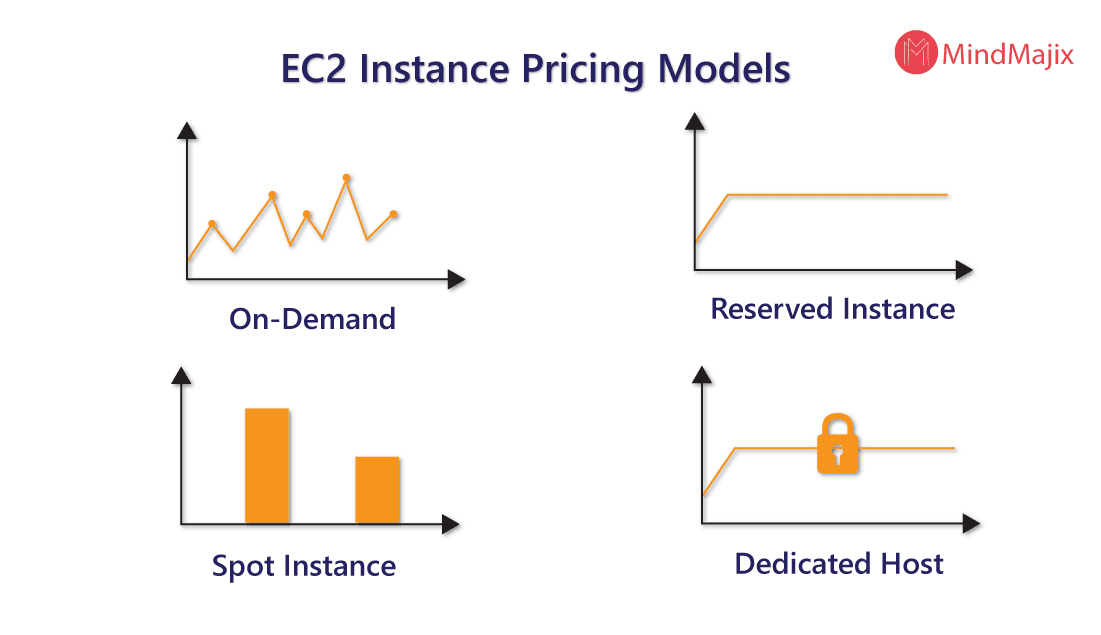
In the following sections, we shall discuss each of these AWS EC2 pricing models in more detail including the type of web applications that they are recommended for.
What are On-Demand instances?
As mentioned earlier, on-demand instances allow you to pay for the instances that you create either by the hour or second (minimum of 60 seconds). Depending on your application, you can either increase or reduce your computing capacity, but only need to pay for the predetermined rate for the instance.
The On-demand pricing model is recommended when:
- You want to utilize the flexibility of the AWS EC2 cloud platform without making any upfront payment or any long-term commitment as a customer.
- You want to deploy web applications that do not have a fixed or predictable workload, including those that are being developed on Amazon EC2 for the first time.
How is the on-demand pricing model beneficial? It allows you to move from higher fixed costs to lower variable costs along with frees you from matters such as planning and purchasing hardware.
You can obtain the hourly rates for On-demand pricing from this AWS EC2 Pricing page. On this page, you can view the rate for each instance type on the basis of the supported OS and the AWS region. For example, here’s a snap of the rates, for instance, type, “General Purpose” on Windows OS and for the “Asia Pacific (Mumbai)” region.
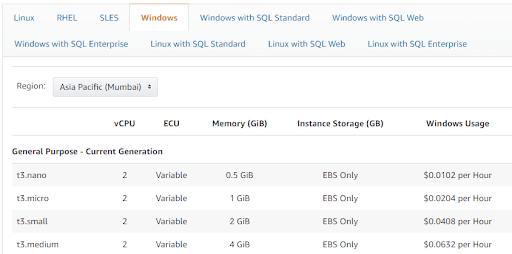
What are Reserved instances?
AWS EC2 Reserved instances enable you to reduce your costs through discounts ranging up to 72%. Using reserved instances, you can avail of a capacity reservation that assigns you a reserved availability zone. This allows you to launch instances whenever you need them. In short, reserved instances is a major cost saver as compared to on-demand instances.
The Reserved pricing model is recommended when:
- You want to deploy applications that have a steady usage pattern and require reserved capacity.
- You are looking for a long-term commitment as a customer – typically one to three years.
How do reserved instances (or RI) work? RI provides you with an hourly rate at a discounted price and optionally, a capacity reservation for running EC2 instances. Additionally, depending on your application needs, you can choose any of the following types of RIs:
Standard RIs offer the best discount – up to 72% off on on-demand pricing – and is designed for applications with steady usage.
Convertible RIs that offer discounts of up to 54% on on-demand pricing, along with the flexibility to modify your RI attributes – for example, instance family, operating system, and tenancy. Like standard RIs, convertible RIs are suited for steady usage applications.
Scheduled RIs that are used to launch instances within a specific time window. This is useful when you want to utilize your available capacity to a predictable and recurring schedule that may require just a fraction of a day, week, or month.
Next, what is the payment model for RIs? Firstly, you can choose between a standard and convertible RI, which are available with the following three payment options:
No Upfront: With no upfront payment, this option offers you a discounted hourly rate - independent of the usage – for the entire 1-year or 3-year term.
Partial Upfront: With this option, you make a low upfront payment and then avail of a discounted hourly rate for the entire term (1-year and 3-year).
All Upfront: Where you pay for the entire RI term with a single upfront payment. This option offers the highest discount (up to 72%) as compared to on-demand instances.
You can obtain the hourly rates for RI pricing from this Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances Pricing page. Here, you can view the hourly rate (and savings over on-demand) for each instance type based on the operating system, standard and convertible plans, term duration (1 or 3 years), and the payment option. For example, here’s a snap of the Standard 1-year term rates for the “a1.medium” instance on Linux OS and for the “Asia Pacific (Mumbai)” region.
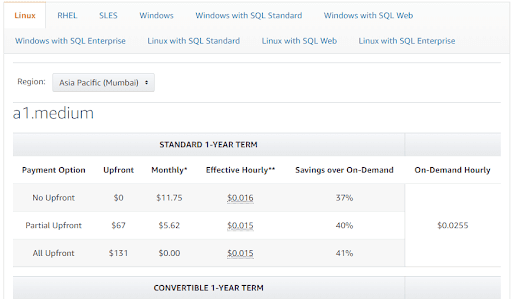
What are Spot instances?
Spot instances enable you to take advantage of unused EC2 capacities and avail of up to 90% discounts on on-demand pricing. This type of instance allows you to bid for available capacities by specifying the maximum spot price that you are willing to pay for an instance. You can then launch your AWS instance whenever its price is lower than your maximum spot price. You can then continue to use the instance until you terminate it or when the spot price exceeds your maximum spot price.
The Spot instance model is recommended when:
- You have applications with flexible start and end times.
- You are looking to run applications at very low compute prices.
- You are looking for large volumes of additional AWS capacities.
As an additional convenience, you can choose to combine spot instances with on-demand or reserved instances that work best to reduce overall costs. You can also run spot instances for a predefined duration – up to six hours – at a discounted price of 30-50% lesser than on-demand prices.
To compare the latest spot prices with the on-demand prices for the same instance configuration, check out the Spot Instance Advisor.
You can also obtain the spot instance prices for Windows and Linux/ UNIX from the Amazon EC2 Spot Instances Pricing page. On this page, you can spot prices for each instance type on the basis of the supported OS (Windows, Linux) and the AWS region. For example, here’s a snap of the spot prices for instance, “General Purpose” for the “Asia Pacific (Mumbai)” region.
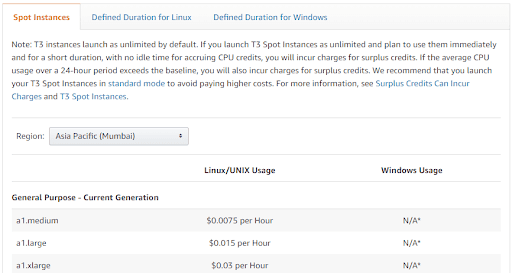
What are Dedicated hosts?
A dedicated host is a physical server allocated by Amazon EC2 for your sole usage in order to address all your compliance-related requirements. The dedicated host is integrated with the AWS License Manager that allows you to use your existing software licenses such as Microsoft Windows Server and SQL Server.
In summary, the AWS Dedicated host combines the flexibility of AWS with the cost-effectiveness of using your existing licenses.
A dedicated host is highly recommended when:
- You need complete visibility and control over how your instances are running on your server.
- You have applications that need to launch dedicated AWS instances on a physical server.
- You need to deploy your application instances on the same server over an extended period of time.
- You already have existing software licenses that need to be deployed on a physical server.
What are the benefits of using a dedicated server? It helps you save money by leveraging on your investments into existing software licenses, and also meets corporate compliance requirements of running application instances on a dedicated physical server.
Next, what is the payment model for dedicated hosts? You can avail of any of the following two payment models:
On-Demand: Here you pay for each second (minimum: 60 seconds) that your dedicated server is active for your purpose. You can also terminate this second-based billing any time by releasing your dedicated host.
Reservation: This works similarly to the way AWS reserved instances work. It can offer up to 70% discount on its price as compared to the on-demand pricing model. Similarly, you can avail of the three payment options – All Upfront, Partial Upfront, and No Upfront – when you purchase a dedicated host through reservation.
You can obtain the hourly price for a dedicated host from this Amazon EC2 Dedicated Hosts Pricing page. Here, you can view the configuration table for dedicated hosts, along with the on-demand and reservation pricing for instance type according to the AWS region. For example, here’s a snap of the on-demand pricing for instance type, “General purpose” and “Asia Pacific (Mumbai)” region.
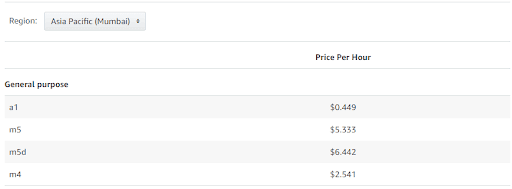
How to Estimate AWS EC2 Instance Cost using AWS Calculator
How do you estimate the cost for a given instance? Here’s what you need to do:
- Create an estimate from the AWS Pricing Calculator page.
- On the next page, click Configure for Amazon EC2 service.
- Select your nearest region and then select the “Quick estimate” option.
- Specify the operating system on which you want to run your EC2 instance.
- For the instance type, either enter the minimum hardware requirements (vCPU, Memory) or search for the desired instance name (example, t3a.nano).
- Next, enter the number of EC2 instances that you would need.
- From the “Pricing strategy” section, specify the following:
-
- Pricing model – On-demand, reserved, or savings plan
- Reservation term – only for reserved instances
- Payment options – only for reserved instances
8. Finally, click “Add to my estimate” to view your estimated price. For example, as shown below:
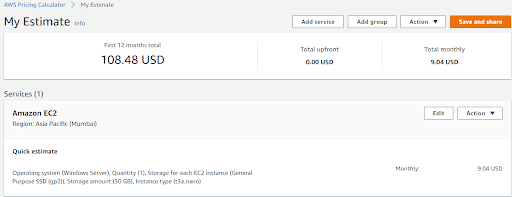
Any More Tips To Save AWS Costs?
Being a flexible platform, AWS EC2 allows you to configure your instance according to your requirements and budget. Additionally, here are useful tips that will further help you save costs on EC2 instances:
Select the cheapest EC2 instance that fulfills your requirements.
You are advised to not spend your money on expensive instance types if you don’t need them. Instead, opt for the auto-scaling groups if you have varying loads on your applications. You can also use auto-scaling to create a cluster of EC2 instances to satisfy your growing business.
Go for minimum instance load.
If you are using an instance type with a large CPU or memory utilization, try minimizing the instance load to reduce the overall costs. Additionally, you can run your entire operation in a hassle-free way.
Use reserved or spot instances.
You can also reduce your costs by opting for reserved or spot instances. The on-demand instance model works best only when you need to run your EC2 instances for a few hours or few days every week. If you need to utilize more from your instances, reserved or spot instances are a better alternative.
Remember to turn off EC2 instances when not required.
Sometimes, EC2 instances can keep running, thus adding to your costs. Learn to switch off non-production systems when they are not required. You can also use automation to turn off such instances when they are no longer in use.
Identify and stop the EC2 instances with low utilization.
Identify the running EC2 instances that are either idle or being under-utilized. You can then reduce your costs by stopping or downsizing them. You can make use of the AWS Billing and Cost Management tool to optimize your ECS costs. Further, you can use the AWS Instance Scheduler to stop instances or the AWS Operations Conductor to downsize the EC2 instances.
Conclusion
At the outset, you can choose from a variety of AWS EC2 services that serve your application needs. This guide provides a basic understanding of pricing models in the AWS EC2 cloud platform. As an AWS user, you can make the most of the detailed EC2 pricing models to determine which works best for your applications.
What has been your key takeaway from this article? Do share your comments on the AWS EC2 instance type that you are using and how are you minimizing your costs?
Looking forward to your views and suggestions.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |
| AWS Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| AWS Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| AWS Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |

Technical Content Writer
















