- Introduction to Amazon Elastic File System
- Amazon On-Demand Instance Pricing
- AWS Kinesis
- Amazon Redshift Tutorial
- Amazon SageMaker - AIs Next Game Changer
- AWS Console - Amazon Web Services
- AWS Architect Interview Questions
- AWS Architecture
- Amazon Athena
- Top 11 AWS Certifications List and Exam Learning Path
- How to Create Alarms in Amazon CloudWatch
- AWS CloudWatch Tutorial
- Introduction To AWS CLI
- AWS Configuration
- AWS Data Pipeline Documentation
- AWS EC2 Instance Types
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk Available in AWS GovCloud (US)
- AWS Free Tier Limits and Faq
- AWS EC2 Instance Pricing
- Choosing The Right EC2 Instance Type For Your Application
- AWS Interview Questions And Answers
- AWS Key Management Service
- AWS Lambda Interview Questions
- AWS Lambda Tutorial
- What Is AWS Management Console?
- Complete AWS Marketplace User Guide
- AWS Outage
- AWS Reserved Instances
- AWS SDK
- What is AWS SNS?
- AWS Simple Queue Service
- AWS SysOps Interview Questions
- AWS vs Azure
- AWS Vs Azure Vs Google Cloud Free Tier
- Introduction to AWS Pricing
- Brief Introduction to Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Clean Up Process in AWS
- Creating a Custom AMI in AWS
- Creating an Elastic Load Balancer in AWS
- How to Deploy Your Web Application into AWS
- How to Launch Amazon EC2 Instance Using AMI?
- How to Launch Amazon EC2 Instances Using Auto Scaling
- How to Sign Up for the AWS Service?
- How to Update Your Amazon EC2 Security Group
- Process of Installing the Command Line Tools in AWS
- Big Data in AWS
- Earning Big Money With AWS Certification
- AWS Certification Without IT Experience. Is It Possible?
- How to deploy a Java enterprise application to AWS cloud
- What is AWS Lambda?
- Top 10 Reasons To Learn AWS
- Run a Controlled Deploy With AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Apache Spark Clusters on Amazon EC2
- Top 30 AWS Services List in 2024
- What is Amazon S3? A Complete AWS S3 Tutorial
- What is AMI in AWS
- What is AWS? Amazon Web Services Introduction
- What is AWS Elasticsearch?
- What is AWS ELB? – A Complete AWS Load Balancer Tutorial
- What is AWS Glue?
- AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management)
- AWS IoT Core Tutorial - What is AWS IoT?
- What is Cloud Computing - Introduction to Cloud Computing
- Why AWS Has Gained Popularity?
- Top 10 Cloud Computing Tools
- AWS Glue Tutorial
- AWS Glue Interview Questions
- AWS S3 Interview Questions
- AWS Projects and Use Cases
- AWS VPC Interview Questions and Answers
- AWS EC2 Tutorial
- AWS VPC Tutorial
- AWS EC2 Interview Questions
- AWS DynamoDB Interview Questions
- AWS API Gateway Interview Questions
- How to Become a Big Data Engineer
- What is AWS Fargate?
- What is AWS CloudFront
- AWS CloudWatch Interview Questions
- What is AWS CloudFormation?
- What is AWS Cloudformation
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions
- What is AWS Batch
- What is AWS Amplify? - AWS Amplify Alternatives
- AWS DevOps Tutorial - A Complete Guide
- What is AWS SageMaker - AWS SageMaker Tutorial
- Amazon Interview Questions
- AWS DevOps Interview Questions
- Cognizant Interview Questions
- Cognizant Genc Interview Questions
- Nutanix Interview Questions
- Cloud Computing Projects and Use Cases
- test info
Businesses consider cloud computing to store and retrieve their data. Clouds can assist businesses in lowering their IT operations expenses, enhancing cybersecurity, and speeding up computing. If you're considering integrating cloud computing services into your company, it's imperative first to understand the types of cloud computing services accessible to you.
This article describes what cloud computing is, the types of cloud computing, and major cloud computing services.
| Types of cloud computing - Table of Contents |
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the supply of on-demand IT resources over the internet, to put it simply. These businesses provide cloud computing services and are known as cloud service providers (CSPs). Through a number of billing models, CSPs charge users or organizations according to the amount of Cloud resources they utilize. With the use of a hypervisor, cloud resources can be separated from the underlying physical hardware. However, because Cloud computing encompasses a variety of service kinds and deployment strategies, there is a great deal of uncertainty surrounding it.
| If you want to become a Certified AWS Solution Architect? then enroll in "AWS Online Course Training". This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
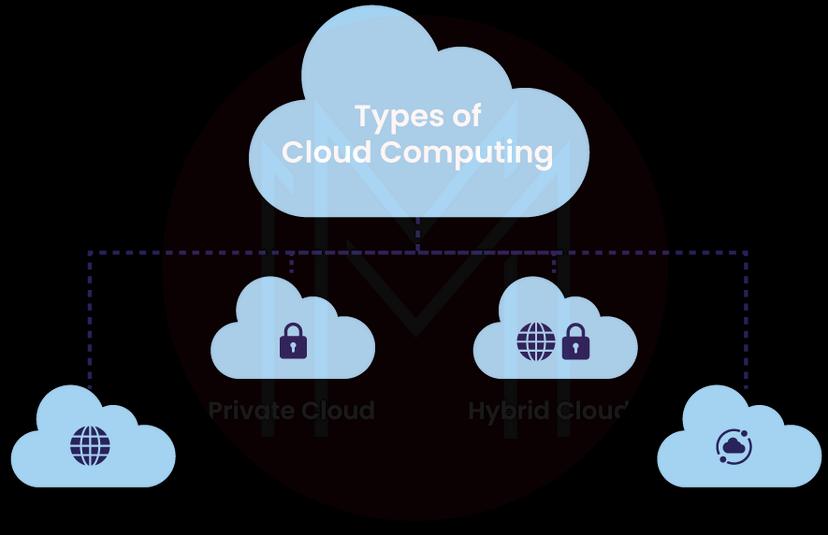
Types of Cloud Computing
Public, hybrid, private, and multi-clouds are the four basic types of cloud computing. Software-as-a-service(SaaS), Platforms-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) are the three major classifications of cloud computing services.
What's the same?
Each cloud pools, abstracts, and distributes scalable computer resources over a network. Every cloud type allows for cloud computing, which is the practice of running workloads there. Additionally, each cloud is built using different technologies, nearly always including an operating system, application programming interfaces (APIs), and a management platform. Automation and virtualization technologies can be added to all types of clouds for additional features or greater efficiency.
What's different?
It used to be simple to distinguish between private clouds, public clouds, multiclouds, and hybrid clouds based on their ownership and location. But things aren't really that easy anymore. As a result, there are many limitations while we compare the differences below.
#1. Public Clouds
IT infrastructure that the end user does not own is frequently used to create public clouds. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Alibaba Cloud, IBM Cloud, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are a few of the biggest public cloud service providers.
Public clouds have always operated off-site in the past, although today's public cloud providers have begun to provide cloud services on clients' on-site data centers. As a result, geographic and ownership disparities are no longer significant.
As soon as the environments are divided up and made available to various tenants, they all become public clouds. Public clouds no longer require cost structures because some cloud service providers offer clients access to their clouds without charge. Additionally, it is feasible to construct and sell a cloud platform as PaaS or to abstract and resell the bare-metal IT infrastructure utilized by public cloud providers as IaaS.

The advantages of using a Public cloud are:
- High Scalability
- Reduces costs
- Dependability and flexibility
The disadvantages of using a Public cloud are:
- Data privacy and security
- Data loss
- Limited visibility
- Unexpected costs
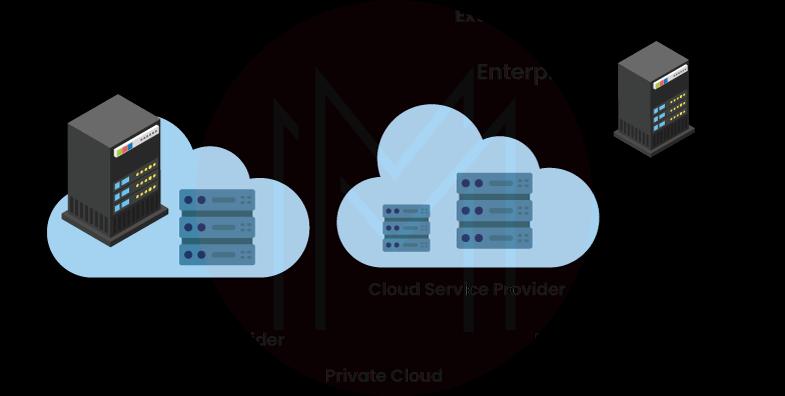
#2. Private Clouds
A private cloud is a cloud environment that is completely dedicated to one group or end user, typically running behind that user's or group's firewall. All clouds become private clouds when the underlying IT infrastructure is given to a single client with completely segregated access.
Private clouds, however, are no longer necessary to be powered by on-site IT infrastructure. All regulations controlling location and ownership are no longer applicable as firms build private clouds in rented data centers, off-site run by vendors. Several private cloud subtypes have also resulted from this, including:
- Managed private clouds
Customers construct and make use of a private cloud that a third-party supplier builds, configures, and operates. Utilizing managed private clouds as a cloud delivery option enables businesses with underqualified or understaffed IT teams to enhance the quality of their infrastructure and private cloud services.
- Dedicated clouds
Cloud encased in another cloud. A dedicated cloud might be located on a private or public cloud (like Red Hat OpenShift® Dedicated). The private cloud of the company, for instance, might contain a specialized cloud for the accounting division.
The advantages of using a private cloud are:
- Customer data protection
- Compliance with standard operations and procedures.
- Infrastructure ensuring SLAs.
The disadvantages of using a private cloud are:
- Restricted operational area.
- Managing private cloud services necessitates skilled personnel.
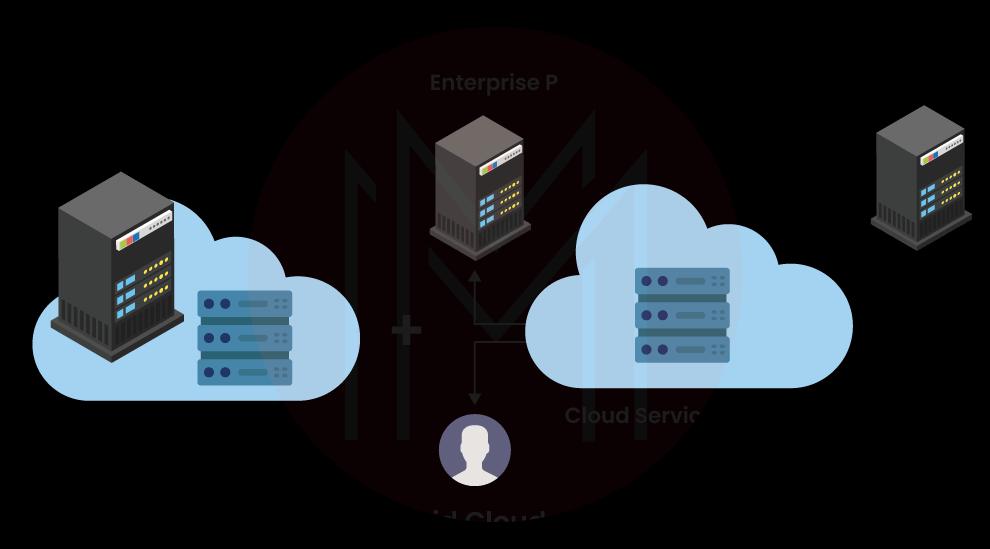
#3. Hybrid Clouds
An IT environment that consists of many environments that seem to be linked through LANs, VPNs, WANs, and/or APIs to create unified, single environment is known as a hybrid cloud.
The definition of hybrid clouds may differ depending on who you ask, and they may have a variety of sophisticated qualities. As an illustration, a hybrid cloud would need:
- A minimum of one public cloud and one private cloud
- at least two private clouds
- at least two public clouds
- a virtual or bare-metal setup coupled with at least one private or public cloud
However, when apps can transition between a variety of varied—yet connected—environments, Every IT device becomes a hybrid cloud. At the absolute least, these environments must be created using centralized IT resources that can scale as necessary. And each of those environments must be managed as a single environment using a platform for integrated administration and orchestration.
The advantages of using a Hybrid cloud are:
- Cheaper than other clouds because a distributed system forms it.
- A hybrid cloud is totally safe and secure.
The disadvantages of using a Hybrid cloud are:
- Managing a hybrid cloud may be more difficult.
#4. Multi-Cloud
Multiple cloud services from different public or private cloud vendors make up a multi-cloud architecture. Although all hybrid clouds are multi-clouds, the bulk of multi-clouds is not hybrid clouds. Hybrid clouds are created when multiple clouds are connected via orchestration or integration.
An environment with many clouds may exist accidentally or on purpose (to protect sensitive data better or provide redundant storage for improved disaster recovery). In any case, businesses that want to enhance performance and security through a broadened portfolio of environments are increasingly likely to have numerous clouds.
Advantages of using multi-cloud:
- Multiple cloud services provide the flexibility to choose the best services based on specific needs.
- Improved performance
- Increased security
Disadvantages of using multi-cloud:
- Managing numerous cloud providers and services can be challenging and demanding and requires a unique skill set.
- Different cloud service providers could use a range of standards and technologies, which could cause issues with compatibility and necessitate more resources to resolve.
- The inability of the many cloud providers to function well together may make it difficult to migrate data and apps across them.
Cloud services
Platforms, infrastructure, or software that are hosted by external providers and made accessible to users online are referred to as cloud services. IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are the three primary categories of as-a-Service solutions. Each one supports the transfer of user data from front-end clients to the cloud service provider's servers and back, but they differ in the features they offer.
# IaaS
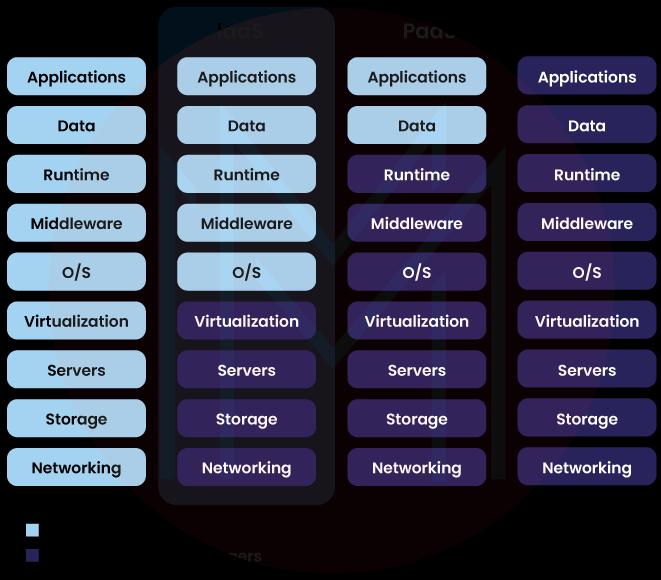
IaaS stands for a cloud service provider that uses an internet connection to handle your infrastructure, including the network, real servers, data storage, and virtualization. The user essentially rents the infrastructure and has access via a dashboard or API. While the provider handles any networking, hardware, data storage, hard drives, and servers, and is in charge of handling repairs, outages, and hardware issues, the user is in charge of things like the operating system, apps, and middleware. This is how most cloud storage companies deploy their systems.
# PaaS
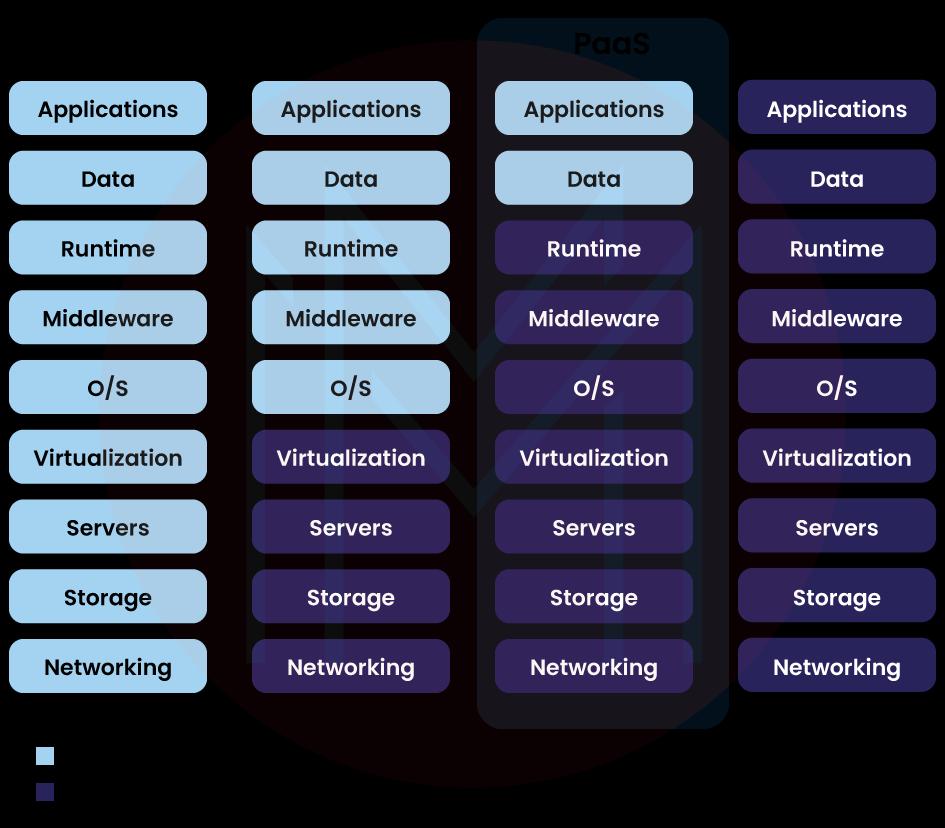
PaaS refers to an external cloud service provider providing and managing an application-software platform and the hardware, but the user is in charge of the apps that run on top of the platform and the data such apps rely on. PaaS provides users with a shared cloud platform for application management and development without their having to construct and maintain the infrastructure typically involved with the process. It is primarily for developers and programmers.
# SaaS
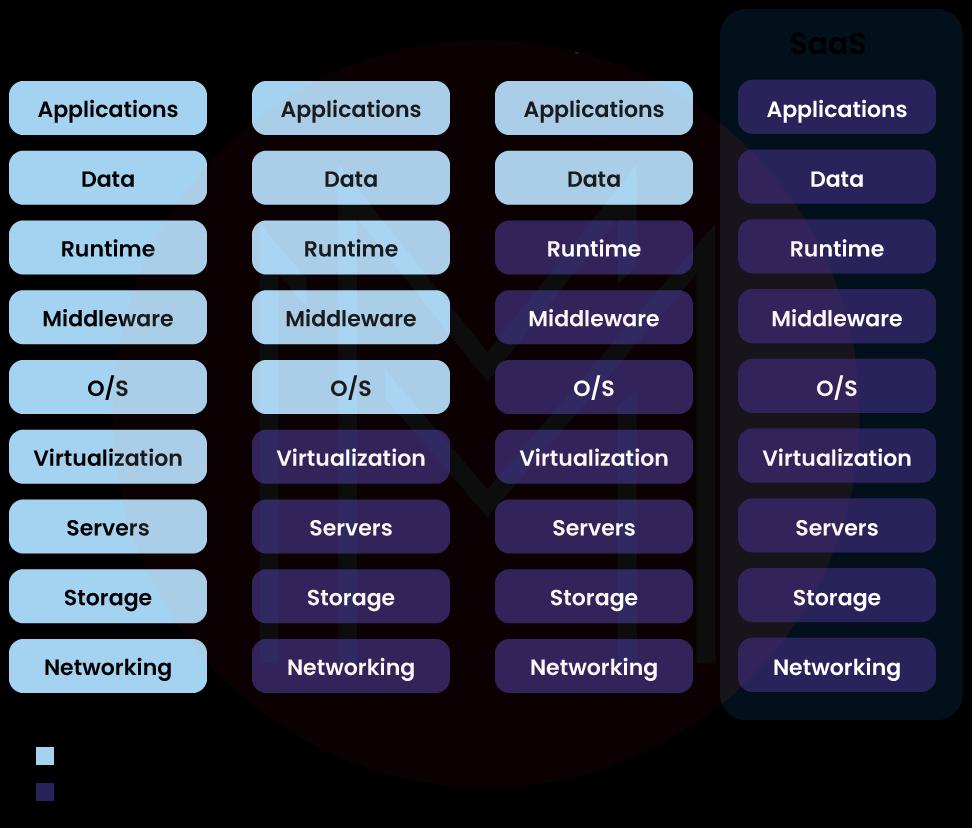
SaaS is a service that gives consumers access to a piece of software that the cloud service provider administers. SaaS apps are often web or mobile applications that consumers can access using a web browser. Users connect to the cloud applications via API or a dashboard, and updates, bug patches, and other routine software maintenance are handled for them. SaaS also removes the requirement for a programme to be locally installed on each user's computer, opening up more options for team or group access to the software.
[Related Article: SAP CPI Interview Questions]
Cloud Computing FAQs
1. What are the 3 service models of cloud computing?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS) are the three main cloud service models.
2. What are the essential services of cloud computing?
There are five key elements of cloud computing. They are resource pooling, on-demand self-service, wide network access, quick elasticity, and measurable service.
3. What are the 4 basic service types that cloud computing should deliver will deliver?
The four main methods for delivering cloud consulting services are SaaS, UCaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
4. What are cloud computing services for example?
Dropbox, Salesforce, and Cisco WebEx are examples of popular SaaS services. Google App Engine, Apache Stratos, and OpenShift are a few examples of PaaS services. Amazon Web Offerings (AWS), Cisco Metapod, and Microsoft Azure are a few well-known IaaS services.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned what cloud computing is, the types of Cloud Computing, its advantages and disadvantages, and many more. Take advantage of the rising need for experts in the field by enrolling in one of our AWS Online Course Training, which will teach you about cloud computing and all of its nuances to make you job-ready.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| AWS Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| AWS Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |
| AWS Training | Mar 10 to Mar 25 | View Details |

Suneel, a Technology Architect with a decade of experience in various tech verticals like BPM, BAM, RPA, cybersecurity, cloud computing, cloud integration, software development, MERN Stack, and containerization (Kubernetes) apps, is dedicated to simplifying complex IT concepts in his articles with examples. Suneel's writing offers clear and engaging insights, making IT accessible to every tech enthusiast and career aspirant. His passion for technology and writing guides you with the latest innovations and technologies in his expertise. You can reach Suneel on LinkedIn and Twitter.
















