- 6 Hot And In-Demand Tech Areas In 2024
- How To Forward Your Career With Cloud Skills?
- Top 7 On-Demand IT Certifications
- Most In-demand Technologies To Upskill Your Career
- Top 10 Hottest Tech Skills to Master in 2024
- Top Skills You Need to Become a Data Scientist
- Groovy Interview Questions
- Facets Interview Questions
- Crystal Reports Tutorial
- VAPT Interview Questions
- Flutter Tutorial
- Saviynt VS Sailpoint
- Flutter vs Xamarin
- PingFederate Interview Questions and Answers
- Dart vs Javascript : What's the Difference?
- Terraform Private Registry
- Cylance Interview Questions and Answers
- Sophos Interview Questions and Answers
- Top Camunda Interview Questions
- NUnit Interview Questions and Answers
- Impala Interview Questions and Answers
- ETL Tutorial
- Ionic Interview Questions
- Grafana Tutorial
- What is VAPT? - A Complete Beginners Tutorial
- SnapLogic Interview Questions
- Saviynt Interview Questions
- What is PingFederate? - A Complete Beginners Tutorial
- SnapLogic Tutorial
- Grafana Interview Questions
- RHCE Interview Questions and Answers
- Web Services Interview Questions
- Domo Interview Questions and Answers
- Terraform Interview Questions
- What is Sophos? | Sophos Turorial for Beginners
- Top Servlet Interview Question And Answers
- NLP Interview Questions and Answers
- Microsoft Intune Interview Questions
- Top XML Interview Questions And Answers
- Tosca Commander
- Katalon vs Cypress
- SQLite Tutorial
- Tosca Tutorial - A Complete Guide for Beginners
- Xamarin Interview Questions and Answers
- UiPath vs Automation Anywhere - The Key Differences
- OpenShift Interview Questions
- What is Katalon Studio - Complete Tutorial Guide
- Kronos Interview Questions
- Tosca Framework
- Burp Suite Tutorial
- Mendix Interview Questions
- Power Platform Interview Questions
- Burp Suite Interview Questions
- What is Mendix
- What is Terraform ?
- Burp Suite Alternatives
- Dart vs Kotlin
- What is Kronos?
- ES6 Interview Questions
- Entity Framework Interview Questions
- COBOL Interview Questions
- Express JS Interview Questions
- OSPF Interview Questions
- LINQ Tutorial
- CSS3 Interview Questions and Answers
- Auth0 Tutorial
- MS Access Interview Questions
- What is SPARQL - A Complete Tutorial Guide
- ExpressJS Tutorial
- UML Tutorial
- HTML vs XML
- Cypress vs Jest
- Impacts of Social Media
- OWASP Interview Questions
- Security Testing Interview Questions
- OpenShift vs Docker
- ES6 Tutorial
- Spark SQL Interview Questions
- Spark SQL Tutorial
- What is OWASP?
- AppDynamics Interview Questions
- Dynatrace Interview Questions
- Rest Assured Tutorial
- New Relic Interview Questions
- REST API Tutorial
- Datadog Interview Questions
- Rest API Interview Questions
- Rest Assured Interview Questions
- PTC Windchill Interview Questions
- Easiest Tech Skills To Learn
- Python SQLite Tutorial - How to Install SQLite
- Datadog Tutorial - Datadog Incident Management
- What is AppDynamics - AppDynamics Architecture
- What is Dynatrace
- Datadog Vs Splunk
- Web Developer Job Description
- JP Morgan Interview Questions
- Types of Corporate Training
- Benefits of Corporate Training
- What is Corporate Restructuring?
- Blended Learning in Corporate Training
- What is Corporate Level Strategy?
- Flutter Projects and Use Cases
- How to Become a Web Developer
- How To Install Keras?
- How to Install Flutter on Windows?
- How to Install Cypress on Windows?
- How to Become a Computer Scientist?
- How to Install Katalon Studio in Windows
- How to Become a Programmer
- OWASP Projects and Use Cases
- How to Install Sophos?
- Workato Tutorial
- Workato Tutorial - What is Workato?
Microservices are becoming increasingly famous in business because they allow developers to implement changes rapidly. They provide several advantages over monolithic architectures, like increased modularity, maintainability, and scalability. Due to these advantages, Software developers choose to develop applications with the microservice architecture. In Microservices architecture, two or microservices will be interconnected with each other to communicate and perform.
To interconnect microservices, we use message brokers like RabbitMQ, Kafka, and Redis to interconnect microservices. Among other message brokers, RabbitMQ is the most widely utilized freeware message broker. It is easy to use, lightweight and supports most of the famous technologies like Docker, Kubernetes, and programming languages like Java, Python, .NET, and GO. So, anyone who wants to start their career will have great demand and massive salaries. That’s why we have brought you these RabbitMQ interview questions. These RabbitMQ Interview Questions and Answers which will help you with different experience levels to get the maximum benefit from this blog.
We have categorized RabbitMQ Interview Questions into different levels they are:
Top 10 RabbitMQ Interview Questions
- What is Binding?
- Define the Routing key?
- Explain RabbitMQ Vhost?
- Is RabbitMQ utilizes a Database?
- Is RabbitMQ support MQTT?
- Describe ZeroMQ?
- Describe Apache Qpid?
- Explain STOMP?
- Explain Spring Cloud Stream
- How is RabbitMQ different from ActiveMQ?
RabbitMQ Interview Questions For Beginners
1. What is RabbitMQ?
RabbitMQ is a freeware message-broker system, and it is also called message queuing technology. It defines the queues to which the applications interact for data transfer and message transmission. Any information can be included in the message. The receiver application will process the message.
2. What is Binding?
Binding acts as the “bridge” that we establish to connect the queue for an exchange.
3. Define the Routing key?
The Routing key is defined as the attribute message that the exchange checks while determining how we route the messages to the queues. The message structure in RabbitMQ is divided into two parts: They are payload and routing key. Routing Key is used for describing the payload sent by the system, and messaging system itself for determining who will be receiver of payload. The Routing Key also allows you to bind the exchanges to the queues.
4. Why RabbitMQ?
Message Queuing is used when we want to exchange the message for utilization of load balancing between the workers with the multiple receivers. The user can take a message from the queue while the producer is in a queue and begin processing. The user can be on a different server or the same server as the publisher.
The requested application can be of one language, and the consumer application is of another language - the message broker will not care about application languages; it just sends the message between the receiver and consumer.
5. Explain Exchange?
Messages are not posted directly in the queue; instead, the user sends the messages to an exchange. An exchange is accountable for routing the messages to different queues. The exchange receives the messages from the producer request and routes them by routing and binding keys to the message queues. Binding serves as the linkage between a queue and an exchange.
6. What are the primary features of RabbitMQ?
The following are the primary features of RabbitMQ:
- RabbitMQ endorses Asynchronous messaging with the multiple messaging protocols, flexible routing, multiple exchange types, delivery acknowledgment, and message queuing.
- Using RabbitMQ, we can get various plugins and tools for supporting continuous integration, operational measures, and integrations to other organization systems.
- It supports the distributed deployment to deploy as the clusters for throughput and high availability.
- It is Cloud and Enterprise-ready since it is easy to deploy in private and public clouds with pluggable authorization, authentication, and LDAP & TLS support.
- It supports many famous languages like .Net, PHP, Java, JavaScript, Ruby, Python, Go, etc.
7. What are the disadvantages of RabbitMQ?
The following are the some disadvantages of RabbitMQ:
- Reduced System Availability
- Repeated Consumption
- MQ Lost Message Consideration
- Uniformity
8. Define Messaging?
Messaging is the communication process utilized for the system interactions. In software development, messaging allows distributed interaction that is loosely coupled. A message client can transmit messages to and receive messages from another client. The structure of the message is as follows:
9. How RabbitMQ works?
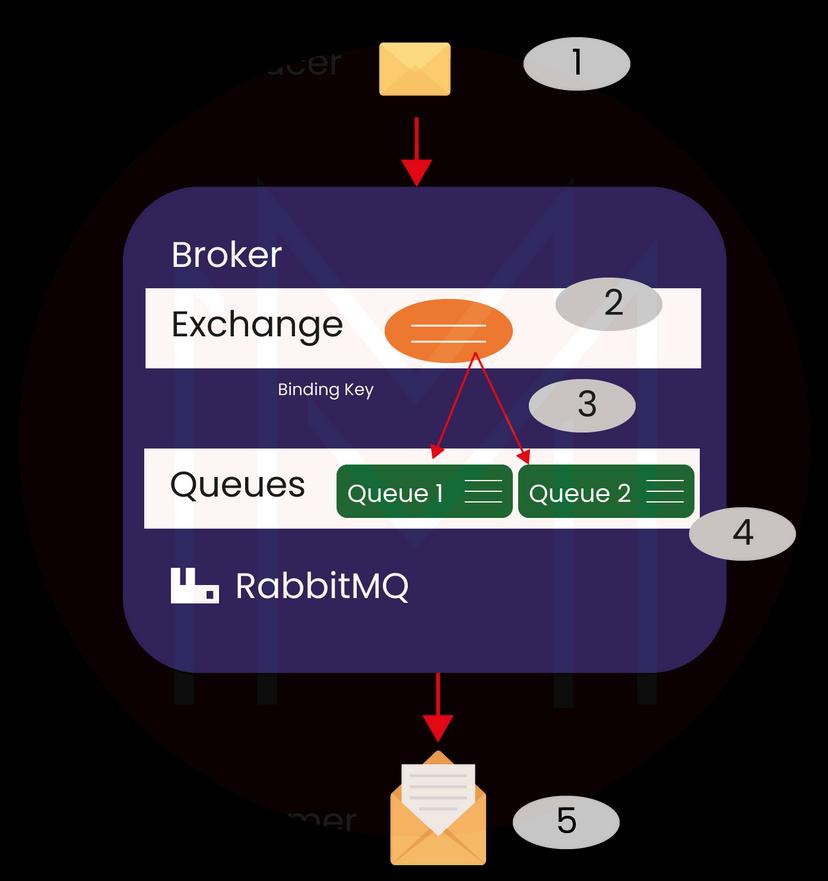
An exchange should accept messages from supplier requests and route them to the message queues through header attributes, routing keys, and bindings. Binding is configured for connecting the queue to the exchange. The standard message flow of RabbitMQ is as follows:
- Producer publishes the message to the exchange. When we create the exchange, we have to specify the kind of it.
- Exchange receives the message and is accountable for routing the message. The exchange considers different message attributes, like the routing key, as per the exchange type.
- Bindings have to develop from the exchange to the queues. In this case, we see the two bindings to two different queues from an exchange. Exchange routes the message into queues as per the message attributes.
- The messages remain in queue until the consumer manages them
- The Consumer manages the message.
10. What is Server in RabbitMQ?
In RabbitMQ, Server is a scalable and robust implementation of the AMQP broker; it allows us to show the banner messages and reports the progress in startup sequence with message broker running, which means the RabbitMQ broker has been commenced successfully.
11. Explain RabbitMQ Vhost?
A Vhost(a.k.a ‘Virtual Host’) in AMQP is the namespace for the messages like Queues, Bindings, and Exchanges. RabbitMQ uses the more tangible implementation of the virtual hosts by making them “virtual clusters” on the top of the broker.
12. Which protocol RabbitMQ utilizes?
RabbitMQ utilizes the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol(AMQP). It is the open standard layer used to communicate the dates throughout the network using a byte stream.
13. Is RabbitMQ utilizes a Database?
RabbitMQ deliberately does not store messages in the database. It writes messages to the disks in the following two ways:
- Messages published in delivery_mode=2
- Memory pressure makes RabbitMQ exhaust RAM and transmits messages to disk to free the memory of RAM.
14. Describe Erlang?
Erlang is a concurrent, general-purpose, functional programming language and garbage-collected runtime system. The RabbitMQ server is developed in the Erlang programming language and is designed on the Open Telecom Platform framework for clustering and fail-over. As RabbitMQ is developed on the top of Erlang, we first have to install Erlang before installing RabbitMQ.
15. Explain pub/sub?
pub/sub messaging is an asynchronous service-to-service interaction; it is a two-way interaction. It is primarily utilized in stateless microservices. In this model, Once the message is published on the topic, it is received immediately by all the subscribers to the topic.
RabbitMQ Interview Questions For Experienced
16. Explain Advanced Message Queuing Protocol(AMQP)?
AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) is the open standard application layer protocol for message-oriented middleware. AMQP 0-9-1 is the binary messaging protocol and semantic framework for microservices and enterprise messaging. RabbitMQ Messaging is based on the AMQP 0-9-1 protocol. RabbitMQ supports:
- MQTT
- HTTP
- STOMP
- AMQP 0-9-1
- AMQP 1.0
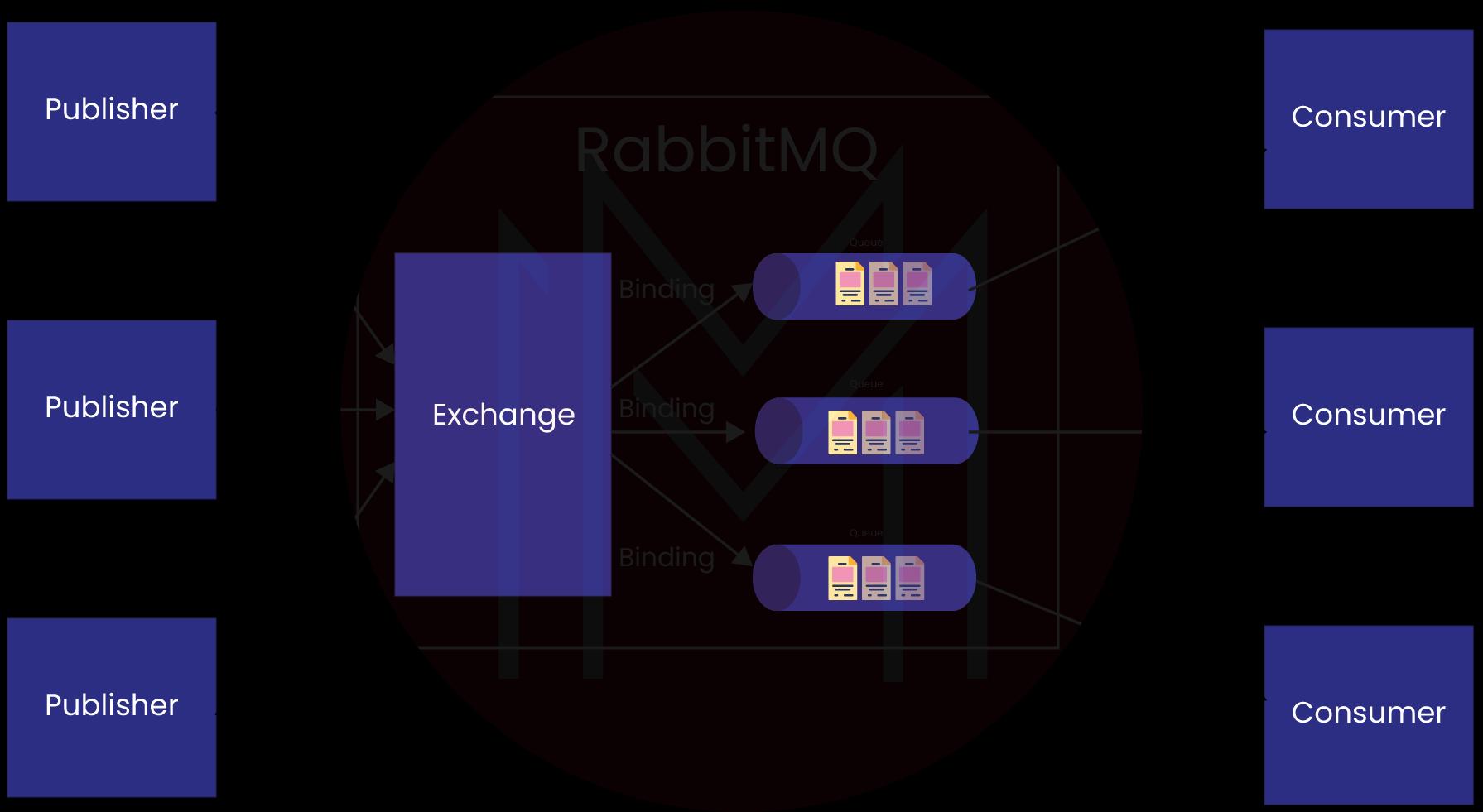
17. Is RabbitMQ persistent?
Having the queue durable is different from making the persistent changes. Messages can be distributed either with the making mode to be transient or persistent. When we post our message, we have to set the delivery mode to persistent if we want it to remain in our long-lasting queue during the restart.
18. Is RabbitMQ support MQTT?
RabbitMQ supports MQTT 3.1.1 using the plugin that carries to core distribution. The following are the features of Supported MQTT:
- QoS2 publish(downgraded to QoS1)
- QoS0 and QoS1 publish & consume
- Session Stickiness
- TLC
- Retained messages with the pluggable storage backends
- Last Will and Testament(LWT)
19. Is RabbitMQ an ESB?
RabbitMQ is the messaging broker, Whereas Mule is the Enterprise Service Bus(ESB). The ESB contains additional layers on top of message brokers like, transformations, business process management, and routing.
20. Explain RabbitMQ Admin?
RabbitMQ Admin allows us to perform the same actions as the web-based UI; it can be carried with a management plugin and offers a suitable way to automate the tasks. This tool enables us to support all the versions of Python and can be downloaded after management plugin is installed.
21. Describe ZeroMQ?
ZeroMQ is the asynchronous messaging library designed by iMatrix to be utilized in distributed applications. It uses the sockets to carry the atomic messages throughout different transports like inter-process, in-process, multicast, and TCP. It is developed in C++ and many contributors design ZerMQ.
22. What are the different kinds of Exchanges?
Following are the different kinds of Exchanges:
Direct: On the basis of routing key, a message is transmitted to binding queue having a similar routing key. The routing key of exchange and binding queue to be the exact match.

Topic: Here also, we use the routing key. But contrary to the direct message type, here routing key of the bound and exchange queues must be different from the exact match. We can transmit the exchange to different bound queries through regular expressions like a wildcard.

Fanout: Message is routed to all the existing bounded queues. The routing key, if given, is ignored, Thus, it is a kind of publish-subscribe design pattern.

Headers: In this kind of message the routing queue is chosen on the criterial defined in the headers rather than in routing key. This is same as topic exchange type, yet here we can define the difficult criteria for choosing the routing queues.
| Related Article: "Kafka vs RabbitMQ" |
23. List the design patterns utilized by RabbitMQ?
Some of the architectural patterns utilized by RabbitMQ are:
- One-Message-to-One-Consumer Model
- This Model is utilized for delivering each task to only one worker. The exchange kinds of this pattern are
- Next Available Worker: RabbitMQ will not give multiple messages to the worker at a time in this type of exchange.
- Round-Robin: RabbitMQ will dispatch every message to the next consumer in a sequence in this pattern type.
- One-Message-to-Multiple-Consumers model
- In this Model, one message is dispatched to multiple consumers. Some exchange kinds of this pattern are:
- Publish/Subscribe: In this pattern, the producer transmits the message to the group of subscribed consumers.
24. Describe Apache Qpid?
Apache Qpid is a freeware messaging system that is implemented on the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol. Apache Software Foundation designs Apache Qpid. This open internet protocol makes it idle for everyone to develop a diverse messaging system to send and receive messages securely. It offers features like queuing, transaction management, security, distribution, clustering, and heterogeneous multi-platform support.
25. Explain Dead Letter Queue?
Generally, the dead letter queue, also called the undelivered message queue, is the holding queue of messages that cannot be transmitted to their destinations for some reason. In the RabbitM, dead letter queue is the service implementation for storing the messages that meet one or more of the below failure criteria:
- Queue length limit exceeded.
- Message that is transmitted to the queue that is not available.
- Message length limit exceeded.
- Message reaches the threshold read counter number, as it is not utilized. Sometimes, this is known as a “back out queue.”
- The queue exchange rejects message.
26. Explain STOMP?
STOMP refers to a simple text-oriented messaging protocol the UI Client utilizes for connecting to the enterprise message brokers. Clients can utilize the “SUBSCRIBE” or “SEND” commands for sending or subscribing to the messages with the “destination” header that explains what the message is about and who must receive it. It specifies the server and client protocol for communicating with the message semantics. It does not specify the implementation details but instead handles easy-to-implement wire protocol for the message integrations. The protocol is the same as HTTP and works on TCP through the below commands:
- SEND
- CONNECT
- BEGIN
- SUBSCRIBE
- UNSUBSCRIBE
- ABORT
- COMMIT
- NACK
- ACK
- DISCONNECT
27. What is the default port of the RabbitMQ management interface?
15672
28. Describe RabbitMQ Channel?
Channels tell us how the RabbitMQ server interacts with our application. It stores one connection per client process and various channels in that process. The RabbitMQ channel allows us to have a single reference to the RabbitMQ server, but the different parts of our application include sandboxed communication.
29. What are Asynchronous and Synchronous Messaging?
Asynchronous Messaging is an interaction where the message is placed in the message queue and does not need an instant response from the receiver. Whereas Synchronous messaging is a two-way interaction, where the sender sends the message to the receiver, and the receiver receives the message and gives a reply to the sender.
30. Which Message Patterns are utilized in RabbitMQ?
Message Patterns are implemented in the RabbitMQ based on exchange bindings and queues. We may differentiate between different approaches for implementing the RabbitMQ Design Pattern. The following are different Message Patterns utilized by RabbitMQ:
- Publish-Subscribe
- Point-to-Point
- Request-Response
31. Define Point-to-Point communication?
Point-to-Point connection is the communication connection between two communication nodes or endpoints.
32. Explain Request-Response communication?
Request-Reply or Request-Response is the strong message pattern where requester sends the message to the replier, and in return, the replier sends the response back to the replier.
Advanced RabbitMQ Interview Questions
33. How can we stop the RabbitMQ server on the local host?
A. By executing the following command, we can stop the RabbitMQ server on the localhost:

34. How do we delete all the RabbitMQ Queues?

35. How do we verify the version of RabbitMQ?

36. How can we delete all the queues from RabbitMQ?

37. How do we implement the RabbitMQ retry mechanism?

38. How does RabbitMQ support the client libraries?
Following are the client libraries that RabbitMQ supports:
- RabbitMQ JMS Client
- RabbitMQ Java Client
- Bunny - RabbitMQ Ruby Client
- RabbitMQ .NET Client - supports .NET core and .NET 4.51+
- March Hare - JRuby RabbitMQ Client
- Aio-amqp - an asynchronous Python Client
- Pika & aio-pika - a pure Python Client
- RawRabbit - a Higher level client who targets .NET Core and ASP.NET vNext
- Php-amqplib - Fully featured PHP RabbitMQ Client
- Lapin & amiquip - RabbitMQ client for rust
- Amqp. node: RabbitMQ client for NodeJS
39. Explain Spring Cloud Stream.
Spring cloud stream is the framework for designing event-driven and highly-scalable microservices linked to shared messaging systems. It offers a flexible programming model that is designed on the established Spring idioms. It supports continuous pub/sub semantics, stateful partitions, and consumer groups. The essential building blocks of Spring Cloud Stream are the Destination Bindings, Destination Binders, and Messages.
40. How is RabbitMQ different from Kafka?
RabbitMQ is the lightweight message broker utilized for interacting messages between producer and consumer. It supports different protocols like MQTT, AMQP, and STOMP. While Kafka handles vast amounts of data with little overhead - Kafka was developed for massive volumes of messages to be distributed and stored.
| Want to Know about Kafka, then CheckOut "Kafka Tutorial" |
41. How do we monitor the RabbitMQ queue?
Monitoring the mechanism of capturing the behavior of our application through health metrics and checks. We have different tools to monitor the applications like DataDog, AppDynamics, AWS CloudWatch, etc.
42. Is RabbitMQ support message priority queues?
For making the queue function as the priority queue, offer the “x-max-priority” property when the queue is set. “x-max-priority” declares the maximum priority number in the queue. We can set the priority as given below:

43. How is RabbitMQ different from ActiveMQ?
RabbitMQ is a freeware message broker supporting various protocols developed in Erlang. While ActiveMQ is a freeware with support for the multiple protocols developed in Java Language.
44. How do we restart the RabbitMQ service?
Like other services, we can restart the RabbitMQ service by executing the below command:

Frequently Asked RabbitMQ Interview Questions
1. What is RabbitMQ used for?
RabbitMQ acts as a message broker for interservice communication. It provides a common platform for the applications to send and receive messages, and your messages will be stored in a safe place until received.
2. Is RabbitMQ pull-based or push-based?
RabbitMQ utilizes the Push-based model with the smart producer, which indicates that the producer can decide when to push the data. A pre-defined limit is specified on the consumer to stop the producer from enormous consumers.
3. What is the difference between RabbitMQ and Kafka?
RabbitMQ is suitable for transactional data, such as order information, placement, and user requests. In contrast, Kafka is ideal for operational data like auditing and logging statistics, system activity, and process operations.
4. What does MQ stand for in RabbitMQ?
In RabbitMQ, MQ stands for “Message Queue.”
5. Is RabbitMQ faster than Kafka?
No, RabbitMQ is not faster than Kafka. Kafka can process millions of messages in a second. Though RabbitMQ messages can also process millions of messages in a second, it needs more resources.
6. How many messages can RabbitMQ handle?
RabbitMQ can handle a million messages per second but needs more resources.
7. Is RabbitMQ a TCP or UDP?
All the protocols supported by RabbitMQ are TCP based. So, RabbitMQ is a TCP.
8. Is RabbitMQ a FIFO?
Yes, the Queues in RabbitMQ are FIFO. Some queue features, like requeuing and priorities by consumers, can impact the ordering.
9. Can RabbitMQ lose messages?
In RabbitMQ, durable queues can withstand the RabbitMQ restart. If the queue is not durable, all messages will be lost if the RabbitMQ is shut down for any reason.
10. Where is RabbitMQ data stored?
In RabbtMQ, versions starting from 3.7.0, all messages data is amalgamated in the msg_stores/vhosts directory and stored in the subdirectory per vhost.
RabbitMQ Interview Preparations Tips
1. Read the Job Description
Before applying, you should read the job description in detail to understand how the employer has explained the positions and type of applicant they are looking for. Attentively analyze the key phrases and keywords the interviewer utilizes to describe their expectations from the candidate.
2. Review your eligibility for the job
Think about your experience and qualification. Evaluate how the job sets into your career path and what value you can add to the organization.
3. Make a list of expected Interview Questions.
Prepare a list of interview questions for the given position and frame good answers. Build attractive responses to that questions to emphasize your expertise and interest in the job. Besides job-oriented questions, prepare for some of the general questions like:
- Why are you looking for a job change?
- Tell me about yourself.
- Why do you want this job?
4. Attempt mock interviews
Irrespective of your preparation, it is natural to feel overwhelmed and anxious during the interview. A mock interview will provide you with excellent assistance in this situation. It will create a real-time interview-like environment and help you improve your confidence. Ask your family members or friends to conduct a mock interview for you. Try to record the complete process to analyze your performance.
5. Update Social Media Profile
If you have LinkedIn, Facebook, or any other social media platform accounts, ensure you have updated the profiles. Employers will check your social media accounts to gain insight into your background and personality. If there is anything offensive, prepare a response if the interviewer asks.
6. Be polite and confident
Be confident and firm while giving the interview. You can begin practicing it the moment you enter the organization. Be careful while smiling and greeting the interviewers.
Conclusion
RabbitMQ has become a popular message broker due to software developers' comprehensive utilization of Microservices. Since it supports all the famous programming languages, it is used by all the top companies like Accenture, Reddit, Stack, etc. So, individuals who have an in-depth knowledge of RabbitMQ will have massive demand. So, if you prepare well for the interview, you can achieve a well-paying job.
This RabbitMQ interview questions blog includes more than 45 frequently asked RabbitMQ interview questions to help you prepare efficiently for the RabbitMQ interviews. Study them thoroughly to answer the interview question confidently. If you want to add more value to your resume, join MindMajix RabbitMQ certification Training to get an industry-recognized RabbitMQ course completion certificate.
 On-Job Support Service
On-Job Support Service
Online Work Support for your on-job roles.

Our work-support plans provide precise options as per your project tasks. Whether you are a newbie or an experienced professional seeking assistance in completing project tasks, we are here with the following plans to meet your custom needs:
- Pay Per Hour
- Pay Per Week
- Monthly
| Name | Dates | |
|---|---|---|
| Apache Kafka Training | Mar 14 to Mar 29 | View Details |
| Apache Kafka Training | Mar 17 to Apr 01 | View Details |
| Apache Kafka Training | Mar 21 to Apr 05 | View Details |
| Apache Kafka Training | Mar 24 to Apr 08 | View Details |

Madhuri is a Senior Content Creator at MindMajix. She has written about a range of different topics on various technologies, which include, Splunk, Tensorflow, Selenium, and CEH. She spends most of her time researching on technology, and startups. Connect with her via LinkedIn and Twitter .
















