- 6 Hot And In-Demand Tech Areas In 2024
- How To Forward Your Career With Cloud Skills?
- Top 7 On-Demand IT Certifications
- Most In-demand Technologies To Upskill Your Career
- Top 10 Hottest Tech Skills to Master in 2024
- Top Skills You Need to Become a Data Scientist
- Groovy Interview Questions
- Facets Interview Questions
- Crystal Reports Tutorial
- VAPT Interview Questions
- Flutter Tutorial
- Saviynt VS Sailpoint
- Flutter vs Xamarin
- PingFederate Interview Questions and Answers
- Dart vs Javascript : What's the Difference?
- Terraform Private Registry
- Cylance Interview Questions and Answers
- Sophos Interview Questions and Answers
- Top Camunda Interview Questions
- NUnit Interview Questions and Answers
- Impala Interview Questions and Answers
- ETL Tutorial
- Ionic Interview Questions
- Grafana Tutorial
- What is VAPT? - A Complete Beginners Tutorial
- SnapLogic Interview Questions
- Saviynt Interview Questions
- What is PingFederate? - A Complete Beginners Tutorial
- SnapLogic Tutorial
- Grafana Interview Questions
- RHCE Interview Questions and Answers
- Web Services Interview Questions
- Domo Interview Questions and Answers
- Terraform Interview Questions
- What is Sophos? | Sophos Turorial for Beginners
- Top Servlet Interview Question And Answers
- NLP Interview Questions and Answers
- Microsoft Intune Interview Questions
- Top XML Interview Questions And Answers
- Tosca Commander
- Katalon vs Cypress
- SQLite Tutorial
- Tosca Tutorial - A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Xamarin Interview Questions and Answers
- UiPath vs Automation Anywhere - The Key Differences
- OpenShift Interview Questions
- What is Katalon Studio - Complete Tutorial Guide
- Kronos Interview Questions
- Tosca Framework
- Burp Suite Tutorial
- Mendix Interview Questions
- Power Platform Interview Questions
- Burp Suite Interview Questions
- What is Mendix
- What is Terraform ?
- Burp Suite Alternatives
- Dart vs Kotlin
- What is Kronos?
- ES6 Interview Questions
- Entity Framework Interview Questions
- COBOL Interview Questions
- Express JS Interview Questions
- LINQ Tutorial
- CSS3 Interview Questions and Answers
- Auth0 Tutorial
- MS Access Interview Questions
- What is SPARQL - A Complete Tutorial Guide
- ExpressJS Tutorial
- UML Tutorial
- HTML vs XML
- Cypress vs Jest
- Impacts of Social Media
- OWASP Interview Questions
- Security Testing Interview Questions
- OpenShift vs Docker
- ES6 Tutorial
- Spark SQL Interview Questions
- Spark SQL Tutorial
- What is OWASP?
- AppDynamics Interview Questions
- Dynatrace Interview Questions
- Rest Assured Tutorial
- New Relic Interview Questions
- REST API Tutorial
- Datadog Interview Questions
- Rest API Interview Questions
- Rest Assured Interview Questions
- PTC Windchill Interview Questions
- Easiest Tech Skills To Learn
- Python SQLite Tutorial - How to Install SQLite
- Datadog Tutorial - Datadog Incident Management
- What is AppDynamics - AppDynamics Architecture
- RabbitMQ Interview Questions And Answers
- What is Dynatrace
- Datadog Vs Splunk
- Web Developer Job Description
- JP Morgan Interview Questions
- Types of Corporate Training
- Benefits of Corporate Training
- What is Corporate Restructuring?
- Blended Learning in Corporate Training
- What is Corporate Level Strategy?
- Flutter Projects and Use Cases
- How to Become a Web Developer
- How To Install Keras?
- How to Install Flutter on Windows?
- How to Install Cypress on Windows?
- How to Become a Computer Scientist?
- How to Install Katalon Studio in Windows
- How to Become a Programmer
- OWASP Projects and Use Cases
- How to Install Sophos?
- Workato Tutorial
- Workato Tutorial - What is Workato?
OSPF is introduced as an IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol) used to determine the shortest path for moving the packets or forwarding the network traffic in an extensive autonomous system or the routing domain. Using OSPF, networks can increase reliability, optimal performance, and speed. It is extensively utilized in service provider networks or enterprise networks because of its outstanding convergence capabilities, scalability, and support for network designs.
Cisco is a member of OSPF and is responsible for various enhancements to OSPF. So, OSPF will play a crucial role in cracking Networking job interviews or passing CISCO certifications. Thus, you must go through these OSPF interview questions and gain extensive knowledge of OSPF before attending networking job interviews and certification exams. These questions are helpful for both Freshers and Experienced Professionals.

We will move to OSPF Interview Questions- 2023 (Updated) for the following:
Top OSPF Interview Questions
- Explain the functioning of OSPF
- Name the five packets used in OSPF
- What is the OSPF router ID?
- What is OSPF adjacency?
- Describe the different router types
- What do you think IP-OSPF-Transmit-Delay is used for?
- Do you need any special commands to run OSPF on BRI/PRI links?
- Describe the role of topology and routing table in OSPF
- Name the different network types in OSPF
- Differentiate between E1 and E2
OSPF Interview Questions for Freshers
If you are new to the world of OSPF, here are some fundamental questions to prepare for your interview.
1. Explain the functioning of OSPF.
OSPF utilizes the Dijkstra Shortest Pathway First algorithm to decide the shortest and the most suitable path. It shows the status of straight related links using LSA- Link State Advertisements. It also notifies in case of any updates or changes in any of the links. Link State Advertisements are refreshed every 30 minutes.
2. Which LSA is used for intra-communication in OSPF?
Type-3 Link State Advertisement is used for communication amongst the regions. Type 4 and Type 5 Link State Advertisements are for communicating within other external protocols.
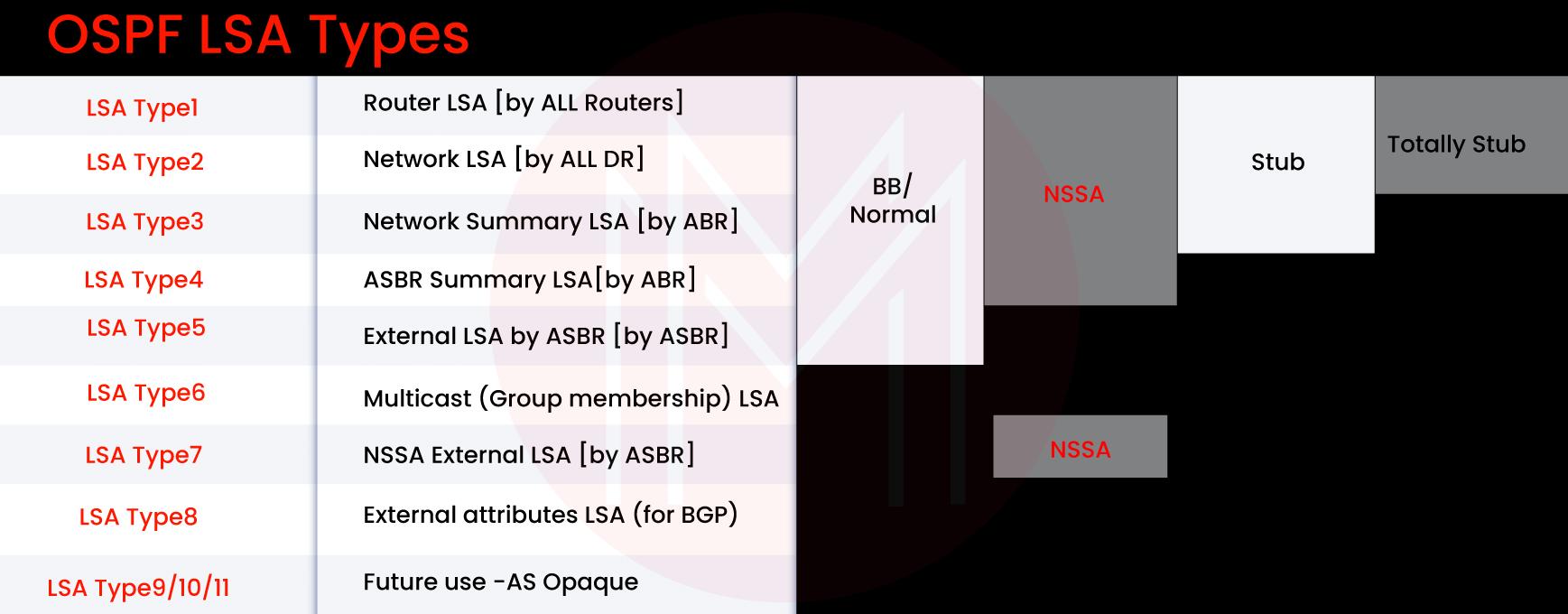
3. Name the different types of LSA- Link State Advertisement used in OSPF.
Different types of LSA used in OSPF are given below:
- External LSA
- Router LSA
- Network LSA
- Network Summary LSA
- ASBR Summary LSA
| If you want to enrich your career and become a professional in CCNA, then Enrol Our "CCNA Online Training" This course will help you to achieve excellence in this domain. |
4. Name the five packets used in OSPF.
There are five types of OSPF packets. These are:
- HELLO
- DBD
- LSR
- LSU
- LSack
5. What are the different area types in OSPF?
Different types of OSPF are:
- Type 1: Represents a router
- Type 2: Represents the pseudo node for a multi-access link
- Type 3- A network link summary that follows the internal route.
- Type 4- Represents an ASBR
- A route that is external to the OSPF domain
- Used in stub areas in place of a type 5 LSA
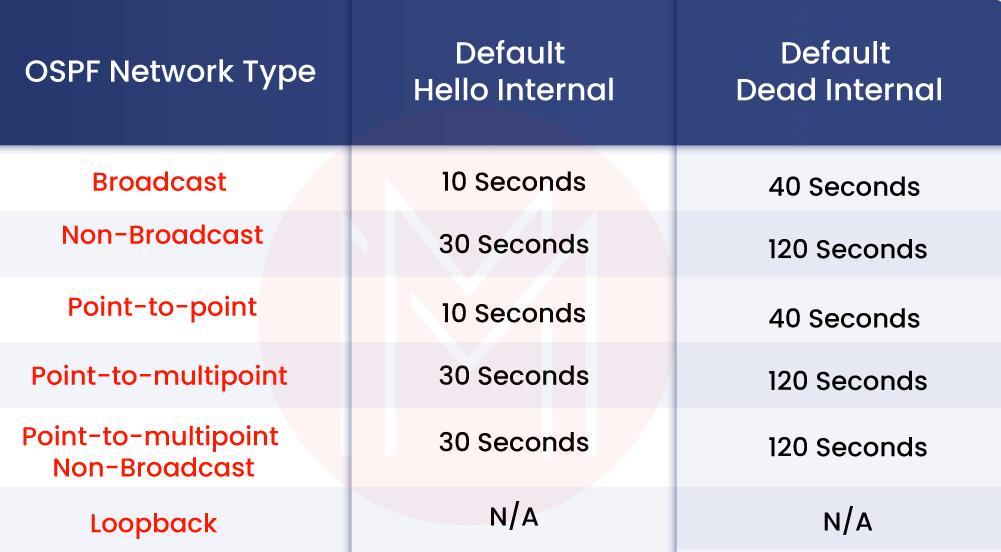
6. What are timers in OSPF?
There are two types of intervals in OSPF. These are:
- Hello Interval: This interval defines the duration of how frequently one OSPF router will send the hello packet to the other OSPF router
- Dead Interval: This interval defines the duration of how much the extended router must wait for hello packets before the neighbors are declared dead.
7. Which multicast address does the OSPF use?
OSPF uses two multicast addresses- 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6
8. What is the OSPF router ID?
OSPF router ID works as an identifier. It is used to recognize the router. It is a 32-bit number.
9. How can you change the reference bandwidth in OSPF?
The 11.2 Cisco IOs Software Release allows the change of Bandwidth. You can change it with the help of the OSPF auto-cost-reference bandwidth command under “router OSPF.” The default bandwidth is 100 Mbps. And the OSPF link cost is a 16-bit number. Thus, the maximum value for this change is 65,535.
10. Are OSPF routing protocol exchanges authenticated?
Yes, the OSPF routing protocol exchanges are authenticated. OSPF can authenticate all the packets to be exchanged between the neighbor routers. This authentication can occur through easy passwords. For configuring the authentication, you can use the command IP OSPF authentication key.
This will assign an eight-octet password to the interface attached to each area. However, if you want to configure the authentication on some interfaces, you can go for alternate methods or different interfaces belonging to the same area.
11. What is OSPF adjacency?
An OSPF adjacency is a theoretical link for a neighbor over which we can send the Link State Advertisements (LSAs).
12. How can you change the neighboring ships into adjacency?
Following are the steps to change neighboring ships into adjacency:
- Firstly, we need to send a state request to create a link. This link will inform packets.
- Then both routers will exchange database description packets. This will ensure database synchronization.
- Once the database synchronization is established, the two routers can be measured as adjacent routers.
13. What is the full form of LSA, LSU, and LSR in OSPF?
In OSPF, LSA means Link State Advertisement. While LSU is Link State Update, LSR stands for Link State Request.
14. What multicast IP does DR/BDR router and non-DR use?
In DR/BDR, it uses 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6.
15. Describe the different router types.
Different router types can be described as follows:
- Autonomous System Boundary Routers: An OSPF Router that advertises exterior routes into the OSPF domain.
- Internal Routers: An OSPF Router whose all interfaces belong to the same area.
- Area Border Routers: An OSPF Router that has interfaces in more than one area.
- Backbone Routers: An OSPF Router that is inside the Router in Area 0.
16. What are the essential features of OSPF?
1. Link-state routing protocol
2. Hierarchical structure with support for areas
3. Scalability
4. Efficient Routing Updates
5. Fast Convergence
6. Classless(supports CIDR)
7. Authentication Capabilities
17. How can we configure the OSPF route redistribution?
The OSPF route redistribution is the mechanism of injecting routes from the connected networks or OSPF protocol into the OSPF domain. Generally, this is performed on an Autonomous System Boundary Router or Area Border Router. The route redistribution is configured using the "redistribute" command in the OSPF routing process configuration mode, declaring the particular protocol, the metric value, and the metric type.
18. Describe the OSPF Graceful Restart feature.
The Graceful Restart Feature of OSPF will allow the OSPF router to temporarily preserve the OSPF routing information during the unplanned or planned restart, reducing the effect of restart on the OSPF network. The restarting router will inform its neighbors about the imminent restart, enabling you to continue using the routing information offered by restarting the router. At the same time, it will re-establish the OSPF adjacencies and resync its link-state database.
19. How can we configure OSPF on the Cisco router?
For configuring the OSPF on the Cisco router, we should follow the below steps:
- Step 1: Enter the global configuration mode through the "configure terminal" command
- Step 2: Enable the OSPF routing process through the "router OSPF" command, a unique identifier for OSPF processes.
- Step 3: Configure the OSPF area assignments for every interface through the "network [ip-address] [wildcard-mask] area [area-id]" command.
- Step 4: Adjust the OSPF parameters as required, like Hello and Dead Intervals, reference bandwidth, and authentication.
20. What is the use of Process ID in OSPF?
Process ID is defined as the unique identifier for the OSPF routing process on the router. It is locally crucial and does not require a match between neighbouring routers. A router can run multiple OSPF processes, each with a unique process ID supporting numerous OSPF routing domains.
21. What are the best practices for OSPF stability and scalability?
1. Restricting the number of routers per area for reducing the SPF calculation overhead.
2. Implementing the hierarchical area design with the well-connected backbone area.
3. Tuning the OSPF parameters and timers for optimizing the control traffic overhead and convergence times.
4. Utilizing the route summarization and the area types for minimising the rerouting information propagation between the areas.
5. Implement OSPF authentication and ensure constant configuration throughout the devices for stability and security.
22. Explain the support of OSPF for IPV6
OSPF provides support for IPV6 using the OSPFv3, an individual version of the protocol mainly developed for the IPV6 networks. The essential features and differences of OSPFv3 are:
- Using IPV6 link-local addresses for the OSPF communication between routers.
- Support for IPV6 routing and addressing.
- Supporting IPV6 address-family and prefix-specific configurations.
- Introducing New LSA types for the IPV6 network.
- Separating the OSPFV3 protocol from IPV6 routing table and enabling the OSPFV3 for supporting multiple instances per link.
23. Explain the OSPF Sham Link.
The OSPF Sham Link is utilized in the OSPF networks with the MPLS layer 3 VPNs for creating a logical link between the OSPF virtual private network instances on the provider edge routers. The Sham link assures that the inter-area in the OSPF VPN layer will have less cost than the external or inter-area routes, preserving the OSPF route selection hierarchy. This feature is useful in the OSPF backdoor links scenarios, where a direct connection between the customer sites is available.
24. How does OSPF interact with VPNs and MPLS?
The OSPF will interact with the Multiprotocol Lable Switching(MPLS) and Virtual Private Networks(VPNs) in various ways:
- OSPF can be utilized with the MPLS traffic engineering to control traffic flows in the network.
- OSPF can be utilized as IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol) in the MPLS network for establishing Label Switching Paths and distributing the routing information between the LSRs(Label Switch Routers).
- OSPF can be utilized as the routing protocol for Layer 3 VPNs like MPLS Layer 3, where the OSPF routes are distributed between the provider and customer edge routers.
25. Explain the Traffic Engineering Capabilities of OSPF.
The traffic engineering capabilities of OSPF are offered using the OSPF TE(Traffic Engineering) extension, which is an improvement to the standard OSPF protocol. The OSPF TE routers will allow routers to distribute the information about available bandwidth and other link attributes in the OSPF network, enabling the traffic engineering system to compute the optimal paths for the traffic flows. Generally, OSPF TE is utilized in conjunction with the MPLS traffic engineering for establishing the LSPs(Label Switched Paths) as per the collected network information.
26. Explain the OSPF neighbor relationship
The OSPF neighbor relationship establishes the bidirectional interaction between two OSPF routers that share the common network segment. It will allow the routers to exchange the routing information and preserve the synchronized link-state database. The OSPF routers will establish the neighbor relationships using the series of Hello packet exchanges.
27. Describe OSPF cost values
The OSPF cost values will depict the link's cost or the path in the OSPF network. Costs will be calculated on the basis of metrics like bandwidth, and are utilized by the Dijkstra algorithm for determining the shortest path to the destination. Lower-cost values are chosen over the higher ones.
28. What is the link-state database?
The OSPF link-state database collects the link-state advertisements that offer the topological map of the OSPF network. Every OSPF router will maintain the LSDB for its area, including information about routers, networks, and the links in the area. OSPF routers will utilize the Dijkastra algorithm for computing the shortest path tree(SPT) as per the LSDB, which will help you decide the best routes to reach the destination.
29. How can we implement Authentication in OSPF?
The OSPF Authentication is utilized for securing the OSPF routing updates and obstructing unauthorized routers from exchanging the routing information. There are two kinds of OSPF authentication:
1) MD5 or SHA Cryptographic Authentication: OSPF routers will exchange the MD5 or SHA cryptographic hashes in the Hello Packets, making it more secure than plain-text authentication. Both routers should have the authentication key for establishing a neighbor relationship.
2) Plain-text authentication: OSPF routers will exchange the plain-text passwords in the Hello packets. This method is not secure since passwords can be intercepted.
To implement the authentication, you must configure the authentication key and type it on every OSPF router in an area or the individual interface, as per the security requirements.
30. Explain the path-selection process of OSPF.
The path selection process of OSPF includes the following steps:
1) OSPF routers will set up the neighbor relationships and exchange the link-state information through the OSPF packet types(DBD, Hello, LSU, LSR, LSAck).
2) Every router builds the link-state database, including the topological map of OSPF network.
3) The Shortest Path First Algorithm(Dijkstra Algorithm) is applied to LSDB for computing the SPT(Shortest Path Tree) for every destination.
4) The SPT is used for populating a routing table with the best routes for every destination at a lower cost.
31. How can we handle Equal-Cost Multi-Path(ECMP) Routing?
OSPF endorses ECMP(Equal-Cost Multi-Path) routing that enables multiple paths with an exact cost to the destination to be installed in the routing table. This balances load throughout multiple paths, enhancing the network's reliability and performance. OSPF routers will utilize maximum-paths command for configuring several equal-cost paths that we can utilize simultaneously.
32. What is the difference between OSPF and other routing protocols?
- OSPF is different from the other routing protocols, like EIGRP and RIP, in various ways:
- OSPF utilizes Dijkstra algorithm, whereas RIP utilizes the Bellman-Ford algorithm, and EIGRP utilizes the DUAL(Diffusing Update Algorithm).
- OSPF is the link-state protocol, RIP is the distance-vector protocol, and EIGRP is the hybrid protocol.
- OSPF endorses the hierarchical design and the area segmentation, while RIP does not.
- OSPF has a higher convergence time than the RIP and is more scalable than EIGRP and RIP.
33. What are the OSPF's considerations in a multi-vendor environment?
In the multi-vendor environment, it is essential to ensure OSPF interoperability between the devices from different vendors. Important Considerations are:
1) All vendors must comply with the OSPF standards (RFC 5340 for OSPFv3 and RFC 2328 for OSPFv2).
2) Assuring the compatibility of the OSPF features like NSSA, stub areas, or the traffic engineering extensions throughout the vendors.
3) Consistent OSPF area and interface configurations throughout devices like network types, authentication settings, and Hello and Dead Intervals.
4) Verify the OSPF adjacencies, routing information, and LSA exchange sharing between the devices from different vendors.
34. Compare OSPF and BGP routing protocols
| Comparison Basis | BGP | OSPF |
| Routing Protocol | Path-vector routing protocol | Link-state routing protocol |
| Type of Protocol | Exterior Gateway Protocol | Interior Gateway Protocol |
| Convergence Speed | Slower Convergence | Fast Convergence |
| Algorithm | Path Selection Process | Dijkastras Algorithm |
| Policy Control | Extensive Policy Control | Limited Policy Control |
35. When should we use OSPF over BGP and conversely?
BGP was developed for use between autonomous systems and offers comprehensive policy control, making it suitable for linking networks operated by different organizations, like ISPs(Internet Service Providers). OSPF is best suited for Autonomous systems because of its fast convergence, hierarchical structure, and ability to scale in the enterprise's network. We can use OSPF when:
- Fast Convergence is required.
- Routing within the AS
- A hierarchical network design is required
We can use BGP when:
- Policy control is crucial
- Connecting the network of different organizations
- Routing between the ASes
36. Explain the route redistribution between OSPF and BGP.
Route Redistribution between BGP and OSPF allows the exchange of routing information between two protocols. Generally, this is achieved through route maps or prefixes, which are the lists for controlling which routes are redistributed and how the routes will be manipulated in the redistribution process.
37. How do BGP and OSPF handle path selection?
BGP utilizes the path selection process that considers multiple attributes, like AS-path length, MED, local preference, and others, for selecting the best path. In contrast, OSPF utilizes Dijkstra's shortest path first algorithm for computing the shortest path to every destination as per the link costs.
38. How does OSPF work on the Cisco routers?
OSPF will work on the Cisco routers by:
- Exchanging the routing information in the Link-State Advertisements with the neighbors.
- Establishing the OSPF neighbor relationships with the adjacent routers through the Hello protocol.
- Running SPF(Shortest Path First) algorithm for computing the best path to every destination.
- Developing the Link-State Database that depicts network topology
- Adjusting to the network changes and recalculating the routes as required.
- Populating the routing table with the OSPF-derived routes.
39. How do we enable the OSPF on a Cisco Switch?
For enabling the OSPF on the Cisco Switch:
- Entering the OSPF routing process configuration mode with the router OSPF.
- Enabling the IP routing if it is not enabled through "ip routing" command.
- Configure the OSPF on the required VLAN interfaces through: ip ospf <process-id> area <area-id>.
40. How do we configure the OSPF authentication on the Cisco routers?
For configuring the OSPF authentication on the Cisco routers, we must follow the below steps:
- Select authentication type: clear-text or MD5.
- Configure the OSPF area for using the selected authentication type
- Configuring the OSPF interface using the same authentication type and offering the authentication key.
41. What is the function of the OSPF ABR?
OSPF ABR(Area Border Routers) will link the backbone area with the regular areas. ABRs condense the routing information and summarise the routes between areas. ABRs flood LSAs between attached and backbone areas.
42. How do we verify the OSPF neighbor adjacency?
The "show ip ospf neighbor" command will display the OSPF neighbor adjacencies, like state, route ID, address, and dead timer.
43. How is the default route configured in the OSPF?
A default route will be injected into OSPF as a type 5 external through the default-information originate command on ASBR. Route Maps and Metrics can set the properties.
44. How do we troubleshoot the OSPF neighbour adjacency issues?
- Verify the interface network types and the hello or dead intervals match
- Ensure no duplicate network addresses or router IDs
- Check for interface authentication mismatches
- Verify the cabling and interface status
- Check for the MTU mismatches or the L2 problems
OSPF Interview Questions for Experienced
If you are upskilling yourself in the OSPF field and looking for advanced-level questions to prepare for, you can get help from the below list.
1. Can you use the distribute-list in/out command with OSPF to filter the routes?
The distribute-list commands are supported in OSPF but only in some conditions. It is also different from a distance vector routing protocol like Routing Information Protocol and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). And it is noteworthy that OSPF routes cannot be filtered while entering the OSPF database. The distribute list in the command only filters from entering the route. It doesn’t prevent the propagation of link-state packets. Thus, the route memory is not conserved in this process. Also, this propagation might affect other routers as well.
Also, it would help if you were careful as the distribution list in the command needs to be implemented carefully. If not, there are chances that loops will occur. This command only works on the routes of Autonomous System boundary Routers.
2. What is Link State Retransmit Interval? Which command is used to set it up?
OSPF is required to send an acknowledgment of every new link state advertisement. This is done by sending LS packets. These packets keep on transiting until they are acknowledged. Retransmissions are defined by this Link State Retransmit Interval. The command for this IP OSPF retransmits interval. The value is 5 seconds by default.
3. What do you think IP-OSPF-Transmit-Delay is used for?
IP-OSPF-Transmit-Delay is used to add a specified time to the age field of an update. It needs to be added before the transmission over a link. If not, then the time in which LSA propagates won’t be considered. The value is 1 second by default. This is more significant on low-speed links for certain reasons.
4. Can an OSPF default be originated into the system based on external information?
Not really. OSPF can only generate a default when it is configured using the command default-information originate. It also works if there is already a default network in the box from a different process. Remember that the default route is 0.0.0.0. If an OSPF-enabled router does not have a default router and you want to generate it, use the command “default-information originate.”
5. Do you need any special commands to run OSPF on BRI/PRI links?
Apart from using the normal commands for OSPF configuration, we require some special commands for running it in the Primary Rate Interface and the Basic Rate Interface. When you use the normal OSPF configuration commands, you should use the dialer map command. Also, broadcast keywords are essential here to indicate that the broadcasts need to be forwarded.
| Related Article: "CCNA Tutorial" |
6. Do you need any special commands to run OSPF on asynchronous links?
We require special commands to run OSPF on links that do not occur at a certain predetermined time. For this, we can use the async default routing command on the asynchronous interfaces. This enables the router to continue passing updates to other routers with the same interfaces.
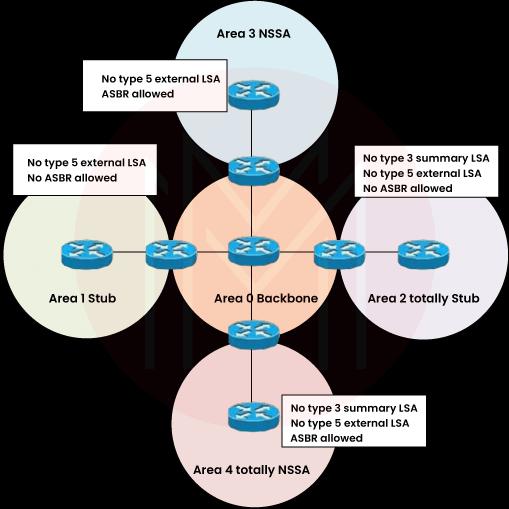
7. What is the significance of area 0 in OSPF?
Area 0 is known as the backbone area in OSPF. In simple language, all other areas send their transfer through this area only. It cannot function without this. The entire routing area is also distributed through this.
8. Describe OSPF stub areas and different kinds of Stub areas.
OSPF stub areas are an area configuration that restricts the number of routes spread into area for reducing LSDB table size and the routing table complexity. We have three kinds of Stub areas:
1)Stub Area: It will not allow the external routes from the independent systems. Instead, the Area Border Router will inject the default route into the stub area.
2) Totally Stub Area: It will not allow inter-area or external routes from the other OSPF areas. The ABR will inject the default route into the area.
3) NSSA(Not-So-Stubby-Area): It will allow the injection of the external routes in the area while filtering the external routes from the independent systems. ABR also injects the default route.
9. Describe the role of topology and routing tables in OSPF.
OSPF maintains the below three tables:
- Topology table: A topology contains all the routes in a particular network area.
- Routing table: A routing table contains the best routes for each network.
- Neighbor Table: The neighbor table contains a list of all neighboring routers.
10. List the benefits of OSPF summarization?
The benefits of OSP summarization are:
- It reduces the update messages.
- It takes the OSPF to larger scales.
- It limits the quantity of information stored in the routing tables.
- It reduces the load on the router processor.
- It reduces the bandwidth practice.
11. Name the different network types in OSPF.
The different network types in OSPF are listed below:
- Broadcast network type- Data packets are sent from one router to another.
- Non-broadcast network type- The network here is not capable of broadcasting. It only supports access to devices.
- Point-to-point network type- Data packets are sent between two routers.
12. Describe the function of the neighbor router.
The functions of the neighbor router are given below:
- It contains the router ID of each neighbor router.
- It knows about the current state of each neighbor router.
- It knows the IP address of the remote interface of each neighbor.
13. What is a Virtual link in OSPF?
According to the OSPF rule, inter-area communication happens when at least one area is 0 or the backbone area. A virtual link has to be used to form a logical association in case it’s not possible. And a virtual link is not feasible via the stub area.
14. What are DR and BR in OSPF?
In OSPF, DR means Designated Router, and BDR means Backup Designated Router. Both of them are used for exchanging information between different routers. DR is the contact point for the network segment by default. BDR is selected for the network to avoid problems with DR whenever these occur.
15. Differentiate between E1 and E2.
E1 is an External Type route that defines the cost that is required to the destination from ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router). Here, the internal cost and the external metric are considered.
E2 is also the External Type route, but it doesn’t include the internal costs. In E2, it calculates only the external metrics for reaching a particular destination.
16. When are the OSPF network LSAs generated?
We generate the OSPF Network LSAs using the designated router on multiaccess networks like Ethernet; Network LSAs discover all the attached routers on segment.
17. What information is included in the OSPF router LSAs?
OSPF router LSAs will describe the cost and state of the router interfaces in an area. LSAs will include:
- Neighboring router IDs
- Router ID
- Interface subnet masks
- Interface IP Addresses
- Other flags/options
- Interface cost
18. What are the properties of the OSPF totally stubby area?
A totally stubby area will only allow a default summary LSA from ABR. No inter-area or external routes are enabled, minimizing LSDB significantly.
19. How can we determine the OSPF Router ID?
Using the "router-id" command, we can manually configure the OSPF router ID. If not configured, the highest IP address on the loopback interface is automatically chosen as the router ID.
20. How can we determine whether the OSPF is enabled on the interface?
The "show ip ospf" interface command will display the OSPF-specific information about the interfaces on which OSPF is enabled. The "show i IP protocols" will also display the OSPF-enabled interfaces.
21. How do we determine the OSPF-designated router?
The "show ip ospf neighbor command detail" will display the backup designated router and designated router for the multiaccess networks. The BDR and DR are chosen as per the priority.
22. What will cause the OSPF LSA flooding issues?
- Managed LSAs from instability/restart
- Network congestion dropping LSAcks
- Authentication failures between neighbors
- Buggy LSA checksum causing the retransmissions
23. What causes the OSPF routing flapping?
The Frequent OSPF recalculations will cause the routing flapping. The Primary causes are:
- CPU hogging SPF Calculations
- Network instability triggering LSAs
- Redistribution churning routes
- Tuning timers too rapid for the convergence
24. What is the difference between cost and metric?
The Metric is the wider term used for any value that the routing protocol utilizes for determining an optimal path to the destination. "Cost" is a particular type of metric that OSPF utilizes, calculated as per the bandwidth of links.
25. Can we have multiple OSPF processes on the router?
Yes, we can configure multiple OSPF processes using the multiple OSPF process IDs. The process will work independently with the separate LSDB, SPG, and adjacencies.
26. What is the maximum number of paths that OSPF ECMP can support?
OSPF can endorse four equal-cost paths to the same destination network. Traffic can be load-balanced throughout the paths.
27. What is the use of Opaque LSAs?
Opaque LSAs will provide the generalised mechanism for carrying the application-specific information in the OSPF. Opaque LSAs can be identified using Opaque ID and type field.
28. What is the use of OSPF link-local signalling?
LLS offers a simple acknowledgement mechanism between neighbours, like confirming the adjacency reset messages. It utilises the OSPF packet encapsulation.
29. What is the maximum number of routers endorsed in the OSPF area?
An OSPF area will support 10,000 routers. Performance and Convergence will suffer with big topology sizes.
30. Can we filter routes in the OSPF through the distribution list?
Yes, we can apply the distribute-lists in or out of the OSPF routing process for filtering which routes will be allowed. This will control the route adoption and exchange.
31. What is the default dead interval?
In OSPF, the default dead interval is 40 seconds. If the neighbour does not receive a hello in the dead interval, the neighbor will be declared down.
32. Why does the OSPF route not appear in the route table?
- Route not inserted in the OSPF with redistribute
- Route filtering with the distribute-list
- Administrative distance securing install
- The higher cost route already in the table
- Summarisation blocking particular subnet
33. How can we perform route summarization in OSPF?
The manual route summarisation can be configured with an area range command on the OSPF ABRs for summarising the inter-area routes. The summary-address command will summarise the external routes on the ASBRs.
Frequently Asked OSPF Interview Questions
1. What is OSPF?
The full form of OSPF is Open Shortest Path First. It is a routing Internet protocol. It is an open link and works by utilizing Dijkstra’s SPF algorithm to find straight paths from your source to your destination. It is an intra-domain protocol. This means that it is used within a particular area of a network. It is designed only for a single autonomous system.
2. What is the OSPF protocol used for?
The work of a router is to learn routes. OSPF does the same. It learns about each router within the entire network. The link-state routing algorithm present in it gives out the information of every domain. OSPF learns the information by sending Link State Advertisements.
3. How does OSPF Work?
The steps are given below:
- Step 1: The first step in the procedure is to become OSPF neighbors. Two routers running on OSPF that too on the same link will create a neighbor relationship.
- Step 2: In the second step, OSPF exchanges LSDB information on the database.
- Step 3: Once the LSDB information is exchanged, OSPF chooses the best route with the help of the SPF calculation.
4. Name the critical attributes of OSPF.
The following are the critical attributes of OSPF:
- Equal Cost Routes management: CEF Load corresponding
- Protocol Type: Link State
- Transport IP (Port 89) submit to network walks website
- Metric: Cost (Bandwidth)
- Standard: RFC2328 (OSPFv2), RF C2740 (OSPFv3/IPv6)
5. What are the characteristics of OSPF?
The characteristics of OSPF are given below:
- OSPF falls under the category of a classless routing procedure that supports VLSM and CIDR.
- The organizational distance of OSPF routes is 110.
- OSPF does not have any hop-count limit. The support is limitless.
- OSPF takes cost as its metric. This is computed based on the link bandwidth.
- OSPF also supports an independent system.
6. Why are DR and BDR important in OSPF?
BDR and DR are important because they solve the following two problems in OSPF:
- Excessive LSA flooding
- High No. of Adjacencies
7. Is it possible to have OSPF over a GRE tunnel?
Yes. It is possible to have OSPF over a GRE tunnel.
8. What do you understand by OSPF summarization?
OSPF summarization, also known as Route summarization, helps in reducing OSPF traffic and computation. This results in preventing memory from getting wasted.
9. Which parameters should match for two routers to become neighbors?
To make two routers neighbors, the following parameters should match:
- Area ID
- Subnet
- Authentication
- Hello and Dead Interval
10. What are the seven stages of OSPF?
OSPF goes through the below seven stages:
- Down
- Attempt
- Two ways
- Exstart
- Exchange
- Loading
- Full
Conclusion
Since the OSPF protocol is widely used in enterprise networks, it is a crucial topic for freshers and experienced network professionals. The OSPF interview questions in this blog will help you prepare for the job interviews and evaluate your knowledge of OSPF protocol. If you have any queries, let us know by commenting below.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| CCNA Training | Feb 24 to Mar 11 | View Details |
| CCNA Training | Feb 28 to Mar 15 | View Details |
| CCNA Training | Mar 03 to Mar 18 | View Details |
| CCNA Training | Mar 07 to Mar 22 | View Details |










